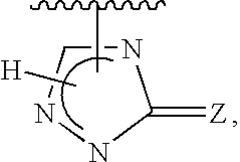
How to Develop Hypertonic Solutions for Enhanced Absorption?
Hypertonic Solutions Background and Objectives
Hypertonic solutions have emerged as a promising approach in the field of enhanced absorption, particularly in pharmaceutical and medical applications. These solutions, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to the surrounding environment, have garnered significant attention due to their potential to improve drug delivery and nutrient absorption.
The development of hypertonic solutions for enhanced absorption has its roots in osmosis principles, dating back to the early 20th century. Initially, these solutions were primarily used in medical settings for rehydration therapy. However, as research progressed, scientists began to explore their potential in improving the absorption of various substances across biological membranes.
Over the past few decades, the focus has shifted towards optimizing hypertonic solutions for specific applications, such as oral drug delivery, transdermal absorption, and targeted nutrient uptake. This evolution has been driven by advancements in pharmaceutical sciences, materials engineering, and a deeper understanding of cellular physiology.
The primary objective in developing hypertonic solutions for enhanced absorption is to create formulations that can effectively increase the bioavailability of active compounds. This involves overcoming various physiological barriers, such as the gastrointestinal epithelium or the stratum corneum of the skin, which often limit the absorption of many therapeutic agents and nutrients.
Researchers aim to design hypertonic solutions that not only facilitate enhanced absorption but also maintain stability, safety, and efficacy. This requires a delicate balance between osmotic pressure, pH, and other physicochemical properties to ensure optimal performance without causing adverse effects on biological tissues.
Another crucial goal is to develop versatile hypertonic solutions that can be tailored for different routes of administration and various types of active compounds. This includes creating formulations suitable for oral, topical, and parenteral applications, as well as solutions capable of enhancing the absorption of both hydrophilic and lipophilic substances.
The development of hypertonic solutions also aims to address specific challenges in drug delivery, such as improving the absorption of poorly soluble drugs, enhancing the permeation of large molecules like proteins and peptides, and achieving sustained or controlled release profiles.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing focus on developing "smart" hypertonic solutions that can respond to environmental stimuli or target specific tissues. This involves incorporating advanced materials and technologies, such as nanocarriers, hydrogels, and responsive polymers, to create more sophisticated and efficient absorption-enhancing systems.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Absorption Products
The market for enhanced absorption products has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness, as well as advancements in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical technologies. This market segment encompasses a wide range of products, including oral medications, topical treatments, and nutritional supplements, all designed to improve the body's ability to absorb and utilize active ingredients more effectively.
One of the key factors fueling market growth is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and conditions that require long-term medication. Enhanced absorption technologies can potentially reduce dosage requirements and minimize side effects, making them particularly attractive for patients with ongoing health concerns. Additionally, the aging global population has created a substantial demand for products that can improve nutrient absorption, as older adults often face challenges with nutrient uptake due to physiological changes.
The nutraceutical sector has been particularly active in adopting enhanced absorption technologies, with many companies developing innovative formulations for vitamins, minerals, and other dietary supplements. These products often command premium prices due to their perceived superior efficacy, contributing to the overall market value. The sports nutrition segment has also shown keen interest in enhanced absorption products, as athletes and fitness enthusiasts seek to maximize the benefits of their nutritional intake.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for enhanced absorption products, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical industries and high consumer spending on health-related products. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable incomes, changing lifestyles, and a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare in countries like China and India.
The competitive landscape of the enhanced absorption product market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies, specialized nutraceutical firms, and innovative startups. Many of these companies are investing heavily in research and development to create proprietary absorption-enhancing technologies, which can provide a significant competitive advantage in this high-value market.
Looking ahead, the market for enhanced absorption products is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors such as ongoing research into novel delivery mechanisms, the increasing popularity of personalized nutrition, and the growing acceptance of alternative medicine are likely to create new opportunities for market expansion. However, regulatory challenges and the need for extensive clinical validation of new technologies may pose hurdles for market players, particularly in the pharmaceutical sector.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Solution Development
The development of hypertonic solutions for enhanced absorption faces several significant challenges that researchers and pharmaceutical companies must address. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining the stability of the hypertonic solution over time. These solutions often contain high concentrations of solutes, which can lead to precipitation or crystallization during storage, potentially altering the solution's efficacy and safety profile.
Another critical challenge lies in optimizing the osmolality of the solution. While higher osmolality can enhance absorption, it may also cause local irritation or damage to mucosal tissues, particularly in sensitive areas such as the nasal passages or gastrointestinal tract. Striking the right balance between improved absorption and minimal adverse effects requires extensive research and careful formulation.
