Optimizing Chiller Startup Sequences for Smooth Operation
JAN 23, 20268 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chiller Startup Tech Background and Goals
Chiller systems represent critical infrastructure components in modern commercial, industrial, and institutional facilities, responsible for maintaining precise temperature control and environmental conditions. These systems typically consume 30-50% of total building energy in large-scale applications, making their operational efficiency a paramount concern for facility managers and energy engineers. The startup phase of chiller operations has historically been identified as a period of significant mechanical stress, energy inefficiency, and potential system instability, directly impacting equipment longevity and operational costs.
Traditional chiller startup procedures often follow rigid, manufacturer-prescribed sequences that may not account for varying operational contexts, ambient conditions, or system-specific characteristics. This approach frequently results in thermal shock to compressor components, excessive inrush currents, hydraulic transients in refrigerant circuits, and suboptimal oil distribution during critical initial operating moments. Research indicates that improper startup sequences contribute to approximately 15-20% of premature chiller failures and can reduce overall system efficiency by 8-12% during the critical first hours of operation.
The primary technical goal of this research focuses on developing intelligent, adaptive startup sequences that minimize mechanical stress while achieving stable operational states more rapidly and efficiently. This involves optimizing the coordination between multiple subsystems including compressor staging, condenser water flow initiation, evaporator loading profiles, and refrigerant migration management. Advanced control algorithms must balance competing objectives such as minimizing startup time, reducing energy consumption during transition phases, preventing liquid slugging, and ensuring adequate lubrication distribution.
Secondary objectives encompass the integration of predictive analytics to customize startup sequences based on real-time system conditions, historical performance data, and anticipated load profiles. This includes developing sensor fusion techniques to monitor critical parameters such as bearing temperatures, oil pressure differentials, refrigerant superheat levels, and motor current signatures. The ultimate aim is establishing a framework for smooth, reliable chiller startups that extend equipment lifespan, reduce maintenance requirements, and optimize energy performance across diverse operational scenarios and equipment configurations.
Traditional chiller startup procedures often follow rigid, manufacturer-prescribed sequences that may not account for varying operational contexts, ambient conditions, or system-specific characteristics. This approach frequently results in thermal shock to compressor components, excessive inrush currents, hydraulic transients in refrigerant circuits, and suboptimal oil distribution during critical initial operating moments. Research indicates that improper startup sequences contribute to approximately 15-20% of premature chiller failures and can reduce overall system efficiency by 8-12% during the critical first hours of operation.
The primary technical goal of this research focuses on developing intelligent, adaptive startup sequences that minimize mechanical stress while achieving stable operational states more rapidly and efficiently. This involves optimizing the coordination between multiple subsystems including compressor staging, condenser water flow initiation, evaporator loading profiles, and refrigerant migration management. Advanced control algorithms must balance competing objectives such as minimizing startup time, reducing energy consumption during transition phases, preventing liquid slugging, and ensuring adequate lubrication distribution.
Secondary objectives encompass the integration of predictive analytics to customize startup sequences based on real-time system conditions, historical performance data, and anticipated load profiles. This includes developing sensor fusion techniques to monitor critical parameters such as bearing temperatures, oil pressure differentials, refrigerant superheat levels, and motor current signatures. The ultimate aim is establishing a framework for smooth, reliable chiller startups that extend equipment lifespan, reduce maintenance requirements, and optimize energy performance across diverse operational scenarios and equipment configurations.
Market Demand for Efficient Chiller Systems
The global demand for efficient chiller systems has experienced substantial growth driven by escalating energy costs, stringent environmental regulations, and increasing awareness of operational sustainability. Commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and data centers represent the primary consumer segments, collectively accounting for the majority of chiller installations worldwide. These sectors face mounting pressure to reduce energy consumption while maintaining reliable cooling performance, creating a compelling market pull for advanced chiller technologies that optimize operational efficiency.
Energy efficiency has emerged as the dominant purchasing criterion across all market segments. Building owners and facility managers increasingly recognize that chillers typically consume a significant portion of total facility energy, making optimization initiatives financially attractive with relatively short payback periods. This economic imperative has intensified focus on technologies that minimize energy waste during transient operations, particularly during startup sequences when systems are most vulnerable to inefficiencies and mechanical stress.
Regulatory frameworks have further accelerated market demand for efficient chiller solutions. Energy performance standards and green building certifications now mandate higher efficiency benchmarks, compelling facility operators to upgrade legacy systems or implement advanced control strategies. The regulatory landscape continues to tighten globally, with progressive jurisdictions introducing carbon pricing mechanisms and energy disclosure requirements that directly impact operational economics.
