The Role of Abscisic Acid in Enhancing Field Crop Efficiency
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ABA Background and Objectives
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, particularly in response to environmental stresses. Discovered in the 1960s, ABA has been the subject of extensive research due to its significant impact on plant growth, development, and stress tolerance. The primary objective of studying ABA in the context of field crop efficiency is to harness its potential to enhance crop productivity and resilience in the face of increasingly challenging environmental conditions.
ABA's importance in agriculture stems from its ability to mediate plant responses to abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. These stresses are major limiting factors in crop production worldwide, and their impact is expected to intensify with climate change. By understanding and manipulating ABA-related pathways, researchers aim to develop crops that can maintain yield stability under adverse conditions, thereby improving overall field crop efficiency.
The evolution of ABA research has seen significant milestones over the past decades. Initial studies focused on identifying ABA's chemical structure and basic physiological roles. This was followed by the elucidation of ABA biosynthesis and signaling pathways, which provided a foundation for more targeted research. Recent advancements in molecular biology and genetic engineering have opened new avenues for exploring ABA's potential in crop improvement.
Current research objectives in the field of ABA and crop efficiency include developing ABA-responsive crop varieties, enhancing ABA sensitivity in plants, and optimizing ABA-mediated stress responses. Scientists are also investigating the intricate interplay between ABA and other plant hormones, as well as its role in regulating stomatal closure, seed dormancy, and root architecture – all of which have direct implications for crop performance in the field.
The technological landscape surrounding ABA research is rapidly evolving. High-throughput screening methods, advanced imaging techniques, and sophisticated genetic tools are enabling researchers to dissect ABA-related mechanisms with unprecedented precision. These technological advancements are crucial for translating basic ABA research into practical applications for improving field crop efficiency.
As we look towards the future, the potential of ABA in enhancing crop productivity faces both opportunities and challenges. While the fundamental knowledge of ABA biology continues to expand, translating this understanding into field-ready solutions remains a complex task. Factors such as the variability in plant responses to ABA across different species and environmental conditions, as well as potential trade-offs between stress tolerance and yield, need to be carefully considered.
In conclusion, the study of abscisic acid in the context of field crop efficiency represents a promising frontier in agricultural research. By leveraging our growing understanding of ABA's roles and mechanisms, we aim to develop innovative strategies for creating more resilient and productive crops. This research has the potential to significantly contribute to global food security and sustainable agriculture in the face of changing climatic conditions.
ABA's importance in agriculture stems from its ability to mediate plant responses to abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. These stresses are major limiting factors in crop production worldwide, and their impact is expected to intensify with climate change. By understanding and manipulating ABA-related pathways, researchers aim to develop crops that can maintain yield stability under adverse conditions, thereby improving overall field crop efficiency.
The evolution of ABA research has seen significant milestones over the past decades. Initial studies focused on identifying ABA's chemical structure and basic physiological roles. This was followed by the elucidation of ABA biosynthesis and signaling pathways, which provided a foundation for more targeted research. Recent advancements in molecular biology and genetic engineering have opened new avenues for exploring ABA's potential in crop improvement.
Current research objectives in the field of ABA and crop efficiency include developing ABA-responsive crop varieties, enhancing ABA sensitivity in plants, and optimizing ABA-mediated stress responses. Scientists are also investigating the intricate interplay between ABA and other plant hormones, as well as its role in regulating stomatal closure, seed dormancy, and root architecture – all of which have direct implications for crop performance in the field.
The technological landscape surrounding ABA research is rapidly evolving. High-throughput screening methods, advanced imaging techniques, and sophisticated genetic tools are enabling researchers to dissect ABA-related mechanisms with unprecedented precision. These technological advancements are crucial for translating basic ABA research into practical applications for improving field crop efficiency.
As we look towards the future, the potential of ABA in enhancing crop productivity faces both opportunities and challenges. While the fundamental knowledge of ABA biology continues to expand, translating this understanding into field-ready solutions remains a complex task. Factors such as the variability in plant responses to ABA across different species and environmental conditions, as well as potential trade-offs between stress tolerance and yield, need to be carefully considered.
