How V2G Supports Emergency Power During Outages?
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V2G Emergency Power Background and Objectives
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology has emerged as a promising solution for enhancing grid resilience and providing emergency power during outages. The concept of V2G has evolved over the past two decades, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the growing need for flexible energy resources. This technology enables bidirectional power flow between EVs and the electrical grid, allowing EVs to serve as mobile energy storage units.
The primary objective of V2G in emergency power scenarios is to leverage the substantial energy storage capacity of EV batteries to support critical infrastructure and maintain essential services during grid failures. This approach aims to mitigate the impact of power outages on communities and improve overall energy security. By utilizing V2G technology, EVs can potentially provide backup power to homes, businesses, and even contribute to grid stabilization efforts during emergencies.
The development of V2G technology for emergency power applications is closely tied to the broader trends in smart grid systems and distributed energy resources. As power grids become more decentralized and digitalized, the integration of EVs as flexible energy assets becomes increasingly feasible and valuable. This aligns with the global push towards renewable energy integration and the need for more resilient power systems in the face of climate change-induced extreme weather events.
Recent advancements in V2G technology have focused on improving the efficiency and reliability of bidirectional power flow, as well as developing standardized communication protocols between vehicles and grid infrastructure. These developments aim to overcome technical barriers and enable seamless integration of EVs into emergency power systems. Additionally, efforts are being made to address regulatory challenges and create incentive structures that encourage EV owners to participate in V2G programs.
The potential impact of V2G technology on emergency power provision is significant. During outages, EVs equipped with V2G capabilities could power essential household appliances, support emergency services, or even feed electricity back into the grid to assist with broader restoration efforts. This distributed approach to emergency power could complement traditional backup generators and enhance community resilience.
As research and development in this field progress, the objectives for V2G emergency power systems continue to evolve. Key goals include increasing the power output capacity of V2G-enabled vehicles, improving the speed and efficiency of power transfer, and developing robust control systems that can effectively manage the flow of electricity between vehicles and the grid during crisis situations. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on integrating V2G capabilities with renewable energy sources and microgrids to create more sustainable and self-sufficient emergency power solutions.
The primary objective of V2G in emergency power scenarios is to leverage the substantial energy storage capacity of EV batteries to support critical infrastructure and maintain essential services during grid failures. This approach aims to mitigate the impact of power outages on communities and improve overall energy security. By utilizing V2G technology, EVs can potentially provide backup power to homes, businesses, and even contribute to grid stabilization efforts during emergencies.
The development of V2G technology for emergency power applications is closely tied to the broader trends in smart grid systems and distributed energy resources. As power grids become more decentralized and digitalized, the integration of EVs as flexible energy assets becomes increasingly feasible and valuable. This aligns with the global push towards renewable energy integration and the need for more resilient power systems in the face of climate change-induced extreme weather events.
Recent advancements in V2G technology have focused on improving the efficiency and reliability of bidirectional power flow, as well as developing standardized communication protocols between vehicles and grid infrastructure. These developments aim to overcome technical barriers and enable seamless integration of EVs into emergency power systems. Additionally, efforts are being made to address regulatory challenges and create incentive structures that encourage EV owners to participate in V2G programs.
The potential impact of V2G technology on emergency power provision is significant. During outages, EVs equipped with V2G capabilities could power essential household appliances, support emergency services, or even feed electricity back into the grid to assist with broader restoration efforts. This distributed approach to emergency power could complement traditional backup generators and enhance community resilience.
As research and development in this field progress, the objectives for V2G emergency power systems continue to evolve. Key goals include increasing the power output capacity of V2G-enabled vehicles, improving the speed and efficiency of power transfer, and developing robust control systems that can effectively manage the flow of electricity between vehicles and the grid during crisis situations. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on integrating V2G capabilities with renewable energy sources and microgrids to create more sustainable and self-sufficient emergency power solutions.
Market Analysis for V2G Emergency Power Solutions
The market for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) emergency power solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing concerns over grid reliability and the need for resilient power systems. As extreme weather events and natural disasters become more frequent, the demand for backup power solutions has surged, particularly in regions prone to outages. V2G technology offers a unique value proposition by leveraging the existing fleet of electric vehicles (EVs) as mobile energy storage units, capable of providing emergency power during grid failures.
Market analysis indicates that the V2G emergency power sector is poised for substantial expansion over the next decade. This growth is fueled by the rapid adoption of EVs, advancements in bidirectional charging technology, and supportive government policies promoting grid resilience. The market potential is particularly strong in areas with high EV penetration and vulnerable power infrastructure, such as coastal regions and urban centers.