The selection of appropriate solutes presents another hurdle. Different solutes exhibit varying degrees of absorption enhancement, and their effectiveness can be influenced by factors such as molecular weight, charge, and lipophilicity. Identifying the ideal combination of solutes that maximizes absorption without compromising safety or stability is a complex task that demands rigorous testing and evaluation.
Bioavailability is a crucial concern in hypertonic solution development. Even with enhanced absorption, ensuring that the active ingredients reach their intended targets in therapeutic concentrations remains challenging. Factors such as first-pass metabolism, enzymatic degradation, and rapid clearance can significantly reduce the bioavailability of drugs delivered via hypertonic solutions.
Regulatory compliance poses additional challenges. Hypertonic solutions, particularly those intended for novel routes of administration or containing new excipients, may face increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Demonstrating safety, efficacy, and quality consistency throughout the development process is essential but can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Manufacturing and scale-up issues also present significant obstacles. Producing hypertonic solutions at commercial scale while maintaining consistent quality and sterility requires specialized equipment and processes. Ensuring batch-to-batch uniformity and preventing contamination during large-scale production can be particularly challenging due to the high solute concentrations involved.
Lastly, patient acceptability and compliance remain ongoing concerns. Hypertonic solutions may have unpleasant tastes or cause temporary discomfort upon administration, potentially leading to poor patient adherence. Developing palatable formulations or innovative delivery systems that minimize discomfort while maintaining efficacy is a critical challenge that continues to drive research in this field.
Existing Hypertonic Solution Formulations
01 Hypertonic solution formulations for enhanced absorption
Hypertonic solutions can be formulated with specific ingredients to enhance absorption through various biological membranes. These formulations may include osmotic agents, penetration enhancers, or other additives that facilitate the movement of active compounds across cellular barriers, improving overall absorption and efficacy.- Hypertonic solution formulations for enhanced absorption: Hypertonic solutions can be formulated with specific ingredients to enhance absorption through various biological membranes. These formulations may include osmotic agents, penetration enhancers, or other additives that facilitate the movement of active compounds across barriers, improving overall absorption and efficacy.
- Medical devices for hypertonic solution delivery: Specialized medical devices can be designed for the controlled delivery of hypertonic solutions to specific body areas. These devices may include catheters, infusion pumps, or other apparatus that allow for precise administration of hypertonic solutions, enhancing absorption and therapeutic effects.
- Hypertonic solutions in cell culture and biotechnology: Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in cell culture techniques and biotechnology applications. They can be used to manipulate cellular environments, induce specific responses, or enhance the absorption of nutrients or compounds of interest in laboratory settings.
- Transdermal absorption of hypertonic solutions: Hypertonic solutions can be formulated for improved transdermal absorption. This approach may involve the use of specific carriers, emulsifiers, or other excipients that enhance the penetration of active ingredients through the skin barrier, allowing for more effective topical treatments.
- Hypertonic solutions for ocular drug delivery: Specialized hypertonic solutions can be developed for ocular drug delivery, enhancing the absorption of therapeutic agents through the eye. These formulations may incorporate specific osmotic agents or penetration enhancers to improve drug bioavailability and efficacy in treating various eye conditions.
02 Medical devices for hypertonic solution delivery
Specialized medical devices can be designed for the controlled delivery of hypertonic solutions to specific body areas. These devices may include catheters, infusion pumps, or other apparatus that allow for precise administration of hypertonic solutions, ensuring optimal absorption and therapeutic effect.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypertonic solutions in cell culture and biotechnology
Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in cell culture techniques and biotechnological applications. These solutions can be used to manipulate cellular environments, induce specific responses, or enhance the production of desired compounds in various biotechnological processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypertonic solutions for wound healing and tissue regeneration
The application of hypertonic solutions in wound healing and tissue regeneration has shown promising results. These solutions can help in reducing edema, promoting cellular migration, and enhancing the overall healing process in various types of wounds and tissue injuries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hypertonic solutions in cryopreservation techniques
Hypertonic solutions are utilized in cryopreservation methods to protect cells and tissues during freezing and thawing processes. These solutions help in minimizing ice crystal formation and cellular damage, thereby improving the viability of preserved biological materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Solution Industry
The development of hypertonic solutions for enhanced absorption is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for such solutions is expanding, driven by applications in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and industrial processes. Technological maturity varies across different sectors, with pharmaceutical companies like LG Chem Ltd., BASF Corp., and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. leading in innovation. Academic institutions such as The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Rutgers State University are contributing to fundamental research. Companies like Toray Industries, Inc. and Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. are advancing material science aspects, while Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Bristol Myers Squibb Co. focus on drug delivery applications, indicating a diverse and competitive landscape.
LG Chem Ltd.
