Nichrome Contribution to Optimizing Automotive Heating Systems
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nichrome in Automotive Heating: Background and Objectives
Nichrome, an alloy primarily composed of nickel and chromium, has played a pivotal role in the evolution of automotive heating systems. The journey of nichrome in this domain traces back to the early 20th century when the automotive industry began to prioritize passenger comfort. As vehicles became more sophisticated, the demand for efficient and reliable heating systems grew exponentially.
The primary objective of incorporating nichrome into automotive heating systems is to optimize thermal efficiency while ensuring durability and cost-effectiveness. Nichrome's unique properties, including high electrical resistance and excellent heat tolerance, make it an ideal candidate for heating elements in vehicles. These characteristics allow for rapid heat generation with minimal energy input, a crucial factor in the automotive sector where energy conservation is paramount.
Over the years, the application of nichrome in automotive heating has evolved from basic resistive heating elements to more complex integrated systems. The technology has progressed to address various challenges, such as uniform heat distribution, rapid warm-up times, and adaptability to different vehicle sizes and configurations. This evolution has been driven by increasing consumer expectations for comfort and the automotive industry's push towards more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
The development of nichrome-based heating systems in automobiles has also been influenced by broader technological trends in the automotive sector. The shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles has further emphasized the importance of efficient heating solutions, as these vehicles lack the excess heat generated by traditional internal combustion engines. This has led to innovative applications of nichrome in battery thermal management systems and cabin heating for electric vehicles.
Current research and development efforts in nichrome-based automotive heating systems are focused on several key areas. These include improving the material's thermal conductivity, enhancing its longevity in harsh automotive environments, and developing more precise control mechanisms for heat output. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring nichrome composites and novel manufacturing techniques to further optimize performance and reduce costs.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the role of nichrome in heating systems is expected to expand. Future objectives include the development of smart heating elements that can adapt to varying environmental conditions and user preferences, as well as the integration of nichrome-based systems with other vehicle components for holistic thermal management solutions. The ongoing research in this field aims to push the boundaries of energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability in automotive heating technology.
The primary objective of incorporating nichrome into automotive heating systems is to optimize thermal efficiency while ensuring durability and cost-effectiveness. Nichrome's unique properties, including high electrical resistance and excellent heat tolerance, make it an ideal candidate for heating elements in vehicles. These characteristics allow for rapid heat generation with minimal energy input, a crucial factor in the automotive sector where energy conservation is paramount.
Over the years, the application of nichrome in automotive heating has evolved from basic resistive heating elements to more complex integrated systems. The technology has progressed to address various challenges, such as uniform heat distribution, rapid warm-up times, and adaptability to different vehicle sizes and configurations. This evolution has been driven by increasing consumer expectations for comfort and the automotive industry's push towards more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
The development of nichrome-based heating systems in automobiles has also been influenced by broader technological trends in the automotive sector. The shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles has further emphasized the importance of efficient heating solutions, as these vehicles lack the excess heat generated by traditional internal combustion engines. This has led to innovative applications of nichrome in battery thermal management systems and cabin heating for electric vehicles.
Current research and development efforts in nichrome-based automotive heating systems are focused on several key areas. These include improving the material's thermal conductivity, enhancing its longevity in harsh automotive environments, and developing more precise control mechanisms for heat output. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring nichrome composites and novel manufacturing techniques to further optimize performance and reduce costs.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the role of nichrome in heating systems is expected to expand. Future objectives include the development of smart heating elements that can adapt to varying environmental conditions and user preferences, as well as the integration of nichrome-based systems with other vehicle components for holistic thermal management solutions. The ongoing research in this field aims to push the boundaries of energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability in automotive heating technology.
Market Analysis for Efficient Automotive Heating Systems
The automotive heating system market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for comfort and safety features in vehicles. As consumers prioritize enhanced driving experiences, efficient heating systems have become a crucial component in modern automobiles. The global market for automotive heating systems is expected to expand steadily, with a particular focus on energy-efficient solutions that align with the industry's shift towards sustainability.
In terms of market segmentation, the automotive heating system market can be broadly categorized into passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles. Passenger vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, and hatchbacks, constitute the largest segment due to higher production volumes and consumer demand for comfort features. Commercial vehicles, while representing a smaller market share, are experiencing growing demand for advanced heating systems, especially in regions with harsh climates.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for automotive heating systems, owing to their mature automotive industries and cold climates. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are showing rapid growth potential as vehicle ownership increases and consumer preferences evolve. These regions are expected to be key drivers of market growth in the coming years.
