Advances in Hypertonic Practices for Cardiovascular Health
Hypertonic Therapy Evolution and Objectives
Hypertonic therapy for cardiovascular health has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by advancements in medical research and technology. This approach, which involves the use of solutions with higher osmotic pressure than blood, has shown promising results in managing various cardiovascular conditions.
The evolution of hypertonic therapy can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers first began exploring the effects of hypertonic solutions on the cardiovascular system. Initially, the focus was primarily on using hypertonic saline solutions for fluid resuscitation in shock patients. However, as understanding of cardiovascular physiology improved, the potential applications of hypertonic therapy expanded.
In the 1980s and 1990s, there was a surge of interest in hypertonic saline solutions for treating intracranial hypertension and cerebral edema. This led to further investigations into the effects of hypertonic solutions on blood volume, cardiac output, and tissue perfusion. As research progressed, scientists began to explore the potential benefits of hypertonic therapy in various cardiovascular conditions, including heart failure, hypertension, and ischemic heart disease.
The objectives of current hypertonic practices in cardiovascular health are multifaceted. One primary goal is to improve cardiac function by optimizing fluid balance and reducing myocardial edema. Hypertonic solutions can help mobilize fluid from the interstitial space into the intravascular compartment, thereby improving cardiac preload and stroke volume. Additionally, these solutions may have direct inotropic effects on the heart, enhancing contractility and cardiac output.
Another important objective is to reduce vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, which are key factors in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Hypertonic solutions have been shown to modulate inflammatory responses and improve endothelial function, potentially offering protective effects against atherosclerosis and other vascular disorders.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the use of hypertonic therapy in ischemia-reperfusion injury, a common complication in cardiovascular procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting and heart transplantation. The goal is to minimize tissue damage and improve outcomes by leveraging the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of hypertonic solutions.
As the field continues to advance, there is a growing focus on developing targeted hypertonic therapies that can be tailored to specific cardiovascular conditions and patient populations. This includes investigating novel hypertonic formulations, optimizing delivery methods, and exploring combination therapies with other cardiovascular medications.
Cardiovascular Health Market Analysis
The cardiovascular health market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of heart-related diseases and the growing aging population worldwide. The global cardiovascular health market was valued at approximately $146 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $208 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period.
One of the key factors contributing to market growth is the rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), which remain the leading cause of death globally. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 17.9 million people die from CVDs each year, representing 31% of all global deaths. This high disease burden has led to increased demand for cardiovascular health products and services, including diagnostics, therapeutics, and preventive measures.
The market for hypertonic practices in cardiovascular health is a subset of this larger market, focusing on the use of hypertonic solutions and therapies to improve cardiovascular function. While specific market size data for hypertonic practices is limited, the growing interest in novel approaches to cardiovascular health management suggests a promising outlook for this segment.
Geographically, North America dominates the cardiovascular health market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds the largest market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and the presence of major pharmaceutical and medical device companies. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years due to improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer, Novartis, and AstraZeneca, as well as medical device manufacturers such as Medtronic and Abbott Laboratories. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative therapies and devices for cardiovascular health management.
In terms of product segments, the market can be broadly categorized into pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and diagnostic equipment. The pharmaceutical segment currently holds the largest market share, driven by the widespread use of drugs for managing conditions like hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and heart failure. However, the medical devices segment, which includes products like stents, pacemakers, and heart valves, is expected to grow at a faster rate due to technological advancements and increasing adoption of minimally invasive procedures.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the cardiovascular health market, with both positive and negative effects. While it initially led to disruptions in healthcare services and delayed elective procedures, it also highlighted the importance of cardiovascular health, as individuals with pre-existing heart conditions were found to be at higher risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes. This has led to increased focus on preventive care and remote monitoring solutions in the cardiovascular health space.
Hypertonic Practices: Current Status and Challenges
Hypertonic practices for cardiovascular health have gained significant attention in recent years, with researchers and clinicians exploring their potential benefits and challenges. The current status of hypertonic practices reveals a complex landscape of promising advancements and persistent obstacles.
