How Hastelloy Enhances Protection against Acidic Corrosion?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hastelloy Corrosion Resistance Evolution
The evolution of Hastelloy's corrosion resistance is a testament to the continuous innovation in materials science and metallurgy. Initially developed in the 1920s by Haynes International, Hastelloy has undergone significant improvements to enhance its protection against acidic corrosion.
In its early stages, Hastelloy was primarily composed of nickel, molybdenum, and chromium. This composition provided a good foundation for corrosion resistance, particularly in reducing environments. However, as industrial applications became more demanding, the need for superior performance in oxidizing acids became apparent.
The 1960s marked a significant milestone in Hastelloy's evolution with the introduction of Hastelloy C-276. This alloy incorporated higher levels of molybdenum and chromium, along with the addition of tungsten. These modifications dramatically improved its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-containing environments, as well as its performance in both oxidizing and reducing acids.
Further advancements came in the 1980s with the development of Hastelloy C-22. This alloy featured an optimized balance of chromium, molybdenum, and tungsten, resulting in exceptional resistance to localized corrosion and stress corrosion cracking. C-22 demonstrated superior performance in a wide range of aggressive media, including hot concentrated nitric acid and chloride-containing oxidizing environments.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the introduction of Hastelloy C-2000 and C-22HS. C-2000 was specifically designed to combat corrosion in sulfuric acid applications, while C-22HS offered improved strength and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. These alloys represented a shift towards more specialized Hastelloy grades tailored for specific industrial challenges.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing Hastelloy's performance in extreme conditions. The introduction of Hastelloy G-35 in 2009 marked a significant advancement in phosphoric acid applications, offering superior resistance to both general and localized corrosion in this medium.
Ongoing research continues to push the boundaries of Hastelloy's capabilities. Current efforts are directed towards improving its resistance to highly oxidizing environments, enhancing its performance at higher temperatures, and developing new grades for emerging industries such as renewable energy and advanced manufacturing processes.
The evolution of Hastelloy's corrosion resistance reflects a continuous cycle of innovation driven by industrial needs and technological advancements. Each new generation of Hastelloy has built upon the strengths of its predecessors while addressing their limitations, resulting in a family of alloys that offer unparalleled protection against acidic corrosion across a wide spectrum of applications.
In its early stages, Hastelloy was primarily composed of nickel, molybdenum, and chromium. This composition provided a good foundation for corrosion resistance, particularly in reducing environments. However, as industrial applications became more demanding, the need for superior performance in oxidizing acids became apparent.
The 1960s marked a significant milestone in Hastelloy's evolution with the introduction of Hastelloy C-276. This alloy incorporated higher levels of molybdenum and chromium, along with the addition of tungsten. These modifications dramatically improved its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-containing environments, as well as its performance in both oxidizing and reducing acids.
Further advancements came in the 1980s with the development of Hastelloy C-22. This alloy featured an optimized balance of chromium, molybdenum, and tungsten, resulting in exceptional resistance to localized corrosion and stress corrosion cracking. C-22 demonstrated superior performance in a wide range of aggressive media, including hot concentrated nitric acid and chloride-containing oxidizing environments.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the introduction of Hastelloy C-2000 and C-22HS. C-2000 was specifically designed to combat corrosion in sulfuric acid applications, while C-22HS offered improved strength and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. These alloys represented a shift towards more specialized Hastelloy grades tailored for specific industrial challenges.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing Hastelloy's performance in extreme conditions. The introduction of Hastelloy G-35 in 2009 marked a significant advancement in phosphoric acid applications, offering superior resistance to both general and localized corrosion in this medium.
Ongoing research continues to push the boundaries of Hastelloy's capabilities. Current efforts are directed towards improving its resistance to highly oxidizing environments, enhancing its performance at higher temperatures, and developing new grades for emerging industries such as renewable energy and advanced manufacturing processes.
The evolution of Hastelloy's corrosion resistance reflects a continuous cycle of innovation driven by industrial needs and technological advancements. Each new generation of Hastelloy has built upon the strengths of its predecessors while addressing their limitations, resulting in a family of alloys that offer unparalleled protection against acidic corrosion across a wide spectrum of applications.
Acidic Corrosion Protection Market Analysis
The acidic corrosion protection market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing industrial activities and the need for durable materials in harsh environments. This market segment is primarily fueled by the demand from industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, and wastewater treatment, where exposure to acidic substances is common and potentially damaging to equipment and infrastructure.
