The Role of Kevlar in High-Performance Sporting Goods
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Kevlar in Sports: Evolution and Objectives
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s, has revolutionized the sporting goods industry since its introduction. Initially designed for use in tires, Kevlar's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability quickly caught the attention of sports equipment manufacturers. The evolution of Kevlar in sports can be traced through several key milestones, each marking a significant advancement in performance and safety.
In the 1970s, Kevlar made its debut in the sporting world, primarily in protective gear such as helmets and body armor for high-impact sports. The material's ability to absorb and dissipate energy while remaining lightweight made it an ideal choice for enhancing athlete safety without compromising mobility. As research and development progressed, the 1980s saw Kevlar expand into racquet sports, where it was used to reinforce tennis and badminton racquets, significantly improving their strength and reducing vibration.
The 1990s marked a turning point in Kevlar's sporting applications, with its integration into a wider range of equipment. Bicycle frames, kayaks, and even running shoes began incorporating Kevlar fibers to enhance durability and performance. This period also saw the development of hybrid materials, combining Kevlar with other high-performance fibers to create composites with tailored properties for specific sporting needs.
As we entered the 21st century, the objectives for Kevlar in sports became increasingly focused on pushing the boundaries of material science. Manufacturers aimed to create even lighter, stronger, and more responsive equipment. This led to the development of nano-scale Kevlar fibers and advanced manufacturing techniques that allowed for more precise control over material properties.
Today, the primary objectives for Kevlar in high-performance sporting goods are multifaceted. First and foremost is the continuous improvement of athlete performance through equipment optimization. This involves reducing weight while maintaining or enhancing strength, improving energy transfer in equipment like golf clubs and tennis racquets, and developing materials that can adapt to different environmental conditions.
Another key objective is to further enhance safety across various sports. As our understanding of sports-related injuries evolves, so does the need for advanced protective gear. Kevlar's role in developing next-generation helmets, body armor, and impact-resistant materials is crucial in this regard.
Sustainability has also emerged as a critical objective in recent years. Researchers are exploring ways to make Kevlar production more environmentally friendly and investigating methods for recycling and repurposing Kevlar-based sporting goods at the end of their lifecycle.
Looking ahead, the future objectives for Kevlar in sports include the development of smart materials that can provide real-time feedback to athletes, further miniaturization of Kevlar fibers for even more precise material control, and the exploration of bio-based alternatives that maintain Kevlar's exceptional properties while reducing environmental impact.
In the 1970s, Kevlar made its debut in the sporting world, primarily in protective gear such as helmets and body armor for high-impact sports. The material's ability to absorb and dissipate energy while remaining lightweight made it an ideal choice for enhancing athlete safety without compromising mobility. As research and development progressed, the 1980s saw Kevlar expand into racquet sports, where it was used to reinforce tennis and badminton racquets, significantly improving their strength and reducing vibration.
The 1990s marked a turning point in Kevlar's sporting applications, with its integration into a wider range of equipment. Bicycle frames, kayaks, and even running shoes began incorporating Kevlar fibers to enhance durability and performance. This period also saw the development of hybrid materials, combining Kevlar with other high-performance fibers to create composites with tailored properties for specific sporting needs.
As we entered the 21st century, the objectives for Kevlar in sports became increasingly focused on pushing the boundaries of material science. Manufacturers aimed to create even lighter, stronger, and more responsive equipment. This led to the development of nano-scale Kevlar fibers and advanced manufacturing techniques that allowed for more precise control over material properties.
Today, the primary objectives for Kevlar in high-performance sporting goods are multifaceted. First and foremost is the continuous improvement of athlete performance through equipment optimization. This involves reducing weight while maintaining or enhancing strength, improving energy transfer in equipment like golf clubs and tennis racquets, and developing materials that can adapt to different environmental conditions.
Another key objective is to further enhance safety across various sports. As our understanding of sports-related injuries evolves, so does the need for advanced protective gear. Kevlar's role in developing next-generation helmets, body armor, and impact-resistant materials is crucial in this regard.
Sustainability has also emerged as a critical objective in recent years. Researchers are exploring ways to make Kevlar production more environmentally friendly and investigating methods for recycling and repurposing Kevlar-based sporting goods at the end of their lifecycle.
Looking ahead, the future objectives for Kevlar in sports include the development of smart materials that can provide real-time feedback to athletes, further miniaturization of Kevlar fibers for even more precise material control, and the exploration of bio-based alternatives that maintain Kevlar's exceptional properties while reducing environmental impact.
Market Demand Analysis for Kevlar-Enhanced Sports Equipment
The market demand for Kevlar-enhanced sports equipment has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing focus on performance and safety in sports. Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont, has found its way into various sporting goods due to its exceptional properties, including high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and heat resistance.
