How to Foster Collaborative V2G Development Partnerships?
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V2G Technology Background and Objectives
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology represents a paradigm shift in the intersection of transportation and energy systems. This innovative approach enables bidirectional power flow between electric vehicles (EVs) and the electrical grid, transforming EVs from mere consumers of electricity into dynamic energy storage units capable of supporting grid stability and efficiency.
The evolution of V2G technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when the concept was first proposed as a means to leverage the growing number of EVs for grid services. Since then, the technology has progressed through various stages of development, from theoretical models to small-scale pilot projects, and now to the cusp of widespread commercial deployment.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a symbiotic relationship between EVs and the electrical grid. This relationship aims to address several critical challenges faced by both the transportation and energy sectors. For the transportation sector, V2G offers the potential to reduce the total cost of EV ownership by allowing vehicle owners to monetize their battery capacity when the vehicle is not in use. For the energy sector, V2G presents an opportunity to enhance grid flexibility, improve renewable energy integration, and reduce the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades.
As the global push towards decarbonization intensifies, V2G technology is poised to play a crucial role in achieving sustainable energy goals. The technology aligns with the broader trends of electrification, decentralization, and digitalization in the energy sector. It offers a unique solution to the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources by providing a distributed network of energy storage units in the form of EV batteries.
The current technological landscape for V2G is characterized by rapid advancements in several key areas. These include improvements in bidirectional charging hardware, development of sophisticated energy management systems, and the creation of standardized communication protocols between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. However, the full realization of V2G potential requires overcoming significant technical, regulatory, and market barriers.
Fostering collaborative V2G development partnerships is crucial for addressing these challenges and accelerating the technology's adoption. Such partnerships bring together diverse stakeholders, including automakers, utility companies, technology providers, and policymakers. By combining their expertise and resources, these collaborations can drive innovation, establish industry standards, and create the necessary ecosystem for V2G technology to thrive.
The evolution of V2G technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when the concept was first proposed as a means to leverage the growing number of EVs for grid services. Since then, the technology has progressed through various stages of development, from theoretical models to small-scale pilot projects, and now to the cusp of widespread commercial deployment.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a symbiotic relationship between EVs and the electrical grid. This relationship aims to address several critical challenges faced by both the transportation and energy sectors. For the transportation sector, V2G offers the potential to reduce the total cost of EV ownership by allowing vehicle owners to monetize their battery capacity when the vehicle is not in use. For the energy sector, V2G presents an opportunity to enhance grid flexibility, improve renewable energy integration, and reduce the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades.
As the global push towards decarbonization intensifies, V2G technology is poised to play a crucial role in achieving sustainable energy goals. The technology aligns with the broader trends of electrification, decentralization, and digitalization in the energy sector. It offers a unique solution to the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources by providing a distributed network of energy storage units in the form of EV batteries.
The current technological landscape for V2G is characterized by rapid advancements in several key areas. These include improvements in bidirectional charging hardware, development of sophisticated energy management systems, and the creation of standardized communication protocols between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. However, the full realization of V2G potential requires overcoming significant technical, regulatory, and market barriers.
Fostering collaborative V2G development partnerships is crucial for addressing these challenges and accelerating the technology's adoption. Such partnerships bring together diverse stakeholders, including automakers, utility companies, technology providers, and policymakers. By combining their expertise and resources, these collaborations can drive innovation, establish industry standards, and create the necessary ecosystem for V2G technology to thrive.
V2G Market Demand Analysis
The Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the need for grid stability. As more EVs enter the market, the potential for V2G technology to provide valuable grid services becomes increasingly apparent. Utility companies and grid operators are recognizing the benefits of V2G in load balancing, peak shaving, and frequency regulation, creating a strong demand for collaborative V2G development partnerships.
The automotive industry is a key driver of V2G market demand. Major automakers are investing heavily in EV technology and are beginning to integrate V2G capabilities into their vehicles. This integration allows EV owners to participate in energy markets, potentially earning revenue by selling excess energy back to the grid during peak demand periods. The growing interest from automakers is creating a ripple effect, stimulating demand for V2G-compatible charging infrastructure and energy management systems.
