Flexible solar roll to roll manufacturing for cost reduction
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Flexible Solar Technology Evolution and Objectives
Flexible solar technology has evolved significantly over the past two decades, transitioning from laboratory curiosities to commercially viable products. The journey began in the early 2000s with the development of first-generation flexible photovoltaic cells based on amorphous silicon, which offered flexibility but suffered from low efficiency rates of 5-7%. By 2010, second-generation technologies emerged, incorporating CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide) and CdTe (Cadmium Telluride) thin-film materials, pushing efficiencies to 10-12% while maintaining flexibility.
The technological evolution accelerated around 2015 with the introduction of organic photovoltaics (OPVs) and perovskite-based flexible solar cells, which promised both improved efficiency and potentially lower manufacturing costs. Current state-of-the-art flexible solar technologies achieve efficiencies approaching 18-20% in laboratory settings, though commercial products typically deliver 12-15% efficiency.
Roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing represents a pivotal advancement in this evolution, enabling continuous production of flexible solar panels on substrates like plastic films or metal foils. This manufacturing approach has progressively matured from batch processing to semi-continuous and now fully continuous production methods, dramatically reducing production time and material waste.
The primary objective of flexible solar R2R manufacturing development is substantial cost reduction while maintaining acceptable efficiency levels. Current production costs for flexible solar panels range from $0.70-1.20 per watt, significantly higher than conventional rigid silicon panels at $0.20-0.30 per watt. The industry aims to reduce flexible solar production costs to below $0.40 per watt within the next five years through manufacturing innovations.
Additional technical objectives include improving production throughput from current rates of 5-10 meters per minute to 30+ meters per minute, enhancing layer uniformity across large areas, and developing in-line quality control systems capable of detecting defects in real-time. Durability improvements represent another critical goal, as flexible solar products currently offer lifespans of 10-15 years compared to 25+ years for traditional panels.
The long-term vision for flexible solar R2R manufacturing centers on creating truly ubiquitous solar technology that can be integrated into everyday surfaces and products, from building materials to consumer goods, vehicles, and wearable technology. This requires not only cost reductions but also advances in encapsulation technology, connection systems, and substrate materials that can withstand diverse environmental conditions while maintaining performance.
The technological evolution accelerated around 2015 with the introduction of organic photovoltaics (OPVs) and perovskite-based flexible solar cells, which promised both improved efficiency and potentially lower manufacturing costs. Current state-of-the-art flexible solar technologies achieve efficiencies approaching 18-20% in laboratory settings, though commercial products typically deliver 12-15% efficiency.
Roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing represents a pivotal advancement in this evolution, enabling continuous production of flexible solar panels on substrates like plastic films or metal foils. This manufacturing approach has progressively matured from batch processing to semi-continuous and now fully continuous production methods, dramatically reducing production time and material waste.
The primary objective of flexible solar R2R manufacturing development is substantial cost reduction while maintaining acceptable efficiency levels. Current production costs for flexible solar panels range from $0.70-1.20 per watt, significantly higher than conventional rigid silicon panels at $0.20-0.30 per watt. The industry aims to reduce flexible solar production costs to below $0.40 per watt within the next five years through manufacturing innovations.
Additional technical objectives include improving production throughput from current rates of 5-10 meters per minute to 30+ meters per minute, enhancing layer uniformity across large areas, and developing in-line quality control systems capable of detecting defects in real-time. Durability improvements represent another critical goal, as flexible solar products currently offer lifespans of 10-15 years compared to 25+ years for traditional panels.
The long-term vision for flexible solar R2R manufacturing centers on creating truly ubiquitous solar technology that can be integrated into everyday surfaces and products, from building materials to consumer goods, vehicles, and wearable technology. This requires not only cost reductions but also advances in encapsulation technology, connection systems, and substrate materials that can withstand diverse environmental conditions while maintaining performance.
Market Analysis for Low-Cost Flexible Solar Solutions
The flexible solar panel market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy solutions across various sectors. Current market valuations indicate the global flexible solar panel market reached approximately 500 million USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 15-17% through 2030. This growth trajectory is supported by declining manufacturing costs, which have decreased by nearly 70% over the past decade, making flexible solar technology increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources.
