How Electromagnetic Waves Promote Efficient Data Encryption?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EM Wave Encryption Background and Objectives
Electromagnetic wave encryption has emerged as a cutting-edge technology in the field of data security, leveraging the unique properties of electromagnetic waves to enhance encryption processes. This innovative approach combines principles from physics, information theory, and cryptography to create robust and efficient encryption methods.
The development of electromagnetic wave encryption can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of using physical layer characteristics for secure communication. As traditional encryption methods faced increasing challenges from advancing computational power, the need for alternative approaches became apparent. Electromagnetic wave encryption offered a promising solution by exploiting the inherent properties of wave propagation and quantum mechanics.
Over the past two decades, significant advancements have been made in this field, driven by the growing demand for secure data transmission in various sectors, including telecommunications, finance, and national security. The evolution of this technology has been marked by key milestones, such as the development of quantum key distribution systems and the integration of artificial intelligence in wave-based encryption algorithms.
The primary objective of electromagnetic wave encryption is to achieve unbreakable security while maintaining high data transmission rates. This technology aims to overcome the limitations of conventional cryptographic methods by introducing physical layer security measures that are inherently resistant to computational attacks. By manipulating the properties of electromagnetic waves, such as phase, amplitude, and polarization, researchers seek to create encryption schemes that are fundamentally secure at the physical level.
Another crucial goal is to develop encryption techniques that can adapt to the rapidly evolving landscape of communication technologies, including 5G and beyond. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, there is an increasing need for lightweight, energy-efficient encryption methods that can be implemented in resource-constrained devices. Electromagnetic wave encryption holds promise in addressing these challenges by offering scalable and flexible security solutions.
Furthermore, the technology aims to provide quantum-resistant encryption capabilities, anticipating the potential threat posed by quantum computers to current cryptographic systems. By leveraging the quantum properties of electromagnetic waves, researchers are working towards creating encryption methods that remain secure even in a post-quantum computing era.
As we look towards the future, the field of electromagnetic wave encryption is poised for significant growth and innovation. The ongoing research and development in this area are expected to yield breakthrough technologies that will reshape the landscape of data security and privacy in the coming years.
The development of electromagnetic wave encryption can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of using physical layer characteristics for secure communication. As traditional encryption methods faced increasing challenges from advancing computational power, the need for alternative approaches became apparent. Electromagnetic wave encryption offered a promising solution by exploiting the inherent properties of wave propagation and quantum mechanics.
Over the past two decades, significant advancements have been made in this field, driven by the growing demand for secure data transmission in various sectors, including telecommunications, finance, and national security. The evolution of this technology has been marked by key milestones, such as the development of quantum key distribution systems and the integration of artificial intelligence in wave-based encryption algorithms.
The primary objective of electromagnetic wave encryption is to achieve unbreakable security while maintaining high data transmission rates. This technology aims to overcome the limitations of conventional cryptographic methods by introducing physical layer security measures that are inherently resistant to computational attacks. By manipulating the properties of electromagnetic waves, such as phase, amplitude, and polarization, researchers seek to create encryption schemes that are fundamentally secure at the physical level.
Another crucial goal is to develop encryption techniques that can adapt to the rapidly evolving landscape of communication technologies, including 5G and beyond. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, there is an increasing need for lightweight, energy-efficient encryption methods that can be implemented in resource-constrained devices. Electromagnetic wave encryption holds promise in addressing these challenges by offering scalable and flexible security solutions.
Furthermore, the technology aims to provide quantum-resistant encryption capabilities, anticipating the potential threat posed by quantum computers to current cryptographic systems. By leveraging the quantum properties of electromagnetic waves, researchers are working towards creating encryption methods that remain secure even in a post-quantum computing era.
As we look towards the future, the field of electromagnetic wave encryption is poised for significant growth and innovation. The ongoing research and development in this area are expected to yield breakthrough technologies that will reshape the landscape of data security and privacy in the coming years.
Market Demand for EM Wave-Based Encryption
The market demand for electromagnetic (EM) wave-based encryption technologies has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing need for secure data transmission in various sectors. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, traditional encryption methods are facing challenges, prompting organizations to seek more advanced and robust solutions.
In the financial sector, banks and financial institutions are showing significant interest in EM wave-based encryption to protect sensitive customer data and financial transactions. The ability to encrypt data at the physical layer offers an additional security measure against potential breaches, making it particularly attractive for high-value transfers and communications.