Energy storage providers are also contributing to the market demand for V2G partnerships. These companies see V2G as a complementary technology to stationary storage solutions, offering a distributed and mobile energy storage network. The combination of V2G and stationary storage can provide more flexible and resilient grid services, attracting interest from utilities and grid operators looking to enhance their energy management capabilities.
Government policies and regulations are playing a crucial role in shaping V2G market demand. Many countries are implementing policies to promote EV adoption and renewable energy integration, indirectly boosting the potential for V2G technology. Incentives for V2G-enabled vehicles and charging infrastructure are being introduced in some regions, further stimulating market growth and partnership opportunities.
The telecommunications sector is emerging as an unexpected player in the V2G market. As 5G networks expand, there is growing interest in using V2G technology to power remote cell towers and provide backup power during outages. This application is creating new partnership opportunities between telecom companies, EV manufacturers, and energy providers.
Smart city initiatives are also driving demand for V2G partnerships. Urban planners and city governments are exploring V2G as part of their sustainable transportation and energy strategies. The integration of V2G into smart city ecosystems is creating opportunities for partnerships between technology companies, urban developers, and energy providers.
The increasing focus on renewable energy integration is another factor contributing to V2G market demand. As the share of intermittent renewable sources in the energy mix grows, there is a greater need for flexible grid balancing solutions. V2G technology offers a distributed and scalable approach to managing these fluctuations, attracting interest from renewable energy developers and grid operators seeking innovative solutions for grid stability.
The automotive industry is a key driver of V2G market demand. Major automakers are investing heavily in EV technology and are beginning to integrate V2G capabilities into their vehicles. This integration allows EV owners to participate in energy markets, potentially earning revenue by selling excess energy back to the grid during peak demand periods. The growing interest from automakers is creating a ripple effect, stimulating demand for V2G-compatible charging infrastructure and energy management systems.
Energy storage providers are also contributing to the market demand for V2G partnerships. These companies see V2G as a complementary technology to stationary storage solutions, offering a distributed and mobile energy storage network. The combination of V2G and stationary storage can provide more flexible and resilient grid services, attracting interest from utilities and grid operators looking to enhance their energy management capabilities.
Government policies and regulations are playing a crucial role in shaping V2G market demand. Many countries are implementing policies to promote EV adoption and renewable energy integration, indirectly boosting the potential for V2G technology. Incentives for V2G-enabled vehicles and charging infrastructure are being introduced in some regions, further stimulating market growth and partnership opportunities.
The telecommunications sector is emerging as an unexpected player in the V2G market. As 5G networks expand, there is growing interest in using V2G technology to power remote cell towers and provide backup power during outages. This application is creating new partnership opportunities between telecom companies, EV manufacturers, and energy providers.
Smart city initiatives are also driving demand for V2G partnerships. Urban planners and city governments are exploring V2G as part of their sustainable transportation and energy strategies. The integration of V2G into smart city ecosystems is creating opportunities for partnerships between technology companies, urban developers, and energy providers.
The increasing focus on renewable energy integration is another factor contributing to V2G market demand. As the share of intermittent renewable sources in the energy mix grows, there is a greater need for flexible grid balancing solutions. V2G technology offers a distributed and scalable approach to managing these fluctuations, attracting interest from renewable energy developers and grid operators seeking innovative solutions for grid stability.
V2G Technical Challenges
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology presents several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation and widespread adoption. One of the primary hurdles is the development of robust and efficient bidirectional charging systems. These systems must be capable of managing power flow in both directions, from the grid to the vehicle and vice versa, while maintaining high efficiency and reliability.
Another critical challenge lies in the integration of V2G systems with existing power grid infrastructure. This requires advanced communication protocols and control systems to ensure seamless coordination between vehicles, charging stations, and the grid. The development of standardized interfaces and protocols is essential to enable interoperability across different vehicle models and charging equipment manufacturers.
Battery degradation is a significant concern in V2G applications. The frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can potentially accelerate battery wear, impacting the overall lifespan of electric vehicle batteries. Addressing this issue requires innovative battery management systems and algorithms that can optimize charging patterns to minimize degradation while maximizing the benefits of V2G services.