Consumer interest in V2G emergency power solutions is on the rise, with homeowners and businesses seeking alternatives to traditional backup generators. The appeal lies in the dual functionality of EVs as both transportation and emergency power sources, offering cost savings and environmental benefits compared to standalone backup systems. This trend is further supported by the increasing range and battery capacity of modern EVs, enhancing their viability as reliable power sources during extended outages.
The commercial and industrial sectors present significant opportunities for V2G emergency power applications. Large-scale implementations at office buildings, manufacturing facilities, and data centers can provide substantial backup capacity while offering potential revenue streams through grid services. Additionally, the public sector, including emergency services and critical infrastructure, is showing growing interest in V2G solutions to enhance community resilience during disasters.
Market challenges include the need for standardization of V2G protocols, integration with existing grid infrastructure, and addressing concerns about battery degradation. However, ongoing technological advancements and collaborative efforts between automakers, utilities, and policymakers are working to overcome these barriers, paving the way for wider adoption.
The competitive landscape is evolving rapidly, with both established automotive companies and innovative startups entering the V2G emergency power market. Strategic partnerships between EV manufacturers, charging infrastructure providers, and energy management companies are becoming increasingly common, aiming to deliver comprehensive V2G solutions to consumers and businesses.
As the market matures, analysts project significant growth potential, with the global V2G market, including emergency power applications, expected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is anticipated to be driven by technological improvements, decreasing costs of bidirectional charging equipment, and increasing awareness of the benefits of V2G systems in enhancing energy security and grid stability.
Market analysis indicates that the V2G emergency power sector is poised for substantial expansion over the next decade. This growth is fueled by the rapid adoption of EVs, advancements in bidirectional charging technology, and supportive government policies promoting grid resilience. The market potential is particularly strong in areas with high EV penetration and vulnerable power infrastructure, such as coastal regions and urban centers.
Consumer interest in V2G emergency power solutions is on the rise, with homeowners and businesses seeking alternatives to traditional backup generators. The appeal lies in the dual functionality of EVs as both transportation and emergency power sources, offering cost savings and environmental benefits compared to standalone backup systems. This trend is further supported by the increasing range and battery capacity of modern EVs, enhancing their viability as reliable power sources during extended outages.
The commercial and industrial sectors present significant opportunities for V2G emergency power applications. Large-scale implementations at office buildings, manufacturing facilities, and data centers can provide substantial backup capacity while offering potential revenue streams through grid services. Additionally, the public sector, including emergency services and critical infrastructure, is showing growing interest in V2G solutions to enhance community resilience during disasters.
Market challenges include the need for standardization of V2G protocols, integration with existing grid infrastructure, and addressing concerns about battery degradation. However, ongoing technological advancements and collaborative efforts between automakers, utilities, and policymakers are working to overcome these barriers, paving the way for wider adoption.
The competitive landscape is evolving rapidly, with both established automotive companies and innovative startups entering the V2G emergency power market. Strategic partnerships between EV manufacturers, charging infrastructure providers, and energy management companies are becoming increasingly common, aiming to deliver comprehensive V2G solutions to consumers and businesses.
As the market matures, analysts project significant growth potential, with the global V2G market, including emergency power applications, expected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is anticipated to be driven by technological improvements, decreasing costs of bidirectional charging equipment, and increasing awareness of the benefits of V2G systems in enhancing energy security and grid stability.
V2G Technology Status and Challenges for Emergency Power
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology has made significant strides in recent years, but its application for emergency power during outages still faces several challenges. The current status of V2G technology for emergency power is characterized by a mix of promising advancements and persistent obstacles.
One of the primary challenges is the limited availability of V2G-capable electric vehicles (EVs) in the market. While many EVs can draw power from the grid, fewer models are equipped with bidirectional charging capabilities necessary for V2G applications. This scarcity of compatible vehicles restricts the potential scale of V2G emergency power systems.
Infrastructure limitations also pose a significant hurdle. The existing power grid infrastructure in many areas is not yet equipped to handle bidirectional power flow on a large scale. Upgrading substations, transformers, and local distribution networks to accommodate V2G technology requires substantial investments and time.
Technical challenges persist in the realm of power conversion and grid synchronization. Ensuring seamless integration of EV batteries with the grid during outages demands sophisticated inverter technologies and control systems. These must be capable of maintaining power quality and grid stability while managing the variable nature of EV battery discharge.
Battery degradation concerns remain a key issue for widespread V2G adoption. The frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can potentially accelerate battery wear, leading to reduced vehicle range and lifespan. Addressing these concerns through advanced battery management systems and optimized cycling strategies is crucial for user acceptance.
Regulatory and policy frameworks present another set of challenges. Many regions lack clear guidelines for V2G implementation, particularly for emergency power applications. Issues such as liability, grid access, and compensation mechanisms for EV owners providing emergency power services need to be addressed through comprehensive policies.