The healthcare industry is another major driver of demand for EM wave-based encryption. With the rise of telemedicine and electronic health records, there is a critical need to ensure patient data confidentiality. EM wave encryption provides a promising solution to safeguard medical information during transmission, complying with stringent regulatory requirements such as HIPAA.
Government and military sectors are also key players in driving market demand. These organizations require ultra-secure communication channels for classified information exchange. EM wave-based encryption offers a potential advantage over traditional methods by making it extremely difficult for adversaries to intercept or decode transmitted data.
The telecommunications industry is exploring EM wave encryption to enhance the security of 5G and future 6G networks. As these networks become more pervasive and critical to infrastructure, the need for robust encryption at the physical layer becomes paramount to protect against emerging threats and ensure network integrity.
In the realm of Internet of Things (IoT), the proliferation of connected devices has created a vast attack surface for cybercriminals. EM wave-based encryption could provide a scalable solution for securing the massive amounts of data generated and transmitted by IoT devices, addressing concerns about privacy and security in smart homes, industrial IoT, and smart cities.
The automotive industry, particularly with the development of autonomous vehicles, is another sector showing interest in EM wave encryption. Secure communication between vehicles and infrastructure is crucial for the safe operation of self-driving cars, making this technology a potential enabler for the future of transportation.
Market analysts project that the global market for quantum-resistant cryptography, which includes EM wave-based solutions, will experience significant growth. This trend is fueled by the looming threat of quantum computers potentially breaking current encryption standards, driving organizations to invest in future-proof security measures.
In the financial sector, banks and financial institutions are showing significant interest in EM wave-based encryption to protect sensitive customer data and financial transactions. The ability to encrypt data at the physical layer offers an additional security measure against potential breaches, making it particularly attractive for high-value transfers and communications.
The healthcare industry is another major driver of demand for EM wave-based encryption. With the rise of telemedicine and electronic health records, there is a critical need to ensure patient data confidentiality. EM wave encryption provides a promising solution to safeguard medical information during transmission, complying with stringent regulatory requirements such as HIPAA.
Government and military sectors are also key players in driving market demand. These organizations require ultra-secure communication channels for classified information exchange. EM wave-based encryption offers a potential advantage over traditional methods by making it extremely difficult for adversaries to intercept or decode transmitted data.
The telecommunications industry is exploring EM wave encryption to enhance the security of 5G and future 6G networks. As these networks become more pervasive and critical to infrastructure, the need for robust encryption at the physical layer becomes paramount to protect against emerging threats and ensure network integrity.
In the realm of Internet of Things (IoT), the proliferation of connected devices has created a vast attack surface for cybercriminals. EM wave-based encryption could provide a scalable solution for securing the massive amounts of data generated and transmitted by IoT devices, addressing concerns about privacy and security in smart homes, industrial IoT, and smart cities.
The automotive industry, particularly with the development of autonomous vehicles, is another sector showing interest in EM wave encryption. Secure communication between vehicles and infrastructure is crucial for the safe operation of self-driving cars, making this technology a potential enabler for the future of transportation.
Market analysts project that the global market for quantum-resistant cryptography, which includes EM wave-based solutions, will experience significant growth. This trend is fueled by the looming threat of quantum computers potentially breaking current encryption standards, driving organizations to invest in future-proof security measures.
Current State and Challenges in EM Wave Encryption
The current state of electromagnetic (EM) wave encryption technology is characterized by significant advancements, yet it faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. Recent developments have led to the integration of quantum key distribution (QKD) with EM wave encryption, enhancing security levels beyond traditional methods. This hybrid approach leverages the inherent randomness of quantum mechanics to generate encryption keys, which are then transmitted via EM waves.
One of the primary challenges in EM wave encryption is the vulnerability to interception during transmission. While encryption algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated, the physical layer of communication remains susceptible to eavesdropping. Researchers are actively working on developing novel modulation techniques and spread spectrum technologies to mitigate this risk, but achieving perfect security in open-air transmission remains elusive.
Another significant hurdle is the trade-off between encryption strength and data transmission rates. As encryption complexity increases to bolster security, it often results in reduced bandwidth and higher latency. This poses a particular challenge in applications requiring real-time data transmission, such as in financial transactions or military communications.
The scalability of EM wave encryption systems presents another obstacle. Current implementations often struggle to maintain efficiency when scaled up to accommodate large networks or high-volume data streams. This limitation is particularly evident in Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where a vast number of devices require secure communication channels.