The global market for acidic corrosion protection solutions is projected to expand at a steady rate, with a particular focus on advanced materials like Hastelloy. These nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys offer superior resistance to a wide range of corrosive media, including both reducing and oxidizing acids. The adoption of Hastelloy and similar high-performance alloys is expected to increase as industries seek more reliable and long-lasting solutions to combat acidic corrosion.
In terms of regional distribution, North America and Europe currently hold significant market shares due to their well-established industrial sectors and stringent environmental regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth area, driven by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. These developing economies are investing heavily in infrastructure and industrial capacity, creating a growing demand for advanced corrosion protection solutions.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized material suppliers. Key players in this space are continuously investing in research and development to enhance the performance of their products and expand their application range. This innovation-driven approach is crucial in addressing the evolving needs of end-users who face increasingly complex corrosion challenges.
One notable trend in the acidic corrosion protection market is the shift towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable solutions. This includes the development of corrosion-resistant materials that are recyclable or have a lower environmental impact during production. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on solutions that can extend the lifespan of industrial equipment, thereby reducing waste and resource consumption.
The oil and gas industry remains a major consumer of acidic corrosion protection solutions, particularly in offshore and deep-sea applications where exposure to highly corrosive environments is common. The chemical processing industry is another significant market segment, with a constant need for materials that can withstand aggressive chemical reactions and maintain structural integrity over extended periods.
The global market for acidic corrosion protection solutions is projected to expand at a steady rate, with a particular focus on advanced materials like Hastelloy. These nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys offer superior resistance to a wide range of corrosive media, including both reducing and oxidizing acids. The adoption of Hastelloy and similar high-performance alloys is expected to increase as industries seek more reliable and long-lasting solutions to combat acidic corrosion.
In terms of regional distribution, North America and Europe currently hold significant market shares due to their well-established industrial sectors and stringent environmental regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth area, driven by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. These developing economies are investing heavily in infrastructure and industrial capacity, creating a growing demand for advanced corrosion protection solutions.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized material suppliers. Key players in this space are continuously investing in research and development to enhance the performance of their products and expand their application range. This innovation-driven approach is crucial in addressing the evolving needs of end-users who face increasingly complex corrosion challenges.
One notable trend in the acidic corrosion protection market is the shift towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable solutions. This includes the development of corrosion-resistant materials that are recyclable or have a lower environmental impact during production. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on solutions that can extend the lifespan of industrial equipment, thereby reducing waste and resource consumption.
The oil and gas industry remains a major consumer of acidic corrosion protection solutions, particularly in offshore and deep-sea applications where exposure to highly corrosive environments is common. The chemical processing industry is another significant market segment, with a constant need for materials that can withstand aggressive chemical reactions and maintain structural integrity over extended periods.
Hastelloy Technology Current Status and Challenges
Hastelloy technology has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in its application for protection against acidic corrosion. The current status of Hastelloy in this field is characterized by its widespread use in industries such as chemical processing, petrochemical, and nuclear power generation, where resistance to highly corrosive environments is crucial.
One of the primary challenges facing Hastelloy technology is the continuous need for improved performance in increasingly aggressive acidic environments. As industrial processes become more demanding, there is a constant push for alloys that can withstand higher temperatures and more corrosive conditions while maintaining structural integrity.
The development of new Hastelloy grades is an ongoing process, with researchers focusing on optimizing the alloy composition to enhance specific properties. For instance, recent advancements have led to the creation of Hastelloy variants with improved resistance to sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, addressing the needs of specific industrial applications.
Another significant challenge lies in balancing the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy with other desirable properties such as mechanical strength, weldability, and formability. Achieving this balance is critical for expanding the range of applications where Hastelloy can be effectively utilized.
The global distribution of Hastelloy technology is concentrated in industrialized nations, with major research and production centers located in the United States, Europe, and Japan. However, there is a growing interest in developing countries as their industrial sectors expand and require more advanced materials for corrosion protection.
One of the current technical hurdles is the optimization of Hastelloy's performance in mixed acid environments, where the synergistic effects of different acids can accelerate corrosion rates. Researchers are exploring novel alloying elements and heat treatment processes to address this challenge.