In conclusion, the study of abscisic acid in the context of field crop efficiency represents a promising frontier in agricultural research. By leveraging our growing understanding of ABA's roles and mechanisms, we aim to develop innovative strategies for creating more resilient and productive crops. This research has the potential to significantly contribute to global food security and sustainable agriculture in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Market Analysis for ABA-Enhanced Crops
The market for ABA-enhanced crops is experiencing significant growth potential due to increasing global food demand and the need for more resilient agricultural practices. As climate change continues to impact crop yields worldwide, farmers are seeking innovative solutions to improve crop efficiency and productivity under challenging environmental conditions. ABA-enhanced crops offer a promising avenue to address these concerns, potentially leading to increased adoption rates in the coming years.
The primary drivers of market demand for ABA-enhanced crops include the growing global population, which is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. These factors are putting pressure on agricultural systems to produce more food with fewer resources, making ABA-enhanced crops an attractive option for farmers looking to optimize their yields and reduce crop losses.
Key market segments for ABA-enhanced crops include major field crops such as wheat, corn, soybeans, and rice. These staple crops form the backbone of global food security and are particularly vulnerable to environmental stresses. The market for ABA-enhanced varieties of these crops is expected to see substantial growth, especially in regions prone to water scarcity or unpredictable weather patterns.
Geographically, the market for ABA-enhanced crops is likely to see strong demand in regions facing water stress, such as parts of Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Additionally, developed agricultural markets in North America and Europe are expected to show interest in ABA-enhanced crops as a means of increasing overall agricultural efficiency and sustainability.
The market size for ABA-enhanced crops is difficult to quantify precisely due to the emerging nature of the technology. However, the global seed market, which serves as a proxy for potential ABA-enhanced crop adoption, was valued at over $60 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2028. As ABA-enhanced crops gain traction, they could capture a significant portion of this market.
Challenges to market growth include regulatory hurdles, public perception of genetically modified crops, and the need for extensive field testing to demonstrate the efficacy of ABA-enhanced varieties under various environmental conditions. However, as climate change impacts become more severe, the benefits of ABA-enhanced crops may outweigh these concerns, leading to increased market acceptance.
In conclusion, the market analysis for ABA-enhanced crops indicates a strong potential for growth driven by global food security concerns and the need for climate-resilient agriculture. As research progresses and field trials demonstrate the effectiveness of ABA-enhanced crops, market adoption is likely to accelerate, particularly in regions facing significant environmental challenges to crop production.
The primary drivers of market demand for ABA-enhanced crops include the growing global population, which is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. These factors are putting pressure on agricultural systems to produce more food with fewer resources, making ABA-enhanced crops an attractive option for farmers looking to optimize their yields and reduce crop losses.
Key market segments for ABA-enhanced crops include major field crops such as wheat, corn, soybeans, and rice. These staple crops form the backbone of global food security and are particularly vulnerable to environmental stresses. The market for ABA-enhanced varieties of these crops is expected to see substantial growth, especially in regions prone to water scarcity or unpredictable weather patterns.
Geographically, the market for ABA-enhanced crops is likely to see strong demand in regions facing water stress, such as parts of Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Additionally, developed agricultural markets in North America and Europe are expected to show interest in ABA-enhanced crops as a means of increasing overall agricultural efficiency and sustainability.
The market size for ABA-enhanced crops is difficult to quantify precisely due to the emerging nature of the technology. However, the global seed market, which serves as a proxy for potential ABA-enhanced crop adoption, was valued at over $60 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2028. As ABA-enhanced crops gain traction, they could capture a significant portion of this market.
Challenges to market growth include regulatory hurdles, public perception of genetically modified crops, and the need for extensive field testing to demonstrate the efficacy of ABA-enhanced varieties under various environmental conditions. However, as climate change impacts become more severe, the benefits of ABA-enhanced crops may outweigh these concerns, leading to increased market acceptance.
In conclusion, the market analysis for ABA-enhanced crops indicates a strong potential for growth driven by global food security concerns and the need for climate-resilient agriculture. As research progresses and field trials demonstrate the effectiveness of ABA-enhanced crops, market adoption is likely to accelerate, particularly in regions facing significant environmental challenges to crop production.