Energy efficiency is an emerging concern in EM wave encryption. The computational power required for complex encryption and decryption processes can be substantial, leading to increased power consumption. This is especially problematic for battery-powered devices and in scenarios where energy conservation is crucial.
Standardization and interoperability issues also plague the field. The lack of universally accepted protocols for EM wave encryption hampers seamless integration across different systems and platforms. This fragmentation not only complicates implementation but also potentially creates security vulnerabilities at interface points between disparate systems.
Lastly, the ongoing arms race between encryption methods and decryption techniques poses a constant challenge. As quantum computing advances, it threatens to render many current encryption methods obsolete. This necessitates continuous innovation in EM wave encryption to stay ahead of potential security breaches, driving research into post-quantum cryptography and other novel approaches.
One of the primary challenges in EM wave encryption is the vulnerability to interception during transmission. While encryption algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated, the physical layer of communication remains susceptible to eavesdropping. Researchers are actively working on developing novel modulation techniques and spread spectrum technologies to mitigate this risk, but achieving perfect security in open-air transmission remains elusive.
Another significant hurdle is the trade-off between encryption strength and data transmission rates. As encryption complexity increases to bolster security, it often results in reduced bandwidth and higher latency. This poses a particular challenge in applications requiring real-time data transmission, such as in financial transactions or military communications.
The scalability of EM wave encryption systems presents another obstacle. Current implementations often struggle to maintain efficiency when scaled up to accommodate large networks or high-volume data streams. This limitation is particularly evident in Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where a vast number of devices require secure communication channels.
Energy efficiency is an emerging concern in EM wave encryption. The computational power required for complex encryption and decryption processes can be substantial, leading to increased power consumption. This is especially problematic for battery-powered devices and in scenarios where energy conservation is crucial.
Standardization and interoperability issues also plague the field. The lack of universally accepted protocols for EM wave encryption hampers seamless integration across different systems and platforms. This fragmentation not only complicates implementation but also potentially creates security vulnerabilities at interface points between disparate systems.
Lastly, the ongoing arms race between encryption methods and decryption techniques poses a constant challenge. As quantum computing advances, it threatens to render many current encryption methods obsolete. This necessitates continuous innovation in EM wave encryption to stay ahead of potential security breaches, driving research into post-quantum cryptography and other novel approaches.
Existing EM Wave Encryption Solutions
01 Quantum key distribution for secure communication
Quantum key distribution techniques are used to enhance data encryption efficiency in electromagnetic wave communications. This method leverages quantum mechanics principles to generate and distribute cryptographic keys, providing a high level of security against eavesdropping and interception attempts.- Quantum key distribution for secure data encryption: Quantum key distribution techniques are used to enhance data encryption efficiency in electromagnetic wave communications. This method leverages quantum mechanics principles to generate and distribute secure encryption keys, providing a high level of security against eavesdropping and interception attempts.
- Electromagnetic wave modulation for improved encryption: Advanced modulation techniques are applied to electromagnetic waves to improve data encryption efficiency. These methods involve manipulating wave properties such as amplitude, frequency, or phase to encode information, making it more difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept and decode the transmitted data.
- Machine learning algorithms for optimizing encryption protocols: Machine learning algorithms are employed to optimize encryption protocols for electromagnetic wave communications. These algorithms analyze patterns in data transmission and adapt encryption strategies in real-time, enhancing both the security and efficiency of data encryption processes.
- Hardware-based encryption acceleration: Specialized hardware components are developed to accelerate encryption and decryption processes in electromagnetic wave communications. These hardware solutions, such as dedicated encryption chips or FPGAs, significantly improve the speed and efficiency of data encryption without compromising security.
- Adaptive encryption techniques for varying electromagnetic environments: Adaptive encryption methods are implemented to optimize data security and efficiency across different electromagnetic environments. These techniques dynamically adjust encryption parameters based on factors such as signal strength, interference levels, and channel characteristics, ensuring robust protection and efficient transmission in diverse conditions.