Consumer demand for low-cost flexible solar solutions spans multiple segments. The building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) sector represents a substantial market opportunity, with commercial and residential buildings seeking aesthetically pleasing and functional energy-generating surfaces. The portable electronics market demonstrates strong interest in lightweight, flexible power sources, while the automotive industry increasingly incorporates solar elements into vehicle designs to extend range and reduce emissions.
Geographic market distribution shows particular strength in Europe, where stringent renewable energy targets drive adoption, and in Asia-Pacific, where manufacturing capabilities and growing energy demands create favorable market conditions. North America follows closely, with increasing policy support for renewable energy technologies. Emerging markets in Africa and South America present significant growth potential due to off-grid applications and rural electrification initiatives.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals that cost remains the primary barrier to widespread adoption. Current flexible solar solutions typically command a 20-30% premium over conventional rigid panels when comparing cost per watt. However, this gap continues to narrow as roll-to-roll manufacturing techniques improve efficiency and reduce material waste. Market research indicates that achieving price parity with conventional solar technologies would trigger exponential market growth, potentially tripling market size within five years.
Customer preference studies show increasing willingness to pay for flexibility, durability, and aesthetic integration capabilities. Industrial and commercial customers prioritize total lifetime value, including installation simplicity and maintenance costs, while residential consumers place higher value on appearance and ease of installation. The military and emergency response sectors represent premium market segments willing to pay higher prices for ultra-lightweight, durable solutions.
Competitive analysis indicates that early market entrants have established strong positions, but the field remains dynamic with new players introducing innovative manufacturing approaches. Distribution channels are evolving rapidly, with direct-to-consumer models gaining traction alongside traditional installer networks and wholesale distribution.
Consumer demand for low-cost flexible solar solutions spans multiple segments. The building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) sector represents a substantial market opportunity, with commercial and residential buildings seeking aesthetically pleasing and functional energy-generating surfaces. The portable electronics market demonstrates strong interest in lightweight, flexible power sources, while the automotive industry increasingly incorporates solar elements into vehicle designs to extend range and reduce emissions.
Geographic market distribution shows particular strength in Europe, where stringent renewable energy targets drive adoption, and in Asia-Pacific, where manufacturing capabilities and growing energy demands create favorable market conditions. North America follows closely, with increasing policy support for renewable energy technologies. Emerging markets in Africa and South America present significant growth potential due to off-grid applications and rural electrification initiatives.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals that cost remains the primary barrier to widespread adoption. Current flexible solar solutions typically command a 20-30% premium over conventional rigid panels when comparing cost per watt. However, this gap continues to narrow as roll-to-roll manufacturing techniques improve efficiency and reduce material waste. Market research indicates that achieving price parity with conventional solar technologies would trigger exponential market growth, potentially tripling market size within five years.
Customer preference studies show increasing willingness to pay for flexibility, durability, and aesthetic integration capabilities. Industrial and commercial customers prioritize total lifetime value, including installation simplicity and maintenance costs, while residential consumers place higher value on appearance and ease of installation. The military and emergency response sectors represent premium market segments willing to pay higher prices for ultra-lightweight, durable solutions.
Competitive analysis indicates that early market entrants have established strong positions, but the field remains dynamic with new players introducing innovative manufacturing approaches. Distribution channels are evolving rapidly, with direct-to-consumer models gaining traction alongside traditional installer networks and wholesale distribution.
Roll-to-Roll Manufacturing Challenges and Constraints
Roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing for flexible solar cells presents significant challenges despite its promise for cost reduction. Material handling issues are paramount, as thin flexible substrates are prone to deformation, wrinkling, and tearing during high-speed processing. Maintaining proper tension control throughout the entire manufacturing line is critical yet technically demanding, especially when dealing with temperature-sensitive materials.
Process integration complexity represents another major constraint. Unlike batch processing, R2R requires seamless coordination between multiple sequential processes including substrate preparation, layer deposition, patterning, and encapsulation. Each process must operate at compatible speeds and conditions, creating a complex optimization problem where the entire production line is only as efficient as its slowest component.
Uniformity and quality control pose persistent challenges across large-area substrates. Achieving consistent layer thickness, material properties, and performance metrics over meters of flexible substrate requires sophisticated in-line monitoring systems. Small variations in deposition parameters can propagate into significant performance differences across the manufactured solar modules, affecting overall yield and reliability.
