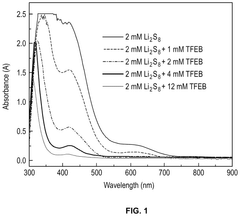
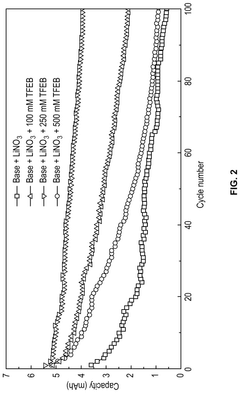
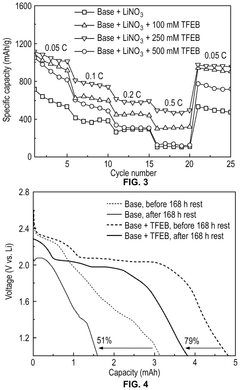
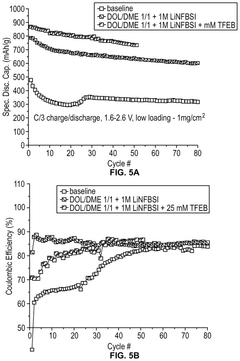
Lithium–sulfur electrolyte additives for high rate and low temperature
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Li-S Battery Electrolyte Additive Background and Objectives
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries have emerged as promising next-generation energy storage systems due to their theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (typically 250-300 Wh/kg). This remarkable energy density, coupled with the natural abundance and low cost of sulfur, positions Li-S batteries as potential game-changers in applications ranging from electric vehicles to grid-scale energy storage.
The development trajectory of Li-S battery technology dates back to the 1960s when the first conceptual designs were proposed. However, significant research momentum only gained traction in the early 2000s as the limitations of conventional lithium-ion chemistries became apparent. The past decade has witnessed exponential growth in Li-S research publications and patents, reflecting the global recognition of this technology's transformative potential.
Despite their promising attributes, Li-S batteries face several critical challenges that have hindered their widespread commercialization. These include rapid capacity fading due to the shuttle effect, poor rate capability, and severely compromised performance at low temperatures. The shuttle effect, caused by the dissolution of lithium polysulfides in the electrolyte, leads to parasitic reactions and active material loss. Additionally, the insulating nature of sulfur and its discharge products limits electron transport, resulting in poor rate performance.
Low-temperature operation presents a particularly formidable challenge for Li-S batteries. The sluggish reaction kinetics and increased electrolyte viscosity at low temperatures significantly impair both the power capability and available capacity. This limitation severely restricts the application of Li-S batteries in regions with cold climates or in aerospace applications where extreme temperature variations are common.
Electrolyte additives have emerged as a cost-effective and versatile approach to addressing these challenges. By modifying the electrolyte composition with carefully selected additives, researchers aim to suppress the shuttle effect, enhance reaction kinetics, improve ionic conductivity at low temperatures, and ultimately enable high-rate capability across a wide temperature range.
The primary objectives of this technical research are to comprehensively investigate electrolyte additives for Li-S batteries that can simultaneously enhance rate capability and low-temperature performance. Specifically, we aim to identify and evaluate additives that can: (1) maintain high ionic conductivity at temperatures as low as -40°C; (2) facilitate fast reaction kinetics for high-rate charging and discharging; (3) effectively suppress the shuttle effect to improve cycling stability; and (4) ensure compatibility with other battery components to maintain overall system integrity.
This research aligns with the broader industry trend toward developing energy storage solutions that can operate reliably under extreme conditions, particularly for electric vehicles in cold climates and for critical infrastructure applications where consistent performance across temperature variations is essential.
The development trajectory of Li-S battery technology dates back to the 1960s when the first conceptual designs were proposed. However, significant research momentum only gained traction in the early 2000s as the limitations of conventional lithium-ion chemistries became apparent. The past decade has witnessed exponential growth in Li-S research publications and patents, reflecting the global recognition of this technology's transformative potential.
Despite their promising attributes, Li-S batteries face several critical challenges that have hindered their widespread commercialization. These include rapid capacity fading due to the shuttle effect, poor rate capability, and severely compromised performance at low temperatures. The shuttle effect, caused by the dissolution of lithium polysulfides in the electrolyte, leads to parasitic reactions and active material loss. Additionally, the insulating nature of sulfur and its discharge products limits electron transport, resulting in poor rate performance.