In the professional sports sector, there is a significant demand for Kevlar-enhanced equipment, particularly in high-impact sports such as football, hockey, and motorsports. The material's ability to provide superior protection without compromising mobility has made it a preferred choice for protective gear manufacturers. This trend is expected to continue as sports leagues and organizations place greater emphasis on player safety.
The recreational sports market has also shown increased interest in Kevlar-enhanced products. Enthusiasts and amateur athletes are willing to invest in higher-quality equipment that offers improved performance and longevity. This has led to a growing market for Kevlar-reinforced bicycles, kayaks, and other outdoor sporting goods.
The fitness industry has embraced Kevlar in the production of high-performance training equipment. Kevlar-enhanced resistance bands, weight lifting belts, and cross-training shoes have gained popularity among fitness enthusiasts seeking durable and reliable gear for intense workouts.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for Kevlar-enhanced sports equipment, owing to the presence of major sports leagues and a strong culture of recreational sports. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential as disposable incomes rise and participation in sports increases.
The market is also influenced by technological advancements in Kevlar application techniques. Innovations in weaving and composite manufacturing have expanded the possibilities for integrating Kevlar into sports equipment, opening up new product categories and market opportunities.
Environmental concerns and sustainability trends are shaping consumer preferences, with a growing demand for eco-friendly and recyclable materials. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity for Kevlar-enhanced products, as manufacturers explore ways to improve the material's environmental profile and end-of-life recyclability.
Overall, the market demand for Kevlar-enhanced sports equipment is projected to continue its upward trajectory. The combination of performance benefits, safety improvements, and durability offered by Kevlar aligns well with the evolving needs of athletes, sports organizations, and recreational users alike.
In the professional sports sector, there is a significant demand for Kevlar-enhanced equipment, particularly in high-impact sports such as football, hockey, and motorsports. The material's ability to provide superior protection without compromising mobility has made it a preferred choice for protective gear manufacturers. This trend is expected to continue as sports leagues and organizations place greater emphasis on player safety.
The recreational sports market has also shown increased interest in Kevlar-enhanced products. Enthusiasts and amateur athletes are willing to invest in higher-quality equipment that offers improved performance and longevity. This has led to a growing market for Kevlar-reinforced bicycles, kayaks, and other outdoor sporting goods.
The fitness industry has embraced Kevlar in the production of high-performance training equipment. Kevlar-enhanced resistance bands, weight lifting belts, and cross-training shoes have gained popularity among fitness enthusiasts seeking durable and reliable gear for intense workouts.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for Kevlar-enhanced sports equipment, owing to the presence of major sports leagues and a strong culture of recreational sports. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential as disposable incomes rise and participation in sports increases.
The market is also influenced by technological advancements in Kevlar application techniques. Innovations in weaving and composite manufacturing have expanded the possibilities for integrating Kevlar into sports equipment, opening up new product categories and market opportunities.
Environmental concerns and sustainability trends are shaping consumer preferences, with a growing demand for eco-friendly and recyclable materials. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity for Kevlar-enhanced products, as manufacturers explore ways to improve the material's environmental profile and end-of-life recyclability.
Overall, the market demand for Kevlar-enhanced sports equipment is projected to continue its upward trajectory. The combination of performance benefits, safety improvements, and durability offered by Kevlar aligns well with the evolving needs of athletes, sports organizations, and recreational users alike.
Current Applications and Challenges in Sporting Goods
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont, has found widespread applications in the sporting goods industry due to its exceptional properties. In the realm of high-performance sporting equipment, Kevlar is primarily utilized for its strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and impact resistance. These characteristics make it an ideal material for enhancing the performance and safety of various sporting goods.
In the field of racquet sports, Kevlar is commonly incorporated into the strings and frames of tennis, badminton, and squash racquets. The addition of Kevlar to racquet strings provides increased durability and tension maintenance, resulting in improved power and control for players. Kevlar-reinforced frames offer enhanced stiffness and vibration dampening, contributing to better energy transfer and reduced player fatigue.
Cycling is another area where Kevlar has made significant inroads. Bicycle tires reinforced with Kevlar offer superior puncture resistance and reduced rolling resistance, leading to improved performance and reliability for both professional and recreational cyclists. Kevlar is also used in the construction of bicycle frames and components, providing a lightweight yet robust alternative to traditional materials.
In water sports, Kevlar has found applications in the manufacturing of kayaks, canoes, and surfboards. The material's high strength and low weight make it ideal for creating rigid and durable watercraft that can withstand the demands of rough waters. Kevlar-reinforced surfboards offer improved strength and flexibility, allowing surfers to tackle more challenging waves with confidence.