The data center sector represents a particularly dynamic growth area for efficient chiller systems. Exponential increases in computing density and continuous operation requirements have made cooling optimization critical to business viability. Data center operators demonstrate strong willingness to invest in advanced chiller technologies that deliver measurable efficiency gains, as cooling costs directly impact competitive positioning and profitability margins.
Industrial applications present distinct market opportunities characterized by diverse cooling loads and process-specific requirements. Manufacturing facilities, pharmaceutical plants, and chemical processing operations require reliable chiller performance while managing operational costs. These environments particularly value startup optimization technologies that reduce mechanical wear, extend equipment lifespan, and minimize production disruptions caused by cooling system instabilities.
Energy efficiency has emerged as the dominant purchasing criterion across all market segments. Building owners and facility managers increasingly recognize that chillers typically consume a significant portion of total facility energy, making optimization initiatives financially attractive with relatively short payback periods. This economic imperative has intensified focus on technologies that minimize energy waste during transient operations, particularly during startup sequences when systems are most vulnerable to inefficiencies and mechanical stress.
Regulatory frameworks have further accelerated market demand for efficient chiller solutions. Energy performance standards and green building certifications now mandate higher efficiency benchmarks, compelling facility operators to upgrade legacy systems or implement advanced control strategies. The regulatory landscape continues to tighten globally, with progressive jurisdictions introducing carbon pricing mechanisms and energy disclosure requirements that directly impact operational economics.
The data center sector represents a particularly dynamic growth area for efficient chiller systems. Exponential increases in computing density and continuous operation requirements have made cooling optimization critical to business viability. Data center operators demonstrate strong willingness to invest in advanced chiller technologies that deliver measurable efficiency gains, as cooling costs directly impact competitive positioning and profitability margins.
Industrial applications present distinct market opportunities characterized by diverse cooling loads and process-specific requirements. Manufacturing facilities, pharmaceutical plants, and chemical processing operations require reliable chiller performance while managing operational costs. These environments particularly value startup optimization technologies that reduce mechanical wear, extend equipment lifespan, and minimize production disruptions caused by cooling system instabilities.
Current Chiller Startup Challenges and Constraints
Chiller startup operations face multiple technical challenges that directly impact system reliability, energy efficiency, and equipment longevity. The primary constraint stems from the inherent thermal and mechanical stress imposed on compressor components during cold starts. When chillers initiate operation from ambient conditions, significant temperature differentials create uneven thermal expansion across critical components, potentially leading to mechanical failures or reduced service life. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in large-capacity centrifugal and screw compressors where rotor clearances must be precisely maintained.
Lubrication system readiness presents another critical constraint during startup sequences. Insufficient oil pressure or improper oil distribution before compressor engagement can result in metal-to-metal contact, causing bearing damage and premature wear. Traditional startup protocols often lack sophisticated pre-lubrication cycles or fail to verify adequate oil film formation before initiating compression cycles. This challenge intensifies in low-ambient conditions where oil viscosity increases substantially, impeding proper circulation through bearing surfaces and hydraulic systems.
Refrigerant migration during shutdown periods creates additional startup complications. When chillers remain idle, refrigerant naturally migrates toward the coldest system components, typically accumulating in the evaporator or compressor crankcase. Sudden startup under these conditions can cause liquid slugging, where incompressible liquid refrigerant enters compression chambers designed for vapor handling. This scenario generates hydraulic shock loads capable of damaging valve assemblies, piston rings, or scroll elements.
Electrical system constraints further complicate optimal startup sequencing. High inrush currents during motor energization can trigger protective relays or cause voltage sags affecting other facility equipment. Variable frequency drives partially mitigate this issue but introduce their own complexity regarding acceleration ramp profiles and torque management during the critical initial rotation phase.
Control system limitations represent a significant barrier to startup optimization. Many existing chiller controllers employ fixed-sequence startup algorithms that cannot adapt to varying ambient conditions, system configurations, or equipment age. These rigid protocols fail to account for factors such as oil temperature, refrigerant distribution, bearing temperature profiles, or historical performance data that could inform more intelligent startup strategies. The absence of real-time condition monitoring and predictive analytics prevents proactive adjustments that could enhance startup smoothness and reliability.
