How to Foster Strategic Partnerships for V2G Growth?
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V2G Evolution and Objectives
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology has evolved significantly over the past decade, transforming from a conceptual idea to a practical solution for grid stability and renewable energy integration. The evolution of V2G can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first proposed the idea of using electric vehicle batteries as distributed energy resources. Since then, advancements in battery technology, smart grid infrastructure, and electric vehicle adoption have accelerated V2G development.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a bidirectional flow of energy between electric vehicles and the power grid. This allows for more efficient use of renewable energy sources, improved grid stability, and potential cost savings for both vehicle owners and utility companies. As the global push for decarbonization intensifies, V2G is increasingly seen as a crucial component in achieving a sustainable energy future.
Recent technological trends in V2G include the development of more sophisticated power electronics, improved communication protocols between vehicles and the grid, and enhanced battery management systems. These advancements aim to optimize the efficiency and reliability of V2G systems, making them more attractive for widespread adoption.
The evolution of V2G technology is closely tied to the growth of the electric vehicle market. As EV adoption rates increase, the potential impact of V2G on grid operations becomes more significant. This has led to increased interest from both automotive manufacturers and utility companies in developing V2G-capable vehicles and infrastructure.
Looking ahead, the objectives for V2G technology are multifaceted. One key goal is to increase the scale of V2G implementation, moving from pilot projects to large-scale deployments. This requires overcoming technical challenges related to grid integration, standardization of protocols, and ensuring the longevity of vehicle batteries under V2G usage.
Another important objective is to develop more sophisticated market mechanisms and business models that can fully capture the value of V2G services. This includes creating incentives for vehicle owners to participate in V2G programs and establishing fair compensation structures for the energy and ancillary services provided to the grid.
Furthermore, there is a growing focus on integrating V2G technology with other smart grid solutions, such as demand response systems and renewable energy forecasting tools. This integration aims to create a more holistic and resilient energy ecosystem that can effectively manage the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a bidirectional flow of energy between electric vehicles and the power grid. This allows for more efficient use of renewable energy sources, improved grid stability, and potential cost savings for both vehicle owners and utility companies. As the global push for decarbonization intensifies, V2G is increasingly seen as a crucial component in achieving a sustainable energy future.
Recent technological trends in V2G include the development of more sophisticated power electronics, improved communication protocols between vehicles and the grid, and enhanced battery management systems. These advancements aim to optimize the efficiency and reliability of V2G systems, making them more attractive for widespread adoption.
The evolution of V2G technology is closely tied to the growth of the electric vehicle market. As EV adoption rates increase, the potential impact of V2G on grid operations becomes more significant. This has led to increased interest from both automotive manufacturers and utility companies in developing V2G-capable vehicles and infrastructure.
Looking ahead, the objectives for V2G technology are multifaceted. One key goal is to increase the scale of V2G implementation, moving from pilot projects to large-scale deployments. This requires overcoming technical challenges related to grid integration, standardization of protocols, and ensuring the longevity of vehicle batteries under V2G usage.
Another important objective is to develop more sophisticated market mechanisms and business models that can fully capture the value of V2G services. This includes creating incentives for vehicle owners to participate in V2G programs and establishing fair compensation structures for the energy and ancillary services provided to the grid.
Furthermore, there is a growing focus on integrating V2G technology with other smart grid solutions, such as demand response systems and renewable energy forecasting tools. This integration aims to create a more holistic and resilient energy ecosystem that can effectively manage the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
V2G Market Demand Analysis
The Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) market is experiencing significant growth potential as the automotive industry shifts towards electrification and renewable energy integration becomes increasingly crucial. Market demand for V2G technology is driven by several key factors, including the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), the need for grid stability and flexibility, and the push for sustainable energy solutions.
The global EV market has been expanding rapidly, with sales reaching record levels in recent years. This surge in EV adoption creates a substantial opportunity for V2G technology, as each new electric vehicle represents a potential mobile energy storage unit. Utility companies and grid operators are increasingly recognizing the value of leveraging this distributed energy resource to balance supply and demand, especially during peak hours.
Energy management and grid stability are becoming more critical as renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, contribute a larger share of the overall energy mix. The intermittent nature of these sources creates challenges for grid operators, making V2G an attractive solution for load balancing and frequency regulation. This demand is further amplified by the growing focus on smart grid technologies and the need for more resilient energy infrastructure.