02 Advanced encryption algorithms for electromagnetic wave transmission
Innovative encryption algorithms are developed specifically for electromagnetic wave data transmission. These algorithms focus on improving encryption speed and efficiency while maintaining a high level of security, making them suitable for real-time communication applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hardware-based encryption solutions
Hardware-based encryption solutions are implemented to enhance data encryption efficiency in electromagnetic wave communications. These solutions include specialized chips or modules that perform encryption and decryption operations at high speeds, reducing the computational load on the main processor.Expand Specific Solutions04 Adaptive encryption techniques for varying electromagnetic environments
Adaptive encryption techniques are developed to optimize data encryption efficiency across different electromagnetic environments. These methods dynamically adjust encryption parameters based on signal strength, interference levels, and other environmental factors to maintain optimal security and performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of AI and machine learning in encryption processes
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are integrated into encryption processes for electromagnetic wave communications. These technologies help in predicting potential security threats, optimizing encryption parameters, and improving overall encryption efficiency in real-time scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in EM Wave Encryption Industry
The field of electromagnetic wave-based data encryption is in a dynamic growth phase, with increasing market size driven by rising cybersecurity concerns. The technology's maturity varies across applications, but it's rapidly evolving. Key players like Samsung Electronics, NEC Corp., and Fujitsu Ltd. are investing heavily in research and development, pushing the boundaries of quantum-resistant encryption methods. Universities such as Zhejiang University and Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology are contributing significant advancements in theoretical frameworks. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established tech giants and specialized security firms like Xiring SA vying for market share. As the technology progresses, we're likely to see increased collaboration between industry and academia to address emerging challenges in secure data transmission.