Applying Nichrome in Advanced Precision Manufacturing
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nichrome in Precision Manufacturing: Background and Objectives
Nichrome, an alloy primarily composed of nickel and chromium, has emerged as a crucial material in advanced precision manufacturing. Its unique properties, including high electrical resistivity, excellent corrosion resistance, and exceptional thermal stability, have positioned it at the forefront of various industrial applications. The evolution of nichrome's use in precision manufacturing can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in recent decades.
The development of nichrome technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. As manufacturing processes have become more sophisticated, the need for materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining precise specifications has grown exponentially. Nichrome's ability to maintain its structural integrity and electrical properties at high temperatures has made it an ideal candidate for these demanding applications.
In the context of advanced precision manufacturing, nichrome has found its niche in several key areas. It is widely used in the production of heating elements, where its consistent electrical resistance and durability are essential. The semiconductor industry relies on nichrome for thin-film resistors and other microelectronic components, leveraging its stability and precise control of electrical properties. Additionally, nichrome plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of sensors and measurement devices, where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
The technological trajectory of nichrome in precision manufacturing has been marked by continuous improvements in composition, processing techniques, and application methodologies. Researchers and engineers have focused on enhancing the alloy's properties through precise control of its nickel-chromium ratio and the addition of trace elements. These efforts have resulted in nichrome variants with tailored characteristics, optimized for specific manufacturing requirements.
Looking ahead, the objectives for nichrome in advanced precision manufacturing are multifaceted. There is a strong emphasis on developing even more refined alloy compositions that can offer superior performance in extreme environments. Researchers are exploring ways to improve nichrome's already impressive corrosion resistance and thermal stability, aiming to extend its applicability in cutting-edge technologies such as additive manufacturing and nanotechnology.
Another key objective is the integration of nichrome into smart manufacturing processes. This involves developing sensors and control systems that can monitor and adjust the properties of nichrome-based components in real-time during manufacturing, ensuring unprecedented levels of precision and quality control. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainable manufacturing practices, with efforts directed towards optimizing nichrome production and recycling processes to minimize environmental impact.
The development of nichrome technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. As manufacturing processes have become more sophisticated, the need for materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining precise specifications has grown exponentially. Nichrome's ability to maintain its structural integrity and electrical properties at high temperatures has made it an ideal candidate for these demanding applications.
In the context of advanced precision manufacturing, nichrome has found its niche in several key areas. It is widely used in the production of heating elements, where its consistent electrical resistance and durability are essential. The semiconductor industry relies on nichrome for thin-film resistors and other microelectronic components, leveraging its stability and precise control of electrical properties. Additionally, nichrome plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of sensors and measurement devices, where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
The technological trajectory of nichrome in precision manufacturing has been marked by continuous improvements in composition, processing techniques, and application methodologies. Researchers and engineers have focused on enhancing the alloy's properties through precise control of its nickel-chromium ratio and the addition of trace elements. These efforts have resulted in nichrome variants with tailored characteristics, optimized for specific manufacturing requirements.
Looking ahead, the objectives for nichrome in advanced precision manufacturing are multifaceted. There is a strong emphasis on developing even more refined alloy compositions that can offer superior performance in extreme environments. Researchers are exploring ways to improve nichrome's already impressive corrosion resistance and thermal stability, aiming to extend its applicability in cutting-edge technologies such as additive manufacturing and nanotechnology.
Another key objective is the integration of nichrome into smart manufacturing processes. This involves developing sensors and control systems that can monitor and adjust the properties of nichrome-based components in real-time during manufacturing, ensuring unprecedented levels of precision and quality control. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainable manufacturing practices, with efforts directed towards optimizing nichrome production and recycling processes to minimize environmental impact.
Market Analysis for Nichrome-based Precision Components
The market for nichrome-based precision components has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials in advanced manufacturing processes. Nichrome, an alloy primarily composed of nickel and chromium, offers exceptional properties such as high temperature resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and superior corrosion resistance, making it an ideal material for precision components in various industries.