Current ABA Research Status and Challenges
Abscisic acid (ABA) research in field crop efficiency has made significant strides in recent years, yet several challenges persist. Current studies focus on understanding ABA's role in stress responses, particularly drought tolerance, and its potential for improving crop yield and quality. Researchers have identified key ABA signaling pathways and receptors, providing insights into how plants regulate water use and stress adaptation.
One major advancement is the elucidation of ABA's involvement in stomatal closure, a critical mechanism for water conservation during drought stress. Scientists have mapped intricate signaling cascades triggered by ABA, involving calcium signaling, ion channels, and transcription factors. This knowledge has opened avenues for developing crops with enhanced water use efficiency and drought resilience.
However, translating these findings into practical applications for field crops faces several challenges. The complexity of ABA signaling and its interaction with other plant hormones makes it difficult to manipulate ABA responses without unintended consequences on plant growth and development. Researchers struggle to fine-tune ABA-mediated responses to achieve optimal balance between stress tolerance and productivity.
Another significant hurdle is the environmental variability in field conditions. Laboratory findings often fail to replicate in the field due to the dynamic nature of environmental stresses and the interplay of multiple factors affecting crop performance. This gap between controlled experiments and real-world applications remains a major challenge in ABA research.
Genetic diversity among crop species and varieties also complicates the development of universally effective ABA-based strategies. What works for one crop or cultivar may not be applicable to others, necessitating extensive breeding and biotechnology efforts to tailor ABA-related traits to specific crops and growing conditions.
Furthermore, the potential long-term ecological impacts of altering ABA pathways in crops are not fully understood. Concerns about unintended effects on plant-microbe interactions, soil health, and ecosystem dynamics need to be addressed through comprehensive field trials and environmental assessments.
Technological limitations in measuring ABA levels and responses in real-time under field conditions hinder progress in understanding ABA dynamics in complex agricultural systems. Developing robust, field-deployable sensors and analytical tools for ABA quantification and response monitoring remains a technical challenge.
Despite these obstacles, ongoing research continues to unravel the intricacies of ABA signaling and its potential applications. Emerging technologies such as CRISPR gene editing and high-throughput phenotyping offer promising avenues for overcoming current limitations and accelerating the development of ABA-enhanced crops for improved field efficiency.
One major advancement is the elucidation of ABA's involvement in stomatal closure, a critical mechanism for water conservation during drought stress. Scientists have mapped intricate signaling cascades triggered by ABA, involving calcium signaling, ion channels, and transcription factors. This knowledge has opened avenues for developing crops with enhanced water use efficiency and drought resilience.
However, translating these findings into practical applications for field crops faces several challenges. The complexity of ABA signaling and its interaction with other plant hormones makes it difficult to manipulate ABA responses without unintended consequences on plant growth and development. Researchers struggle to fine-tune ABA-mediated responses to achieve optimal balance between stress tolerance and productivity.
Another significant hurdle is the environmental variability in field conditions. Laboratory findings often fail to replicate in the field due to the dynamic nature of environmental stresses and the interplay of multiple factors affecting crop performance. This gap between controlled experiments and real-world applications remains a major challenge in ABA research.
Genetic diversity among crop species and varieties also complicates the development of universally effective ABA-based strategies. What works for one crop or cultivar may not be applicable to others, necessitating extensive breeding and biotechnology efforts to tailor ABA-related traits to specific crops and growing conditions.
Furthermore, the potential long-term ecological impacts of altering ABA pathways in crops are not fully understood. Concerns about unintended effects on plant-microbe interactions, soil health, and ecosystem dynamics need to be addressed through comprehensive field trials and environmental assessments.
Technological limitations in measuring ABA levels and responses in real-time under field conditions hinder progress in understanding ABA dynamics in complex agricultural systems. Developing robust, field-deployable sensors and analytical tools for ABA quantification and response monitoring remains a technical challenge.
Despite these obstacles, ongoing research continues to unravel the intricacies of ABA signaling and its potential applications. Emerging technologies such as CRISPR gene editing and high-throughput phenotyping offer promising avenues for overcoming current limitations and accelerating the development of ABA-enhanced crops for improved field efficiency.