Low-temperature operation presents a particularly formidable challenge for Li-S batteries. The sluggish reaction kinetics and increased electrolyte viscosity at low temperatures significantly impair both the power capability and available capacity. This limitation severely restricts the application of Li-S batteries in regions with cold climates or in aerospace applications where extreme temperature variations are common.
Electrolyte additives have emerged as a cost-effective and versatile approach to addressing these challenges. By modifying the electrolyte composition with carefully selected additives, researchers aim to suppress the shuttle effect, enhance reaction kinetics, improve ionic conductivity at low temperatures, and ultimately enable high-rate capability across a wide temperature range.
The primary objectives of this technical research are to comprehensively investigate electrolyte additives for Li-S batteries that can simultaneously enhance rate capability and low-temperature performance. Specifically, we aim to identify and evaluate additives that can: (1) maintain high ionic conductivity at temperatures as low as -40°C; (2) facilitate fast reaction kinetics for high-rate charging and discharging; (3) effectively suppress the shuttle effect to improve cycling stability; and (4) ensure compatibility with other battery components to maintain overall system integrity.
This research aligns with the broader industry trend toward developing energy storage solutions that can operate reliably under extreme conditions, particularly for electric vehicles in cold climates and for critical infrastructure applications where consistent performance across temperature variations is essential.
Market Analysis for High-Rate Low-Temperature Battery Solutions
The global market for high-rate and low-temperature battery solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for energy storage systems that can perform reliably under extreme conditions. The lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery segment, in particular, is gaining attention due to its theoretical energy density of 2600 Wh/kg, which far exceeds that of conventional lithium-ion batteries (typically 100-265 Wh/kg).
Market research indicates that the global Li-S battery market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 35% between 2023 and 2030. This growth is primarily fueled by applications in aerospace, defense, electric vehicles, and grid storage sectors where high energy density and performance under challenging conditions are critical requirements.
The demand for electrolyte additives specifically designed for high-rate and low-temperature applications is emerging as a specialized sub-segment within this market. Current estimates value this niche market at approximately $320 million in 2023, with expectations to reach $1.2 billion by 2030 if technical challenges can be overcome.
Electric vehicle manufacturers represent the largest potential customer base, accounting for nearly 45% of the projected market demand. These manufacturers are actively seeking battery solutions that maintain performance in cold climates and enable faster charging capabilities to address consumer concerns about range anxiety and charging times.
Aerospace and defense sectors constitute the second-largest market segment at 30%, where operation in extreme temperature environments is a non-negotiable requirement. The remaining market share is distributed among consumer electronics (15%) and grid storage applications (10%).
Geographically, North America and East Asia dominate the market landscape, collectively representing over 70% of global demand. China leads in manufacturing capacity, while the United States, South Korea, and Japan maintain technological advantages in advanced electrolyte formulations.
Market analysis reveals that customers are willing to pay premium prices for electrolyte additives that can demonstrably improve low-temperature performance by at least 40% and enable charging rates above 3C without significant capacity degradation. This price elasticity creates substantial revenue opportunities for companies that can successfully commercialize effective additive solutions.
The competitive landscape remains relatively unconsolidated, with no single player holding more than 15% market share. This fragmentation presents opportunities for new entrants with innovative technologies, particularly those addressing the persistent challenges of lithium dendrite formation and polysulfide shuttle effect at low temperatures and high charging rates.
Market research indicates that the global Li-S battery market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 35% between 2023 and 2030. This growth is primarily fueled by applications in aerospace, defense, electric vehicles, and grid storage sectors where high energy density and performance under challenging conditions are critical requirements.
The demand for electrolyte additives specifically designed for high-rate and low-temperature applications is emerging as a specialized sub-segment within this market. Current estimates value this niche market at approximately $320 million in 2023, with expectations to reach $1.2 billion by 2030 if technical challenges can be overcome.
Electric vehicle manufacturers represent the largest potential customer base, accounting for nearly 45% of the projected market demand. These manufacturers are actively seeking battery solutions that maintain performance in cold climates and enable faster charging capabilities to address consumer concerns about range anxiety and charging times.