In the aerospace sector, nichrome-based components are widely used in jet engines, turbines, and other high-temperature applications. The global aerospace market is projected to grow steadily, with a particular emphasis on fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft designs. This trend is expected to boost the demand for nichrome components that can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions.
The automotive industry is another key market for nichrome-based precision components. As vehicle manufacturers focus on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, there is a growing need for lightweight, high-performance materials. Nichrome components are increasingly being used in exhaust systems, sensors, and other critical parts that require resistance to high temperatures and corrosive environments.
The electronics industry represents a rapidly expanding market for nichrome-based precision components. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing complexity of integrated circuits, there is a rising demand for precision heating elements and resistors made from nichrome. These components play a crucial role in maintaining stable temperatures in sensitive electronic equipment and ensuring accurate performance in various applications.
In the medical device sector, nichrome-based components are gaining traction due to their biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes. The growing adoption of minimally invasive surgical techniques and the development of advanced diagnostic equipment are driving the demand for precision components that can meet stringent quality and performance requirements.
The global market for nichrome-based precision components is characterized by intense competition among key players, including established manufacturers and emerging companies specializing in advanced materials. Market leaders are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the properties of nichrome alloys and develop innovative manufacturing techniques to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of performance and efficiency, the market for nichrome-based precision components is expected to expand further. The increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency across sectors is likely to drive the adoption of high-performance materials like nichrome in advanced manufacturing processes, creating new opportunities for growth and innovation in the coming years.
In the aerospace sector, nichrome-based components are widely used in jet engines, turbines, and other high-temperature applications. The global aerospace market is projected to grow steadily, with a particular emphasis on fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft designs. This trend is expected to boost the demand for nichrome components that can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions.
The automotive industry is another key market for nichrome-based precision components. As vehicle manufacturers focus on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, there is a growing need for lightweight, high-performance materials. Nichrome components are increasingly being used in exhaust systems, sensors, and other critical parts that require resistance to high temperatures and corrosive environments.
The electronics industry represents a rapidly expanding market for nichrome-based precision components. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing complexity of integrated circuits, there is a rising demand for precision heating elements and resistors made from nichrome. These components play a crucial role in maintaining stable temperatures in sensitive electronic equipment and ensuring accurate performance in various applications.
In the medical device sector, nichrome-based components are gaining traction due to their biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes. The growing adoption of minimally invasive surgical techniques and the development of advanced diagnostic equipment are driving the demand for precision components that can meet stringent quality and performance requirements.
The global market for nichrome-based precision components is characterized by intense competition among key players, including established manufacturers and emerging companies specializing in advanced materials. Market leaders are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the properties of nichrome alloys and develop innovative manufacturing techniques to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of performance and efficiency, the market for nichrome-based precision components is expected to expand further. The increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency across sectors is likely to drive the adoption of high-performance materials like nichrome in advanced manufacturing processes, creating new opportunities for growth and innovation in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Nichrome Application
Despite its widespread use in various industries, nichrome faces several challenges in advanced precision manufacturing applications. One of the primary issues is the material's thermal expansion characteristics. While nichrome's resistance to oxidation at high temperatures is advantageous, its thermal expansion coefficient can lead to dimensional instability in precision components. This becomes particularly problematic in applications requiring tight tolerances, as the material's expansion and contraction during heating and cooling cycles can compromise the accuracy of manufactured parts.
Another significant challenge lies in the machining and forming processes of nichrome. The material's high strength and hardness, which are beneficial for many applications, make it difficult to machine with conventional tools. This results in increased tool wear, longer production times, and higher manufacturing costs. Additionally, the material's tendency to work harden during machining processes further complicates the achievement of precise geometries and surface finishes required in advanced manufacturing.
The welding of nichrome components also presents challenges in precision manufacturing. While the material is generally considered weldable, achieving consistent, high-quality welds can be difficult due to its high melting point and the formation of chromium oxides. These factors can lead to weld defects, reduced joint strength, and potential failure points in precision assemblies.
Furthermore, the electrical properties of nichrome, while advantageous in many applications, can pose challenges in certain precision manufacturing scenarios. The material's relatively high electrical resistance, which makes it ideal for heating elements, can interfere with electrical discharge machining (EDM) processes, limiting the achievable precision in some complex geometries.