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed a quantum-based encryption system that utilizes electromagnetic waves for secure data transmission. Their approach involves generating quantum keys using single photons, which are then transmitted via electromagnetic waves. This system employs quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols to ensure the security of the encryption process[1]. Samsung's technology integrates with existing fiber optic networks, allowing for long-distance secure communication. The company has also implemented post-quantum cryptography algorithms to future-proof their encryption methods against potential quantum computer attacks[2].
Strengths: Advanced quantum encryption technology, integration with existing infrastructure, future-proofed against quantum attacks. Weaknesses: High implementation costs, limited scalability for mass-market adoption.
Fujitsu Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fujitsu has pioneered a novel approach to electromagnetic wave-based encryption using chaos theory. Their system generates chaotic electromagnetic signals that are inherently unpredictable, making them ideal for encryption purposes. The company's technology employs multiple antennas to create a complex, multi-dimensional chaotic signal that serves as the encryption key[3]. This method allows for high-speed, real-time encryption of data streams. Fujitsu has also developed specialized hardware to efficiently process these chaotic signals, enabling practical implementation in various communication systems[4].
Strengths: High-speed real-time encryption, unique chaos-based approach, specialized hardware support. Weaknesses: Complexity in implementation, potential vulnerability to advanced signal analysis techniques.
Core Innovations in EM Wave Encryption
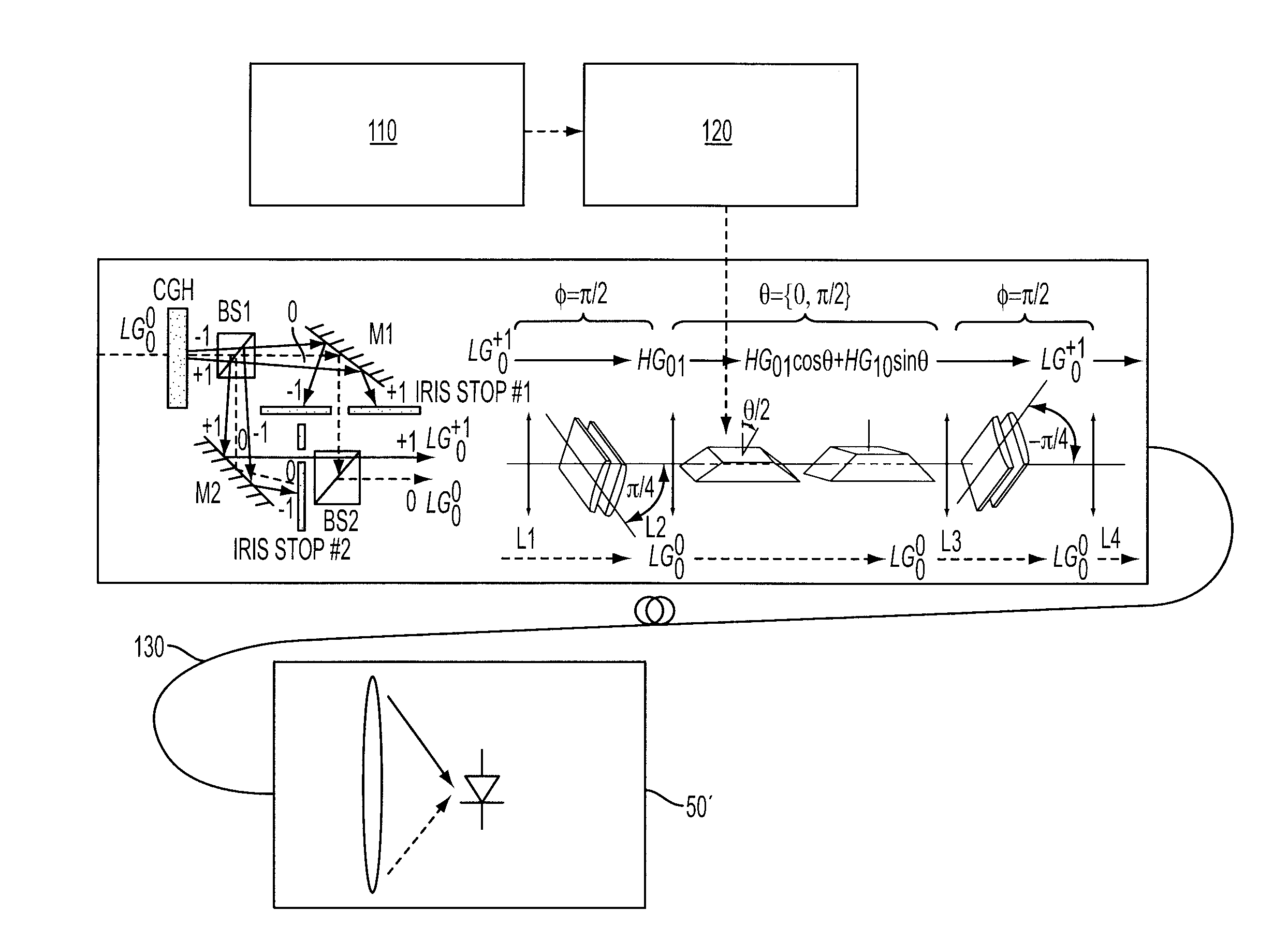
Method and apparatus relating to secure communication
PatentInactiveUS8184972B2
Innovation
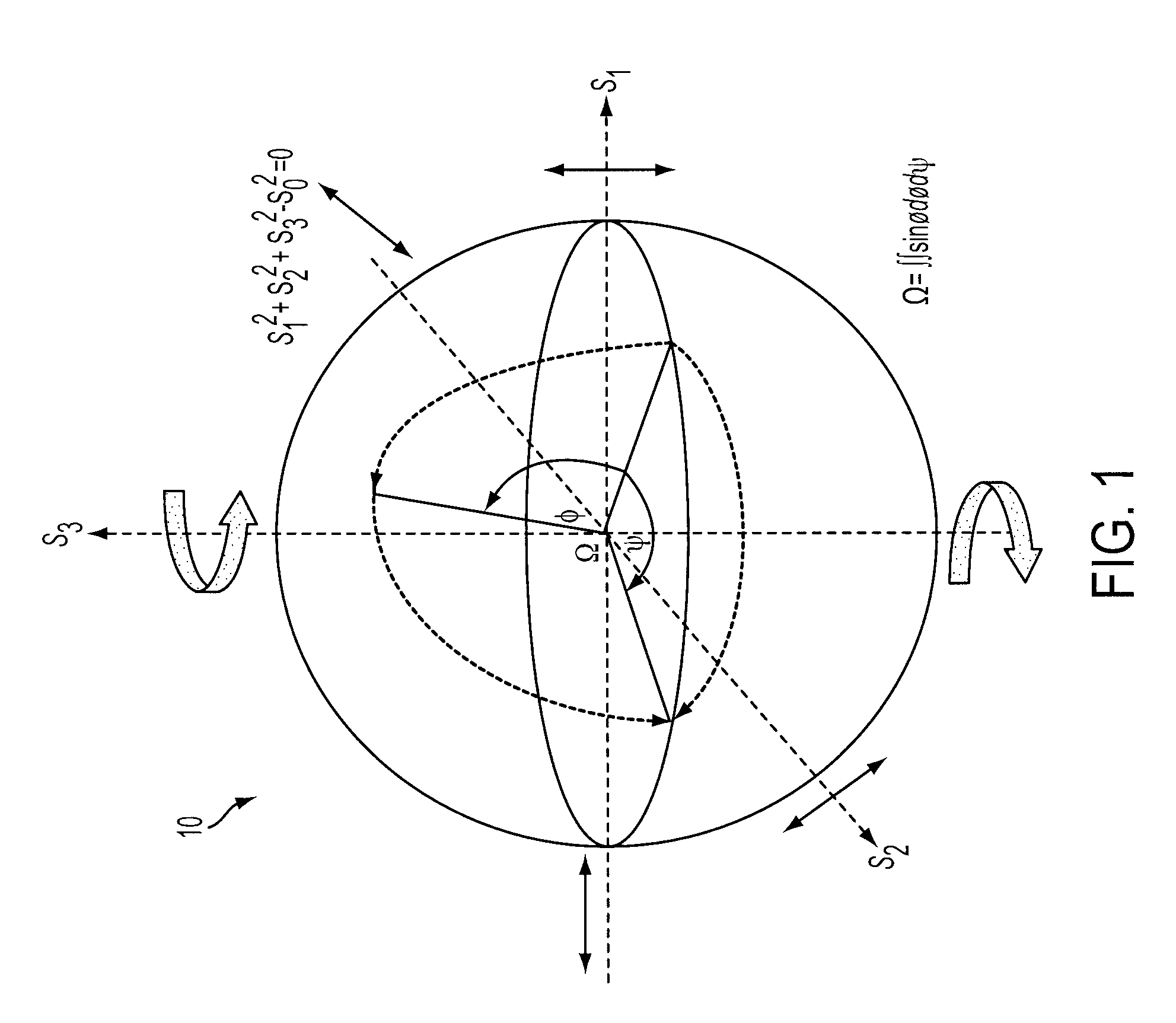
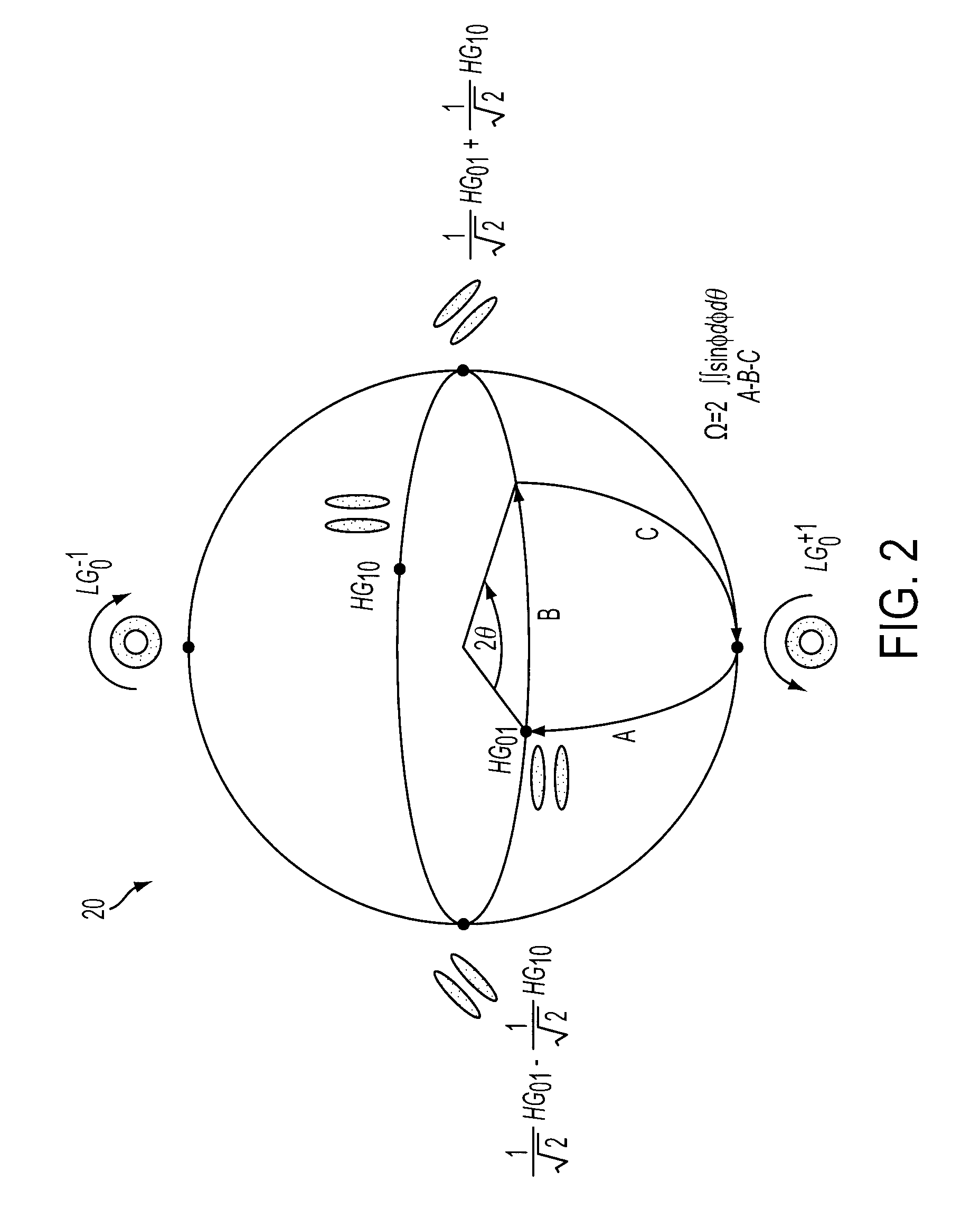
- The method involves encrypting data onto an electromagnetic beam by accumulating geometric phase through modal state transformations, using a signal component and a reference component, where the signal component undergoes transformations on a Poincaré Sphere to modulate the geometric phase with data, providing a secure key for encryption and decryption.
Methods and systems for encrypting data using object-based screens