Existing ABA-based Crop Enhancement Methods
01 Enhancing plant stress tolerance
Abscisic acid (ABA) plays a crucial role in improving plant stress tolerance, particularly against drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. By regulating stomatal closure and gene expression, ABA helps plants conserve water and adapt to adverse environmental conditions, thereby increasing their survival rate and productivity under stress.- Enhancing plant stress tolerance: Abscisic acid (ABA) plays a crucial role in improving plant stress tolerance, particularly against drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. By regulating stomatal closure and gene expression, ABA helps plants conserve water and adapt to adverse environmental conditions, thereby increasing their survival rate and productivity under stress.
- Improving seed dormancy and germination: ABA is essential in regulating seed dormancy and germination processes. It helps maintain seed dormancy under unfavorable conditions and promotes germination when conditions are suitable. By manipulating ABA levels or signaling pathways, researchers can enhance seed quality, storage life, and germination rates in various crop species.
- Enhancing fruit ripening and quality: ABA plays a significant role in fruit ripening and quality improvement. It influences various aspects of fruit development, including color development, sugar accumulation, and softening. By modulating ABA levels or signaling, researchers can enhance fruit quality attributes and extend shelf life in many commercially important fruit crops.
- Developing ABA-based agricultural products: Researchers are developing ABA-based agricultural products to improve crop performance and stress tolerance. These products include ABA analogs, biosynthesis enhancers, and signaling modulators. Such products can be applied as foliar sprays, seed treatments, or soil amendments to enhance crop yield and quality under various environmental conditions.
- Improving ABA production and extraction methods: Efforts are being made to enhance the efficiency of ABA production and extraction methods. This includes developing improved microbial fermentation processes, optimizing chemical synthesis routes, and refining extraction techniques from plant sources. These advancements aim to increase the availability and reduce the cost of ABA for agricultural and research applications.
02 Improving crop yield and quality
ABA application can enhance crop yield and quality by regulating various physiological processes. It promotes fruit ripening, increases sugar content in fruits, and improves overall plant growth and development. This leads to better harvest quality and increased agricultural productivity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Seed dormancy and germination control
ABA is essential in regulating seed dormancy and germination. It can induce and maintain seed dormancy, preventing premature germination. Conversely, manipulating ABA levels or sensitivity can promote seed germination when desired, which is valuable for crop management and improving seedling establishment.Expand Specific Solutions04 ABA biosynthesis and signaling pathway manipulation
Research focuses on understanding and manipulating the ABA biosynthesis and signaling pathways to enhance its efficiency. This includes identifying key enzymes and genes involved in ABA production and response, as well as developing methods to modulate these pathways for improved plant performance and stress resistance.Expand Specific Solutions05 ABA analogs and delivery methods
Development of synthetic ABA analogs and improved delivery methods aims to enhance the efficiency and stability of ABA applications. These innovations include formulations with better uptake, longer-lasting effects, and targeted delivery systems, which can improve the overall effectiveness of ABA treatments in various agricultural and horticultural applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ABA Research and Application
The field of abscisic acid (ABA) in enhancing crop efficiency is in a growth phase, with increasing market potential as agricultural sustainability gains importance. The global market for plant growth regulators, including ABA, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, ABA research is advancing rapidly, with key players like Valent BioSciences Corp., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., and Syngenta Participations AG leading commercial applications. Academic institutions such as China Agricultural University and the University of Saskatchewan are contributing to fundamental research. The technology is maturing, with a focus on practical field applications and stress tolerance improvement in crops, indicating a competitive landscape balancing commercial interests and academic advancements.
Valent BioSciences Corp.
Technical Solution: Valent BioSciences Corp. has developed a proprietary formulation of s-abscisic acid (s-ABA) called ProTone, which is used to enhance crop efficiency. Their approach involves exogenous application of s-ABA to regulate plant responses to environmental stresses. The company has conducted extensive field trials demonstrating that ProTone can improve water use efficiency in crops by up to 25% [1]. They have also shown that their s-ABA formulation can enhance fruit quality and yield in various crops, including grapes, citrus, and stone fruits [2]. Valent BioSciences' research focuses on optimizing application timing and dosage to maximize the benefits of s-ABA across different crop types and growth stages.