Lubrication system readiness presents another critical constraint during startup sequences. Insufficient oil pressure or improper oil distribution before compressor engagement can result in metal-to-metal contact, causing bearing damage and premature wear. Traditional startup protocols often lack sophisticated pre-lubrication cycles or fail to verify adequate oil film formation before initiating compression cycles. This challenge intensifies in low-ambient conditions where oil viscosity increases substantially, impeding proper circulation through bearing surfaces and hydraulic systems.
Refrigerant migration during shutdown periods creates additional startup complications. When chillers remain idle, refrigerant naturally migrates toward the coldest system components, typically accumulating in the evaporator or compressor crankcase. Sudden startup under these conditions can cause liquid slugging, where incompressible liquid refrigerant enters compression chambers designed for vapor handling. This scenario generates hydraulic shock loads capable of damaging valve assemblies, piston rings, or scroll elements.
Electrical system constraints further complicate optimal startup sequencing. High inrush currents during motor energization can trigger protective relays or cause voltage sags affecting other facility equipment. Variable frequency drives partially mitigate this issue but introduce their own complexity regarding acceleration ramp profiles and torque management during the critical initial rotation phase.
Control system limitations represent a significant barrier to startup optimization. Many existing chiller controllers employ fixed-sequence startup algorithms that cannot adapt to varying ambient conditions, system configurations, or equipment age. These rigid protocols fail to account for factors such as oil temperature, refrigerant distribution, bearing temperature profiles, or historical performance data that could inform more intelligent startup strategies. The absence of real-time condition monitoring and predictive analytics prevents proactive adjustments that could enhance startup smoothness and reliability.
Existing Chiller Startup Sequence Solutions
01 Sequential compressor startup control
Implementing a controlled sequence for starting multiple compressors in a chiller system to prevent electrical overload and mechanical stress. The startup sequence staggers the activation of compressors with predetermined time delays between each unit, allowing the system to gradually reach full capacity while maintaining stable operation. This approach reduces peak power demand and minimizes voltage drops during startup.- Sequential compressor startup control: Implementing controlled sequential startup of multiple compressors in a chiller system to prevent electrical overload and mechanical stress. The startup sequence is managed through a controller that staggers the activation of each compressor with predetermined time delays, ensuring smooth power draw and reducing inrush current. This approach minimizes voltage drops and mechanical shock to the system components during the initial startup phase.
- Soft start mechanisms for motor protection: Utilizing soft start technology to gradually ramp up motor speed and torque during chiller startup, reducing mechanical stress and electrical surge. This includes variable frequency drives or soft starters that control the voltage and current supplied to the compressor motors, allowing for a smooth acceleration curve. The gradual startup extends equipment life and prevents sudden pressure spikes in the refrigeration system.
- Pre-startup system checks and diagnostics: Implementing automated pre-startup diagnostic routines that verify system conditions before initiating chiller operation. These checks include monitoring oil levels, refrigerant pressures, temperature sensors, and electrical connections to ensure all parameters are within acceptable ranges. The diagnostic system can prevent startup if unsafe conditions are detected, protecting equipment from damage and ensuring smooth operation when startup proceeds.
- Load balancing during startup transition: Managing the gradual application of cooling load during the startup phase to prevent system shock and ensure stable operation. This involves controlling the opening of expansion valves, modulating water flow rates, and coordinating the activation of multiple circuits in a staged manner. The load balancing strategy allows the system to reach steady-state operation smoothly without excessive cycling or pressure fluctuations.
- Pressure equalization and oil management: Ensuring proper pressure equalization across the refrigeration system and adequate oil circulation before and during startup. This includes implementing delay timers to allow pressure to equalize between high and low sides, preventing hard starts. Oil management systems ensure sufficient lubrication reaches all compressor components during the critical startup phase, with oil heaters activated prior to startup to maintain proper viscosity and circulation.