Equipment design limitations further constrain R2R manufacturing capabilities. Many existing tools were originally developed for rigid substrate processing and require substantial modification for flexible materials. Specialized equipment for flexible electronics often lacks the maturity and optimization of conventional semiconductor manufacturing tools, resulting in higher capital costs and lower throughput.
Environmental control presents additional difficulties, as many thin-film deposition processes are highly sensitive to contamination, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. Maintaining clean-room conditions across large open-air processing lines is technically challenging and expensive, particularly for moisture-sensitive organic photovoltaic materials.
Scaling barriers exist when transitioning from laboratory-scale demonstrations to industrial production. Processes that work well for small samples often encounter unforeseen complications at production scales, including edge effects, substrate heating uniformity, and material utilization efficiency. These scaling issues can significantly impact the economic viability of R2R solar manufacturing.
Registration accuracy between successive layers represents a critical technical hurdle, especially for multi-junction solar cells requiring precise alignment of multiple functional layers. Substrate dimensional changes due to thermal expansion or mechanical stress during processing compound this challenge, necessitating advanced optical registration systems and compensation algorithms.
Finally, defect management strategies must be developed specifically for continuous processing environments. Unlike batch processes where defective units can be individually rejected, defects in R2R manufacturing can affect significant lengths of produced material before detection, creating substantial waste and reducing overall production efficiency.
Process integration complexity represents another major constraint. Unlike batch processing, R2R requires seamless coordination between multiple sequential processes including substrate preparation, layer deposition, patterning, and encapsulation. Each process must operate at compatible speeds and conditions, creating a complex optimization problem where the entire production line is only as efficient as its slowest component.
Uniformity and quality control pose persistent challenges across large-area substrates. Achieving consistent layer thickness, material properties, and performance metrics over meters of flexible substrate requires sophisticated in-line monitoring systems. Small variations in deposition parameters can propagate into significant performance differences across the manufactured solar modules, affecting overall yield and reliability.
Equipment design limitations further constrain R2R manufacturing capabilities. Many existing tools were originally developed for rigid substrate processing and require substantial modification for flexible materials. Specialized equipment for flexible electronics often lacks the maturity and optimization of conventional semiconductor manufacturing tools, resulting in higher capital costs and lower throughput.
Environmental control presents additional difficulties, as many thin-film deposition processes are highly sensitive to contamination, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. Maintaining clean-room conditions across large open-air processing lines is technically challenging and expensive, particularly for moisture-sensitive organic photovoltaic materials.
Scaling barriers exist when transitioning from laboratory-scale demonstrations to industrial production. Processes that work well for small samples often encounter unforeseen complications at production scales, including edge effects, substrate heating uniformity, and material utilization efficiency. These scaling issues can significantly impact the economic viability of R2R solar manufacturing.
Registration accuracy between successive layers represents a critical technical hurdle, especially for multi-junction solar cells requiring precise alignment of multiple functional layers. Substrate dimensional changes due to thermal expansion or mechanical stress during processing compound this challenge, necessitating advanced optical registration systems and compensation algorithms.
Finally, defect management strategies must be developed specifically for continuous processing environments. Unlike batch processes where defective units can be individually rejected, defects in R2R manufacturing can affect significant lengths of produced material before detection, creating substantial waste and reducing overall production efficiency.
Current Roll-to-Roll Production Methodologies
01 Advanced manufacturing techniques for flexible solar cells
Roll-to-roll manufacturing techniques have been developed to produce flexible solar cells at reduced costs. These techniques include continuous processing methods that allow for high-volume production with minimal material waste. The manufacturing processes involve specialized equipment designed for handling flexible substrates and applying thin-film photovoltaic materials efficiently. These advanced techniques significantly reduce production time and labor costs compared to traditional batch processing methods.- Roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for flexible solar cells: Roll-to-roll manufacturing processes enable continuous production of flexible solar cells on substrates that can be processed in roll form. This approach significantly reduces production costs compared to batch processing methods by increasing throughput and reducing handling time. The continuous nature of the process allows for higher production volumes and more efficient use of materials and energy, contributing to overall cost reduction in flexible solar panel manufacturing.