Aerospace and defense sectors constitute the second-largest market segment at 30%, where operation in extreme temperature environments is a non-negotiable requirement. The remaining market share is distributed among consumer electronics (15%) and grid storage applications (10%).
Geographically, North America and East Asia dominate the market landscape, collectively representing over 70% of global demand. China leads in manufacturing capacity, while the United States, South Korea, and Japan maintain technological advantages in advanced electrolyte formulations.
Market analysis reveals that customers are willing to pay premium prices for electrolyte additives that can demonstrably improve low-temperature performance by at least 40% and enable charging rates above 3C without significant capacity degradation. This price elasticity creates substantial revenue opportunities for companies that can successfully commercialize effective additive solutions.
The competitive landscape remains relatively unconsolidated, with no single player holding more than 15% market share. This fragmentation presents opportunities for new entrants with innovative technologies, particularly those addressing the persistent challenges of lithium dendrite formation and polysulfide shuttle effect at low temperatures and high charging rates.
Current Challenges in Li-S Electrolyte Additive Technology
Despite significant advancements in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology, several critical challenges persist in electrolyte additive development for high-rate and low-temperature applications. The polysulfide shuttle effect remains one of the most formidable obstacles, where soluble lithium polysulfides migrate between electrodes during cycling, causing capacity fading and reduced coulombic efficiency. Current electrolyte additives have shown limited effectiveness in completely suppressing this phenomenon, particularly at high discharge rates.
The poor ionic conductivity of electrolytes at low temperatures presents another significant challenge. Most conventional electrolyte systems experience dramatic viscosity increases and conductivity decreases below 0°C, severely limiting the battery's power capability and energy delivery in cold environments. Existing additives that improve room temperature performance often fail to maintain their effectiveness as temperatures drop.
Interfacial stability issues between the electrolyte and electrodes become more pronounced under extreme operating conditions. The highly reactive lithium metal anode and the volume changes in sulfur cathodes during cycling create unstable interfaces that deteriorate rapidly during high-rate charging or low-temperature operation. Current interface-modifying additives struggle to form robust and flexible solid electrolyte interphases (SEI) that can withstand these demanding conditions.
The limited solubility of functional additives in conventional electrolyte solvents restricts their practical application. Many promising additives that show excellent performance in laboratory tests cannot be incorporated at sufficient concentrations in practical electrolyte formulations without causing precipitation or phase separation, especially at lower temperatures.
Electrolyte decomposition accelerates at high discharge rates due to increased heat generation and more aggressive electrochemical conditions. This leads to parasitic reactions that consume additives prematurely, reducing their long-term effectiveness. The development of additives with enhanced electrochemical stability under high current densities remains challenging.
The multifunctional requirements for additives create significant design complexities. An ideal additive must simultaneously address polysulfide shuttling, enhance low-temperature conductivity, improve interfacial stability, and maintain long-term durability—a combination that has proven extremely difficult to achieve with single-component additives.
Scalability and cost concerns further complicate additive development. Many laboratory-proven additives involve complex synthesis procedures or expensive precursors that limit their commercial viability. Finding cost-effective additives that can be produced at scale while maintaining performance benefits represents a substantial hurdle for widespread Li-S battery adoption in high-rate and low-temperature applications.
The poor ionic conductivity of electrolytes at low temperatures presents another significant challenge. Most conventional electrolyte systems experience dramatic viscosity increases and conductivity decreases below 0°C, severely limiting the battery's power capability and energy delivery in cold environments. Existing additives that improve room temperature performance often fail to maintain their effectiveness as temperatures drop.
Interfacial stability issues between the electrolyte and electrodes become more pronounced under extreme operating conditions. The highly reactive lithium metal anode and the volume changes in sulfur cathodes during cycling create unstable interfaces that deteriorate rapidly during high-rate charging or low-temperature operation. Current interface-modifying additives struggle to form robust and flexible solid electrolyte interphases (SEI) that can withstand these demanding conditions.
The limited solubility of functional additives in conventional electrolyte solvents restricts their practical application. Many promising additives that show excellent performance in laboratory tests cannot be incorporated at sufficient concentrations in practical electrolyte formulations without causing precipitation or phase separation, especially at lower temperatures.