The cost of Hastelloy remains a limiting factor for its wider adoption, particularly in industries where large quantities of material are required. Efforts are underway to develop more cost-effective manufacturing processes and to identify alternative alloying elements that can provide similar performance at a lower cost.
In conclusion, while Hastelloy technology has proven highly effective in protecting against acidic corrosion, ongoing research and development are essential to overcome current challenges and push the boundaries of its capabilities. The future of Hastelloy lies in the development of more specialized grades, improved manufacturing techniques, and broader applications across various industries requiring superior corrosion resistance.
One of the primary challenges facing Hastelloy technology is the continuous need for improved performance in increasingly aggressive acidic environments. As industrial processes become more demanding, there is a constant push for alloys that can withstand higher temperatures and more corrosive conditions while maintaining structural integrity.
The development of new Hastelloy grades is an ongoing process, with researchers focusing on optimizing the alloy composition to enhance specific properties. For instance, recent advancements have led to the creation of Hastelloy variants with improved resistance to sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, addressing the needs of specific industrial applications.
Another significant challenge lies in balancing the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy with other desirable properties such as mechanical strength, weldability, and formability. Achieving this balance is critical for expanding the range of applications where Hastelloy can be effectively utilized.
The global distribution of Hastelloy technology is concentrated in industrialized nations, with major research and production centers located in the United States, Europe, and Japan. However, there is a growing interest in developing countries as their industrial sectors expand and require more advanced materials for corrosion protection.
One of the current technical hurdles is the optimization of Hastelloy's performance in mixed acid environments, where the synergistic effects of different acids can accelerate corrosion rates. Researchers are exploring novel alloying elements and heat treatment processes to address this challenge.
The cost of Hastelloy remains a limiting factor for its wider adoption, particularly in industries where large quantities of material are required. Efforts are underway to develop more cost-effective manufacturing processes and to identify alternative alloying elements that can provide similar performance at a lower cost.
In conclusion, while Hastelloy technology has proven highly effective in protecting against acidic corrosion, ongoing research and development are essential to overcome current challenges and push the boundaries of its capabilities. The future of Hastelloy lies in the development of more specialized grades, improved manufacturing techniques, and broader applications across various industries requiring superior corrosion resistance.
Hastelloy Composition and Manufacturing Techniques
01 Corrosion-resistant coatings for Hastelloy
Various coating techniques are employed to enhance the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy alloys. These coatings provide an additional protective layer against harsh environments, extending the lifespan of Hastelloy components. Methods may include thermal spraying, electroplating, or application of specialized protective films.- Corrosion-resistant coatings for Hastelloy: Various coating techniques are employed to enhance the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy alloys. These coatings can include ceramic-based materials, nanocomposites, or specialized metal alloys that form a protective layer on the Hastelloy surface. The coatings are designed to withstand harsh chemical environments and high temperatures, extending the lifespan of Hastelloy components in industrial applications.
- Surface treatment methods for Hastelloy protection: Surface treatment processes are developed to improve the protective properties of Hastelloy. These methods may include chemical passivation, electropolishing, or thermal treatments that alter the surface composition and structure. Such treatments can enhance the formation of protective oxide layers, increase hardness, and improve overall corrosion resistance of Hastelloy components.
- Hastelloy alloy composition modifications: Research focuses on modifying the composition of Hastelloy alloys to enhance their protective properties. This involves adjusting the percentages of key elements or introducing new elements to the alloy. These modifications aim to improve corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and high-temperature performance while maintaining the desirable characteristics of Hastelloy.
- Protective systems for Hastelloy in extreme environments: Specialized protective systems are developed for Hastelloy components used in extreme environments. These systems may include multi-layer coatings, sacrificial anodes, or advanced cathodic protection methods. The focus is on providing comprehensive protection against various forms of corrosion, erosion, and high-temperature degradation in aggressive industrial settings.
- Monitoring and maintenance techniques for Hastelloy protection: Advanced monitoring and maintenance techniques are implemented to ensure the ongoing protection of Hastelloy components. These may include non-destructive testing methods, real-time corrosion monitoring systems, and predictive maintenance algorithms. Such techniques help in early detection of potential issues and optimization of protection strategies for Hastelloy in various applications.