Corporate and government initiatives to reduce carbon emissions are also driving demand for V2G solutions. Many countries have set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption and carbon neutrality, creating a favorable regulatory environment for V2G technology. Additionally, businesses are increasingly looking to integrate EVs into their fleets and leverage V2G capabilities to optimize energy costs and contribute to sustainability goals.
Consumer interest in energy independence and the potential for cost savings through V2G participation is another significant market driver. As electricity prices fluctuate and time-of-use rates become more common, EV owners are showing interest in technologies that allow them to use their vehicles as power sources during peak periods and charge during off-peak hours.
The market for V2G hardware, including bidirectional chargers and smart charging stations, is expected to grow substantially in the coming years. Software solutions for managing V2G systems, including aggregation platforms and energy trading applications, are also seeing increased demand as the ecosystem develops.
While the V2G market shows promising growth potential, several challenges need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. These include the need for standardization across different EV models and charging systems, concerns about battery degradation, and the development of appropriate regulatory frameworks and incentive structures to encourage participation in V2G programs.
The global EV market has been expanding rapidly, with sales reaching record levels in recent years. This surge in EV adoption creates a substantial opportunity for V2G technology, as each new electric vehicle represents a potential mobile energy storage unit. Utility companies and grid operators are increasingly recognizing the value of leveraging this distributed energy resource to balance supply and demand, especially during peak hours.
Energy management and grid stability are becoming more critical as renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, contribute a larger share of the overall energy mix. The intermittent nature of these sources creates challenges for grid operators, making V2G an attractive solution for load balancing and frequency regulation. This demand is further amplified by the growing focus on smart grid technologies and the need for more resilient energy infrastructure.
Corporate and government initiatives to reduce carbon emissions are also driving demand for V2G solutions. Many countries have set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption and carbon neutrality, creating a favorable regulatory environment for V2G technology. Additionally, businesses are increasingly looking to integrate EVs into their fleets and leverage V2G capabilities to optimize energy costs and contribute to sustainability goals.
Consumer interest in energy independence and the potential for cost savings through V2G participation is another significant market driver. As electricity prices fluctuate and time-of-use rates become more common, EV owners are showing interest in technologies that allow them to use their vehicles as power sources during peak periods and charge during off-peak hours.
The market for V2G hardware, including bidirectional chargers and smart charging stations, is expected to grow substantially in the coming years. Software solutions for managing V2G systems, including aggregation platforms and energy trading applications, are also seeing increased demand as the ecosystem develops.
While the V2G market shows promising growth potential, several challenges need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. These include the need for standardization across different EV models and charging systems, concerns about battery degradation, and the development of appropriate regulatory frameworks and incentive structures to encourage participation in V2G programs.
V2G Technical Challenges
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology faces several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed to foster its growth and widespread adoption. One of the primary hurdles is the development of robust and efficient bidirectional charging systems. These systems must be capable of seamlessly managing power flow in both directions, from the grid to the vehicle and vice versa, while maintaining high efficiency and reliability.
Another critical challenge lies in the battery management systems of electric vehicles. V2G operations can potentially accelerate battery degradation due to increased cycling and depth of discharge. Developing advanced battery management algorithms and technologies that can mitigate these effects is crucial for the long-term viability of V2G systems.
Grid integration poses a substantial challenge for V2G implementation. The existing power grid infrastructure was not designed to accommodate large-scale bidirectional power flows from distributed sources like electric vehicles. Upgrading and adapting the grid to handle these new demands requires significant investment and technological innovation in areas such as smart grid technologies, power electronics, and energy management systems.
Communication and cybersecurity present another set of technical hurdles. V2G systems rely heavily on real-time data exchange between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. Ensuring secure, reliable, and standardized communication protocols is essential to protect against potential cyber threats and maintain system integrity.
The development of accurate prediction and optimization algorithms is crucial for effective V2G operations. These algorithms must forecast energy demand, supply, and pricing, as well as optimize charging and discharging schedules for individual vehicles and fleets. The complexity of these algorithms increases with the scale of V2G implementation, requiring advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques.