02 Soft start mechanisms for motor protection
Utilizing soft start technology to gradually ramp up motor speed and torque during chiller startup, reducing mechanical shock and electrical stress on components. This method employs variable frequency drives or electronic starters to control the acceleration profile, preventing sudden current surges and extending equipment lifespan. The soft start approach ensures smooth transitions from standby to full operational mode.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pre-startup system checks and diagnostics
Performing automated diagnostic routines before initiating chiller startup to verify system readiness and identify potential issues. These checks include monitoring refrigerant levels, oil pressure, temperature sensors, and electrical connections to ensure all parameters are within acceptable ranges. The diagnostic sequence prevents startup attempts when conditions are unfavorable, protecting equipment from damage.Expand Specific Solutions04 Load balancing during startup phase
Managing the distribution of cooling load across multiple chillers or compressor stages during the startup sequence to achieve balanced operation. The control system monitors demand and gradually brings additional capacity online as needed, preventing any single unit from being overloaded. This strategy optimizes energy efficiency while ensuring stable system performance throughout the startup transition.Expand Specific Solutions05 Pressure equalization and oil management
Implementing procedures to equalize refrigerant pressures and ensure proper oil circulation before and during chiller startup. The system allows time for pressure differentials to stabilize across components and verifies adequate oil return to compressors, preventing liquid slugging and ensuring proper lubrication. These measures protect mechanical components and enable smooth, reliable startup operations.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Players in Chiller Manufacturing Industry
The chiller startup sequence optimization field is experiencing steady growth as energy efficiency becomes critical for commercial and industrial facilities. The market is driven by rising operational costs and sustainability mandates, with significant opportunities in data centers, manufacturing plants, and large-scale HVAC systems. Technology maturity varies across players: established manufacturers like Gree Electric Appliances, Haier Smart Home, Midea Group, and Mitsubishi Electric have developed sophisticated control algorithms integrated into their equipment, while Johnson Controls, Carrier Corporation, and Trane International offer advanced building management systems with predictive optimization capabilities. Specialized firms like Tekworx focus exclusively on chiller plant optimization solutions, demonstrating niche expertise. The competitive landscape shows consolidation among major HVAC manufacturers who are incorporating AI-driven controls and IoT connectivity, while traditional players like Siemens and General Electric leverage their automation expertise to enhance system-level efficiency and reliability.
Gree Electric Appliances, Inc. of Zhuhai
Technical Solution: Gree has developed a multi-stage startup control system for their centrifugal and screw chillers that emphasizes mechanical protection and energy efficiency. Their technology implements a three-phase startup sequence: pre-lubrication phase where oil pumps operate for 60-90 seconds before compressor engagement, soft-start phase utilizing frequency conversion technology to gradually accelerate the compressor from 15% to full speed over 2-4 minutes, and load stabilization phase where cooling capacity incrementally increases while monitoring system pressures and temperatures. The control system incorporates intelligent sensors that detect abnormal vibration, temperature spikes, or pressure fluctuations during startup, automatically adjusting parameters or aborting the sequence if safety thresholds are exceeded. Gree's solution includes anti-surge protection for centrifugal compressors and liquid slugging prevention mechanisms that ensure only gaseous refrigerant enters the compressor during initial operation.
Strengths: Cost-effective implementation, strong focus on mechanical component protection, suitable for various chiller types. Weaknesses: Less sophisticated predictive capabilities compared to Western competitors, limited integration with non-Gree equipment in multi-brand installations.
Midea Group Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Midea has engineered an intelligent startup optimization system for their chiller product line that combines IoT connectivity with cloud-based analytics to continuously refine startup procedures. Their solution employs variable speed drive technology with customized acceleration curves tailored to specific compressor types and capacities, reducing mechanical stress by up to 45% during the startup phase. The system features pre-startup condition assessment that evaluates oil temperature, refrigerant distribution, and system pressures to determine the optimal initialization sequence. Midea's technology includes coordinated control for chiller plants with multiple units, implementing staggered startup timing with 30-60 second intervals to minimize electrical demand spikes and maintain power quality. The platform utilizes predictive maintenance algorithms that analyze startup performance trends to identify developing issues before they cause failures, and automatically adjusts startup parameters to compensate for component wear or seasonal variations in operating conditions.
Strengths: Excellent cost-performance ratio, strong IoT integration for remote monitoring and optimization, effective for medium to large commercial applications. Weaknesses: Cloud dependency may raise data security concerns for some clients, relatively newer technology with less long-term field validation compared to established competitors.
Core Patents in Startup Optimization Tech
Start sequence generation device, start sequence generation method, and program for turbo refrigerator
PatentInactiveJP2024011843A
Innovation
- A startup sequence generation device and method that optimize compressor operation by calculating optimal manipulated variables using a mathematical model, state variables, and constraint conditions to reduce startup time.