PatentActiveUS20210248257A1
Innovation
- The method employs object-based wave screens, stumbling blocks, and XOR blocks to encrypt data, using block map layouts and remapping instructions to securely position and transform data segments, allowing for secure storage and transport while maintaining accessibility through decryption with corresponding screens and blocks.
Regulatory Framework for EM Wave Encryption
The regulatory framework for electromagnetic (EM) wave encryption is a complex and evolving landscape that aims to balance national security concerns with the need for technological innovation and privacy protection. Governments worldwide have recognized the potential of EM wave-based encryption methods to enhance data security, leading to the development of specific regulations and guidelines.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of EM waves for encryption purposes. The FCC has established frequency allocation guidelines and power limitations for devices utilizing EM waves in encryption processes. These regulations ensure that such devices do not interfere with other critical communication systems while maintaining the integrity of encrypted data.
The European Union has taken a comprehensive approach through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which indirectly impacts EM wave encryption technologies. While not specifically addressing EM wave encryption, the GDPR's stringent data protection requirements have led to increased adoption of advanced encryption methods, including those leveraging EM waves.
International bodies such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) have also contributed to the regulatory framework by developing standards for EM wave-based communication and encryption. These standards promote interoperability and ensure that encryption technologies using EM waves can be deployed globally without compromising security or causing interference.
Many countries have implemented export control regulations on encryption technologies, including those utilizing EM waves. These controls aim to prevent advanced encryption methods from falling into the hands of malicious actors or hostile nations. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for companies developing and deploying EM wave encryption solutions.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the potential health and environmental impacts of EM wave-based technologies. Agencies such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and national health authorities have established guidelines for electromagnetic field exposure, which indirectly affect the development and deployment of EM wave encryption systems.