Despite these challenges, V2G technology has shown promising results in pilot projects and small-scale implementations. Several successful demonstrations have proven the concept's viability for providing emergency backup power to critical facilities and residential areas during outages.
Advancements in smart grid technologies and energy management systems are gradually improving the integration capabilities of V2G systems. These developments are enhancing the ability to coordinate multiple EVs as distributed energy resources, optimizing their collective contribution to grid stability and emergency power supply.
As the technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of V2G as a reliable source of emergency power during outages. Overcoming these obstacles will require collaborative efforts from automakers, utility companies, policymakers, and technology developers to create a robust and scalable V2G ecosystem.
One of the primary challenges is the limited availability of V2G-capable electric vehicles (EVs) in the market. While many EVs can draw power from the grid, fewer models are equipped with bidirectional charging capabilities necessary for V2G applications. This scarcity of compatible vehicles restricts the potential scale of V2G emergency power systems.
Infrastructure limitations also pose a significant hurdle. The existing power grid infrastructure in many areas is not yet equipped to handle bidirectional power flow on a large scale. Upgrading substations, transformers, and local distribution networks to accommodate V2G technology requires substantial investments and time.
Technical challenges persist in the realm of power conversion and grid synchronization. Ensuring seamless integration of EV batteries with the grid during outages demands sophisticated inverter technologies and control systems. These must be capable of maintaining power quality and grid stability while managing the variable nature of EV battery discharge.
Battery degradation concerns remain a key issue for widespread V2G adoption. The frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can potentially accelerate battery wear, leading to reduced vehicle range and lifespan. Addressing these concerns through advanced battery management systems and optimized cycling strategies is crucial for user acceptance.
Regulatory and policy frameworks present another set of challenges. Many regions lack clear guidelines for V2G implementation, particularly for emergency power applications. Issues such as liability, grid access, and compensation mechanisms for EV owners providing emergency power services need to be addressed through comprehensive policies.
Despite these challenges, V2G technology has shown promising results in pilot projects and small-scale implementations. Several successful demonstrations have proven the concept's viability for providing emergency backup power to critical facilities and residential areas during outages.
Advancements in smart grid technologies and energy management systems are gradually improving the integration capabilities of V2G systems. These developments are enhancing the ability to coordinate multiple EVs as distributed energy resources, optimizing their collective contribution to grid stability and emergency power supply.
As the technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of V2G as a reliable source of emergency power during outages. Overcoming these obstacles will require collaborative efforts from automakers, utility companies, policymakers, and technology developers to create a robust and scalable V2G ecosystem.
Current V2G Emergency Power Solutions
01 V2G emergency power supply systems
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) systems can be utilized as emergency power sources during grid outages or disasters. These systems allow electric vehicles to supply power back to the grid or directly to buildings, providing a reliable backup power source in critical situations. The integration of V2G technology with emergency response systems enhances overall grid resilience and community preparedness.- V2G systems for emergency power supply: Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) systems can be utilized to provide emergency power during grid outages or disasters. These systems allow electric vehicles to feed power back into the grid or directly to buildings, acting as mobile power sources. This capability enhances grid resilience and provides backup power for critical infrastructure and households during emergencies.
- Bidirectional charging infrastructure for V2G: Bidirectional charging stations and infrastructure are crucial for enabling V2G emergency power capabilities. These systems allow for two-way power flow between electric vehicles and the grid, facilitating both charging and discharging of vehicle batteries. Advanced control systems manage the power flow to ensure grid stability and optimal use of vehicle batteries during emergencies.
- Smart grid integration for V2G emergency power: Integration of V2G systems with smart grid technologies enhances the effectiveness of emergency power provision. Smart grid systems can dynamically manage power distribution, prioritize critical loads, and coordinate multiple V2G-enabled vehicles to provide a stable power supply during emergencies. This integration improves overall grid resilience and responsiveness to power outages.
- Battery management for V2G emergency applications: Effective battery management is essential for V2G emergency power applications. Advanced battery management systems optimize the use of vehicle batteries, balancing the needs of emergency power provision with maintaining sufficient charge for vehicle operation. These systems monitor battery health, manage discharge rates, and implement protective measures to ensure long-term battery life while providing reliable emergency power.
- V2G communication protocols for emergency scenarios: Specialized communication protocols are developed for V2G systems to facilitate rapid and reliable emergency power deployment. These protocols enable seamless communication between vehicles, charging infrastructure, and grid operators during emergency situations. They support quick activation of V2G resources, coordinate power distribution, and ensure secure and efficient data exchange in critical scenarios.