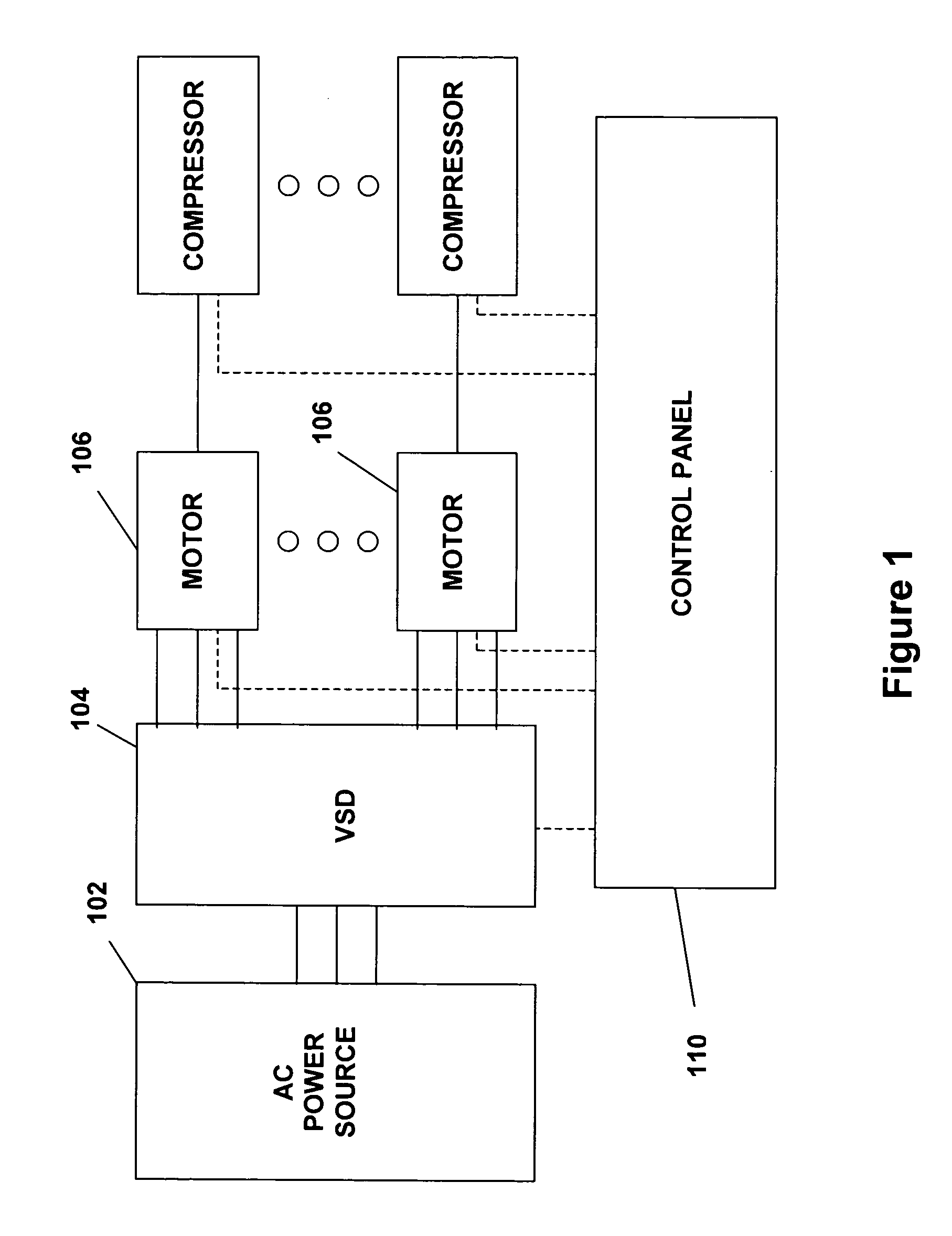
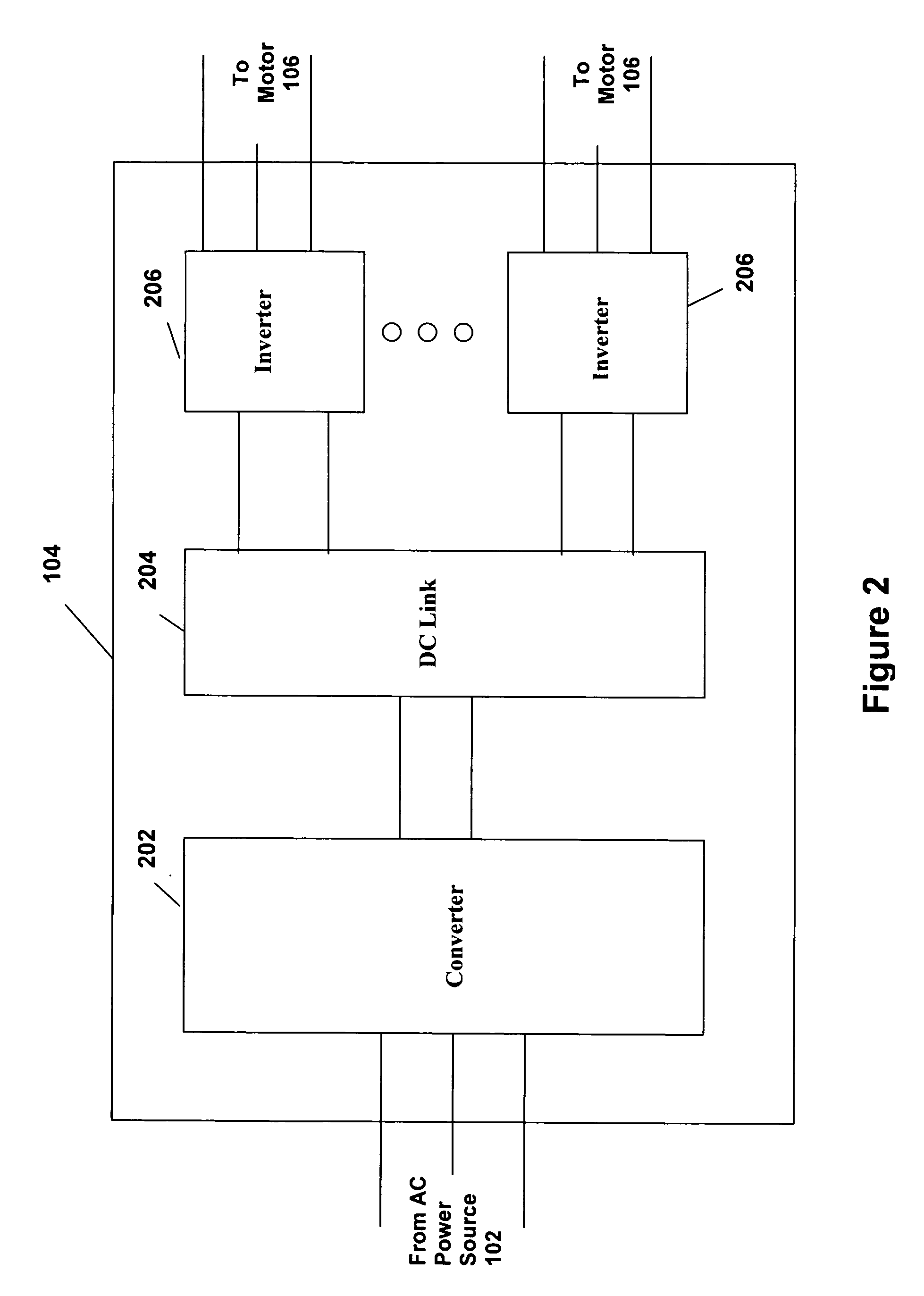
Startup control system and method for a multiple compressor chiller system
PatentInactiveUS7231773B2
Innovation
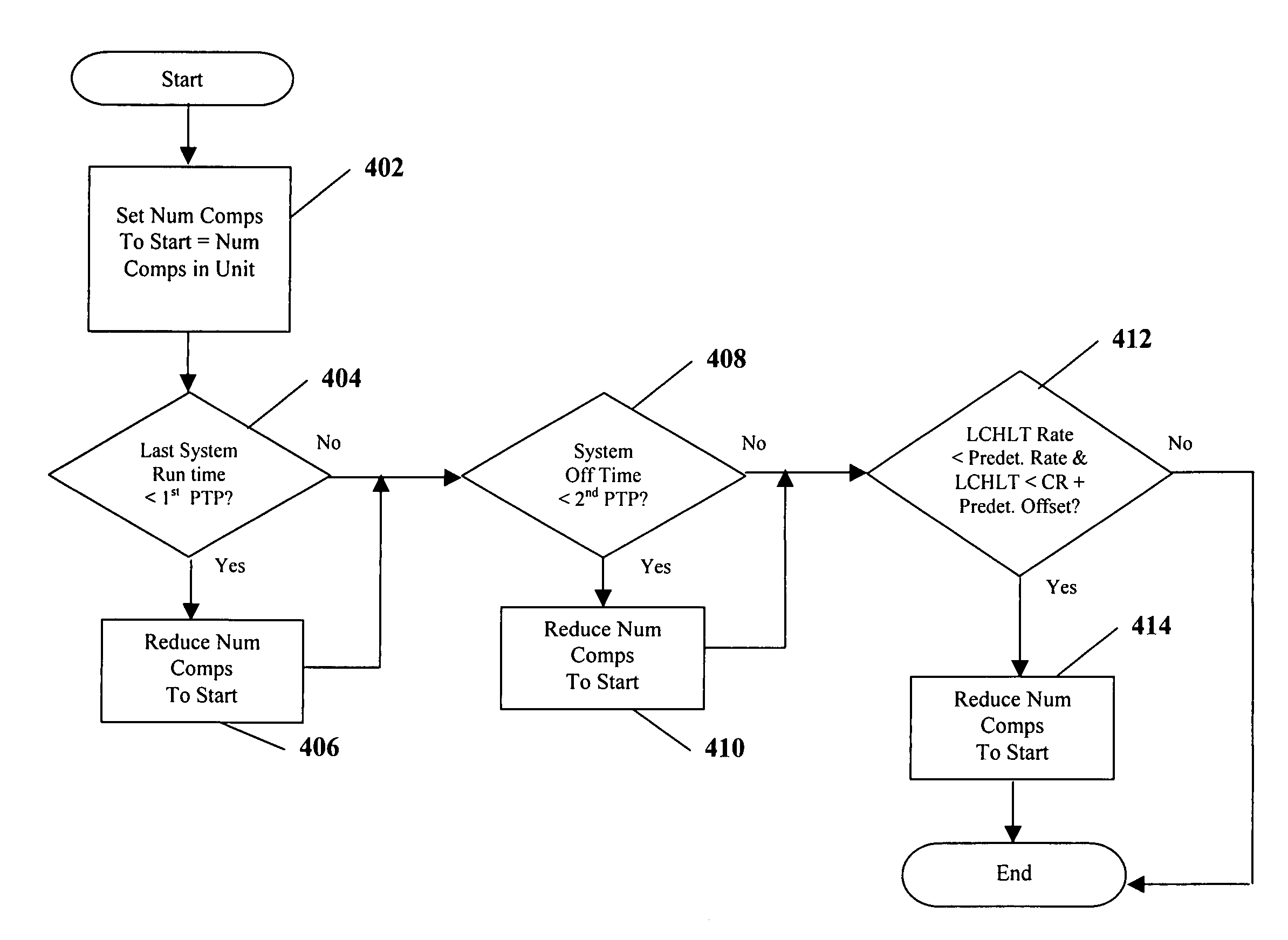
- A method and system that utilize a variable speed drive with multiple inverters to dynamically determine and adjust the number of compressors to start based on system conditions, such as recent operation time, shutdown time, and chilled liquid temperature changes, allowing for the maximum number of compressors to be started efficiently at system initialization.
Energy Efficiency Standards and Regulations
Energy efficiency standards and regulations form the foundational framework governing chiller system operations globally. These regulatory mechanisms establish minimum performance thresholds, operational protocols, and environmental compliance requirements that directly influence startup sequence optimization strategies. International standards