Lastly, the cost and availability of high-purity nichrome alloys suitable for advanced precision manufacturing can be a limiting factor. As the demand for higher performance and more stringent material specifications increases, sourcing nichrome that meets these exacting requirements becomes more challenging and expensive, potentially impacting the economic viability of certain precision manufacturing applications.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in material science, manufacturing processes, and quality control. Researchers and engineers are actively exploring solutions such as advanced heat treatment techniques, novel machining strategies, and the development of composite materials that retain nichrome's beneficial properties while mitigating its limitations in precision manufacturing contexts.
Another significant challenge lies in the machining and forming processes of nichrome. The material's high strength and hardness, which are beneficial for many applications, make it difficult to machine with conventional tools. This results in increased tool wear, longer production times, and higher manufacturing costs. Additionally, the material's tendency to work harden during machining processes further complicates the achievement of precise geometries and surface finishes required in advanced manufacturing.
The welding of nichrome components also presents challenges in precision manufacturing. While the material is generally considered weldable, achieving consistent, high-quality welds can be difficult due to its high melting point and the formation of chromium oxides. These factors can lead to weld defects, reduced joint strength, and potential failure points in precision assemblies.
Furthermore, the electrical properties of nichrome, while advantageous in many applications, can pose challenges in certain precision manufacturing scenarios. The material's relatively high electrical resistance, which makes it ideal for heating elements, can interfere with electrical discharge machining (EDM) processes, limiting the achievable precision in some complex geometries.
Lastly, the cost and availability of high-purity nichrome alloys suitable for advanced precision manufacturing can be a limiting factor. As the demand for higher performance and more stringent material specifications increases, sourcing nichrome that meets these exacting requirements becomes more challenging and expensive, potentially impacting the economic viability of certain precision manufacturing applications.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in material science, manufacturing processes, and quality control. Researchers and engineers are actively exploring solutions such as advanced heat treatment techniques, novel machining strategies, and the development of composite materials that retain nichrome's beneficial properties while mitigating its limitations in precision manufacturing contexts.
Existing Nichrome Processing Methods
01 Composition and properties of nichrome alloys
Nichrome is an alloy primarily composed of nickel and chromium, with varying proportions depending on the specific application. It is known for its high electrical resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. These properties make it suitable for use in heating elements, resistors, and other high-temperature applications.- Composition and properties of nichrome alloys: Nichrome is an alloy primarily composed of nickel and chromium, with varying compositions for different applications. It is known for its high electrical resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. These properties make it suitable for use in heating elements, resistors, and other high-temperature applications.
- Nichrome in heating elements and electrical resistors: Nichrome is widely used in the manufacturing of heating elements and electrical resistors due to its high electrical resistance and heat-generating properties. It is commonly found in appliances such as hair dryers, toasters, and electric heaters. The alloy's stability at high temperatures makes it ideal for these applications.
- Nichrome in thin film technology: Nichrome is utilized in thin film technology for various electronic applications. It can be deposited as a thin film using techniques such as sputtering or evaporation. These thin films are used in the production of resistors, sensors, and other microelectronic components.
- Nichrome in aerospace and high-temperature applications: The high temperature resistance and stability of nichrome make it suitable for aerospace and other high-temperature applications. It is used in components that require resistance to heat and corrosion, such as in jet engines, furnaces, and industrial ovens.
- Surface treatment and coating of nichrome: Various surface treatment and coating techniques are applied to nichrome to enhance its properties or protect it from oxidation. These treatments can improve the alloy's performance in specific applications, such as increasing its lifespan in heating elements or improving its adhesion in thin film applications.