Grid stability and power quality are also crucial considerations. As the number of electric vehicles participating in V2G increases, there is a need for sophisticated load balancing and power management strategies to prevent grid instabilities and maintain power quality. This includes developing advanced forecasting models to predict energy demand and supply fluctuations, as well as implementing real-time control systems to manage power flows effectively.
Cybersecurity presents another significant challenge in V2G systems. The interconnected nature of these systems creates potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Ensuring the security and integrity of communication channels, data exchanges, and control systems is paramount to protect both the grid and individual vehicle owners from cyber threats.
Lastly, the development of accurate and fair pricing mechanisms for V2G services remains a complex challenge. This involves creating dynamic pricing models that can account for various factors such as time of day, grid demand, and the state of charge of participating vehicles. Implementing such systems requires advanced metering infrastructure and sophisticated algorithms to ensure equitable compensation for vehicle owners while maintaining grid stability and efficiency.
Another critical challenge lies in the integration of V2G systems with existing power grid infrastructure. This requires advanced communication protocols and control systems to ensure seamless coordination between vehicles, charging stations, and the grid. The development of standardized interfaces and protocols is essential to enable interoperability across different vehicle models and charging equipment manufacturers.
Battery degradation is a significant concern in V2G applications. The frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can potentially accelerate battery wear, impacting the overall lifespan of electric vehicle batteries. Addressing this issue requires innovative battery management systems and algorithms that can optimize charging patterns to minimize degradation while maximizing the benefits of V2G services.
Grid stability and power quality are also crucial considerations. As the number of electric vehicles participating in V2G increases, there is a need for sophisticated load balancing and power management strategies to prevent grid instabilities and maintain power quality. This includes developing advanced forecasting models to predict energy demand and supply fluctuations, as well as implementing real-time control systems to manage power flows effectively.
Cybersecurity presents another significant challenge in V2G systems. The interconnected nature of these systems creates potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Ensuring the security and integrity of communication channels, data exchanges, and control systems is paramount to protect both the grid and individual vehicle owners from cyber threats.
Lastly, the development of accurate and fair pricing mechanisms for V2G services remains a complex challenge. This involves creating dynamic pricing models that can account for various factors such as time of day, grid demand, and the state of charge of participating vehicles. Implementing such systems requires advanced metering infrastructure and sophisticated algorithms to ensure equitable compensation for vehicle owners while maintaining grid stability and efficiency.
Current V2G Collaboration Models
01 Bidirectional charging systems for V2G
V2G technology utilizes bidirectional charging systems that allow electric vehicles to not only receive power from the grid but also feed power back into it. This enables EVs to act as mobile energy storage units, providing grid support during peak demand periods or emergencies.- Bidirectional charging systems for electric vehicles: V2G technology enables electric vehicles to not only receive power from the grid but also feed power back into it. This bidirectional charging system allows for more efficient energy management and grid stabilization. The technology includes advanced power electronics and control systems to manage the flow of electricity between the vehicle and the grid.
- Grid integration and load balancing: V2G systems can help balance the electrical grid by using electric vehicles as distributed energy storage units. During peak demand periods, vehicles can supply power to the grid, while charging during off-peak hours. This integration helps to stabilize the grid, reduce the need for additional power plants, and accommodate the increasing share of renewable energy sources.
- Smart charging and energy management: V2G technology incorporates smart charging algorithms and energy management systems to optimize the charging and discharging of electric vehicles. These systems consider factors such as electricity prices, grid demand, and user preferences to determine the best times for charging and discharging, maximizing both grid stability and cost savings for vehicle owners.
- Communication protocols and infrastructure: Effective V2G systems require robust communication protocols and infrastructure to facilitate seamless interaction between vehicles, charging stations, and the grid. This includes standardized interfaces, secure data exchange, and real-time monitoring capabilities to ensure efficient and reliable operation of the V2G network.
- Economic incentives and business models: The implementation of V2G technology involves developing new economic incentives and business models to encourage participation from vehicle owners and utilities. This may include compensation schemes for providing grid services, dynamic pricing structures, and innovative ownership models that balance the benefits and costs of V2G participation among stakeholders.