Interoperability and standardization remain significant challenges in the V2G ecosystem. The lack of universal standards for hardware interfaces, communication protocols, and data formats hinders seamless integration between different vehicle models, charging infrastructure, and grid systems. Developing and adopting industry-wide standards is essential for fostering strategic partnerships and accelerating V2G growth.
Lastly, the challenge of scalability looms large in V2G technology. As the number of electric vehicles participating in V2G programs grows, managing the increased complexity of power flows, data processing, and system coordination becomes increasingly difficult. Developing scalable solutions that can handle millions of connected vehicles while maintaining system stability and efficiency is a critical technical challenge that must be addressed to support widespread V2G adoption.
Another critical challenge lies in the battery management systems of electric vehicles. V2G operations can potentially accelerate battery degradation due to increased cycling and depth of discharge. Developing advanced battery management algorithms and technologies that can mitigate these effects is crucial for the long-term viability of V2G systems.
Grid integration poses a substantial challenge for V2G implementation. The existing power grid infrastructure was not designed to accommodate large-scale bidirectional power flows from distributed sources like electric vehicles. Upgrading and adapting the grid to handle these new demands requires significant investment and technological innovation in areas such as smart grid technologies, power electronics, and energy management systems.
Communication and cybersecurity present another set of technical hurdles. V2G systems rely heavily on real-time data exchange between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. Ensuring secure, reliable, and standardized communication protocols is essential to protect against potential cyber threats and maintain system integrity.
The development of accurate prediction and optimization algorithms is crucial for effective V2G operations. These algorithms must forecast energy demand, supply, and pricing, as well as optimize charging and discharging schedules for individual vehicles and fleets. The complexity of these algorithms increases with the scale of V2G implementation, requiring advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques.
Interoperability and standardization remain significant challenges in the V2G ecosystem. The lack of universal standards for hardware interfaces, communication protocols, and data formats hinders seamless integration between different vehicle models, charging infrastructure, and grid systems. Developing and adopting industry-wide standards is essential for fostering strategic partnerships and accelerating V2G growth.
Lastly, the challenge of scalability looms large in V2G technology. As the number of electric vehicles participating in V2G programs grows, managing the increased complexity of power flows, data processing, and system coordination becomes increasingly difficult. Developing scalable solutions that can handle millions of connected vehicles while maintaining system stability and efficiency is a critical technical challenge that must be addressed to support widespread V2G adoption.
Current V2G Partnership Models
01 Integration of V2G technology in electric vehicles
V2G technology is being integrated into electric vehicles, allowing them to not only consume energy from the grid but also feed energy back when needed. This bidirectional flow of electricity enables better grid management and utilization of renewable energy sources. The integration involves advanced power electronics, communication systems, and control algorithms to ensure seamless interaction between vehicles and the grid.- Integration of V2G technology in electric vehicles: V2G technology is being integrated into electric vehicles, allowing them to not only consume energy from the grid but also feed energy back when needed. This bidirectional flow of electricity enables better grid management and provides additional value to electric vehicle owners.
- Smart charging and energy management systems: Advanced charging and energy management systems are being developed to optimize V2G operations. These systems can predict energy demand, manage charging schedules, and facilitate seamless energy transfer between vehicles and the grid, enhancing overall efficiency.
- V2G infrastructure development: The growth of V2G technology is supported by the development of necessary infrastructure, including bidirectional charging stations, communication networks, and grid integration systems. This infrastructure enables widespread adoption of V2G technology in various settings.
- V2G market expansion and business models: New business models and market opportunities are emerging around V2G technology. These include energy trading platforms, grid services provided by electric vehicle fleets, and innovative pricing structures for V2G participants, driving the growth of this technology.
- V2G technology for grid stability and renewable energy integration: V2G technology is increasingly being used to enhance grid stability and support the integration of renewable energy sources. By using electric vehicles as distributed energy storage units, V2G systems can help balance supply and demand, reduce peak loads, and accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy.