02 Surface treatment methods for Hastelloy protection
Surface treatment processes are developed to improve the protective properties of Hastelloy surfaces. These treatments may involve chemical passivation, mechanical polishing, or heat treatments to create a more resistant outer layer. Such methods can enhance the material's resistance to corrosion, wear, and other forms of degradation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective alloy compositions for Hastelloy
Specialized alloy compositions are formulated to provide enhanced protection for Hastelloy components. These may include modifications to the base Hastelloy composition or the development of new alloy systems designed to work in conjunction with Hastelloy. The aim is to improve overall resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and high-temperature degradation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Protective equipment and systems for Hastelloy components
Engineered protective equipment and systems are designed specifically for Hastelloy components used in challenging environments. These may include specialized containment vessels, protective housings, or monitoring systems that help prevent or detect potential damage to Hastelloy parts, ensuring their longevity and performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Maintenance and cleaning methods for Hastelloy protection
Specific maintenance and cleaning procedures are developed to preserve the protective properties of Hastelloy surfaces. These methods may involve specialized cleaning agents, controlled cleaning processes, or periodic treatments to remove contaminants and maintain the integrity of the Hastelloy surface, thereby extending its protective capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers in Corrosion-Resistant Alloy Industry
The market for Hastelloy in acidic corrosion protection is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in industries like chemical processing, oil & gas, and aerospace. The global corrosion-resistant alloy market, which includes Hastelloy, is projected to reach $10.6 billion by 2025. Technologically, Hastelloy is well-established but continues to evolve, with companies like Haynes International, Nippon Steel, and Mitsubishi Materials leading in innovation. These firms are developing advanced Hastelloy grades with enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, catering to more extreme environments and specialized applications in various industries.
NIPPON STEEL CORP.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL CORP. has developed advanced Hastelloy alloys with enhanced corrosion resistance for acidic environments. Their proprietary manufacturing process involves precise control of alloying elements, particularly molybdenum and chromium, to create a stable passive film on the metal surface[1]. This film acts as a barrier against acid attack, significantly improving the material's longevity in corrosive conditions. The company has also implemented a unique heat treatment process that optimizes the microstructure of the alloy, further enhancing its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion[3]. Additionally, NIPPON STEEL has developed a surface modification technique that increases the alloy's resistance to sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, making it suitable for use in chemical processing industries[5].
Strengths: Superior corrosion resistance in highly acidic environments, extended lifespan of equipment, and reduced maintenance costs. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to standard stainless steel, and potential limitations in extreme temperature applications.
Mitsubishi Materials Corp.
Technical Solution: Mitsubishi Materials Corp. has engineered a series of Hastelloy-based alloys specifically designed for acidic corrosion protection. Their approach involves a multi-layer coating system that combines the inherent corrosion resistance of Hastelloy with additional protective layers[2]. The base Hastelloy layer is enhanced with a nanostructured ceramic coating, which provides an extra barrier against acid penetration. This composite structure has shown remarkable resistance to a wide range of acids, including nitric, sulfuric, and hydrochloric acids[4]. Mitsubishi has also developed a novel electrochemical treatment process that modifies the surface of the Hastelloy, creating a more stable oxide layer that further improves its corrosion resistance in acidic media[6].
Strengths: Exceptional resistance to a broad spectrum of acids, improved durability in harsh chemical environments. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process may lead to higher production costs, and potential challenges in repairing or modifying the multi-layer coating in the field.
Innovative Hastelloy Grades for Acidic Environments
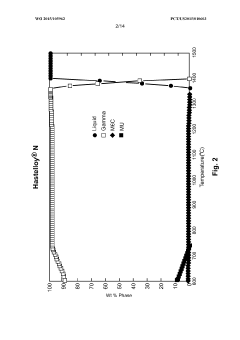
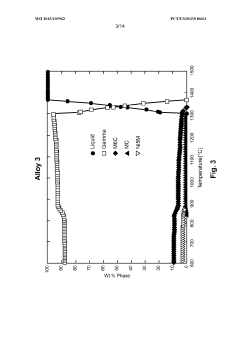
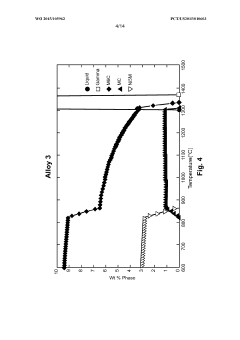
Ni-Mo-Cr OR Ni-Cr-Mo ALLOYS FOR LIQUID-SALT COOLING SYSTEMS
PatentWO2015105962A1
Innovation
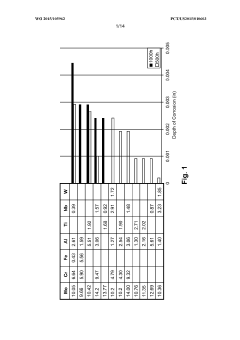
- Development of Ni-Mo-Cr or Ni-Cr-Mo alloys with specific composition ranges (6-8.5 Cr, 5.5-13.5 Mo, 0.4-7.5 W, 1-2 Ti, 0.7-0.85 Mn, 0.05-0.3 Al, 0.08-0.5 C, 1-5 Ta, 1-4 Nb, 1-3 Hf, balance Ni) that provide enhanced yield strength, tensile strength, creep rupture life, and corrosion resistance through solid solution strengthening and carbide precipitation mechanisms, minimizing interdiffusion coefficients to prevent brittle phase formation.