such as ISO 50001 for energy management systems and ASHRAE Standard 90.1 for energy-efficient building design provide comprehensive guidelines for chiller operations, including startup procedures that minimize energy waste during transitional phases.
Regional regulatory bodies have implemented increasingly stringent efficiency mandates that impact chiller startup optimization. The European Union's Ecodesign Directive sets mandatory efficiency requirements for cooling equipment, while the United States Department of Energy enforces efficiency standards through its appliance and equipment regulations. These frameworks typically specify metrics such as Integrated Part Load Value (IPLV) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), which inherently reward optimized startup sequences that reduce energy consumption during partial load conditions.
Compliance with these standards necessitates sophisticated control strategies during chiller startup. Regulations increasingly emphasize dynamic performance rather than steady-state efficiency, recognizing that startup transients significantly contribute to overall energy consumption. Modern standards encourage the adoption of variable speed drives, intelligent sequencing algorithms, and predictive control systems that align with regulatory efficiency targets while maintaining operational stability.
The regulatory landscape continues evolving toward performance-based standards that incentivize innovation in startup optimization. Recent amendments to standards incorporate real-time monitoring requirements and demand response capabilities, pushing manufacturers and operators to develop startup sequences that respond adaptively to grid conditions and building loads. These regulatory trends create both compliance obligations and competitive advantages for organizations implementing advanced startup optimization technologies, making regulatory awareness essential for effective chiller system design and operation.