02 Manufacturing processes for nichrome components
Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce nichrome components, including wire drawing, thin film deposition, and powder metallurgy. These processes allow for the creation of nichrome elements in different forms such as wires, films, and powders, each suited for specific applications in electronics and heating systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in heating elements and resistors
Nichrome is widely used in the production of heating elements and resistors due to its high electrical resistance and heat-resistant properties. It is commonly found in household appliances, industrial heating equipment, and electronic devices where precise temperature control or electrical resistance is required.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nichrome in thin film technology
Nichrome thin films are utilized in various electronic applications, including the fabrication of resistors, sensors, and microelectronic devices. The thin film deposition of nichrome allows for precise control of electrical properties and enables the creation of miniaturized components for advanced electronic systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovations in nichrome-based materials and coatings
Ongoing research and development efforts focus on improving the properties of nichrome-based materials and exploring new applications. This includes the development of novel nichrome alloy compositions, surface treatments, and coating technologies to enhance performance in specific industrial and technological applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nichrome Precision Manufacturing
The application of Nichrome in advanced precision manufacturing is in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by its unique properties. The global market for precision manufacturing materials is expanding, with Nichrome playing a crucial role due to its high temperature resistance and electrical conductivity. Companies like Gaona Aero Material Co., Ltd. and ATI Properties, Inc. are at the forefront of developing advanced Nichrome alloys for aerospace and industrial applications. The technology is relatively mature, with ongoing research by institutions such as Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Beijing University of Technology focusing on enhancing Nichrome's properties and exploring new applications in emerging fields like nanotechnology and additive manufacturing.
ATI Properties, Inc.
Technical Solution: ATI Properties has developed a range of advanced nichrome alloys optimized for precision manufacturing applications. Their proprietary manufacturing process involves vacuum induction melting followed by electroslag remelting, resulting in exceptionally clean and homogeneous nichrome materials[1]. ATI's nichrome alloys feature carefully controlled compositions with additions of rare earth elements to enhance grain boundary strength and improve creep resistance at elevated temperatures[2]. The company has also developed specialized heat treatment processes to optimize the microstructure of nichrome components, resulting in improved dimensional stability and reduced thermal expansion[3]. ATI's nichrome materials are particularly well-suited for applications requiring tight tolerances and excellent surface finish, such as precision molds and dies used in advanced manufacturing processes[4].
Strengths: Exceptional material purity, improved high-temperature mechanical properties, and excellent dimensional stability. Weaknesses: Higher material costs and potential limitations in complex geometries.
Fort Wayne Metals Research Products LLC
Technical Solution: Fort Wayne Metals has developed innovative nichrome wire and fine wire products specifically designed for advanced precision manufacturing applications. Their proprietary drawing and heat treatment processes allow for the production of ultra-fine nichrome wires with diameters as small as 0.0005 inches (12.7 microns)[1]. The company utilizes advanced surface treatment techniques to enhance the electrical and thermal properties of their nichrome wires, making them ideal for use in precision sensors and micro-heating elements[2]. Fort Wayne Metals has also developed specialized nichrome alloy compositions that offer improved fatigue resistance and shape memory properties, enabling the creation of highly responsive actuators and control elements in precision manufacturing equipment[3]. Their nichrome materials exhibit excellent biocompatibility, making them suitable for use in medical device manufacturing and other sensitive applications[4].
Strengths: Ultra-fine wire capabilities, enhanced electrical and thermal properties, and biocompatibility. Weaknesses: Limited to wire-based applications and potential higher costs for specialized alloy compositions.
Innovative Nichrome Alloy Developments
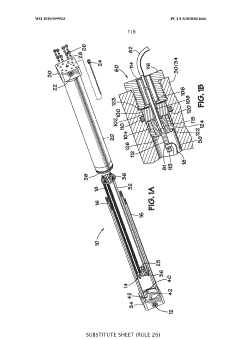
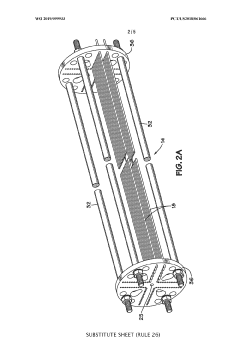
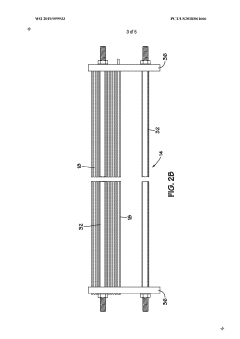
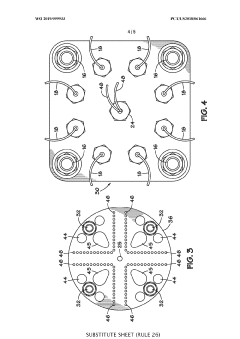
In-line electric heater for plural component materials
PatentWO2019099933A1
Innovation
- An in-line electric heater design featuring a housing with multiple electric resistance heating elements along the fluid flow path, supported by a wire loom assembly and temperature sensors, using INCONEL wires coated with Teflon for improved durability and insulation, and a power feedthrough system for secure electrical connections, enhancing heat transfer and temperature control.