Despite its numerous advantages, the integration of Kevlar in sporting goods faces several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost of the material, which can significantly increase the price of end products. This cost factor often limits the widespread adoption of Kevlar-enhanced sporting goods, particularly in the consumer market.
Another challenge lies in the complexity of manufacturing processes involving Kevlar. The material requires specialized equipment and expertise to work with, which can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers or those looking to incorporate Kevlar into their product lines. Additionally, the bonding of Kevlar with other materials can be challenging, requiring advanced techniques to ensure proper adhesion and performance.
Environmental concerns also pose a challenge to the use of Kevlar in sporting goods. As a synthetic material, Kevlar is not biodegradable, raising questions about its long-term environmental impact. The sporting goods industry is increasingly focused on sustainability, and finding ways to recycle or dispose of Kevlar-containing products at the end of their lifecycle remains an ongoing challenge.
In the field of racquet sports, Kevlar is commonly incorporated into the strings and frames of tennis, badminton, and squash racquets. The addition of Kevlar to racquet strings provides increased durability and tension maintenance, resulting in improved power and control for players. Kevlar-reinforced frames offer enhanced stiffness and vibration dampening, contributing to better energy transfer and reduced player fatigue.
Cycling is another area where Kevlar has made significant inroads. Bicycle tires reinforced with Kevlar offer superior puncture resistance and reduced rolling resistance, leading to improved performance and reliability for both professional and recreational cyclists. Kevlar is also used in the construction of bicycle frames and components, providing a lightweight yet robust alternative to traditional materials.
In water sports, Kevlar has found applications in the manufacturing of kayaks, canoes, and surfboards. The material's high strength and low weight make it ideal for creating rigid and durable watercraft that can withstand the demands of rough waters. Kevlar-reinforced surfboards offer improved strength and flexibility, allowing surfers to tackle more challenging waves with confidence.
Despite its numerous advantages, the integration of Kevlar in sporting goods faces several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost of the material, which can significantly increase the price of end products. This cost factor often limits the widespread adoption of Kevlar-enhanced sporting goods, particularly in the consumer market.
Another challenge lies in the complexity of manufacturing processes involving Kevlar. The material requires specialized equipment and expertise to work with, which can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers or those looking to incorporate Kevlar into their product lines. Additionally, the bonding of Kevlar with other materials can be challenging, requiring advanced techniques to ensure proper adhesion and performance.
Environmental concerns also pose a challenge to the use of Kevlar in sporting goods. As a synthetic material, Kevlar is not biodegradable, raising questions about its long-term environmental impact. The sporting goods industry is increasingly focused on sustainability, and finding ways to recycle or dispose of Kevlar-containing products at the end of their lifecycle remains an ongoing challenge.
Existing Kevlar Integration Methods in Sports Equipment
01 Kevlar-reinforced composite materials
Kevlar fibers are used to reinforce various composite materials, enhancing their strength, durability, and impact resistance. These composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, and protective equipment industries.- Kevlar-reinforced composite materials: Kevlar fibers are used to reinforce various composite materials, enhancing their strength, durability, and impact resistance. These composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, and protective equipment industries.
- Kevlar in protective gear and clothing: Kevlar is extensively used in the manufacture of protective gear and clothing, including bulletproof vests, helmets, and cut-resistant gloves. Its high tensile strength and lightweight properties make it ideal for personal protection equipment.
- Kevlar-based fire-resistant materials: Kevlar is incorporated into fire-resistant materials and fabrics, providing enhanced thermal protection and flame retardancy. These materials are used in firefighting equipment, industrial safety gear, and high-temperature applications.
- Kevlar in automotive and aerospace applications: Kevlar is utilized in various automotive and aerospace components to reduce weight while maintaining strength. It is used in tires, body panels, and structural parts to improve fuel efficiency and performance.
- Kevlar in sports and recreational equipment: Kevlar is incorporated into sports and recreational equipment such as bicycle frames, kayaks, and tennis rackets. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and vibration-damping properties enhance performance and durability in these applications.