Electrolyte decomposition accelerates at high discharge rates due to increased heat generation and more aggressive electrochemical conditions. This leads to parasitic reactions that consume additives prematurely, reducing their long-term effectiveness. The development of additives with enhanced electrochemical stability under high current densities remains challenging.
The multifunctional requirements for additives create significant design complexities. An ideal additive must simultaneously address polysulfide shuttling, enhance low-temperature conductivity, improve interfacial stability, and maintain long-term durability—a combination that has proven extremely difficult to achieve with single-component additives.
Scalability and cost concerns further complicate additive development. Many laboratory-proven additives involve complex synthesis procedures or expensive precursors that limit their commercial viability. Finding cost-effective additives that can be produced at scale while maintaining performance benefits represents a substantial hurdle for widespread Li-S battery adoption in high-rate and low-temperature applications.
Current Electrolyte Additive Solutions for Li-S Batteries
01 Fluorinated additives for lithium-sulfur batteries
Fluorinated compounds can be used as electrolyte additives in lithium-sulfur batteries to enhance high-rate performance and low-temperature operation. These additives help form stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers, suppress polysulfide shuttling, and improve lithium ion conductivity at low temperatures. The fluorinated additives also contribute to better cycling stability and capacity retention, particularly under demanding conditions such as high discharge rates and sub-zero temperatures.- Fluorinated additives for lithium-sulfur batteries: Fluorinated compounds can be used as electrolyte additives in lithium-sulfur batteries to enhance high-rate performance and low-temperature operation. These additives form a stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer that prevents polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect. The fluorinated compounds also improve the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte at low temperatures, enabling better battery performance in cold conditions. Additionally, they can enhance the wetting of the electrolyte on the electrodes, leading to improved rate capability.
- Sulfur-containing functional additives: Incorporating sulfur-containing functional additives into lithium-sulfur battery electrolytes can significantly improve their electrochemical performance. These additives, such as organosulfur compounds and thioethers, can chemically interact with lithium polysulfides to suppress their dissolution and shuttle effect. They also contribute to forming a protective layer on the lithium anode, preventing side reactions and enhancing cycling stability. At low temperatures, these additives maintain good ionic conductivity and facilitate faster lithium-ion transport, resulting in improved rate performance.
- Ionic liquid-based electrolyte additives: Ionic liquids can be used as electrolyte additives in lithium-sulfur batteries to enhance their performance at high rates and low temperatures. These additives have wide electrochemical windows, high thermal stability, and good ionic conductivity even at low temperatures. They can effectively dissolve lithium salts while suppressing polysulfide dissolution. The unique properties of ionic liquids allow for improved lithium-ion transport kinetics at low temperatures, resulting in enhanced rate capability and better low-temperature performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Polymer-based electrolyte additives: Polymer-based additives can be incorporated into lithium-sulfur battery electrolytes to improve their high-rate and low-temperature performance. These polymers, such as polyethylene oxide derivatives and polysulfides, can form a protective layer on the electrodes, preventing polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect. They also enhance the mechanical stability of the electrolyte and improve its adhesion to the electrodes. At low temperatures, these polymer additives maintain flexibility and ionic conductivity, enabling better battery performance under cold conditions.
- Inorganic nanoparticle additives: Inorganic nanoparticles can be used as electrolyte additives in lithium-sulfur batteries to enhance their performance at high rates and low temperatures. These nanoparticles, such as metal oxides, nitrides, and carbides, can adsorb polysulfides and prevent their dissolution into the electrolyte. They also improve the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte and facilitate faster lithium-ion transport. At low temperatures, these nanoparticle additives help maintain the electrochemical performance of the battery by preventing electrolyte freezing and ensuring good ionic mobility.