02 Smart charging and energy management systems
Development of intelligent charging and energy management systems is crucial for V2G growth. These systems optimize charging schedules, predict energy demand, and manage the flow of electricity between vehicles and the grid. They incorporate machine learning algorithms and real-time data analysis to maximize efficiency and minimize costs for both vehicle owners and grid operators.Expand Specific Solutions03 V2G infrastructure and standardization
The growth of V2G technology relies heavily on the development of supporting infrastructure and standardization of protocols. This includes the installation of bidirectional charging stations, upgrading grid components, and establishing communication standards between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. Efforts are being made to create universal standards to ensure interoperability and widespread adoption of V2G technology.Expand Specific Solutions04 Economic incentives and business models for V2G adoption
To promote the growth of V2G technology, various economic incentives and business models are being developed. These include time-of-use pricing, demand response programs, and grid services markets that compensate vehicle owners for providing energy storage and grid support. New business models are emerging, such as aggregator services that manage fleets of V2G-enabled vehicles to provide grid services at scale.Expand Specific Solutions05 V2G applications in renewable energy integration
V2G technology is playing a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. Electric vehicles can act as distributed energy storage systems, helping to balance the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation. This application of V2G technology contributes to grid stability, reduces the need for conventional peaker plants, and supports the transition to a cleaner energy system.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V2G Industry Players
The V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) market is in its early growth stage, characterized by increasing strategic partnerships among key players. The market size is expanding, driven by the growing adoption of electric vehicles and the need for grid stabilization. Technologically, V2G is progressing rapidly, with companies like Huawei, LG Electronics, and Panasonic leading innovation. State Grid Corporation of China and its subsidiaries are actively involved in infrastructure development. Automotive giants such as Hyundai, Kia, and Bosch are integrating V2G capabilities into their vehicles. Research institutions like the Chinese Academy of Science Guangzhou Energy Research Institute are contributing to technological advancements, while telecom companies like Ericsson and NTT Docomo are exploring V2G's potential in smart grid communications.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei's approach to fostering strategic partnerships for V2G growth involves: 1) Developing advanced 5G and IoT technologies to enable seamless communication between EVs and the grid[1]. 2) Creating cloud-based platforms for efficient management of V2G operations and data analytics[2]. 3) Collaborating with energy companies to integrate V2G capabilities into smart home and building systems[3]. 4) Partnering with automotive manufacturers to develop V2G-ready onboard systems for EVs[4]. 5) Investing in AI and machine learning algorithms to optimize V2G energy flows and predict grid demand[5].
Strengths: Strong technological capabilities in 5G and IoT, global presence, and experience in large-scale system integration. Weaknesses: Potential geopolitical challenges in some markets, and the need to build trust in the energy sector.
State Grid Corp. of China
Technical Solution: State Grid Corp. of China has developed a comprehensive V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) strategy to foster strategic partnerships. Their approach includes: 1) Establishing a nationwide charging infrastructure network, with over 1 million charging piles deployed[1]. 2) Implementing smart grid technologies to enable bidirectional power flow between EVs and the grid[2]. 3) Collaborating with major automakers to ensure EV compatibility with V2G systems[3]. 4) Developing advanced energy management systems to optimize V2G operations and grid stability[4]. 5) Partnering with local governments to create supportive policies and incentives for V2G adoption[5].
Strengths: Extensive grid infrastructure, strong government support, and technological expertise. Weaknesses: Potential resistance from traditional energy stakeholders, and the need for significant investment in grid upgrades.
V2G Collaboration Innovations
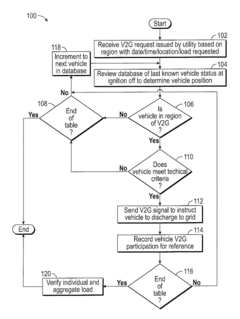
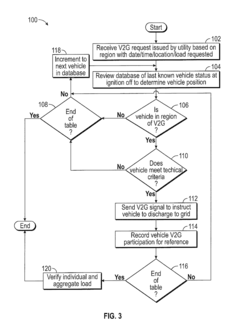
Priority based vehicle control strategy
PatentActiveUS9987940B2
Innovation
- A method and system that prioritize V2G requests based on vehicle location and historical data to select vehicles that meet specific criteria, such as state of charge, charge cycles, and geographic proximity, to reduce battery degradation, involving a network with a server that determines eligible vehicles and sends signals for participation, thereby limiting V2G participation and extending battery life.