The market is characterized by intense competition among major automotive suppliers and OEMs. Key players are focusing on developing innovative heating solutions that offer improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced thermal comfort. There is a growing trend towards the integration of smart heating systems that can be controlled via mobile applications or voice commands, catering to the increasing demand for connected car features.
Environmental regulations and the push for vehicle electrification are significantly influencing the market dynamics. As automakers strive to meet stringent emissions standards, there is a growing emphasis on developing heating systems that minimize energy consumption and reduce the overall carbon footprint of vehicles. This trend is particularly evident in the electric vehicle segment, where efficient heating systems are crucial for maximizing battery range.
The aftermarket segment for automotive heating systems also presents substantial opportunities. As vehicles age, the demand for replacement parts and upgrades to heating systems increases. This segment is expected to grow steadily, driven by the rising average age of vehicles on the road and consumer desire for improved comfort features in older models.
In terms of market segmentation, the automotive heating system market can be broadly categorized into passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles. Passenger vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, and hatchbacks, constitute the largest segment due to higher production volumes and consumer demand for comfort features. Commercial vehicles, while representing a smaller market share, are experiencing growing demand for advanced heating systems, especially in regions with harsh climates.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for automotive heating systems, owing to their mature automotive industries and cold climates. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are showing rapid growth potential as vehicle ownership increases and consumer preferences evolve. These regions are expected to be key drivers of market growth in the coming years.
The market is characterized by intense competition among major automotive suppliers and OEMs. Key players are focusing on developing innovative heating solutions that offer improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced thermal comfort. There is a growing trend towards the integration of smart heating systems that can be controlled via mobile applications or voice commands, catering to the increasing demand for connected car features.
Environmental regulations and the push for vehicle electrification are significantly influencing the market dynamics. As automakers strive to meet stringent emissions standards, there is a growing emphasis on developing heating systems that minimize energy consumption and reduce the overall carbon footprint of vehicles. This trend is particularly evident in the electric vehicle segment, where efficient heating systems are crucial for maximizing battery range.
The aftermarket segment for automotive heating systems also presents substantial opportunities. As vehicles age, the demand for replacement parts and upgrades to heating systems increases. This segment is expected to grow steadily, driven by the rising average age of vehicles on the road and consumer desire for improved comfort features in older models.
Current Challenges in Automotive Heating Technology
The automotive industry is currently grappling with several significant challenges in heating technology. One of the primary issues is the need for more efficient and environmentally friendly heating systems. Traditional combustion engine vehicles rely on waste heat from the engine to warm the cabin, but this approach is not viable for electric vehicles (EVs). As the automotive sector shifts towards electrification, developing effective heating solutions for EVs has become a critical challenge.
Energy consumption is another major concern. Heating systems in EVs can significantly reduce the vehicle's range, especially in cold climates. This issue has led to a growing demand for heating technologies that can provide adequate warmth without excessively draining the battery. The industry is actively seeking solutions that can balance comfort with energy efficiency.
Rapid temperature control is also a persistent challenge. Modern consumers expect quick cabin warm-up times, even in extremely cold conditions. However, achieving this without compromising energy efficiency or overall vehicle performance remains difficult. Engineers are working to develop systems that can provide fast heating while minimizing power consumption.
Material limitations present another hurdle. The automotive industry requires heating elements that are not only efficient but also durable, lightweight, and cost-effective. Finding materials that meet all these criteria while withstanding the harsh conditions of automotive use is an ongoing challenge. This has sparked interest in advanced materials and innovative designs for heating elements.
Space constraints within vehicles pose additional difficulties. As vehicles become more compact and filled with various technologies, finding room for efficient heating systems becomes increasingly challenging. This has led to a push for more compact and integrated heating solutions that can be seamlessly incorporated into vehicle designs without compromising interior space or aesthetics.