One of the primary areas of focus in hypertonic practices is the use of hypertonic saline solutions in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions. These solutions have shown potential in managing acute decompensated heart failure, reducing pulmonary congestion, and improving hemodynamics. However, the optimal concentration and administration protocols remain subjects of ongoing debate and research.
Another emerging application is the use of hypertonic solutions in resuscitation strategies for patients with severe shock or trauma. While initial studies have shown promising results in terms of rapid volume expansion and improved tissue perfusion, concerns about potential adverse effects, such as electrolyte imbalances and renal complications, persist.
The field of hypertonic preconditioning has also gained traction, with researchers investigating its potential to protect the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Preliminary studies have demonstrated that exposure to hypertonic solutions prior to cardiac procedures may enhance the heart's resilience to stress. However, translating these findings into clinical practice remains challenging due to the need for precise timing and dosing protocols.
Despite these advancements, several challenges continue to hinder the widespread adoption of hypertonic practices in cardiovascular care. One significant obstacle is the lack of standardized protocols for hypertonic solution administration. The optimal concentration, duration, and frequency of treatment vary widely across studies, making it difficult to establish consistent guidelines for clinical practice.
Additionally, concerns about potential side effects and long-term safety profiles of hypertonic interventions persist. While short-term benefits have been observed, the long-term impact on cardiovascular health, renal function, and overall patient outcomes requires further investigation through large-scale, longitudinal studies.
The integration of hypertonic practices into existing treatment paradigms also presents a challenge. Clinicians must carefully consider how these interventions interact with other cardiovascular therapies and how they fit into the overall management strategy for patients with complex cardiovascular conditions.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of hypertonic practices compared to conventional treatments remains a point of contention. While some studies suggest potential cost savings through reduced hospital stays and improved outcomes, others argue that the expenses associated with specialized hypertonic solutions and monitoring requirements may offset these benefits.
In conclusion, the current status of hypertonic practices in cardiovascular health is characterized by a mix of promising advancements and significant challenges. As research continues to evolve, addressing these obstacles will be crucial in realizing the full potential of hypertonic interventions and establishing their role in the future of cardiovascular care.
Existing Hypertonic Treatment Protocols
01 Hypertonic saline solutions for cardiovascular health
Hypertonic saline solutions are used to improve cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure, enhancing fluid balance, and supporting cardiac function. These solutions can be administered intravenously or through other methods to address various cardiovascular conditions and improve overall heart health.- Hypertonic saline solutions for cardiovascular health: Hypertonic saline solutions are used to improve cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure, enhancing fluid balance, and reducing inflammation. These solutions can be administered intravenously or through other methods to support heart function and overall cardiovascular well-being.
- Monitoring cardiovascular parameters during hypertonic practices: Various devices and methods are employed to monitor cardiovascular parameters during hypertonic practices. These include measuring blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs to assess the impact of hypertonic interventions on cardiovascular health and adjust treatments accordingly.
- Hypertonic dietary practices for cardiovascular health: Specific dietary practices involving hypertonic foods or supplements are used to promote cardiovascular health. These may include consuming foods with high mineral content or using hypertonic nutritional supplements to support heart function and blood vessel health.
- Exercise protocols combined with hypertonic practices: Specialized exercise protocols are developed in conjunction with hypertonic practices to enhance cardiovascular health. These may involve specific physical activities or training regimens designed to work synergistically with hypertonic interventions for improved heart and circulatory system function.
- Data analysis and AI in hypertonic cardiovascular health management: Advanced data analysis techniques and artificial intelligence are utilized to optimize hypertonic practices for cardiovascular health. These technologies help in analyzing patient data, predicting outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans to maximize the benefits of hypertonic interventions on heart health.