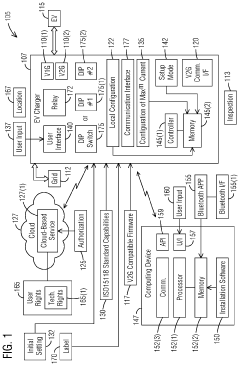
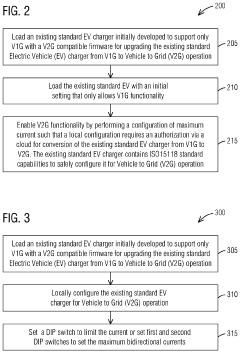
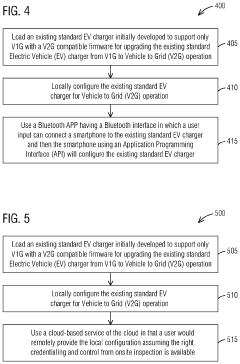
Upgrading an existing standard electric vehicle (EV) charger from grid to vehicle (V1G) to v1g plus vehicle to grid (V2G) operation
PatentPendingUS20240201974A1
Innovation
- A method to locally configure existing standard AC EV chargers with ISO15118 capabilities for V2G operation by loading V2G compatible firmware, authorizing via the cloud, and configuring maximum current, allowing bi-directional charging/discharging through a communication interface.
V2G Policy and Regulations
The development of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology requires a robust policy and regulatory framework to foster strategic partnerships and drive growth. Governments play a crucial role in creating an enabling environment for V2G adoption through supportive policies and regulations.
One key aspect of V2G policy is the establishment of clear guidelines for grid integration. Regulatory bodies need to define standards for bidirectional charging infrastructure, communication protocols, and grid interconnection requirements. These standards ensure interoperability and facilitate seamless integration of electric vehicles (EVs) with the power grid.
Incentive programs are another essential component of V2G policy. Governments can offer financial incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, to encourage EV owners to participate in V2G programs. Additionally, utility companies can be incentivized to invest in V2G infrastructure through regulatory mechanisms that allow for cost recovery and return on investment.
Market design is a critical consideration in V2G policy development. Regulators must establish frameworks that enable fair compensation for V2G services, including energy arbitrage, frequency regulation, and demand response. This may involve creating new market products or adapting existing ones to accommodate the unique characteristics of V2G resources.
Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations are paramount in the V2G ecosystem. Policymakers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information related to EV charging patterns, energy consumption, and grid interactions. Cybersecurity standards should be developed to protect V2G systems from potential threats and ensure the integrity of the power grid.
Regulatory sandboxes can be instrumental in fostering innovation and strategic partnerships in the V2G space. These controlled environments allow companies to test new V2G technologies and business models under relaxed regulatory conditions, enabling rapid iteration and learning.
Cross-sector collaboration is essential for effective V2G policy development. Regulators should engage with stakeholders from the automotive, energy, and technology sectors to ensure that policies address the needs and concerns of all parties involved. This collaborative approach can lead to more comprehensive and effective regulations that support V2G growth.
As V2G technology evolves, policies and regulations must remain flexible and adaptable. Regular review and updating of regulatory frameworks are necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and changing market dynamics. This agility in policymaking can help create a supportive environment for strategic partnerships and accelerate V2G adoption.
One key aspect of V2G policy is the establishment of clear guidelines for grid integration. Regulatory bodies need to define standards for bidirectional charging infrastructure, communication protocols, and grid interconnection requirements. These standards ensure interoperability and facilitate seamless integration of electric vehicles (EVs) with the power grid.
Incentive programs are another essential component of V2G policy. Governments can offer financial incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, to encourage EV owners to participate in V2G programs. Additionally, utility companies can be incentivized to invest in V2G infrastructure through regulatory mechanisms that allow for cost recovery and return on investment.
Market design is a critical consideration in V2G policy development. Regulators must establish frameworks that enable fair compensation for V2G services, including energy arbitrage, frequency regulation, and demand response. This may involve creating new market products or adapting existing ones to accommodate the unique characteristics of V2G resources.
Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations are paramount in the V2G ecosystem. Policymakers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information related to EV charging patterns, energy consumption, and grid interactions. Cybersecurity standards should be developed to protect V2G systems from potential threats and ensure the integrity of the power grid.
Regulatory sandboxes can be instrumental in fostering innovation and strategic partnerships in the V2G space. These controlled environments allow companies to test new V2G technologies and business models under relaxed regulatory conditions, enabling rapid iteration and learning.