02 Kevlar in protective gear and clothing
Kevlar is utilized in the manufacture of protective gear and clothing, including bulletproof vests, helmets, and cut-resistant gloves. Its high tensile strength and lightweight properties make it ideal for personal protection equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Kevlar-based fire-resistant materials
Kevlar is incorporated into fire-resistant materials and fabrics, providing enhanced thermal protection and flame retardancy. These materials are used in firefighting equipment, industrial safety gear, and high-temperature applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Kevlar in automotive and transportation applications
Kevlar is used in various automotive and transportation applications, including tire reinforcement, brake pads, and structural components. Its high strength-to-weight ratio contributes to improved fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Kevlar in sports and recreational equipment
Kevlar is incorporated into sports and recreational equipment, such as bicycle frames, kayaks, and tennis rackets. Its lightweight and high-strength properties enhance performance and durability in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Suppliers in Kevlar Sports Market
The competitive landscape for Kevlar in high-performance sporting goods is characterized by a mature market with steady growth. The global market size for high-performance materials in sports equipment is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, with Kevlar playing a significant role. Technologically, Kevlar is well-established, with ongoing research focused on enhancing its properties and applications. Key players like DuPont (original developer of Kevlar) dominate, while companies such as RMA Armament and Continuous Composites are exploring innovative applications. Universities like MIT and Harvard contribute to advanced research, potentially influencing future developments. The industry sees collaboration between material manufacturers, sporting goods companies, and research institutions to drive innovation and market expansion.
RMA Armament, Inc.
Technical Solution: RMA Armament, Inc. specializes in the development and production of high-performance body armor, including products that incorporate Kevlar. While primarily focused on protective equipment for law enforcement and military applications, their technology has found use in high-impact sports. RMA has developed a proprietary layering system that combines Kevlar with other advanced materials to create lightweight, flexible, and highly protective gear[7]. This technology has been adapted for use in sports such as motocross, mountain biking, and extreme sports, where impact protection is crucial. The company's research into ballistic materials has led to innovations in energy absorption and distribution, which translate well to sporting applications[8].
Strengths: Expertise in high-performance protective gear, advanced layering techniques for optimal protection and flexibility. Weaknesses: Primary focus on military and law enforcement markets may limit sports-specific product development and marketing.