02 Monitoring cardiovascular parameters during hypertonic practices
Advanced monitoring systems and methods are employed to track various cardiovascular parameters during hypertonic practices. These systems can measure blood pressure, heart rate, cardiac output, and other vital signs to ensure the safety and efficacy of hypertonic treatments for cardiovascular health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypertonic exercise protocols for cardiovascular improvement
Specialized exercise protocols incorporating hypertonic practices are designed to enhance cardiovascular health. These protocols may include high-intensity interval training, resistance exercises, or other forms of physical activity that challenge the cardiovascular system and promote adaptations beneficial to heart health.Expand Specific Solutions04 Personalized hypertonic therapies for cardiovascular conditions
Tailored hypertonic therapies are developed to address specific cardiovascular conditions. These personalized approaches consider individual patient factors, such as medical history, genetic predisposition, and current health status, to optimize the effectiveness of hypertonic practices in improving cardiovascular health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of hypertonic practices with other cardiovascular treatments
Hypertonic practices are integrated with other established cardiovascular treatments to create comprehensive approaches to heart health. This may involve combining hypertonic therapies with medication regimens, lifestyle modifications, or other interventions to achieve synergistic effects and improve overall cardiovascular outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Cardiovascular Research
The field of hypertonic practices for cardiovascular health is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for cardiovascular health solutions is expanding rapidly, driven by an aging population and rising prevalence of heart diseases. Technologically, the sector is progressing from established treatments to more innovative approaches. Companies like Medtronic, Abbott Laboratories, and Novartis AG are at the