Cross-sector collaboration is essential for effective V2G policy development. Regulators should engage with stakeholders from the automotive, energy, and technology sectors to ensure that policies address the needs and concerns of all parties involved. This collaborative approach can lead to more comprehensive and effective regulations that support V2G growth.
As V2G technology evolves, policies and regulations must remain flexible and adaptable. Regular review and updating of regulatory frameworks are necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and changing market dynamics. This agility in policymaking can help create a supportive environment for strategic partnerships and accelerate V2G adoption.
V2G Economic Impact Assessment
The economic impact of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology extends far beyond the automotive and energy sectors, potentially reshaping the entire energy ecosystem and creating new revenue streams for various stakeholders. As V2G systems become more prevalent, they are expected to significantly influence electricity markets, grid stability, and overall energy efficiency.
One of the primary economic benefits of V2G is its potential to reduce the need for expensive peaker plants and grid infrastructure upgrades. By utilizing electric vehicle batteries as distributed energy storage units, V2G can help balance supply and demand, potentially saving billions in infrastructure costs. This cost-saving aspect is particularly crucial for utilities and grid operators, who can defer or avoid substantial capital expenditures.
For electric vehicle owners, V2G presents an opportunity to monetize their vehicle's battery when not in use. By participating in grid services, EV owners can earn revenue through demand response programs, frequency regulation, and energy arbitrage. These additional income streams could offset the higher upfront costs of electric vehicles, making them more attractive to consumers and potentially accelerating EV adoption.
The widespread implementation of V2G technology is also expected to create new jobs and business opportunities. This includes roles in software development, grid management, and specialized V2G equipment manufacturing. Additionally, new service providers may emerge to aggregate and manage fleets of V2G-enabled vehicles, acting as intermediaries between EV owners and grid operators.
From a macroeconomic perspective, V2G could contribute to enhanced energy security and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. By enabling greater integration of renewable energy sources, V2G systems can help countries reduce their energy import dependencies and associated economic vulnerabilities. This shift towards a more resilient and sustainable energy system could have far-reaching economic implications, including potential reductions in healthcare costs associated with air pollution.
However, the economic impact of V2G is not without challenges. The technology requires significant upfront investments in infrastructure and software systems. There are also concerns about battery degradation and its impact on vehicle resale values, which need to be carefully balanced against the potential revenue from grid services. Regulatory frameworks and market structures will need to evolve to fully capture the economic benefits of V2G while ensuring fair compensation for all participants in the ecosystem.
One of the primary economic benefits of V2G is its potential to reduce the need for expensive peaker plants and grid infrastructure upgrades. By utilizing electric vehicle batteries as distributed energy storage units, V2G can help balance supply and demand, potentially saving billions in infrastructure costs. This cost-saving aspect is particularly crucial for utilities and grid operators, who can defer or avoid substantial capital expenditures.
For electric vehicle owners, V2G presents an opportunity to monetize their vehicle's battery when not in use. By participating in grid services, EV owners can earn revenue through demand response programs, frequency regulation, and energy arbitrage. These additional income streams could offset the higher upfront costs of electric vehicles, making them more attractive to consumers and potentially accelerating EV adoption.
The widespread implementation of V2G technology is also expected to create new jobs and business opportunities. This includes roles in software development, grid management, and specialized V2G equipment manufacturing. Additionally, new service providers may emerge to aggregate and manage fleets of V2G-enabled vehicles, acting as intermediaries between EV owners and grid operators.
From a macroeconomic perspective, V2G could contribute to enhanced energy security and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. By enabling greater integration of renewable energy sources, V2G systems can help countries reduce their energy import dependencies and associated economic vulnerabilities. This shift towards a more resilient and sustainable energy system could have far-reaching economic implications, including potential reductions in healthcare costs associated with air pollution.
However, the economic impact of V2G is not without challenges. The technology requires significant upfront investments in infrastructure and software systems. There are also concerns about battery degradation and its impact on vehicle resale values, which need to be carefully balanced against the potential revenue from grid services. Regulatory frameworks and market structures will need to evolve to fully capture the economic benefits of V2G while ensuring fair compensation for all participants in the ecosystem.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!