02 Smart grid integration and management
V2G systems incorporate advanced smart grid technologies for efficient integration and management of electric vehicles. This includes intelligent charging scheduling, real-time monitoring of grid conditions, and automated power flow control between vehicles and the grid.Expand Specific Solutions03 V2G communication protocols and interfaces
Specialized communication protocols and interfaces are developed to facilitate seamless interaction between electric vehicles and the power grid. These protocols ensure secure and efficient data exchange for coordinating charging, discharging, and grid support functions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy market participation and incentives
V2G technology enables electric vehicle owners to participate in energy markets by providing grid services. This includes mechanisms for compensating EV owners for their contribution to grid stability, demand response programs, and integration with renewable energy sources.Expand Specific Solutions05 Battery management and longevity in V2G applications
Advanced battery management systems are developed to optimize the use of electric vehicle batteries in V2G applications. These systems aim to balance grid support functions with battery longevity, considering factors such as state of charge, temperature, and cycling patterns.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V2G Industry Players
The development of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is in its early stages, with the market showing significant growth potential. The global V2G market is expected to expand rapidly, driven by increasing electric vehicle adoption and the need for grid stability. While the technology is still maturing, several key players are actively involved in advancing V2G solutions. Companies like Huawei, Ericsson, and LG Electronics are leveraging their expertise in telecommunications and electronics to develop V2G communication systems. Automotive giants such as Bosch and Fiat (through Centro Ricerche Fiat) are integrating V2G capabilities into vehicle designs. Energy and utility companies like NTT Docomo and Bank of America are exploring V2G's potential for grid management and financial services. As the technology evolves, collaborative partnerships between these diverse sectors will be crucial for fostering widespread V2G adoption and overcoming implementation challenges.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei's V2G collaborative development approach focuses on creating an open ecosystem for vehicle-to-grid integration. They have developed a comprehensive V2G solution that includes smart charging infrastructure, energy management systems, and cloud-based platforms. Huawei's strategy involves partnering with automotive manufacturers, utility companies, and software developers to create a seamless V2G experience. Their solution utilizes AI and big data analytics to optimize charging schedules, predict energy demand, and balance grid loads. Huawei has also implemented blockchain technology to ensure secure and transparent energy transactions between vehicles and the grid[1][3].
Strengths: Strong technological capabilities, extensive partner network, and integrated solution approach. Weaknesses: Potential geopolitical challenges in some markets, and reliance on partnerships for automotive expertise.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch's collaborative V2G development strategy centers on their expertise in automotive systems and IoT technologies. They have developed a modular V2G system that can be easily integrated into various vehicle models and charging infrastructures. Bosch's approach includes smart charging controllers, vehicle communication modules, and grid integration software. They collaborate with energy providers and car manufacturers to create standardized V2G protocols and interfaces. Bosch has also invested in developing bidirectional charging technologies that enable vehicles to not only consume but also supply energy back to the grid, enhancing grid stability and providing additional value to vehicle owners[2][4].
Strengths: Extensive automotive industry experience, strong reputation for quality and reliability. Weaknesses: May face competition from pure-play tech companies in software and data analytics aspects of V2G.
V2G Partnership Case Studies
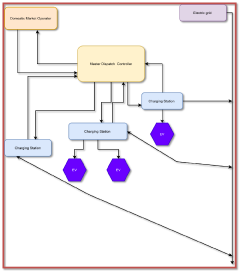
Vehicle to grid (V2G) for ev charging energy management system
PatentPendingIN202141051391A
Innovation
- A discrete unidirectional frequency control approach is implemented, where electric vehicles (EVs) are optimally switched on and off using a dispatch controller to reduce communication messages while ensuring fairness in charging, utilizing a meta-optimizer to select power flow management strategies and allocate target energy proportions to EVs based on priority levels.