Comfortect LLC
Technical Solution: Comfortect LLC has developed innovative applications of Kevlar in sports apparel and protective gear. Their patented technology integrates Kevlar fibers into fabric structures in a way that maximizes flexibility while maintaining high levels of cut and abrasion resistance[9]. This approach has been particularly successful in creating lightweight, breathable protective gear for sports such as hockey, lacrosse, and skateboarding. Comfortect has also developed a proprietary coating process that enhances the moisture-wicking properties of Kevlar-based fabrics, improving comfort in high-performance sportswear[10].
Strengths: Innovative integration of Kevlar into flexible, comfortable sportswear and protective gear. Weaknesses: Relatively small company with potentially limited production capacity and market reach compared to larger competitors.
Innovative Kevlar Composites for Enhanced Performance
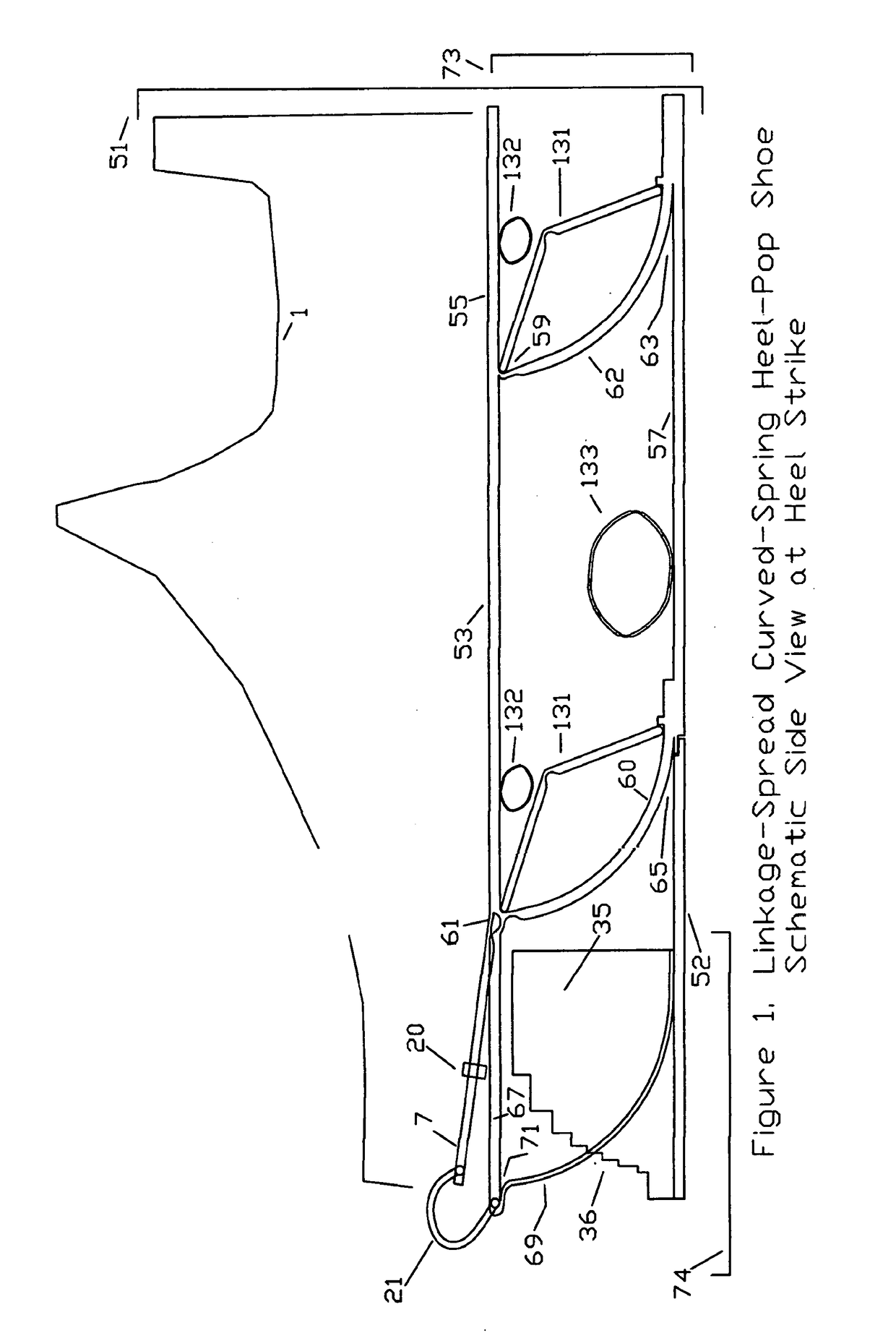
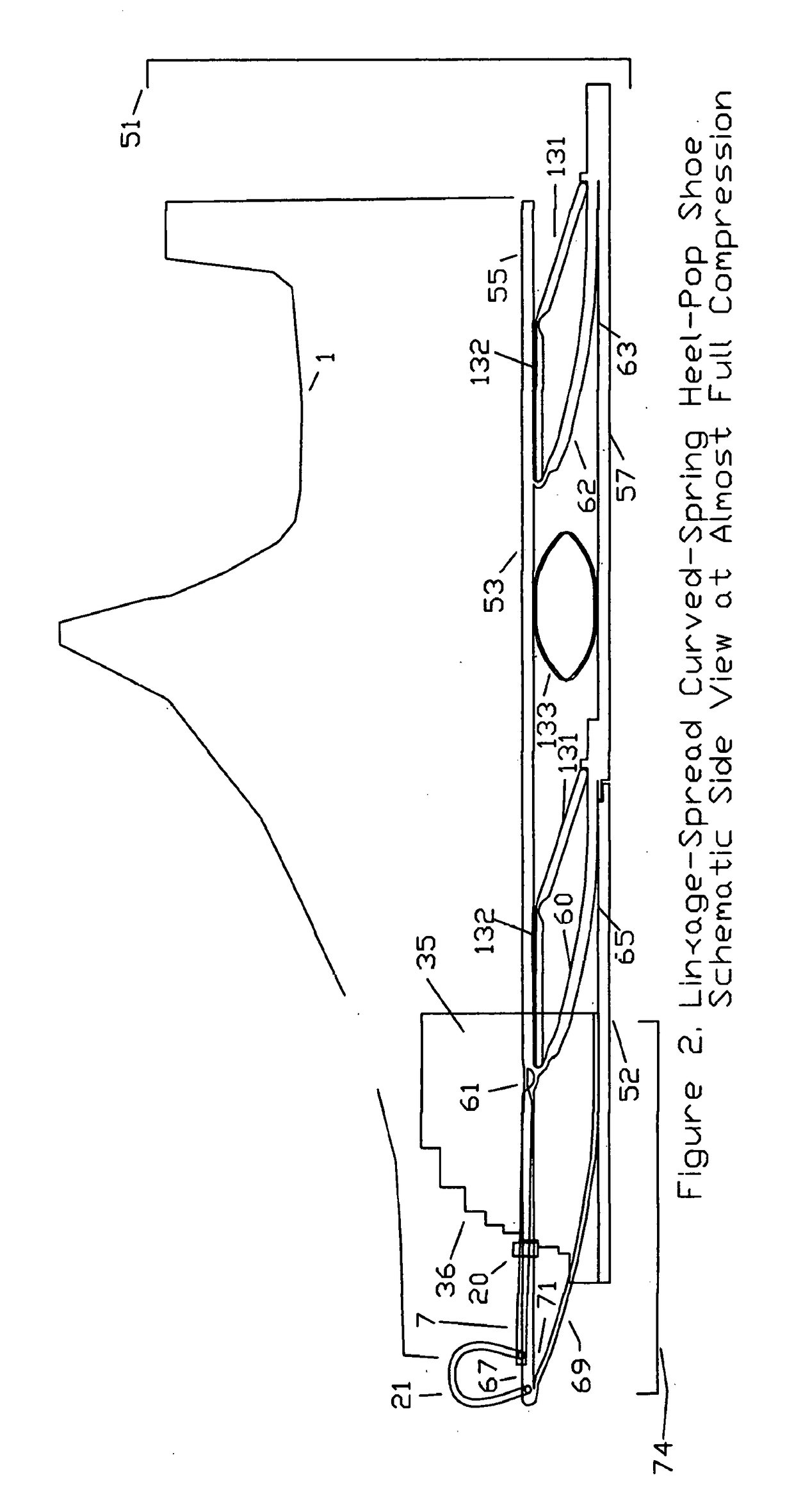
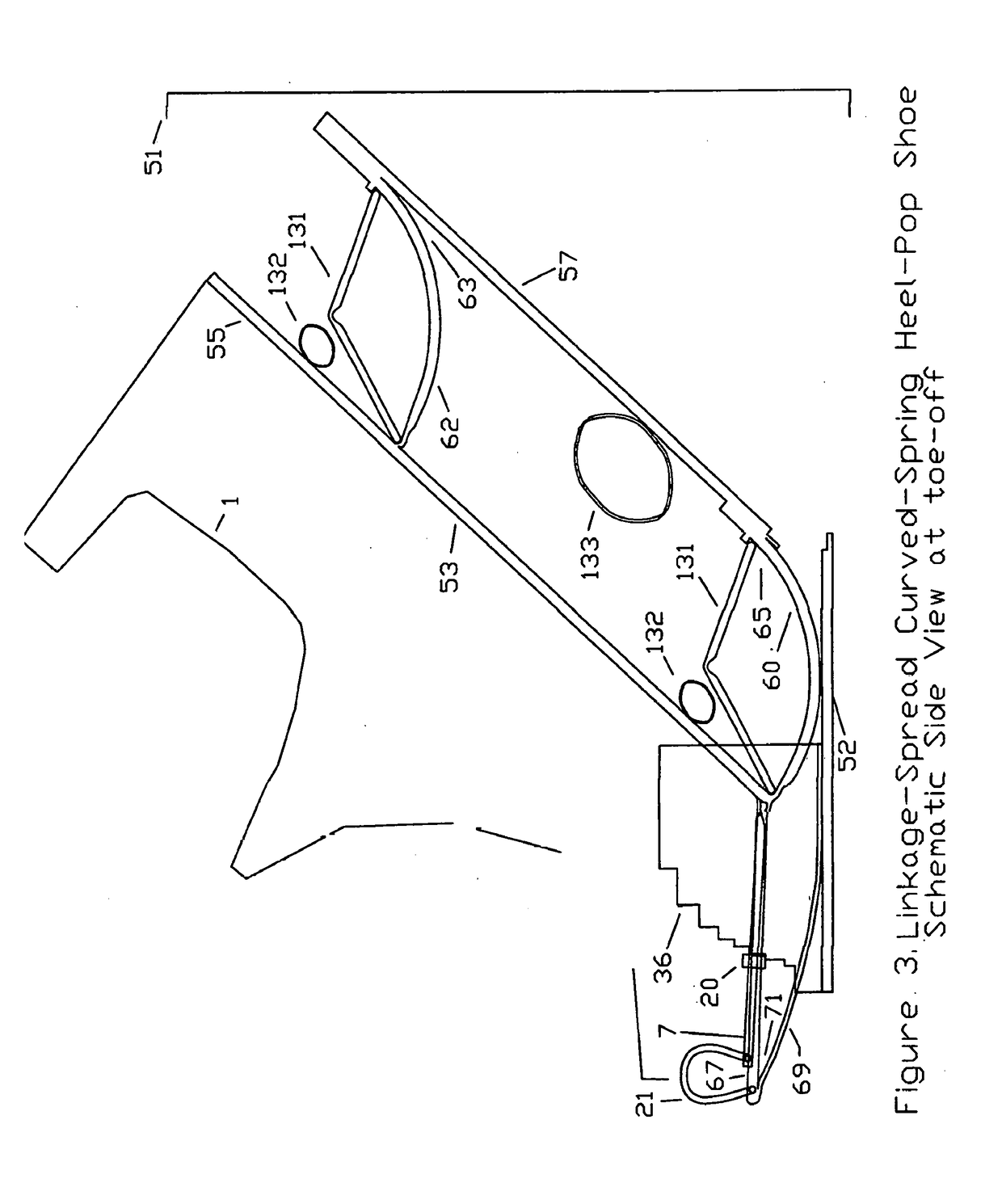
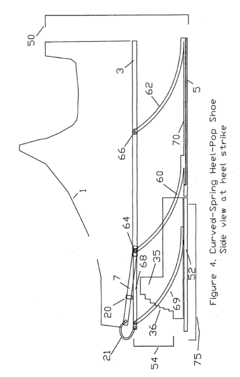
Substantial energy return shoe with optimal low-impact springs, tuned gear change, and smart knee brace
PatentInactiveUS20180220738A1
Innovation
- The design incorporates enhanced heel-lift mechanisms with anti-toe-sink mechanisms and automatic gear changers, utilizing optimized low-impact springs and linkage systems to ensure full sole compression and efficient energy storage and release, reducing the maximum impact force and increasing energy return.