Uniformity of heat distribution is another area of concern. Ensuring even heating throughout the cabin, especially in larger vehicles, remains a technical challenge. Hotspots and cold zones can lead to passenger discomfort and reduced overall heating efficiency. Developing systems that can provide consistent warmth across the entire cabin space is a key focus for automotive engineers.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in terms of cost-effectiveness. While there is a demand for advanced heating technologies, they need to be economically viable for mass production. Balancing the costs of new technologies with the need for affordability in consumer vehicles is an ongoing struggle for manufacturers.
Energy consumption is another major concern. Heating systems in EVs can significantly reduce the vehicle's range, especially in cold climates. This issue has led to a growing demand for heating technologies that can provide adequate warmth without excessively draining the battery. The industry is actively seeking solutions that can balance comfort with energy efficiency.
Rapid temperature control is also a persistent challenge. Modern consumers expect quick cabin warm-up times, even in extremely cold conditions. However, achieving this without compromising energy efficiency or overall vehicle performance remains difficult. Engineers are working to develop systems that can provide fast heating while minimizing power consumption.
Material limitations present another hurdle. The automotive industry requires heating elements that are not only efficient but also durable, lightweight, and cost-effective. Finding materials that meet all these criteria while withstanding the harsh conditions of automotive use is an ongoing challenge. This has sparked interest in advanced materials and innovative designs for heating elements.
Space constraints within vehicles pose additional difficulties. As vehicles become more compact and filled with various technologies, finding room for efficient heating systems becomes increasingly challenging. This has led to a push for more compact and integrated heating solutions that can be seamlessly incorporated into vehicle designs without compromising interior space or aesthetics.
Uniformity of heat distribution is another area of concern. Ensuring even heating throughout the cabin, especially in larger vehicles, remains a technical challenge. Hotspots and cold zones can lead to passenger discomfort and reduced overall heating efficiency. Developing systems that can provide consistent warmth across the entire cabin space is a key focus for automotive engineers.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in terms of cost-effectiveness. While there is a demand for advanced heating technologies, they need to be economically viable for mass production. Balancing the costs of new technologies with the need for affordability in consumer vehicles is an ongoing struggle for manufacturers.
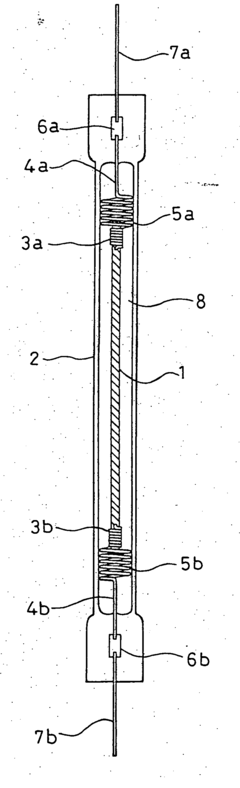
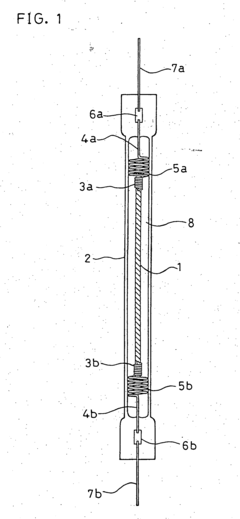
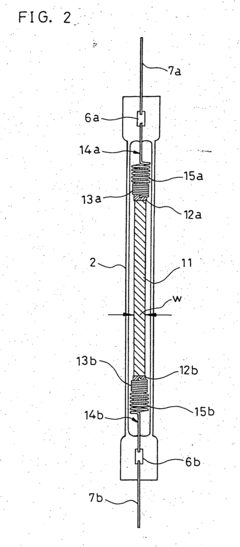
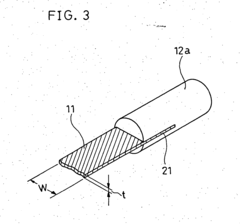
Existing Nichrome-based Heating Solutions
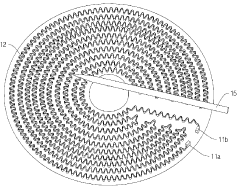
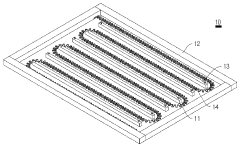
01 Composition and structure optimization
Improving the composition and structure of nichrome alloys can enhance heating efficiency. This includes adjusting the ratio of nickel and chromium, adding other elements, or modifying the microstructure to optimize electrical resistance and heat distribution.- Composition and structure optimization: Improving the composition and structure of nichrome alloys can enhance heating efficiency. This includes adjusting the ratio of nickel and chromium, adding other elements, or modifying the microstructure to optimize electrical resistance and heat distribution.