- Material selection and substrate optimization for cost reduction: The selection of cost-effective materials and optimization of flexible substrates plays a crucial role in reducing manufacturing costs. Using alternative materials to replace expensive components like indium tin oxide (ITO) with more affordable options, and developing thinner substrates that require less material while maintaining performance characteristics can significantly lower production costs. Optimized material formulations also improve the efficiency of the deposition process and reduce waste.
- Advanced deposition techniques for thin-film solar cells: Advanced deposition techniques enable the creation of thin-film solar cells with reduced material usage and improved efficiency. Methods such as solution processing, vapor deposition, and printing technologies allow for precise control of layer thickness and composition while maintaining high throughput in roll-to-roll manufacturing. These techniques minimize material waste and energy consumption during production, leading to significant cost reductions in the manufacturing process.
- Process automation and integration for manufacturing efficiency: Automation and integration of manufacturing processes improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs in flexible solar cell manufacturing. Implementing advanced control systems, robotics, and real-time monitoring enables continuous operation with minimal human intervention. Integrated production lines that combine multiple manufacturing steps in a single continuous process reduce handling requirements and production time, resulting in lower overall manufacturing costs.
- Quality control and yield improvement strategies: Implementing effective quality control systems and yield improvement strategies reduces waste and rework in flexible solar manufacturing. In-line inspection techniques, defect detection systems, and process optimization methods ensure consistent product quality while minimizing material waste. Statistical process control and continuous improvement methodologies help identify and eliminate sources of defects, leading to higher production yields and lower costs per unit of energy output.
02 Material innovations for cost-effective solar production
Cost reduction in flexible solar manufacturing has been achieved through innovations in materials. These include the development of lower-cost substrate materials, alternative semiconductor materials that require less energy to produce, and reduced use of expensive materials like indium and silver. Some approaches involve replacing traditional glass substrates with flexible polymers or metal foils that are compatible with roll-to-roll processing. These material innovations help reduce raw material costs while maintaining or improving solar cell efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Process optimization and automation for manufacturing efficiency
Significant cost reductions in flexible solar manufacturing have been achieved through process optimization and automation. This includes the development of integrated production lines that minimize handling steps, automated quality control systems that reduce defects, and optimized deposition techniques that increase material utilization rates. Energy consumption during manufacturing has been reduced through improved thermal management and process efficiency. These optimizations collectively reduce production costs while maintaining product quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel encapsulation and packaging solutions
Cost-effective encapsulation and packaging solutions have been developed for flexible solar modules. These include simplified lamination processes, reduced-cost edge sealing techniques, and innovative connector designs that are compatible with roll-to-roll manufacturing. Some approaches use alternative encapsulant materials that provide adequate protection at lower cost than traditional materials. These solutions not only reduce material costs but also simplify the manufacturing process, leading to overall cost reduction while maintaining the necessary protection for the solar cells.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of multiple production steps in continuous processing
Cost reduction has been achieved by integrating multiple production steps into continuous roll-to-roll processing. This includes combining deposition, patterning, and interconnection steps in a single production line, reducing handling and transfer operations between different equipment. Some approaches integrate in-line quality monitoring to immediately identify and address defects, reducing waste. The integration of multiple steps reduces capital equipment costs, floor space requirements, and production time, leading to significant overall cost savings in flexible solar manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders in Flexible Solar and R2R Processing
The flexible solar roll-to-roll manufacturing market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for cost-effective renewable energy solutions. The global market is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth as manufacturers seek to reduce production costs and increase efficiency. Technologically, the field is advancing from early-stage development to commercial maturity, with companies like Applied Materials, Energy Materials Corp., and Exeger Operations leading innovation in high-throughput manufacturing processes. Established players such as Kolon Industries, ULVAC, and Nitto Denko are leveraging their expertise in materials and equipment to develop advanced roll-to-roll technologies. Research institutions including PARC, Fudan University, and AIST are contributing breakthrough technologies, while newer entrants like SolarPaint and NthDegree Technologies are introducing disruptive approaches to flexible solar manufacturing.
Applied Materials, Inc.
Technical Solution: Applied Materials has developed advanced roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing solutions specifically for flexible solar production. Their SmartWeb™ platform integrates multiple deposition processes in a single vacuum system, enabling continuous thin-film deposition on flexible substrates. The system incorporates precision web handling with tension control mechanisms that maintain substrate flatness during high-speed processing. Applied Materials' technology utilizes rotary magnetron sputtering for uniform thin-film deposition across large areas, achieving thickness variations of less than ±2%. Their integrated approach combines PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) and PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) processes in sequence without breaking vacuum, significantly reducing manufacturing steps and associated costs. The company has demonstrated production speeds exceeding 10 meters per minute while maintaining cell efficiency comparable to batch processes, representing a critical breakthrough for cost-effective manufacturing.