Environmental Impact of Nichrome Manufacturing
The environmental impact of nichrome manufacturing is a critical consideration in the application of this alloy in advanced precision manufacturing. The production process of nichrome involves several stages that can have significant environmental implications. Mining of raw materials, primarily nickel and chromium, is the first step that can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution if not managed responsibly. The extraction and refining of these metals often require substantial energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
During the alloying process, high temperatures are necessary to melt and combine the constituent metals, resulting in considerable energy consumption. This energy-intensive phase often relies on fossil fuels, further exacerbating the carbon footprint of nichrome production. Additionally, the process can release harmful emissions, including particulate matter and volatile organic compounds, which may contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers and surrounding communities if not properly controlled.
Water usage is another environmental concern in nichrome manufacturing. Large volumes of water are required for cooling and processing, potentially leading to water scarcity issues in regions where the manufacturing takes place. The wastewater generated during production may contain heavy metals and other contaminants, necessitating careful treatment and disposal to prevent water pollution and ecosystem damage.
The use of chemicals in the manufacturing process, such as acids for cleaning and etching, can also have environmental repercussions. Improper handling or disposal of these substances can lead to soil and groundwater contamination. Furthermore, the production of nichrome generates solid waste, including slag and other byproducts, which require proper management to minimize landfill impact and potential leaching of hazardous materials into the environment.
However, it is important to note that the precision manufacturing industry has been making strides in adopting more sustainable practices. Recycling of nichrome scrap and other metal waste has become increasingly common, reducing the demand for raw material extraction. Advanced filtration systems and emission control technologies are being implemented to mitigate air and water pollution. Some manufacturers are also exploring cleaner energy sources, such as renewable electricity, to power their operations and reduce the carbon intensity of nichrome production.
As the demand for nichrome in advanced precision manufacturing continues to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing more environmentally friendly production methods. Research into alternative alloying techniques, such as powder metallurgy, shows promise in reducing energy consumption and waste generation. Additionally, life cycle assessments are being conducted to identify areas for improvement in the environmental performance of nichrome throughout its production, use, and end-of-life stages.
During the alloying process, high temperatures are necessary to melt and combine the constituent metals, resulting in considerable energy consumption. This energy-intensive phase often relies on fossil fuels, further exacerbating the carbon footprint of nichrome production. Additionally, the process can release harmful emissions, including particulate matter and volatile organic compounds, which may contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers and surrounding communities if not properly controlled.
Water usage is another environmental concern in nichrome manufacturing. Large volumes of water are required for cooling and processing, potentially leading to water scarcity issues in regions where the manufacturing takes place. The wastewater generated during production may contain heavy metals and other contaminants, necessitating careful treatment and disposal to prevent water pollution and ecosystem damage.
The use of chemicals in the manufacturing process, such as acids for cleaning and etching, can also have environmental repercussions. Improper handling or disposal of these substances can lead to soil and groundwater contamination. Furthermore, the production of nichrome generates solid waste, including slag and other byproducts, which require proper management to minimize landfill impact and potential leaching of hazardous materials into the environment.
However, it is important to note that the precision manufacturing industry has been making strides in adopting more sustainable practices. Recycling of nichrome scrap and other metal waste has become increasingly common, reducing the demand for raw material extraction. Advanced filtration systems and emission control technologies are being implemented to mitigate air and water pollution. Some manufacturers are also exploring cleaner energy sources, such as renewable electricity, to power their operations and reduce the carbon intensity of nichrome production.