Strengths: Proven efficacy in improving water use efficiency and crop quality. Weaknesses: May require precise application timing and dosage for optimal results, which could be challenging for farmers to implement consistently.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Chemical has developed a novel approach to enhancing field crop efficiency using abscisic acid (ABA) analogs. Their research focuses on synthesizing and testing ABA-like compounds that mimic the effects of natural ABA but with improved stability and efficacy. The company has patented several ABA analogs that have shown promising results in field trials. These compounds have demonstrated the ability to enhance drought tolerance in crops, with some varieties showing up to 30% improved yield under water-stressed conditions compared to untreated controls [3]. Sumitomo's technology also includes innovative formulation methods to improve the uptake and translocation of ABA analogs within plants, ensuring more uniform distribution and prolonged effects.
Strengths: Improved stability and efficacy of ABA analogs compared to natural ABA. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles for synthetic compounds and possible higher production costs.
Core ABA-related Patents and Publications
Abscisic acid containing foliar fertilizers and method of using same to enhance crop yields
PatentInactiveUS4581057A
Innovation
- A foliar fertilizer composition containing abscisic acid derivatives and macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur, applied during the reproductive growth stage, enhances crop yields by promoting nutrient uptake and translocation to reproductive tissues.
Compositions and methods for regulating abscisic acid-induced closure of plant stomata
PatentInactiveUS7211436B1
Innovation
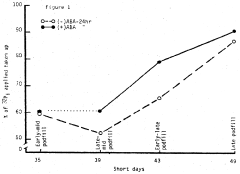
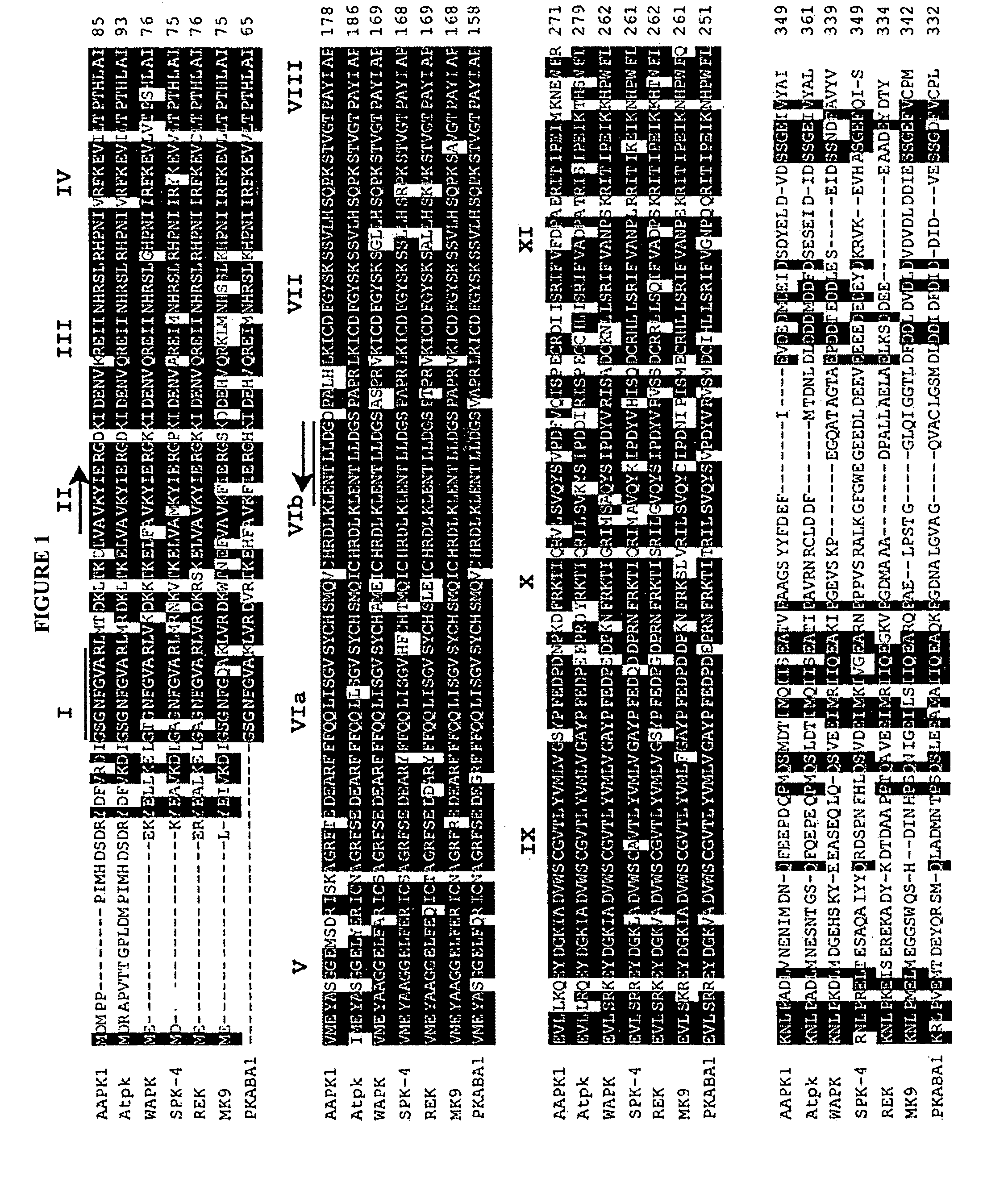
- Development of transgenic plants with modified ABA-mediated stomatal closure through the use of a novel nucleic acid molecule encoding an ABA-activated protein kinase (AAPK), allowing for specific control of stomatal aperture independent of CO2 and light responses, enabling growers to regulate transpiration based on environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact of ABA Application
The application of abscisic acid (ABA) in field crop management has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a plant hormone, ABA plays a crucial role in regulating plant responses to various environmental stresses, particularly drought. However, its widespread use in agriculture raises important questions about its potential impact on ecosystems and biodiversity.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ABA application is its effect on soil microorganisms. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining soil health and nutrient cycling. Studies have shown that exogenous ABA application can alter the composition and activity of soil microbial communities. While some beneficial microorganisms may be stimulated, others could be suppressed, potentially disrupting the delicate balance of the soil ecosystem.