Strengths: Industry-leading expertise in semiconductor and thin-film manufacturing equipment; established global supply chain and service network; proven scalability for industrial production. Weaknesses: Higher initial capital investment compared to traditional batch systems; technology primarily optimized for CIGS and amorphous silicon rather than all flexible solar technologies; requires specialized technical expertise for operation and maintenance.
Energy Materials Corp.
Technical Solution: Energy Materials Corporation (EMC) has developed a revolutionary roll-to-roll manufacturing platform specifically designed for perovskite solar cells. Their technology, branded as "PV Flex," utilizes a multi-stage deposition process that enables continuous production of perovskite photovoltaics on flexible substrates at speeds up to 100 feet per minute. EMC's approach incorporates slot-die coating for the deposition of perovskite precursor solutions, followed by precisely controlled thermal processing zones that optimize crystallization. The system features a proprietary encapsulation technology that addresses perovskite stability concerns while maintaining flexibility. EMC has demonstrated that their roll-to-roll process can achieve material utilization rates above 95%, significantly reducing waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Their integrated quality control system uses in-line optical inspection and electrical testing to ensure consistent performance. The company has reported production costs below $0.20 per watt at scale, representing a significant advancement toward cost-competitive flexible solar manufacturing.
Strengths: Specialized focus on perovskite technology with high efficiency potential; significantly lower capital equipment costs compared to vacuum-based systems; rapid production speeds enabling high throughput. Weaknesses: Perovskite stability and durability challenges remain; relatively new company with less established manufacturing track record; technology still scaling toward full commercial production.
Key Patents and Innovations in Flexible Solar Manufacturing
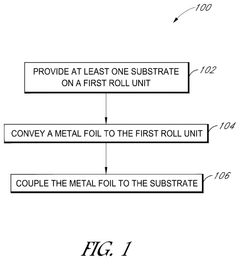
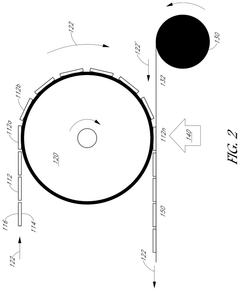
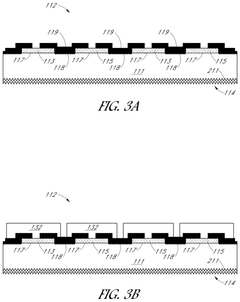
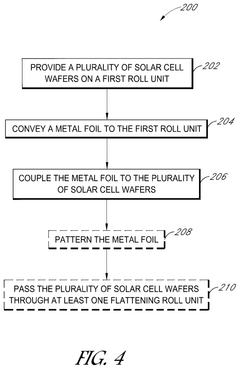
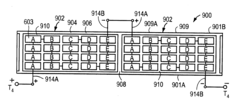
Roll-to-roll metallization of solar cells
PatentPendingUS20250056914A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a roll-to-roll foil-based metallization approach for fabricating solar cells, which involves providing a silicon substrate on a first roll unit, conveying a metal foil to contact the substrate, and coupling the metal foil to the substrate to form a metallized solar cell, thereby simplifying the manufacturing process and reducing costs.
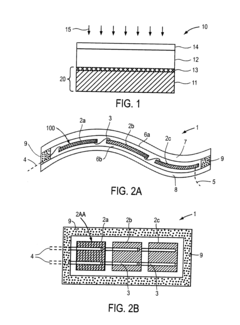
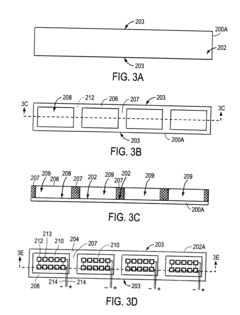
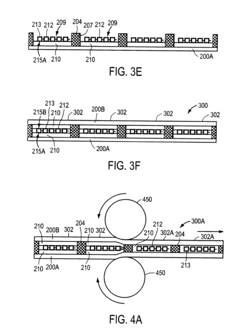
Roll-to-roll manufacturing of flexible thin film photovoltaic modules
PatentInactiveUS20110239450A1
Innovation
- A roll-to-roll manufacturing process is employed to create a continuous packaging structure with moisture barrier layers and a separation region, ensuring each module is encapsulated with a moisture-resistant protective shell, including a top and bottom protective sheet and a moisture sealant along the circumference, to prevent moisture ingress and enhance module reliability.