forefront, developing advanced solutions such as implantable devices and novel pharmaceuticals. Emerging players like EBR Systems and CVRx are introducing disruptive technologies, while research institutions like the University of Florida and Brigham & Women's Hospital contribute to the scientific foundation. The technology maturity varies, with some established practices and numerous cutting-edge developments in clinical trials, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
Medtronic, Inc.
Novartis AG
Breakthrough Hypertonic Techniques for Heart Health
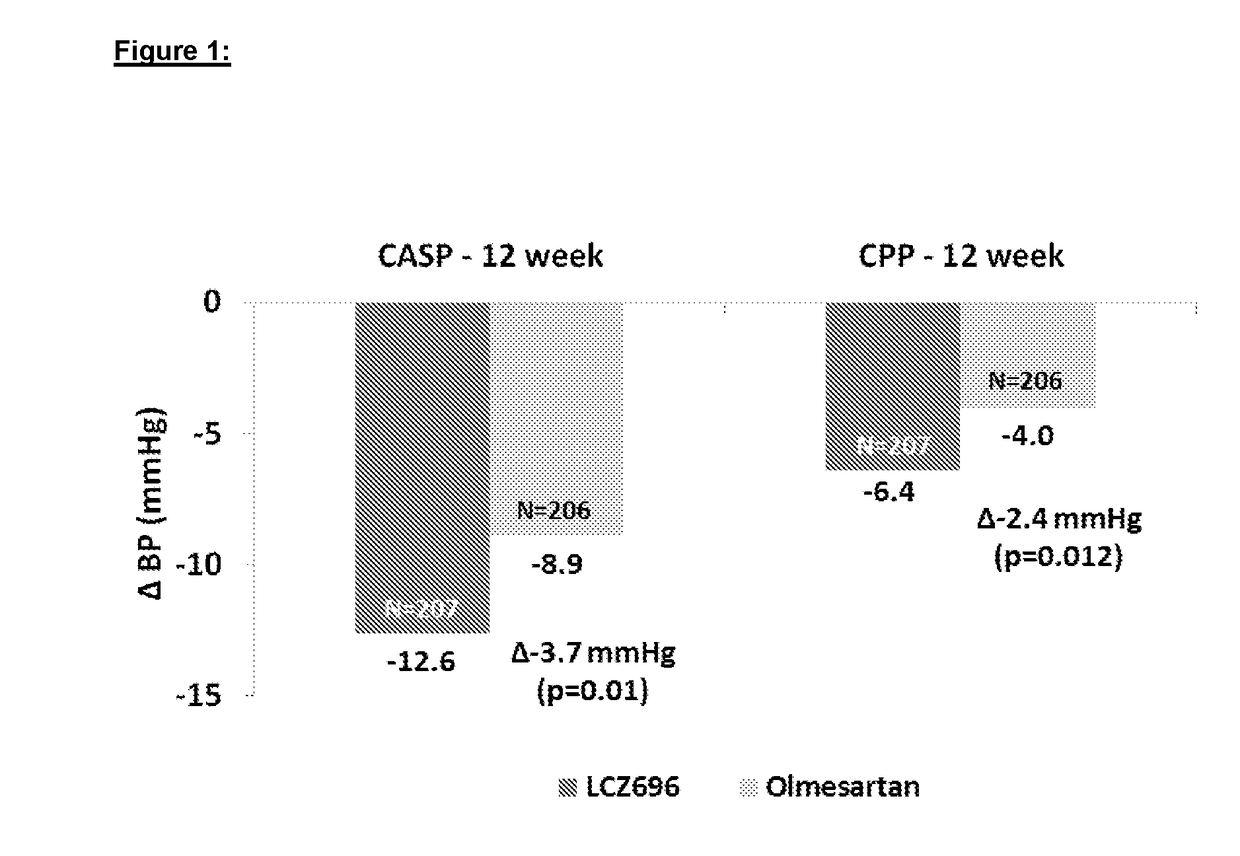
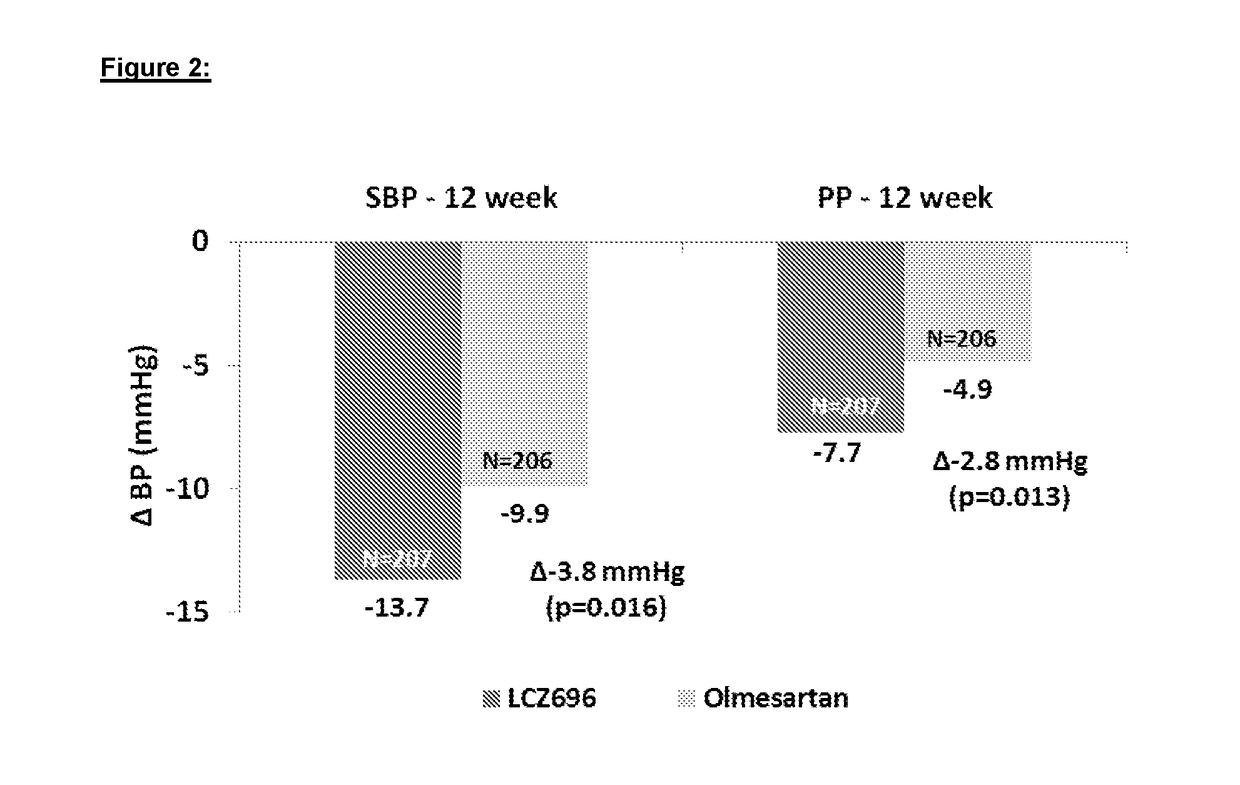
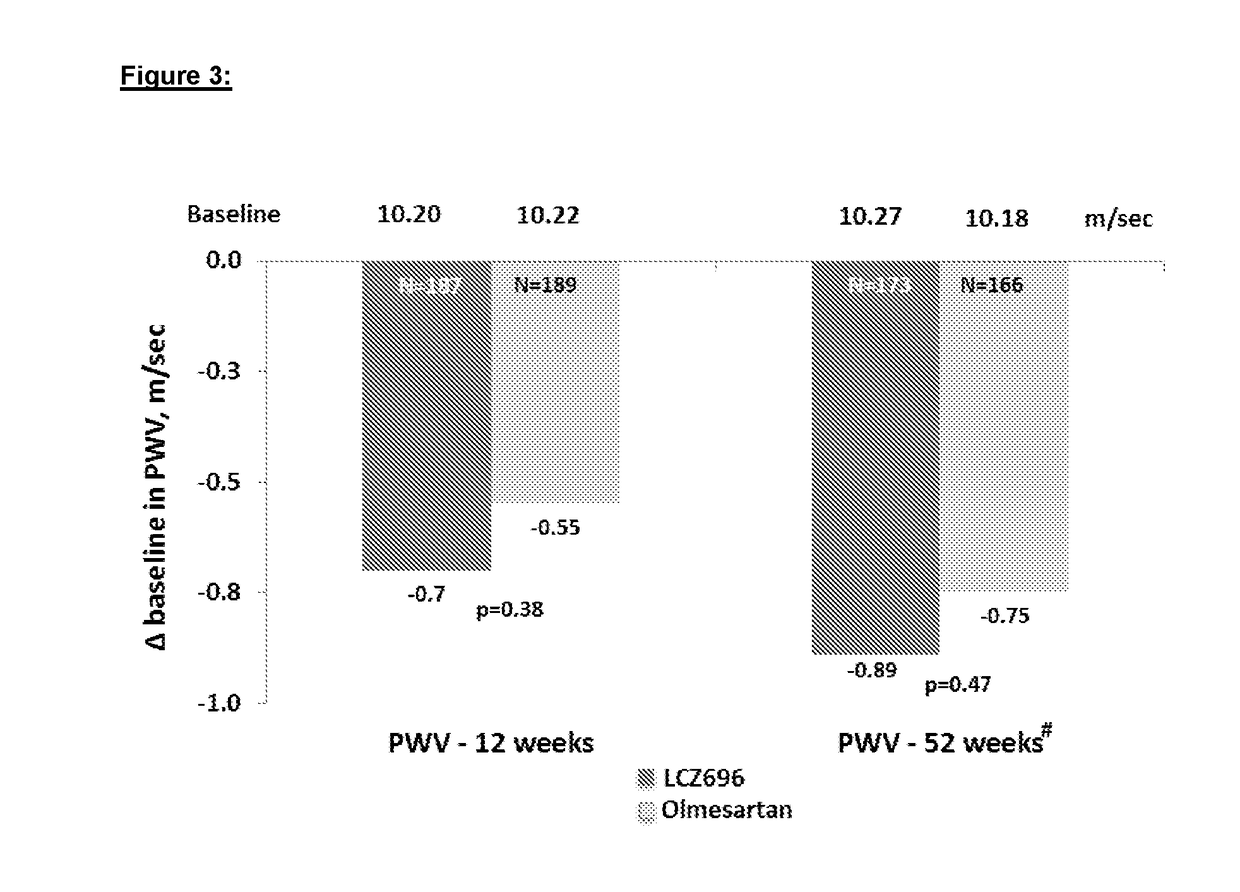
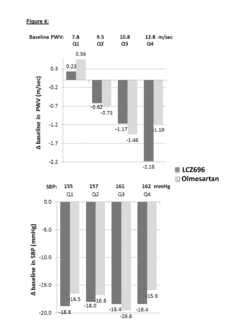
- Administration of a combination of sacubitril and valsartan in a 1:1 molar ratio, which acts as an Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin inhibitor, to effectively reduce arterial stiffness by blocking the angiotensin receptor and inhibiting the NEP enzyme, thereby improving central aortic hemodynamics and reducing pulse wave velocity.