Water conservation is a key benefit of ABA application, as it enhances plants' ability to cope with water stress. This can lead to reduced irrigation requirements, which in turn helps conserve water resources and reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture. However, the long-term effects of ABA-induced changes in plant water use on local hydrological cycles and groundwater recharge rates remain unclear and require further investigation.
The use of ABA in crop management may also impact non-target organisms in the agricultural landscape. Insects, birds, and other wildlife that interact with treated crops could be affected by changes in plant physiology and chemistry induced by ABA. While direct toxicity to these organisms is generally low, indirect effects through alterations in food availability or habitat quality need to be carefully assessed.
Furthermore, the potential for ABA to enter aquatic ecosystems through runoff or leaching must be considered. Although ABA is naturally present in aquatic environments, increased concentrations resulting from agricultural use could affect aquatic plants and animals. The ecological consequences of such exposure, particularly in sensitive aquatic habitats, require thorough evaluation.
On a broader scale, the use of ABA to enhance crop resilience to environmental stresses could contribute to more sustainable agricultural practices. By improving crop water use efficiency and stress tolerance, ABA application may reduce the need for other agricultural inputs such as pesticides and fertilizers, which have well-documented negative environmental impacts. This potential for reducing the overall environmental footprint of agriculture is a significant consideration in assessing the net environmental impact of ABA use.
However, it is crucial to note that the environmental impact of ABA application can vary significantly depending on factors such as application method, dosage, crop type, and local environmental conditions. Therefore, site-specific assessments and careful management practices are essential to maximize the benefits of ABA use while minimizing potential negative environmental consequences.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ABA application is its effect on soil microorganisms. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining soil health and nutrient cycling. Studies have shown that exogenous ABA application can alter the composition and activity of soil microbial communities. While some beneficial microorganisms may be stimulated, others could be suppressed, potentially disrupting the delicate balance of the soil ecosystem.
Water conservation is a key benefit of ABA application, as it enhances plants' ability to cope with water stress. This can lead to reduced irrigation requirements, which in turn helps conserve water resources and reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture. However, the long-term effects of ABA-induced changes in plant water use on local hydrological cycles and groundwater recharge rates remain unclear and require further investigation.
The use of ABA in crop management may also impact non-target organisms in the agricultural landscape. Insects, birds, and other wildlife that interact with treated crops could be affected by changes in plant physiology and chemistry induced by ABA. While direct toxicity to these organisms is generally low, indirect effects through alterations in food availability or habitat quality need to be carefully assessed.