High Strength Alloys for High Temperature Service in Liquid-Salt Cooled Energy Systems
PatentActiveUS20140271338A1
Innovation
- Development of a cobalt-free alloy with specific weight percent compositions, including Cr, Al, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ta, Ti, Nb, W, C, B, and N, that achieves high yield and tensile strengths, creep rupture life, and resistance to liquid fluoride salt corrosion through γ′ microstructural components and solid solution strengthening, while avoiding brittle intermetallic phases.
Environmental Impact of Hastelloy Production
The production of Hastelloy, while crucial for its corrosion-resistant properties, carries significant environmental implications. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive methods and the use of various raw materials, which contribute to its environmental footprint. The primary components of Hastelloy, including nickel, chromium, and molybdenum, require extensive mining operations that can lead to habitat disruption and soil erosion.
The extraction and refining of these metals often involve processes that release greenhouse gases and other pollutants into the atmosphere. For instance, nickel mining and smelting are known to emit sulfur dioxide, which contributes to acid rain formation. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of metal refining processes results in substantial carbon dioxide emissions, further exacerbating climate change concerns.
Water usage and potential contamination are also critical environmental factors in Hastelloy production. The manufacturing process requires large volumes of water for cooling and processing, which can strain local water resources. Moreover, without proper treatment, wastewater from these operations may contain heavy metals and other pollutants that can harm aquatic ecosystems if released into water bodies.
The production of Hastelloy also generates solid waste, including slag and other byproducts. While some of these materials can be recycled or repurposed, others may require special disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. The management of these waste products presents ongoing challenges for manufacturers and environmental regulators alike.
However, it's important to note that the long-term environmental benefits of using Hastelloy in corrosive environments may offset some of its production impacts. Its exceptional resistance to acidic corrosion means that equipment and structures made from Hastelloy have extended lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated environmental costs of manufacturing new components.
Efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of Hastelloy production. These include improving energy efficiency in manufacturing processes, implementing more effective waste management strategies, and exploring cleaner extraction methods for raw materials. Additionally, the recycling of Hastelloy at the end of its useful life is becoming increasingly important, as it reduces the demand for new raw materials and minimizes waste.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, manufacturers of Hastelloy are likely to face increased pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. This may drive innovation in production techniques and encourage the development of alternative materials that offer similar corrosion resistance with a reduced environmental footprint.
The extraction and refining of these metals often involve processes that release greenhouse gases and other pollutants into the atmosphere. For instance, nickel mining and smelting are known to emit sulfur dioxide, which contributes to acid rain formation. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of metal refining processes results in substantial carbon dioxide emissions, further exacerbating climate change concerns.
Water usage and potential contamination are also critical environmental factors in Hastelloy production. The manufacturing process requires large volumes of water for cooling and processing, which can strain local water resources. Moreover, without proper treatment, wastewater from these operations may contain heavy metals and other pollutants that can harm aquatic ecosystems if released into water bodies.
The production of Hastelloy also generates solid waste, including slag and other byproducts. While some of these materials can be recycled or repurposed, others may require special disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. The management of these waste products presents ongoing challenges for manufacturers and environmental regulators alike.
However, it's important to note that the long-term environmental benefits of using Hastelloy in corrosive environments may offset some of its production impacts. Its exceptional resistance to acidic corrosion means that equipment and structures made from Hastelloy have extended lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated environmental costs of manufacturing new components.
Efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of Hastelloy production. These include improving energy efficiency in manufacturing processes, implementing more effective waste management strategies, and exploring cleaner extraction methods for raw materials. Additionally, the recycling of Hastelloy at the end of its useful life is becoming increasingly important, as it reduces the demand for new raw materials and minimizes waste.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, manufacturers of Hastelloy are likely to face increased pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. This may drive innovation in production techniques and encourage the development of alternative materials that offer similar corrosion resistance with a reduced environmental footprint.
Hastelloy Applications in Chemical Processing
Hastelloy alloys have revolutionized chemical processing industries by providing exceptional resistance to acidic corrosion in harsh environments. These nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys are extensively used in various chemical processing applications due to their superior performance in corrosive conditions.
In the petrochemical industry, Hastelloy is employed in the construction of reactors, heat exchangers, and piping systems. These components are exposed to highly corrosive substances, such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, during processes like catalytic reforming and hydrocracking. Hastelloy's resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion ensures the longevity and reliability of equipment in these critical operations.
The pharmaceutical sector also benefits from Hastelloy's properties in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Many APIs require processing in acidic media, and Hastelloy-lined reactors and storage tanks provide the necessary protection against corrosion. This application is particularly crucial in maintaining product purity and preventing contamination during drug manufacturing.
In the pulp and paper industry, Hastelloy finds application in digesters and bleaching equipment. The alloy's resistance to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking makes it ideal for handling chlorine-based bleaching agents and acidic pulping liquors. This ensures the integrity of processing equipment and reduces maintenance downtime.
The food and beverage industry utilizes Hastelloy in processing equipment for acidic foods and beverages. For instance, in fruit juice production, where citric acid is prevalent, Hastelloy-lined tanks and piping systems prevent metal leaching and maintain product quality. Similarly, in the production of vinegar and other acidic condiments, Hastelloy components ensure long-term reliability of processing equipment.
Wastewater treatment plants also employ Hastelloy in critical components exposed to acidic effluents. The alloy's resistance to a wide range of pH levels makes it suitable for use in pumps, valves, and piping systems that handle corrosive wastewater streams. This application is essential in maintaining environmental compliance and ensuring the longevity of treatment infrastructure.
In the production of specialty chemicals, Hastelloy is used in reactors and storage vessels for handling corrosive intermediates and end products. Its ability to withstand a variety of aggressive chemicals, including organic acids and chlorinated compounds, makes it invaluable in the manufacture of pesticides, dyes, and other specialty chemicals.
In the petrochemical industry, Hastelloy is employed in the construction of reactors, heat exchangers, and piping systems. These components are exposed to highly corrosive substances, such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, during processes like catalytic reforming and hydrocracking. Hastelloy's resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion ensures the longevity and reliability of equipment in these critical operations.
The pharmaceutical sector also benefits from Hastelloy's properties in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Many APIs require processing in acidic media, and Hastelloy-lined reactors and storage tanks provide the necessary protection against corrosion. This application is particularly crucial in maintaining product purity and preventing contamination during drug manufacturing.
In the pulp and paper industry, Hastelloy finds application in digesters and bleaching equipment. The alloy's resistance to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking makes it ideal for handling chlorine-based bleaching agents and acidic pulping liquors. This ensures the integrity of processing equipment and reduces maintenance downtime.
The food and beverage industry utilizes Hastelloy in processing equipment for acidic foods and beverages. For instance, in fruit juice production, where citric acid is prevalent, Hastelloy-lined tanks and piping systems prevent metal leaching and maintain product quality. Similarly, in the production of vinegar and other acidic condiments, Hastelloy components ensure long-term reliability of processing equipment.
Wastewater treatment plants also employ Hastelloy in critical components exposed to acidic effluents. The alloy's resistance to a wide range of pH levels makes it suitable for use in pumps, valves, and piping systems that handle corrosive wastewater streams. This application is essential in maintaining environmental compliance and ensuring the longevity of treatment infrastructure.
In the production of specialty chemicals, Hastelloy is used in reactors and storage vessels for handling corrosive intermediates and end products. Its ability to withstand a variety of aggressive chemicals, including organic acids and chlorinated compounds, makes it invaluable in the manufacture of pesticides, dyes, and other specialty chemicals.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!