- A combination pharmaceutical composition comprising a non-dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (preferably verapamil), an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor (ACEI, such as trandolapril), and a diuretic (like hydrochlorothiazide) is used to treat hypertension, with specific dosage ranges and formulations for controlled release to achieve and maintain target blood pressures.
Regulatory Framework for Hypertonic Treatments
The regulatory framework for hypertonic treatments in cardiovascular health is a complex and evolving landscape. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and protocols to ensure the safety and efficacy of these treatments. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development, approval, and marketing of hypertonic solutions for cardiovascular applications.
The FDA has implemented a rigorous approval process for hypertonic treatments, which includes extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. These trials typically involve multiple phases, starting with small-scale safety studies and progressing to larger efficacy trials. The agency also requires manufacturers to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality and safety.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulatory process for hypertonic treatments. The EMA's approach is similar to the FDA's, with a focus on evidence-based approval and post-market surveillance. However, there are some differences in the specific requirements and timelines for approval between the two regulatory bodies.
Regulatory frameworks also address the labeling and marketing of hypertonic treatments. Clear and accurate labeling is mandated to inform healthcare providers and patients about proper usage, potential side effects, and contraindications. Off-label use of hypertonic solutions is closely monitored and regulated to prevent misuse and ensure patient safety.
Post-market surveillance is another critical component of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to report adverse events and conduct ongoing safety studies to identify any long-term effects or rare complications associated with hypertonic treatments. This continuous monitoring helps regulatory agencies make informed decisions about the continued use and potential modifications to approved treatments.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different countries. These initiatives facilitate the global development and approval of hypertonic treatments, potentially accelerating patient access to innovative cardiovascular therapies.
As research in hypertonic practices for cardiovascular health advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and treatment modalities. This includes the development of guidelines for personalized medicine approaches and the integration of digital health technologies in hypertonic treatments. Regulatory bodies are also focusing on expedited approval pathways for breakthrough therapies that show significant promise in addressing unmet medical needs in cardiovascular health.
Patient Safety and Ethical Considerations
The implementation of hypertonic practices for cardiovascular health raises significant patient safety and ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. One primary concern is the potential for adverse effects on patients with pre-existing conditions, such as renal impairment or heart failure. Hypertonic solutions can lead to rapid fluid shifts, potentially exacerbating these conditions if not properly managed. Healthcare providers must conduct thorough patient assessments and risk stratification before initiating hypertonic therapies.
Informed consent is a critical ethical consideration in the application of hypertonic practices. Patients must be fully informed about the potential benefits and risks associated with these treatments, including possible side effects and alternative options. This process should involve clear communication and documentation, ensuring that patients or their legal representatives can make autonomous decisions regarding their care.
The long-term effects of hypertonic therapies on cardiovascular health are not yet fully understood, raising ethical questions about their widespread use. Ongoing research and post-treatment monitoring are essential to gather data on long-term outcomes and potential unforeseen consequences. Healthcare institutions should establish robust follow-up protocols to track patient progress and identify any delayed adverse effects.
Equitable access to hypertonic treatments is another important ethical consideration. These advanced therapies may be costly or require specialized equipment, potentially limiting their availability to certain patient populations or healthcare settings. Efforts should be made to ensure fair distribution of resources and access to these treatments across diverse socioeconomic groups.
Patient privacy and data protection are paramount when implementing hypertonic practices, particularly as they often involve extensive monitoring and data collection. Healthcare providers must adhere to strict confidentiality protocols and secure data management practices to protect sensitive patient information.
The potential for off-label use of hypertonic solutions in cardiovascular care raises additional ethical concerns. While such use may be beneficial in certain cases, it requires careful consideration of the risk-benefit ratio and should be supported by sound clinical judgment and available evidence. Clear guidelines and institutional policies should be established to govern off-label applications.
Lastly, the ethical implications of resource allocation must be considered. As healthcare systems face increasing pressure to optimize resource utilization, the cost-effectiveness of hypertonic practices compared to traditional treatments should be evaluated. This assessment should balance potential improvements in patient outcomes against the overall impact on healthcare resources and accessibility.