As the field of EM wave encryption continues to advance, regulatory bodies are working to keep pace with technological developments. This includes ongoing efforts to update existing regulations and create new frameworks that address emerging challenges and opportunities in the field of quantum encryption and other cutting-edge EM wave-based security methods.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of EM waves for encryption purposes. The FCC has established frequency allocation guidelines and power limitations for devices utilizing EM waves in encryption processes. These regulations ensure that such devices do not interfere with other critical communication systems while maintaining the integrity of encrypted data.
The European Union has taken a comprehensive approach through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which indirectly impacts EM wave encryption technologies. While not specifically addressing EM wave encryption, the GDPR's stringent data protection requirements have led to increased adoption of advanced encryption methods, including those leveraging EM waves.
International bodies such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) have also contributed to the regulatory framework by developing standards for EM wave-based communication and encryption. These standards promote interoperability and ensure that encryption technologies using EM waves can be deployed globally without compromising security or causing interference.
Many countries have implemented export control regulations on encryption technologies, including those utilizing EM waves. These controls aim to prevent advanced encryption methods from falling into the hands of malicious actors or hostile nations. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for companies developing and deploying EM wave encryption solutions.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the potential health and environmental impacts of EM wave-based technologies. Agencies such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and national health authorities have established guidelines for electromagnetic field exposure, which indirectly affect the development and deployment of EM wave encryption systems.