Regional regulatory bodies have implemented increasingly stringent efficiency mandates that impact chiller startup optimization. The European Union's Ecodesign Directive sets mandatory efficiency requirements for cooling equipment, while the United States Department of Energy enforces efficiency standards through its appliance and equipment regulations. These frameworks typically specify metrics such as Integrated Part Load Value (IPLV) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), which inherently reward optimized startup sequences that reduce energy consumption during partial load conditions.
Compliance with these standards necessitates sophisticated control strategies during chiller startup. Regulations increasingly emphasize dynamic performance rather than steady-state efficiency, recognizing that startup transients significantly contribute to overall energy consumption. Modern standards encourage the adoption of variable speed drives, intelligent sequencing algorithms, and predictive control systems that align with regulatory efficiency targets while maintaining operational stability.
The regulatory landscape continues evolving toward performance-based standards that incentivize innovation in startup optimization. Recent amendments to standards incorporate real-time monitoring requirements and demand response capabilities, pushing manufacturers and operators to develop startup sequences that respond adaptively to grid conditions and building loads. These regulatory trends create both compliance obligations and competitive advantages for organizations implementing advanced startup optimization technologies, making regulatory awareness essential for effective chiller system design and operation.
Predictive Maintenance Integration Strategies
Integrating predictive maintenance strategies into chiller startup sequence optimization represents a paradigm shift from reactive to proactive operational management. By leveraging real-time sensor data, historical performance records, and advanced analytics, facilities can anticipate component degradation before it impacts startup reliability. This integration enables maintenance teams to address potential issues during planned downtime rather than experiencing unexpected failures during critical startup phases, thereby reducing operational disruptions and extending equipment lifespan.
The foundation of effective predictive maintenance integration lies in establishing comprehensive data collection frameworks across all chiller subsystems. Critical parameters including compressor vibration signatures, bearing temperature profiles, refrigerant pressure fluctuations, and oil quality indicators must be continuously monitored and analyzed. Machine learning algorithms can identify subtle deviations from normal operating patterns that precede component failures, allowing maintenance interventions to be scheduled strategically around operational demands rather than emergency responses.
Advanced predictive models should be designed to assess the health status of components specifically stressed during startup sequences, such as motor windings, starter contactors, and expansion valves. These models can generate risk scores that inform startup protocols, potentially triggering modified sequences for equipment showing early degradation signs. For instance, chillers with elevated bearing wear indicators might benefit from extended pre-lubrication cycles or reduced initial loading rates to minimize mechanical stress.
Integration strategies must also address the interoperability between predictive maintenance platforms and building management systems. Seamless data exchange enables automated adjustments to startup sequences based on real-time equipment health assessments. This connectivity allows for dynamic optimization where startup parameters are continuously refined according to current component conditions, ambient factors, and predicted maintenance windows. Furthermore, predictive insights can inform long-term capital planning by identifying equipment approaching end-of-life conditions, enabling proactive replacement scheduling that minimizes operational impact while optimizing budget allocation.
The foundation of effective predictive maintenance integration lies in establishing comprehensive data collection frameworks across all chiller subsystems. Critical parameters including compressor vibration signatures, bearing temperature profiles, refrigerant pressure fluctuations, and oil quality indicators must be continuously monitored and analyzed. Machine learning algorithms can identify subtle deviations from normal operating patterns that precede component failures, allowing maintenance interventions to be scheduled strategically around operational demands rather than emergency responses.
Advanced predictive models should be designed to assess the health status of components specifically stressed during startup sequences, such as motor windings, starter contactors, and expansion valves. These models can generate risk scores that inform startup protocols, potentially triggering modified sequences for equipment showing early degradation signs. For instance, chillers with elevated bearing wear indicators might benefit from extended pre-lubrication cycles or reduced initial loading rates to minimize mechanical stress.
Integration strategies must also address the interoperability between predictive maintenance platforms and building management systems. Seamless data exchange enables automated adjustments to startup sequences based on real-time equipment health assessments. This connectivity allows for dynamic optimization where startup parameters are continuously refined according to current component conditions, ambient factors, and predicted maintenance windows. Furthermore, predictive insights can inform long-term capital planning by identifying equipment approaching end-of-life conditions, enabling proactive replacement scheduling that minimizes operational impact while optimizing budget allocation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!