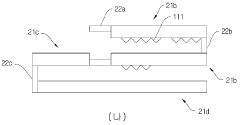
- Surface treatment and coating: Applying surface treatments or coatings to nichrome heating elements can improve their performance. These treatments may enhance heat radiation, prevent oxidation, or increase durability, ultimately leading to better heating efficiency.
- Heating element design: Optimizing the design of nichrome heating elements, such as their shape, size, and arrangement, can significantly impact heating efficiency. This includes creating specific patterns or configurations to maximize heat distribution and energy transfer.
- Integration with other materials: Combining nichrome with other materials or embedding it in composite structures can enhance overall heating efficiency. This approach may involve using insulating materials, heat-conducting substrates, or creating multi-layered structures to optimize heat generation and distribution.
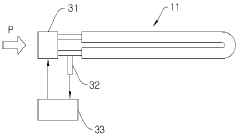
- Control systems and power management: Implementing advanced control systems and power management techniques can improve the heating efficiency of nichrome elements. This includes using precise temperature sensors, intelligent power regulation, and adaptive heating algorithms to optimize energy consumption and heat output.
02 Surface treatment and coating
Applying surface treatments or coatings to nichrome heating elements can improve their performance. These treatments may enhance heat radiation, prevent oxidation, or improve electrical conductivity, leading to better heating efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Heating element design
Optimizing the design of nichrome heating elements, such as their shape, size, and arrangement, can significantly impact heating efficiency. This includes creating specific patterns or configurations to maximize heat distribution and minimize energy loss.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with other materials
Combining nichrome with other materials or embedding it in composite structures can enhance overall heating efficiency. This approach may involve using insulating materials, heat-conducting substrates, or creating multi-layered structures to optimize heat generation and transfer.Expand Specific Solutions05 Control and power management
Implementing advanced control systems and power management techniques can improve the heating efficiency of nichrome elements. This includes using precise temperature sensors, intelligent power regulation, and adaptive heating algorithms to optimize energy consumption and heat output.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Automotive Heating Industry
The automotive heating system optimization market, driven by nichrome contributions, is in a growth phase characterized by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. The market size is expanding due to stricter emissions regulations and consumer preferences for improved vehicle comfort. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Eaton Intelligent Power, Hyundai Motor, and Kia Corp leading innovations. Established players such as Siemens Energy and ABB Group are leveraging their expertise in power systems to develop cutting-edge heating solutions. Emerging companies like Yancheng Xinyang Electric Heating Material are specializing in high-temperature alloys, indicating a trend towards material-focused advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, with automotive manufacturers, technology conglomerates, and specialized material suppliers all contributing to the sector's evolution.
Eaton Intelligent Power Ltd.
Technical Solution: Eaton has developed a sophisticated nichrome-based heating system for commercial vehicles, focusing on optimizing power management and energy efficiency. Their system utilizes high-precision nichrome heating elements integrated with an intelligent power distribution unit. This setup allows for dynamic allocation of power between various vehicle systems, including cabin heating, battery thermal management, and drivetrain preconditioning. Eaton's technology employs advanced predictive algorithms that anticipate heating needs based on route information, weather conditions, and historical usage patterns, potentially reducing energy consumption by up to 20%[9]. The system also features a rapid heating mode for defrosting and defogging, enhancing safety in adverse weather conditions. Eaton's nichrome heaters are designed for durability, with a projected operational life of over 500,000 miles in heavy-duty applications.
Strengths: Intelligent power management, predictive heating optimization, high durability for commercial applications. Weaknesses: May be overly complex for smaller vehicles, potentially higher initial cost compared to simpler heating systems.
Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hyundai has innovated in automotive heating systems by developing a nichrome-based heat pump system that combines heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functions. This integrated approach utilizes waste heat from the vehicle's powertrain and electrical systems, supplemented by nichrome heating elements for rapid temperature adjustments. The system employs a sophisticated control algorithm that optimizes heat distribution based on real-time data from multiple sensors throughout the vehicle[2]. Hyundai's technology has shown to improve overall energy efficiency by up to 25% in electric vehicles, extending driving range in cold weather conditions[4]. The nichrome elements are designed for longevity, with a projected lifespan exceeding 10 years of normal vehicle operation.