Materials Science Advancements for Flexible Photovoltaics
Recent advancements in materials science have revolutionized the field of flexible photovoltaics, creating unprecedented opportunities for cost reduction in roll-to-roll manufacturing processes. The evolution from rigid silicon-based solar cells to flexible alternatives has been driven by innovations in semiconductor materials, conductive polymers, and thin-film deposition techniques.
Flexible substrates such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), and polyimide films have emerged as viable alternatives to traditional glass substrates. These materials offer excellent mechanical flexibility while maintaining reasonable thermal stability required for photovoltaic applications. The development of ultra-thin barrier layers with enhanced moisture and oxygen resistance has significantly extended the operational lifetime of flexible solar devices.
Perovskite materials represent one of the most promising breakthroughs, with power conversion efficiencies exceeding 25% in laboratory settings. Their solution processability makes them particularly suitable for high-throughput roll-to-roll manufacturing. Concurrent advances in organic photovoltaic materials have yielded more stable compounds with improved charge carrier mobility and broader spectral absorption ranges.
Transparent conductive electrodes have undergone substantial innovation, moving beyond traditional indium tin oxide (ITO) to incorporate silver nanowires, carbon nanotubes, and graphene-based composites. These alternatives offer superior flexibility, maintaining conductivity under repeated bending cycles while potentially reducing material costs through decreased reliance on rare elements.
Interface engineering has become a critical focus area, with novel buffer layers and passivation techniques addressing the challenges of charge recombination at material boundaries. Self-assembling monolayers and gradient composition interfaces have demonstrated enhanced charge extraction efficiency while being compatible with solution-based deposition methods essential for roll-to-roll processing.
Encapsulation technologies have evolved to provide effective barriers against environmental degradation while maintaining flexibility. Multi-layer approaches combining organic and inorganic materials have achieved water vapor transmission rates below 10^-6 g/m²/day, approaching the requirements for long-term stability in commercial applications.
Additive manufacturing techniques, particularly aerosol jet printing and slot-die coating, have enabled precise deposition of functional materials with minimal waste. These processes operate at lower temperatures than traditional methods, expanding the range of compatible substrate materials and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing.
Flexible substrates such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), and polyimide films have emerged as viable alternatives to traditional glass substrates. These materials offer excellent mechanical flexibility while maintaining reasonable thermal stability required for photovoltaic applications. The development of ultra-thin barrier layers with enhanced moisture and oxygen resistance has significantly extended the operational lifetime of flexible solar devices.
Perovskite materials represent one of the most promising breakthroughs, with power conversion efficiencies exceeding 25% in laboratory settings. Their solution processability makes them particularly suitable for high-throughput roll-to-roll manufacturing. Concurrent advances in organic photovoltaic materials have yielded more stable compounds with improved charge carrier mobility and broader spectral absorption ranges.
Transparent conductive electrodes have undergone substantial innovation, moving beyond traditional indium tin oxide (ITO) to incorporate silver nanowires, carbon nanotubes, and graphene-based composites. These alternatives offer superior flexibility, maintaining conductivity under repeated bending cycles while potentially reducing material costs through decreased reliance on rare elements.
Interface engineering has become a critical focus area, with novel buffer layers and passivation techniques addressing the challenges of charge recombination at material boundaries. Self-assembling monolayers and gradient composition interfaces have demonstrated enhanced charge extraction efficiency while being compatible with solution-based deposition methods essential for roll-to-roll processing.
Encapsulation technologies have evolved to provide effective barriers against environmental degradation while maintaining flexibility. Multi-layer approaches combining organic and inorganic materials have achieved water vapor transmission rates below 10^-6 g/m²/day, approaching the requirements for long-term stability in commercial applications.