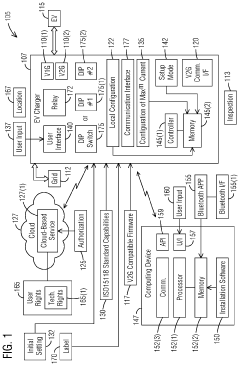
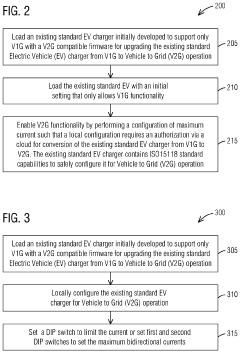
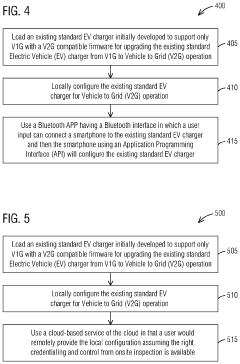
Upgrading an existing standard electric vehicle (EV) charger from grid to vehicle (V1G) to v1g plus vehicle to grid (V2G) operation
PatentPendingUS20240201974A1
Innovation
- A method to locally configure existing standard AC EV chargers with ISO15118 capabilities for V2G operation by loading V2G compatible firmware, authorizing via the cloud, and configuring maximum current, allowing bi-directional charging/discharging through a communication interface.
V2G Policy and Regulatory Framework
The development of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology requires a robust policy and regulatory framework to foster collaborative partnerships and drive innovation. This framework must address several key areas to create an environment conducive to V2G development.
Firstly, clear guidelines for grid integration and interconnection standards are essential. Regulatory bodies need to establish protocols for how electric vehicles (EVs) can safely and efficiently interact with the power grid. These standards should cover technical specifications, communication protocols, and safety measures to ensure seamless integration of V2G systems.
Secondly, the framework must address the complex issue of energy market participation. Regulations should define how EV owners and aggregators can participate in electricity markets, including mechanisms for bidding, pricing, and settlement. This may involve creating new market products or adapting existing ones to accommodate the unique characteristics of V2G services.
Thirdly, data privacy and cybersecurity regulations are crucial. As V2G systems involve the exchange of sensitive information between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators, robust data protection measures must be in place. Regulations should outline data handling practices, consent requirements, and security protocols to safeguard user information and prevent cyber threats.
Furthermore, the policy framework should include incentives to encourage V2G adoption and collaboration. This could involve tax credits for V2G-enabled vehicles, grants for research and development, or preferential rates for grid services provided by EVs. Such incentives can stimulate investment and accelerate the deployment of V2G technology.
The regulatory landscape must also address liability and consumer protection issues. Clear guidelines should be established regarding responsibility for potential damages or malfunctions in V2G systems. Additionally, consumer rights and protections should be defined to ensure fair treatment and transparency in V2G transactions.
Lastly, the framework should promote interoperability and open standards. Regulations should encourage the development of standardized interfaces and protocols to enable seamless communication between different V2G systems, regardless of vehicle make or charging infrastructure provider. This approach fosters innovation and prevents market fragmentation.
By addressing these key areas, a comprehensive policy and regulatory framework can create a fertile ground for collaborative V2G development partnerships, driving the technology forward and realizing its potential to transform the energy landscape.
Firstly, clear guidelines for grid integration and interconnection standards are essential. Regulatory bodies need to establish protocols for how electric vehicles (EVs) can safely and efficiently interact with the power grid. These standards should cover technical specifications, communication protocols, and safety measures to ensure seamless integration of V2G systems.
Secondly, the framework must address the complex issue of energy market participation. Regulations should define how EV owners and aggregators can participate in electricity markets, including mechanisms for bidding, pricing, and settlement. This may involve creating new market products or adapting existing ones to accommodate the unique characteristics of V2G services.
Thirdly, data privacy and cybersecurity regulations are crucial. As V2G systems involve the exchange of sensitive information between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators, robust data protection measures must be in place. Regulations should outline data handling practices, consent requirements, and security protocols to safeguard user information and prevent cyber threats.
Furthermore, the policy framework should include incentives to encourage V2G adoption and collaboration. This could involve tax credits for V2G-enabled vehicles, grants for research and development, or preferential rates for grid services provided by EVs. Such incentives can stimulate investment and accelerate the deployment of V2G technology.