Furthermore, the potential for ABA to enter aquatic ecosystems through runoff or leaching must be considered. Although ABA is naturally present in aquatic environments, increased concentrations resulting from agricultural use could affect aquatic plants and animals. The ecological consequences of such exposure, particularly in sensitive aquatic habitats, require thorough evaluation.
On a broader scale, the use of ABA to enhance crop resilience to environmental stresses could contribute to more sustainable agricultural practices. By improving crop water use efficiency and stress tolerance, ABA application may reduce the need for other agricultural inputs such as pesticides and fertilizers, which have well-documented negative environmental impacts. This potential for reducing the overall environmental footprint of agriculture is a significant consideration in assessing the net environmental impact of ABA use.
However, it is crucial to note that the environmental impact of ABA application can vary significantly depending on factors such as application method, dosage, crop type, and local environmental conditions. Therefore, site-specific assessments and careful management practices are essential to maximize the benefits of ABA use while minimizing potential negative environmental consequences.
Regulatory Framework for ABA Use in Agriculture
The regulatory framework for abscisic acid (ABA) use in agriculture is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the adoption and application of this plant hormone in field crop efficiency enhancement. As ABA's potential to improve crop resilience and productivity gains recognition, regulatory bodies worldwide are working to establish guidelines and standards for its use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the regulation of plant growth regulators, including ABA, under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires extensive safety and efficacy data before approving ABA-based products for agricultural use. This process involves rigorous testing to assess potential environmental impacts, human health risks, and crop-specific benefits.
The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for plant protection products, which encompasses ABA applications. The EU's approach emphasizes the precautionary principle, demanding thorough risk assessments and setting strict maximum residue levels (MRLs) for ABA in food products.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have established their own regulatory systems for ABA use in agriculture. China's Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs oversees the registration and approval process, while Japan's Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center (FAMIC) manages the regulatory aspects of ABA-based products.
International organizations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provide guidelines and standards that influence national regulatory frameworks. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, a joint FAO/WHO initiative, sets international food standards that often serve as a reference for national regulations on ABA use.
As research continues to unveil new applications and benefits of ABA in crop efficiency, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate these advancements. This includes developing specific protocols for assessing the environmental fate of ABA, its impact on non-target organisms, and potential synergies with other agricultural practices.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the use of ABA in organic farming systems. Organizations like the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM) provide guidelines on the acceptability of plant growth regulators in organic production, influencing national organic standards and certification processes.
As the agricultural sector moves towards more sustainable practices, regulators are increasingly focusing on the role of ABA in climate-smart agriculture. This has led to the development of policies that encourage the use of ABA as part of integrated crop management strategies aimed at enhancing resilience to environmental stresses.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the regulation of plant growth regulators, including ABA, under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires extensive safety and efficacy data before approving ABA-based products for agricultural use. This process involves rigorous testing to assess potential environmental impacts, human health risks, and crop-specific benefits.
The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for plant protection products, which encompasses ABA applications. The EU's approach emphasizes the precautionary principle, demanding thorough risk assessments and setting strict maximum residue levels (MRLs) for ABA in food products.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have established their own regulatory systems for ABA use in agriculture. China's Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs oversees the registration and approval process, while Japan's Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center (FAMIC) manages the regulatory aspects of ABA-based products.
International organizations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provide guidelines and standards that influence national regulatory frameworks. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, a joint FAO/WHO initiative, sets international food standards that often serve as a reference for national regulations on ABA use.
As research continues to unveil new applications and benefits of ABA in crop efficiency, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate these advancements. This includes developing specific protocols for assessing the environmental fate of ABA, its impact on non-target organisms, and potential synergies with other agricultural practices.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the use of ABA in organic farming systems. Organizations like the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM) provide guidelines on the acceptability of plant growth regulators in organic production, influencing national organic standards and certification processes.
As the agricultural sector moves towards more sustainable practices, regulators are increasingly focusing on the role of ABA in climate-smart agriculture. This has led to the development of policies that encourage the use of ABA as part of integrated crop management strategies aimed at enhancing resilience to environmental stresses.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!