Additive manufacturing techniques, particularly aerosol jet printing and slot-die coating, have enabled precise deposition of functional materials with minimal waste. These processes operate at lower temperatures than traditional methods, expanding the range of compatible substrate materials and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing.
Sustainability Impact and Lifecycle Assessment
Flexible solar roll-to-roll manufacturing represents a significant advancement in sustainable energy production technology. The environmental impact of this manufacturing approach extends far beyond the immediate cost benefits, encompassing the entire lifecycle of solar products from raw material extraction to end-of-life management.
The sustainability advantages of roll-to-roll manufacturing begin with material efficiency. This process significantly reduces material waste compared to traditional batch processing methods, with studies indicating up to 30% reduction in raw material consumption. Additionally, the continuous nature of roll-to-roll processing decreases energy consumption during manufacturing by approximately 25%, further reducing the carbon footprint of production.
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies reveal that flexible solar panels produced via roll-to-roll manufacturing achieve carbon payback periods of 0.8-1.5 years, substantially shorter than the 2-3 years typical for conventional rigid panels. This accelerated environmental return on investment stems from both manufacturing efficiencies and the expanded application potential of flexible modules.
The reduced weight and material content of flexible solar products also translate to lower transportation emissions, with logistics-related carbon footprint reductions of approximately 40% compared to glass-based panels. Furthermore, the elimination of heavy mounting structures for installation provides additional embodied carbon savings estimated at 15-20% over system lifetime.
End-of-life considerations represent another sustainability advantage. The simplified material composition of roll-to-roll manufactured flexible solar products facilitates more effective recycling processes. Recent technological developments have demonstrated recovery rates exceeding 90% for semiconductor materials from flexible substrates, compared to 60-70% recovery rates for conventional panels.
Water usage in roll-to-roll manufacturing deserves particular attention, as continuous processing can reduce water consumption by up to 45% compared to batch methods. This aspect is increasingly critical as solar manufacturing expands in water-stressed regions globally.
The scalability of roll-to-roll manufacturing also contributes to sustainability through economies of scale. As production volumes increase, the environmental efficiency of the process improves, with studies indicating that doubling production capacity typically results in 8-12% reduction in per-unit environmental impact across multiple indicators.
These sustainability benefits collectively strengthen the case for accelerated adoption of flexible solar roll-to-roll manufacturing, positioning it as not merely a cost-reduction strategy but as a comprehensive approach to improving the environmental profile of photovoltaic technology throughout its lifecycle.
The sustainability advantages of roll-to-roll manufacturing begin with material efficiency. This process significantly reduces material waste compared to traditional batch processing methods, with studies indicating up to 30% reduction in raw material consumption. Additionally, the continuous nature of roll-to-roll processing decreases energy consumption during manufacturing by approximately 25%, further reducing the carbon footprint of production.
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies reveal that flexible solar panels produced via roll-to-roll manufacturing achieve carbon payback periods of 0.8-1.5 years, substantially shorter than the 2-3 years typical for conventional rigid panels. This accelerated environmental return on investment stems from both manufacturing efficiencies and the expanded application potential of flexible modules.
The reduced weight and material content of flexible solar products also translate to lower transportation emissions, with logistics-related carbon footprint reductions of approximately 40% compared to glass-based panels. Furthermore, the elimination of heavy mounting structures for installation provides additional embodied carbon savings estimated at 15-20% over system lifetime.
End-of-life considerations represent another sustainability advantage. The simplified material composition of roll-to-roll manufactured flexible solar products facilitates more effective recycling processes. Recent technological developments have demonstrated recovery rates exceeding 90% for semiconductor materials from flexible substrates, compared to 60-70% recovery rates for conventional panels.
Water usage in roll-to-roll manufacturing deserves particular attention, as continuous processing can reduce water consumption by up to 45% compared to batch methods. This aspect is increasingly critical as solar manufacturing expands in water-stressed regions globally.
The scalability of roll-to-roll manufacturing also contributes to sustainability through economies of scale. As production volumes increase, the environmental efficiency of the process improves, with studies indicating that doubling production capacity typically results in 8-12% reduction in per-unit environmental impact across multiple indicators.
These sustainability benefits collectively strengthen the case for accelerated adoption of flexible solar roll-to-roll manufacturing, positioning it as not merely a cost-reduction strategy but as a comprehensive approach to improving the environmental profile of photovoltaic technology throughout its lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!