An improved process for fabricating kevlar fabric composite for multifunctional soft body armor
PatentPendingIN202321039845A
Innovation
- A composite material process involving Kevlar fabric impregnated with shear thickening fluid (STF) and shear-stiffening gel (STG), utilizing metal phosphate and carbon nanotubes, to enhance impact resistance, electrical conductivity, and flame retardancy, while allowing for temperature regulation.
Environmental Impact of Kevlar in Sporting Goods
The environmental impact of Kevlar in sporting goods is a complex issue that requires careful consideration. Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber, has become increasingly popular in the production of various sporting equipment due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability. However, its widespread use raises concerns about its environmental footprint throughout its lifecycle.
The production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemicals, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing process requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in significant energy consumption. Additionally, the chemicals used in production, such as sulfuric acid and organic solvents, can pose environmental risks if not properly managed.
On the positive side, Kevlar's durability and longevity can potentially reduce the overall environmental impact of sporting goods. Products made with Kevlar tend to have a longer lifespan compared to those made with traditional materials, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements and thus decreasing waste generation. This extended product life cycle can lead to a reduction in raw material consumption and manufacturing-related emissions over time.
However, the end-of-life management of Kevlar-containing products presents challenges. Kevlar is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. Recycling Kevlar is technically possible but not widely implemented due to the complexity and cost of the process. As a result, many Kevlar-containing sporting goods end up in landfills, contributing to long-term waste accumulation.
The use of Kevlar in sporting goods also has indirect environmental implications. Its lightweight properties can contribute to improved fuel efficiency in transportation-related sports, potentially reducing carbon emissions. However, the increased performance capabilities of Kevlar-enhanced equipment may encourage more frequent product upgrades, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits of its durability.
Water pollution is another concern associated with Kevlar production and use. The manufacturing process can generate wastewater containing harmful chemicals if not properly treated. Additionally, microfiber shedding from Kevlar-containing products during use and washing can contribute to microplastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems.
To mitigate the environmental impact of Kevlar in sporting goods, several approaches are being explored. These include developing more sustainable production methods, improving recycling technologies, and designing products for easier disassembly and material recovery. Some manufacturers are also investigating bio-based alternatives that could offer similar performance characteristics with a reduced environmental footprint.
In conclusion, while Kevlar offers significant performance benefits in sporting goods, its environmental impact is multifaceted. Balancing its advantages with ecological concerns requires ongoing research, innovation, and responsible manufacturing and disposal practices to ensure a more sustainable future for high-performance sporting equipment.
The production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemicals, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing process requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in significant energy consumption. Additionally, the chemicals used in production, such as sulfuric acid and organic solvents, can pose environmental risks if not properly managed.
On the positive side, Kevlar's durability and longevity can potentially reduce the overall environmental impact of sporting goods. Products made with Kevlar tend to have a longer lifespan compared to those made with traditional materials, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements and thus decreasing waste generation. This extended product life cycle can lead to a reduction in raw material consumption and manufacturing-related emissions over time.
However, the end-of-life management of Kevlar-containing products presents challenges. Kevlar is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. Recycling Kevlar is technically possible but not widely implemented due to the complexity and cost of the process. As a result, many Kevlar-containing sporting goods end up in landfills, contributing to long-term waste accumulation.
The use of Kevlar in sporting goods also has indirect environmental implications. Its lightweight properties can contribute to improved fuel efficiency in transportation-related sports, potentially reducing carbon emissions. However, the increased performance capabilities of Kevlar-enhanced equipment may encourage more frequent product upgrades, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits of its durability.