Strengths: Integrated HVAC solution, improved energy efficiency in EVs, extended component lifespan. Weaknesses: System complexity may lead to higher maintenance costs, potential for increased vehicle weight.
Innovations in Nichrome Alloy Technology
Heating apparatus having structure of nichrome strip
PatentInactiveKR1020150058831A
Innovation
- A heater device with a nichrome strip structure that extends in a screw or zigzag form, varying in thickness and length to optimize resistance and heat generation, incorporating a detection sensor and control unit for voltage regulation to enhance efficiency.
Infrared lamp, method of manufacturing the same, and heating apparatus using the infrared lamp
PatentInactiveUS20050136785A1
Innovation
- A carbon-based heating element with a specific resistance change rate between lit and unlit states is controlled within ±20%, using a sintered body formed by mixing carbon with metallic or semi-metallic compounds, and connecting multiple short heating elements via electrodes and terminals to form a long heating element, ensuring stability and efficient thermal distribution.
Environmental Impact of Nichrome Heating Systems
The environmental impact of nichrome heating systems in automotive applications is a critical consideration as the automotive industry strives for sustainability. Nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium, has been widely used in heating elements due to its excellent electrical resistance and heat-generating properties. However, its environmental footprint extends beyond its operational phase to include production, disposal, and recycling processes.
During the production of nichrome, the mining and refining of nickel and chromium contribute to environmental degradation. These processes often involve significant energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and potential habitat destruction. The extraction of these metals can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and the release of toxic substances into the environment. Furthermore, the manufacturing of nichrome wire requires additional energy and resources, adding to its overall environmental impact.
In the operational phase, nichrome heating systems in automobiles generally demonstrate high energy efficiency. This efficiency translates to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions compared to less efficient heating methods. However, the environmental benefits during operation must be weighed against the energy-intensive production process and the potential for increased vehicle weight, which can affect overall fuel efficiency.
The disposal and recycling of nichrome heating systems present both challenges and opportunities. While nichrome is recyclable, the process of separating it from other vehicle components can be complex and energy-intensive. Improper disposal can lead to the release of heavy metals into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. On the other hand, effective recycling programs can recover valuable metals, reducing the need for new raw material extraction and mitigating environmental impacts.
Advancements in nichrome heating system design are focusing on improving energy efficiency and reducing material usage. Innovations such as thinner wire configurations and more precise temperature controls can minimize the amount of nichrome required while maintaining or enhancing performance. These improvements not only reduce the environmental impact of production but also contribute to lighter vehicles, potentially improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions during the vehicle's lifetime.
The automotive industry is also exploring alternative materials and technologies to complement or replace nichrome in heating systems. These include carbon-based heating elements, ceramic heating elements, and advanced polymer-based systems. While these alternatives may offer environmental benefits, their overall impact must be carefully assessed through comprehensive life cycle analyses to ensure they truly represent an improvement over nichrome systems.
During the production of nichrome, the mining and refining of nickel and chromium contribute to environmental degradation. These processes often involve significant energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and potential habitat destruction. The extraction of these metals can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and the release of toxic substances into the environment. Furthermore, the manufacturing of nichrome wire requires additional energy and resources, adding to its overall environmental impact.
In the operational phase, nichrome heating systems in automobiles generally demonstrate high energy efficiency. This efficiency translates to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions compared to less efficient heating methods. However, the environmental benefits during operation must be weighed against the energy-intensive production process and the potential for increased vehicle weight, which can affect overall fuel efficiency.
The disposal and recycling of nichrome heating systems present both challenges and opportunities. While nichrome is recyclable, the process of separating it from other vehicle components can be complex and energy-intensive. Improper disposal can lead to the release of heavy metals into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. On the other hand, effective recycling programs can recover valuable metals, reducing the need for new raw material extraction and mitigating environmental impacts.
Advancements in nichrome heating system design are focusing on improving energy efficiency and reducing material usage. Innovations such as thinner wire configurations and more precise temperature controls can minimize the amount of nichrome required while maintaining or enhancing performance. These improvements not only reduce the environmental impact of production but also contribute to lighter vehicles, potentially improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions during the vehicle's lifetime.