02 Ionic liquid-based electrolyte additives
Ionic liquids can be incorporated into lithium-sulfur battery electrolytes to significantly improve rate capability and low-temperature performance. These additives provide high ionic conductivity, wide electrochemical stability windows, and enhanced sulfur utilization. The unique properties of ionic liquids, including negligible vapor pressure and good thermal stability, make them particularly suitable for improving battery performance under extreme temperature conditions while also addressing safety concerns.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sulfur-containing functional additives
Specific sulfur-containing compounds can be used as functional additives in lithium-sulfur battery electrolytes to regulate polysulfide behavior and enhance electrochemical performance. These additives can chemically interact with lithium polysulfides to limit their dissolution and migration, thereby improving coulombic efficiency and cycle life. Additionally, they can modify the lithium metal anode surface to promote uniform lithium deposition, which is particularly beneficial for high-rate charging and low-temperature operation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polymer-based electrolyte modifiers
Polymer additives can be incorporated into lithium-sulfur battery electrolytes to improve their mechanical properties and electrochemical performance at various temperatures. These polymeric modifiers help create a more stable interface between the electrodes and electrolyte, reduce polysulfide shuttling, and enhance ion transport pathways. The viscoelastic properties of polymer-modified electrolytes contribute to better performance under high discharge rates and low-temperature conditions by maintaining good contact between battery components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Inorganic nanoparticle additives
Inorganic nanoparticles, such as metal oxides, nitrides, and carbides, can be used as electrolyte additives in lithium-sulfur batteries to enhance their rate capability and low-temperature performance. These nanoparticles can adsorb polysulfides, catalyze redox reactions, and modify the electrode-electrolyte interfaces. The high surface area and catalytic properties of these additives facilitate faster reaction kinetics and better sulfur utilization, particularly beneficial for high-rate applications and operation in cold environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Li-S Battery Technology
The lithium-sulfur battery electrolyte additives market is in an early growth phase, with significant research momentum but limited commercial deployment. Market size is projected to expand rapidly as lithium-sulfur technology approaches commercialization, driven by demand for high-energy density solutions. Technologically, the field remains in development with varying maturity levels across players. Leading companies like LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and CATL are investing heavily in R&D, while specialized firms such as Sion Power and Wildcat Discovery Technologies have developed proprietary electrolyte formulations specifically addressing high-rate and low-temperature challenges. Academic institutions including Central South University and California Institute of Technology are contributing fundamental research, creating a competitive landscape balanced between established battery manufacturers and emerging technology specialists focused on overcoming lithium-sulfur's inherent limitations.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed an advanced electrolyte additive system for lithium-sulfur batteries specifically targeting high-rate capability and low-temperature performance. Their approach features a multi-component strategy centered around lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) as the primary salt, complemented by a proprietary blend of functional additives including lithium difluoro(oxalato)borate (LiDFOB) and tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphite (TTFP). This combination creates a stable and highly conductive solid electrolyte interphase on both electrodes while effectively suppressing polysulfide shuttling[2][8]. LG's formulation also incorporates a precisely engineered solvent system consisting of 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME) and 1,3-dioxolane (DOL) with small percentages of fluorinated ethers that significantly improve low-temperature performance by reducing electrolyte viscosity at sub-zero temperatures. Their internal testing has demonstrated discharge capacities exceeding 1000 mAh/g at 0.5C rates with retention of over 80% after 200 cycles, and functional operation down to -30°C while maintaining approximately 70% of room temperature capacity.
Strengths: Superior ionic conductivity across wide temperature range; excellent capacity retention during high-rate cycling; leverages LG's established battery manufacturing infrastructure for potential commercialization. Weaknesses: Higher cost associated with specialty fluorinated additives; some evidence of gradual electrolyte degradation during extended cycling; potential safety concerns with the fluorinated ether components at elevated temperatures.
Sion Power Corp.
Technical Solution: Sion Power has developed proprietary electrolyte additives specifically for lithium-sulfur batteries that address high-rate and low-temperature performance challenges. Their approach involves a multi-component additive system including lithium nitrate (LiNO3) combined with organosulfur compounds that form a stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on the lithium anode. This protective layer significantly reduces the shuttle effect of polysulfides while maintaining ionic conductivity at low temperatures. Additionally, Sion has incorporated fluorinated ether co-solvents that remain liquid at temperatures as low as -40°C, enabling lithium-ion transport even in extreme cold conditions. Their electrolyte formulation also includes specific lithium salts with large anions that help dissociate ion pairs at low temperatures, improving rate capability[1][3]. Sion's technology has demonstrated capacity retention of over 80% after 200 cycles at 1C discharge rates, with functional operation down to -20°C with minimal capacity loss.