Water pollution is another concern associated with Kevlar production and use. The manufacturing process can generate wastewater containing harmful chemicals if not properly treated. Additionally, microfiber shedding from Kevlar-containing products during use and washing can contribute to microplastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems.
To mitigate the environmental impact of Kevlar in sporting goods, several approaches are being explored. These include developing more sustainable production methods, improving recycling technologies, and designing products for easier disassembly and material recovery. Some manufacturers are also investigating bio-based alternatives that could offer similar performance characteristics with a reduced environmental footprint.
In conclusion, while Kevlar offers significant performance benefits in sporting goods, its environmental impact is multifaceted. Balancing its advantages with ecological concerns requires ongoing research, innovation, and responsible manufacturing and disposal practices to ensure a more sustainable future for high-performance sporting equipment.
Safety Standards and Regulations for Kevlar Sports Equipment
The integration of Kevlar in high-performance sporting goods has necessitated the development of comprehensive safety standards and regulations. These guidelines are crucial to ensure the protection of athletes and consumers while maintaining the integrity of sporting competitions.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established several standards specifically addressing Kevlar-reinforced sports equipment. ISO 13506, for instance, outlines the requirements for protective clothing made with Kevlar, including those used in high-impact sports. This standard focuses on the heat and flame resistance properties of Kevlar, ensuring that protective gear maintains its structural integrity under extreme conditions.
In the United States, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has implemented regulations for various sports equipment incorporating Kevlar. The CPSC's guidelines cover aspects such as impact resistance, durability, and potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to Kevlar fibers. These regulations are particularly stringent for youth sports equipment, where safety is paramount.
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has also developed standards for Kevlar-based sports equipment. EN 13158, for example, specifies the requirements for protective jackets, body, and shoulder protectors for equestrian use, many of which utilize Kevlar for enhanced protection.
For motorsports, the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA) has established strict safety standards for racing suits and other protective gear incorporating Kevlar. These standards, such as FIA Standard 8856-2000, mandate specific levels of fire resistance and impact protection that Kevlar-based materials must meet.
In the realm of cycling, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has developed the F1447 standard for bicycle helmets, which includes specifications for Kevlar-reinforced designs. This standard ensures that helmets provide adequate protection against impact and penetration.
Manufacturers of Kevlar-based sporting goods must also adhere to labeling requirements set forth by various regulatory bodies. These labels typically include information on the product's composition, care instructions, and any potential risks associated with its use.
Compliance with these safety standards and regulations is typically verified through rigorous testing procedures. Independent laboratories conduct tests to assess the performance of Kevlar-reinforced equipment under various conditions, including impact resistance, flame retardancy, and durability.
As the application of Kevlar in sporting goods continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are continuously updating their standards to address new technologies and potential risks. This ongoing process ensures that safety regulations remain relevant and effective in protecting athletes and consumers.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established several standards specifically addressing Kevlar-reinforced sports equipment. ISO 13506, for instance, outlines the requirements for protective clothing made with Kevlar, including those used in high-impact sports. This standard focuses on the heat and flame resistance properties of Kevlar, ensuring that protective gear maintains its structural integrity under extreme conditions.
In the United States, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has implemented regulations for various sports equipment incorporating Kevlar. The CPSC's guidelines cover aspects such as impact resistance, durability, and potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to Kevlar fibers. These regulations are particularly stringent for youth sports equipment, where safety is paramount.
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has also developed standards for Kevlar-based sports equipment. EN 13158, for example, specifies the requirements for protective jackets, body, and shoulder protectors for equestrian use, many of which utilize Kevlar for enhanced protection.
For motorsports, the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA) has established strict safety standards for racing suits and other protective gear incorporating Kevlar. These standards, such as FIA Standard 8856-2000, mandate specific levels of fire resistance and impact protection that Kevlar-based materials must meet.
In the realm of cycling, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has developed the F1447 standard for bicycle helmets, which includes specifications for Kevlar-reinforced designs. This standard ensures that helmets provide adequate protection against impact and penetration.
Manufacturers of Kevlar-based sporting goods must also adhere to labeling requirements set forth by various regulatory bodies. These labels typically include information on the product's composition, care instructions, and any potential risks associated with its use.
Compliance with these safety standards and regulations is typically verified through rigorous testing procedures. Independent laboratories conduct tests to assess the performance of Kevlar-reinforced equipment under various conditions, including impact resistance, flame retardancy, and durability.
As the application of Kevlar in sporting goods continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are continuously updating their standards to address new technologies and potential risks. This ongoing process ensures that safety regulations remain relevant and effective in protecting athletes and consumers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!