The automotive industry is also exploring alternative materials and technologies to complement or replace nichrome in heating systems. These include carbon-based heating elements, ceramic heating elements, and advanced polymer-based systems. While these alternatives may offer environmental benefits, their overall impact must be carefully assessed through comprehensive life cycle analyses to ensure they truly represent an improvement over nichrome systems.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Nichrome Implementation
The implementation of nichrome in automotive heating systems presents a compelling case for cost-benefit analysis. Initial investment costs for nichrome-based heating elements are generally higher than traditional alternatives. However, the long-term operational benefits often outweigh these upfront expenses.
Nichrome's superior electrical resistance properties allow for rapid heating, reducing the time required to reach optimal temperatures. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption, potentially decreasing fuel usage in combustion engine vehicles or extending the range of electric vehicles. The reduced energy demand can lead to significant cost savings over the vehicle's lifetime, particularly in regions with high fuel prices or electricity costs.
Durability is another key factor in the cost-benefit equation. Nichrome's resistance to oxidation and corrosion contributes to extended component lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated maintenance costs. This longevity is particularly valuable in automotive applications, where harsh environmental conditions and frequent thermal cycling can quickly degrade less robust materials.
Manufacturing processes for nichrome heating elements have become increasingly streamlined, potentially offsetting some of the higher material costs. Advanced production techniques, such as precision winding and automated assembly, can improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce labor costs associated with the production of nichrome-based heating systems.
The improved performance of nichrome heating systems can also contribute to enhanced user comfort and satisfaction. Faster heating times and more uniform heat distribution may increase perceived value, potentially justifying higher vehicle prices or improving brand reputation. This indirect benefit, while challenging to quantify, can positively impact overall vehicle sales and market positioning.
Environmental considerations also play a role in the cost-benefit analysis. The increased efficiency of nichrome heating systems can lead to reduced emissions in combustion engine vehicles, potentially helping manufacturers meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations. In some regions, this may translate to financial benefits through carbon credits or avoided penalties.
However, the cost-benefit analysis must also consider potential drawbacks. The higher initial cost of nichrome may impact profit margins or necessitate price increases, potentially affecting market competitiveness. Additionally, the specialized nature of nichrome production may expose manufacturers to supply chain risks or price volatility in the nichrome market.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of nichrome implementation in automotive heating systems are higher, the long-term benefits in efficiency, durability, and performance often justify the investment. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider not only direct financial impacts but also indirect benefits such as improved user satisfaction and environmental performance.
Nichrome's superior electrical resistance properties allow for rapid heating, reducing the time required to reach optimal temperatures. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption, potentially decreasing fuel usage in combustion engine vehicles or extending the range of electric vehicles. The reduced energy demand can lead to significant cost savings over the vehicle's lifetime, particularly in regions with high fuel prices or electricity costs.
Durability is another key factor in the cost-benefit equation. Nichrome's resistance to oxidation and corrosion contributes to extended component lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated maintenance costs. This longevity is particularly valuable in automotive applications, where harsh environmental conditions and frequent thermal cycling can quickly degrade less robust materials.
Manufacturing processes for nichrome heating elements have become increasingly streamlined, potentially offsetting some of the higher material costs. Advanced production techniques, such as precision winding and automated assembly, can improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce labor costs associated with the production of nichrome-based heating systems.
The improved performance of nichrome heating systems can also contribute to enhanced user comfort and satisfaction. Faster heating times and more uniform heat distribution may increase perceived value, potentially justifying higher vehicle prices or improving brand reputation. This indirect benefit, while challenging to quantify, can positively impact overall vehicle sales and market positioning.
Environmental considerations also play a role in the cost-benefit analysis. The increased efficiency of nichrome heating systems can lead to reduced emissions in combustion engine vehicles, potentially helping manufacturers meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations. In some regions, this may translate to financial benefits through carbon credits or avoided penalties.
However, the cost-benefit analysis must also consider potential drawbacks. The higher initial cost of nichrome may impact profit margins or necessitate price increases, potentially affecting market competitiveness. Additionally, the specialized nature of nichrome production may expose manufacturers to supply chain risks or price volatility in the nichrome market.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of nichrome implementation in automotive heating systems are higher, the long-term benefits in efficiency, durability, and performance often justify the investment. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider not only direct financial impacts but also indirect benefits such as improved user satisfaction and environmental performance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!