BASF Corp.
Innovative Approaches in Osmotic Pressure Manipulation
- Use of polymers at or above their limiting concentration to generate osmotic pressure in hypertonic solutions for enhanced macromolecule introduction into cells.
- Specific concentration thresholds identified for different polymers (polyethylene glycol, glucose polymer, sucrose-epichlorohydrin copolymer) to ensure entangled chain formation.
- Application of the hypertonic solution method specifically for introducing macromolecules into mammalian cells.
- A percutaneous absorption preparation containing a compound with angiotensin II antagonistic activity, combined with fatty acid esters, polyols, and nonionic surfactants, which facilitates sustained skin permeation and maintains effective blood concentrations for an extended period without peak blood levels.
Regulatory Framework for Hypertonic Solutions
The regulatory framework for hypertonic solutions is a critical aspect of their development and commercialization. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of hypertonic solutions, which are typically classified as medical devices or drugs depending on their intended use and mechanism of action.
For hypertonic solutions intended for medical purposes, manufacturers must comply with the FDA's premarket approval (PMA) process or the 510(k) clearance pathway. The PMA process is more rigorous and is required for Class III medical devices, which are those that support or sustain human life, are of substantial importance in preventing impairment of human health, or present a potential, unreasonable risk of illness or injury. The 510(k) pathway is for devices that are substantially equivalent to legally marketed predicate devices.
In the European Union, hypertonic solutions fall under the purview of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), depending on their intended use. These regulations require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and performance of their products through clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance.
Quality management systems are a crucial component of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must implement and maintain a quality management system that complies with ISO 13485 standards, which are specific to medical devices. This system ensures consistent production and helps maintain compliance with regulatory requirements throughout the product lifecycle.
Labeling and packaging regulations are also stringent for hypertonic solutions. The FDA and EMA have specific requirements for product labeling, including clear instructions for use, warnings, and contraindications. These must be accurately communicated to healthcare providers and patients to ensure safe and effective use of the product.
Post-market surveillance is an ongoing requirement for manufacturers of hypertonic solutions. This involves monitoring the safety and performance of the product after it has been released to the market, reporting adverse events, and implementing corrective actions when necessary. Both the FDA and EMA have established systems for reporting and tracking adverse events related to medical devices and drugs.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different regions. These initiatives can help manufacturers navigate the complex global regulatory landscape for hypertonic solutions, potentially reducing the time and cost associated with bringing products to multiple markets.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The development of hypertonic solutions for enhanced absorption requires careful consideration of safety and efficacy factors. These solutions, designed to increase osmotic pressure and promote absorption, must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure they do not pose undue risks to patients while delivering the intended therapeutic benefits.
Safety considerations are paramount in the development process. Hypertonic solutions can potentially cause tissue irritation or damage if not properly formulated. The osmolality and pH of the solution must be carefully balanced to minimize adverse effects on mucosal surfaces or other tissues with which they come into contact. Additionally, the potential for systemic effects, such as electrolyte imbalances or fluid shifts, must be thoroughly assessed and mitigated.
Toxicological studies are essential to evaluate the short-term and long-term safety profiles of hypertonic solutions. These studies should assess local tissue reactions, systemic absorption, and potential interactions with other medications or physiological processes. The choice of excipients and preservatives must also be scrutinized for their safety profiles, especially in chronic use scenarios.
Efficacy considerations are equally critical in the development of hypertonic solutions. The primary goal is to enhance absorption of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or other target molecules. This requires a deep understanding of the mechanisms by which hypertonicity promotes absorption, such as osmotic gradients, tight junction modulation, and cellular uptake pathways.
Formulation scientists must optimize the concentration and composition of solutes to achieve the desired osmotic effect without compromising the stability or bioavailability of the API. The kinetics of absorption enhancement should be characterized to inform dosing strategies and administration protocols. Moreover, the duration of the absorption-enhancing effect must be determined to guide the design of sustained-release formulations or repeated dosing regimens.
Comparative studies against isotonic formulations or other absorption-enhancing technologies are crucial to demonstrate the superior efficacy of hypertonic solutions. These studies should encompass various physiological conditions and target tissues to establish the robustness and versatility of the approach.
Importantly, the interplay between safety and efficacy must be carefully balanced. While higher tonicity may lead to greater absorption enhancement, it may also increase the risk of adverse effects. Therefore, developers must identify the optimal range where absorption is significantly improved without compromising safety.
In conclusion, the development of hypertonic solutions for enhanced absorption demands a multifaceted approach that rigorously addresses both safety and efficacy considerations. By systematically evaluating these factors, researchers can create innovative formulations that safely and effectively improve the delivery of therapeutic agents across various physiological barriers.