As the field of EM wave encryption continues to advance, regulatory bodies are working to keep pace with technological developments. This includes ongoing efforts to update existing regulations and create new frameworks that address emerging challenges and opportunities in the field of quantum encryption and other cutting-edge EM wave-based security methods.
Quantum-Resistant EM Wave Encryption Methods
Quantum-resistant electromagnetic wave encryption methods represent a cutting-edge approach to safeguarding data transmission against the looming threat of quantum computing. These methods leverage the unique properties of electromagnetic waves to create encryption schemes that remain secure even in the face of advanced quantum attacks.
One prominent quantum-resistant EM wave encryption method is the use of high-frequency millimeter waves. These waves, typically in the 30-300 GHz range, offer inherent security advantages due to their short wavelengths and high atmospheric attenuation. By encoding data onto these waves using advanced modulation techniques, such as quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) or phase-shift keying (PSK), encryption becomes intrinsically tied to the physical properties of the wave itself.
Another promising approach involves the application of chaos theory to EM wave encryption. Chaotic systems, characterized by their sensitivity to initial conditions, can be used to generate pseudo-random sequences for encryption. When applied to EM waves, this results in a highly complex and unpredictable signal that is extremely difficult to intercept or decode without knowledge of the initial conditions.
Metamaterial-based encryption is an emerging field that shows great potential for quantum resistance. By designing artificial materials with specific electromagnetic properties, it becomes possible to manipulate EM waves in ways that are not possible with natural materials. This allows for the creation of unique encryption signatures that are tied to the physical structure of the metamaterial, making them highly resistant to computational attacks.
The use of spread spectrum techniques in EM wave encryption also offers quantum resistance. By spreading the signal across a wide frequency band, often much wider than the original signal bandwidth, the encrypted data becomes more resilient to interception and jamming. Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) and direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) are two common implementations that can be adapted for quantum-resistant encryption.
Lastly, the integration of quantum key distribution (QKD) with EM wave encryption provides a hybrid approach that combines the best of both worlds. While QKD secures the key exchange process using quantum mechanical principles, the actual data transmission can still utilize classical EM wave encryption methods, creating a robust and quantum-resistant communication system.
These quantum-resistant EM wave encryption methods represent the forefront of secure communication technology, offering promising solutions to the challenges posed by the advent of quantum computing. As research in this field continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and secure encryption techniques to emerge, ensuring the confidentiality of data transmission in the quantum era.
One prominent quantum-resistant EM wave encryption method is the use of high-frequency millimeter waves. These waves, typically in the 30-300 GHz range, offer inherent security advantages due to their short wavelengths and high atmospheric attenuation. By encoding data onto these waves using advanced modulation techniques, such as quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) or phase-shift keying (PSK), encryption becomes intrinsically tied to the physical properties of the wave itself.
Another promising approach involves the application of chaos theory to EM wave encryption. Chaotic systems, characterized by their sensitivity to initial conditions, can be used to generate pseudo-random sequences for encryption. When applied to EM waves, this results in a highly complex and unpredictable signal that is extremely difficult to intercept or decode without knowledge of the initial conditions.
Metamaterial-based encryption is an emerging field that shows great potential for quantum resistance. By designing artificial materials with specific electromagnetic properties, it becomes possible to manipulate EM waves in ways that are not possible with natural materials. This allows for the creation of unique encryption signatures that are tied to the physical structure of the metamaterial, making them highly resistant to computational attacks.
The use of spread spectrum techniques in EM wave encryption also offers quantum resistance. By spreading the signal across a wide frequency band, often much wider than the original signal bandwidth, the encrypted data becomes more resilient to interception and jamming. Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) and direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) are two common implementations that can be adapted for quantum-resistant encryption.
Lastly, the integration of quantum key distribution (QKD) with EM wave encryption provides a hybrid approach that combines the best of both worlds. While QKD secures the key exchange process using quantum mechanical principles, the actual data transmission can still utilize classical EM wave encryption methods, creating a robust and quantum-resistant communication system.
These quantum-resistant EM wave encryption methods represent the forefront of secure communication technology, offering promising solutions to the challenges posed by the advent of quantum computing. As research in this field continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and secure encryption techniques to emerge, ensuring the confidentiality of data transmission in the quantum era.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!