As the demand for nichrome in advanced precision manufacturing continues to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing more environmentally friendly production methods. Research into alternative alloying techniques, such as powder metallurgy, shows promise in reducing energy consumption and waste generation. Additionally, life cycle assessments are being conducted to identify areas for improvement in the environmental performance of nichrome throughout its production, use, and end-of-life stages.
Quality Control in Nichrome-based Products
Quality control in Nichrome-based products is a critical aspect of advanced precision manufacturing. The unique properties of Nichrome, particularly its high electrical resistance and temperature stability, make it essential for various applications, but also present challenges in maintaining consistent quality.
One of the primary quality control measures for Nichrome-based products is the precise control of alloy composition. The ratio of nickel to chromium must be carefully monitored and maintained within tight tolerances to ensure the desired electrical and thermal characteristics. Advanced spectrometric techniques, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), are employed to verify the elemental composition of Nichrome alloys.
Dimensional accuracy is another crucial factor in quality control. Nichrome wires and ribbons used in precision applications require strict adherence to specified dimensions. Laser micrometry and high-resolution optical measurement systems are utilized to ensure that the cross-sectional area and length of Nichrome components meet the required specifications. These measurements are often performed at multiple points along the product to detect any variations in thickness or width.
Surface quality is equally important, particularly for Nichrome products used in sensitive electronic applications. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) are employed to inspect the surface morphology and detect any imperfections or contamination. These techniques can identify microscopic defects that could affect the performance or reliability of the final product.
Electrical properties testing is a fundamental aspect of quality control for Nichrome-based products. Precision resistance measurements are conducted using four-wire Kelvin probes to accurately determine the electrical resistance of Nichrome components. Temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) testing is also performed to ensure that the Nichrome alloy maintains its electrical characteristics across the intended operating temperature range.
Thermal cycling tests are crucial for evaluating the long-term stability and reliability of Nichrome products. These tests subject the components to repeated heating and cooling cycles, simulating real-world operating conditions. The electrical and mechanical properties are measured before and after thermal cycling to detect any degradation or changes in performance.
Corrosion resistance is another important quality parameter for Nichrome products. Accelerated corrosion testing, such as salt spray tests and humidity chamber exposure, is conducted to assess the material's resistance to environmental factors. These tests help ensure that Nichrome components maintain their integrity and performance in various operating environments.
One of the primary quality control measures for Nichrome-based products is the precise control of alloy composition. The ratio of nickel to chromium must be carefully monitored and maintained within tight tolerances to ensure the desired electrical and thermal characteristics. Advanced spectrometric techniques, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), are employed to verify the elemental composition of Nichrome alloys.
Dimensional accuracy is another crucial factor in quality control. Nichrome wires and ribbons used in precision applications require strict adherence to specified dimensions. Laser micrometry and high-resolution optical measurement systems are utilized to ensure that the cross-sectional area and length of Nichrome components meet the required specifications. These measurements are often performed at multiple points along the product to detect any variations in thickness or width.
Surface quality is equally important, particularly for Nichrome products used in sensitive electronic applications. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) are employed to inspect the surface morphology and detect any imperfections or contamination. These techniques can identify microscopic defects that could affect the performance or reliability of the final product.
Electrical properties testing is a fundamental aspect of quality control for Nichrome-based products. Precision resistance measurements are conducted using four-wire Kelvin probes to accurately determine the electrical resistance of Nichrome components. Temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) testing is also performed to ensure that the Nichrome alloy maintains its electrical characteristics across the intended operating temperature range.
Thermal cycling tests are crucial for evaluating the long-term stability and reliability of Nichrome products. These tests subject the components to repeated heating and cooling cycles, simulating real-world operating conditions. The electrical and mechanical properties are measured before and after thermal cycling to detect any degradation or changes in performance.
Corrosion resistance is another important quality parameter for Nichrome products. Accelerated corrosion testing, such as salt spray tests and humidity chamber exposure, is conducted to assess the material's resistance to environmental factors. These tests help ensure that Nichrome components maintain their integrity and performance in various operating environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!