The regulatory landscape must also address liability and consumer protection issues. Clear guidelines should be established regarding responsibility for potential damages or malfunctions in V2G systems. Additionally, consumer rights and protections should be defined to ensure fair treatment and transparency in V2G transactions.
Lastly, the framework should promote interoperability and open standards. Regulations should encourage the development of standardized interfaces and protocols to enable seamless communication between different V2G systems, regardless of vehicle make or charging infrastructure provider. This approach fosters innovation and prevents market fragmentation.
By addressing these key areas, a comprehensive policy and regulatory framework can create a fertile ground for collaborative V2G development partnerships, driving the technology forward and realizing its potential to transform the energy landscape.
V2G Ecosystem Integration Strategies
Fostering collaborative V2G development partnerships requires a comprehensive approach to integrate various stakeholders within the V2G ecosystem. A key strategy is to establish industry-wide standards and protocols that facilitate seamless communication and interoperability between different V2G components. This includes developing common interfaces for vehicle-to-grid communication, standardized charging protocols, and unified data exchange formats. By creating a standardized framework, companies can more easily collaborate and develop compatible solutions, reducing barriers to entry and promoting innovation.
Another crucial aspect of V2G ecosystem integration is the creation of collaborative platforms and consortiums. These platforms bring together automakers, utility companies, charging infrastructure providers, and technology firms to share knowledge, resources, and expertise. Such collaborations can lead to joint research and development initiatives, accelerating the pace of technological advancements and reducing individual company risks. Additionally, these platforms can serve as forums for discussing regulatory challenges and developing unified industry positions to engage with policymakers effectively.
Implementing pilot projects and demonstration programs is essential for testing and refining V2G technologies in real-world scenarios. These initiatives should involve multiple stakeholders, including local governments, utilities, and end-users, to gather comprehensive data and feedback. By showcasing the benefits of V2G technology across various use cases, these projects can help build confidence among potential partners and investors, fostering further collaboration and ecosystem growth.
Developing flexible business models that accommodate the diverse interests of V2G ecosystem participants is crucial for successful integration. This may include revenue-sharing agreements between vehicle owners, aggregators, and utilities, as well as innovative pricing structures for grid services provided by electric vehicles. By creating win-win scenarios for all parties involved, these business models can encourage wider participation and investment in V2G technologies.
Lastly, fostering a supportive regulatory environment is vital for V2G ecosystem integration. This involves working with policymakers to develop regulations that incentivize V2G adoption, clarify market structures for grid services, and address potential barriers such as double taxation of electricity used in V2G transactions. Collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders to engage with regulators can help create a more favorable landscape for V2G development and deployment.
Another crucial aspect of V2G ecosystem integration is the creation of collaborative platforms and consortiums. These platforms bring together automakers, utility companies, charging infrastructure providers, and technology firms to share knowledge, resources, and expertise. Such collaborations can lead to joint research and development initiatives, accelerating the pace of technological advancements and reducing individual company risks. Additionally, these platforms can serve as forums for discussing regulatory challenges and developing unified industry positions to engage with policymakers effectively.
Implementing pilot projects and demonstration programs is essential for testing and refining V2G technologies in real-world scenarios. These initiatives should involve multiple stakeholders, including local governments, utilities, and end-users, to gather comprehensive data and feedback. By showcasing the benefits of V2G technology across various use cases, these projects can help build confidence among potential partners and investors, fostering further collaboration and ecosystem growth.
Developing flexible business models that accommodate the diverse interests of V2G ecosystem participants is crucial for successful integration. This may include revenue-sharing agreements between vehicle owners, aggregators, and utilities, as well as innovative pricing structures for grid services provided by electric vehicles. By creating win-win scenarios for all parties involved, these business models can encourage wider participation and investment in V2G technologies.
Lastly, fostering a supportive regulatory environment is vital for V2G ecosystem integration. This involves working with policymakers to develop regulations that incentivize V2G adoption, clarify market structures for grid services, and address potential barriers such as double taxation of electricity used in V2G transactions. Collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders to engage with regulators can help create a more favorable landscape for V2G development and deployment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!