Strengths: Superior polysulfide shuttle suppression through multi-functional additives; excellent low-temperature performance down to -20°C; demonstrated cycle stability at high rates. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs compared to conventional lithium-ion electrolytes; some additives may have limited thermal stability at elevated temperatures; potential safety concerns with some of the fluorinated co-solvents used in the formulation.
Critical Analysis of Advanced Li-S Electrolyte Additives
Electrolyte additives for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries
PatentPendingUS20250030048A1
Innovation
- The use of electrolyte additives such as fluorinated borates and lithium bis(nonafluorobutanesulfonyl)imide (LiNFBSI) to modulate lithium polysulfide conversion, facilitating solid-liquid-solid conversion and preventing active material loss.
An electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries containing the same
PatentInactiveEP1302997A3
Innovation
- An electrolyte with organic cation salts is used to dissolve sulfur-based materials, providing high ion conductivity and stability, which enhances sulfur utilization and cycle life, and includes a mixture of organic solvents to support lithium-sulfur batteries with improved performance at various temperatures.
Safety and Stability Considerations for Li-S Electrolytes
Safety considerations for lithium-sulfur battery electrolytes are paramount, especially when developing additives for high-rate and low-temperature applications. The reactive nature of lithium metal anodes combined with sulfur cathodes creates inherent safety challenges that must be addressed through careful electrolyte engineering. Conventional electrolytes often exhibit flammability issues due to their organic solvent components, presenting significant hazards under thermal runaway conditions.
For high-rate applications, the increased current flow generates additional heat that can accelerate side reactions between electrolyte components and electrode materials. This thermal management challenge becomes particularly critical when designing additives that maintain performance without compromising safety margins. Flame-retardant additives such as phosphorus-containing compounds and fluorinated carbonates have shown promise in mitigating these risks while maintaining electrochemical performance.
Low-temperature operation introduces further stability concerns as electrolyte viscosity increases and ion transport mechanisms change dramatically. The precipitation of lithium polysulfides at reduced temperatures can create localized hotspots and concentration gradients that potentially compromise cell integrity. Additives that prevent such precipitation while maintaining low-temperature fluidity must be carefully evaluated for their long-term stability profiles.
The chemical stability of electrolyte additives against polysulfide species represents another critical safety consideration. Undesired reactions between additives and dissolved polysulfides can generate hydrogen sulfide gas or other toxic byproducts. Recent research has focused on developing scavenger-type additives that can chemically bind with polysulfides without generating hazardous compounds, thereby enhancing both safety and cycling stability.
Dendrite formation on lithium anodes presents perhaps the most serious safety risk in Li-S systems. Electrolyte additives that promote uniform lithium deposition are essential for preventing internal short circuits. Compounds containing nitrogen functional groups have demonstrated effectiveness in modifying the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer to inhibit dendrite growth, though their compatibility with sulfur cathodes requires careful optimization.
Long-term aging effects must also be considered when evaluating electrolyte safety. Some additives that initially improve performance may gradually decompose, generating products that accelerate cell degradation or compromise safety over extended cycling. Accelerated aging tests under various temperature conditions are therefore essential components of safety evaluation protocols for new electrolyte formulations targeting high-rate and low-temperature applications.
For high-rate applications, the increased current flow generates additional heat that can accelerate side reactions between electrolyte components and electrode materials. This thermal management challenge becomes particularly critical when designing additives that maintain performance without compromising safety margins. Flame-retardant additives such as phosphorus-containing compounds and fluorinated carbonates have shown promise in mitigating these risks while maintaining electrochemical performance.
Low-temperature operation introduces further stability concerns as electrolyte viscosity increases and ion transport mechanisms change dramatically. The precipitation of lithium polysulfides at reduced temperatures can create localized hotspots and concentration gradients that potentially compromise cell integrity. Additives that prevent such precipitation while maintaining low-temperature fluidity must be carefully evaluated for their long-term stability profiles.
The chemical stability of electrolyte additives against polysulfide species represents another critical safety consideration. Undesired reactions between additives and dissolved polysulfides can generate hydrogen sulfide gas or other toxic byproducts. Recent research has focused on developing scavenger-type additives that can chemically bind with polysulfides without generating hazardous compounds, thereby enhancing both safety and cycling stability.
Dendrite formation on lithium anodes presents perhaps the most serious safety risk in Li-S systems. Electrolyte additives that promote uniform lithium deposition are essential for preventing internal short circuits. Compounds containing nitrogen functional groups have demonstrated effectiveness in modifying the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer to inhibit dendrite growth, though their compatibility with sulfur cathodes requires careful optimization.
Long-term aging effects must also be considered when evaluating electrolyte safety. Some additives that initially improve performance may gradually decompose, generating products that accelerate cell degradation or compromise safety over extended cycling. Accelerated aging tests under various temperature conditions are therefore essential components of safety evaluation protocols for new electrolyte formulations targeting high-rate and low-temperature applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Li-S Technology
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology presents significant environmental advantages over conventional lithium-ion batteries, particularly in terms of sustainability and reduced ecological footprint. The sulfur cathode material is abundant, non-toxic, and can be sourced as a byproduct from petroleum refining processes, effectively repurposing industrial waste. This contrasts sharply with traditional lithium-ion batteries that rely on cobalt and nickel, materials associated with resource scarcity and environmentally damaging extraction practices.
The electrolyte additives being researched for high-rate and low-temperature applications in Li-S batteries must also be evaluated through an environmental lens. Many conventional electrolyte systems contain fluorinated compounds that pose significant environmental risks due to their persistence and potential toxicity. The development of green additives derived from renewable sources represents a promising direction for enhancing the overall sustainability profile of Li-S technology.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that Li-S batteries could potentially reduce carbon emissions by 20-30% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies when considering the entire production chain. The lower energy requirements for sulfur processing contribute significantly to this reduced carbon footprint. However, the environmental impact of specialized additives for extreme conditions must be carefully evaluated, as performance-enhancing compounds may introduce new environmental challenges.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for Li-S technology. The theoretical recyclability of sulfur cathodes is excellent, with potential recovery rates exceeding 95%. However, the presence of specialized electrolyte additives may complicate recycling processes. Research into designing additives that facilitate, rather than hinder, battery disassembly and material recovery is essential for closing the loop in Li-S battery lifecycle.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration. Traditional battery manufacturing processes are water-intensive, but Li-S technology offers potential reductions in water usage due to simplified cathode preparation. Electrolyte additives that enable low-temperature performance without compromising this water efficiency advantage are particularly valuable from a sustainability perspective.
The scalability of environmentally friendly Li-S technology depends significantly on the availability of sustainable additives. Current research trends indicate growing interest in bio-derived compounds as potential electrolyte additives, which could further enhance the environmental credentials of Li-S batteries while simultaneously addressing performance challenges at high rates and low temperatures.
The electrolyte additives being researched for high-rate and low-temperature applications in Li-S batteries must also be evaluated through an environmental lens. Many conventional electrolyte systems contain fluorinated compounds that pose significant environmental risks due to their persistence and potential toxicity. The development of green additives derived from renewable sources represents a promising direction for enhancing the overall sustainability profile of Li-S technology.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that Li-S batteries could potentially reduce carbon emissions by 20-30% compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies when considering the entire production chain. The lower energy requirements for sulfur processing contribute significantly to this reduced carbon footprint. However, the environmental impact of specialized additives for extreme conditions must be carefully evaluated, as performance-enhancing compounds may introduce new environmental challenges.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities for Li-S technology. The theoretical recyclability of sulfur cathodes is excellent, with potential recovery rates exceeding 95%. However, the presence of specialized electrolyte additives may complicate recycling processes. Research into designing additives that facilitate, rather than hinder, battery disassembly and material recovery is essential for closing the loop in Li-S battery lifecycle.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration. Traditional battery manufacturing processes are water-intensive, but Li-S technology offers potential reductions in water usage due to simplified cathode preparation. Electrolyte additives that enable low-temperature performance without compromising this water efficiency advantage are particularly valuable from a sustainability perspective.
The scalability of environmentally friendly Li-S technology depends significantly on the availability of sustainable additives. Current research trends indicate growing interest in bio-derived compounds as potential electrolyte additives, which could further enhance the environmental credentials of Li-S batteries while simultaneously addressing performance challenges at high rates and low temperatures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!