02 Bidirectional charging infrastructure for V2G
Bidirectional charging stations and infrastructure are crucial for enabling V2G emergency power capabilities. These systems allow for seamless power flow between vehicles and the grid, facilitating both charging and discharging operations. Advanced control algorithms and communication protocols ensure efficient power management and coordination between multiple vehicles and the grid during emergency situations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Smart grid integration and management for V2G
Integration of V2G systems with smart grid technologies enables more effective management of emergency power resources. This includes real-time monitoring of vehicle battery status, predictive analytics for power demand, and automated load balancing. Smart grid integration enhances the reliability and efficiency of V2G emergency power distribution, ensuring optimal utilization of available resources.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mobile emergency power units using V2G technology
Mobile V2G units can be deployed as flexible emergency power sources in various scenarios. These units consist of specially equipped electric vehicles or trailers with high-capacity batteries and power conversion systems. They can be quickly dispatched to disaster-stricken areas or temporary shelters, providing essential power for critical services and equipment.Expand Specific Solutions05 V2G emergency power management software and algorithms
Specialized software and algorithms are developed to optimize the use of V2G systems for emergency power applications. These include power allocation strategies, battery state-of-charge management, and prioritization of critical loads. Advanced algorithms also consider factors such as vehicle availability, grid stability, and energy pricing to maximize the effectiveness of V2G emergency power systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in V2G Emergency Power Industry
The V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) technology market is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest from automotive manufacturers, utilities, and energy companies. The market size is expanding, driven by the growing adoption of electric vehicles and the need for grid stability. While still evolving, V2G technology is progressing towards maturity, with companies like Hyundai, Kia, and Toyota leading innovation in the automotive sector. State Grid Corporation of China and its regional subsidiaries are actively exploring V2G applications for grid support. Research institutions such as the Chinese Academy of Science Guangzhou Energy Research Institute and universities like Sichuan University and Tianjin University are contributing to technological advancements. As the technology matures, collaboration between automakers, utilities, and technology providers will be crucial for widespread V2G implementation and emergency power support during outages.
State Grid Corp. of China
Technical Solution: State Grid Corp. of China has developed a comprehensive V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) system to support emergency power during outages. Their solution integrates electric vehicles (EVs) into the power grid, allowing bidirectional power flow. During outages, EVs can discharge stored energy back to the grid or directly to critical infrastructure. The system includes smart charging stations, advanced power electronics, and a centralized management platform. It can prioritize power distribution based on emergency needs, ensuring essential services remain operational. The V2G system also incorporates load forecasting and real-time monitoring to optimize grid stability[1][3]. State Grid has implemented this technology in several pilot projects across China, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing grid resilience and emergency response capabilities[5].
Strengths: Extensive grid infrastructure, large-scale implementation capability, advanced power management technology. Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment costs, reliance on widespread EV adoption.
China Southern Power Grid Research Institute Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: China Southern Power Grid Research Institute has developed an innovative V2G system focused on microgrid integration for emergency power support. Their approach involves creating localized V2G-enabled microgrids that can operate independently during outages. The system utilizes advanced power electronics and control algorithms to seamlessly transition between grid-connected and islanded modes. It incorporates machine learning for predicting power demand and optimizing EV charging/discharging schedules. The institute has also developed specialized V2G chargers with enhanced efficiency and faster response times for emergency situations. Their solution includes a mobile app for EV owners to participate in emergency power provision, offering incentives for those who contribute during critical periods[2][4].
Strengths: Microgrid expertise, advanced control algorithms, user-friendly interface for EV owners. Weaknesses: Limited to regions with developed microgrid infrastructure, potential scalability challenges.
Core V2G Technologies for Emergency Power Supply
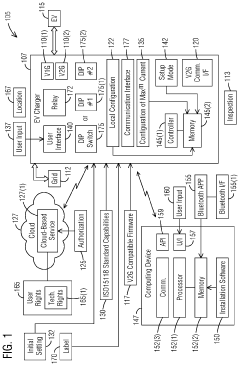
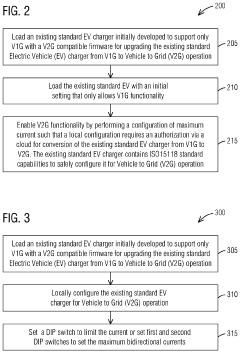
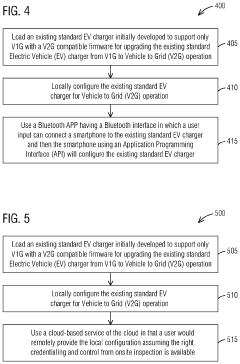
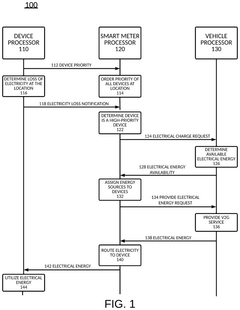
Upgrading an existing standard electric vehicle (EV) charger from grid to vehicle (V1G) to v1g plus vehicle to grid (V2G) operation
PatentPendingUS20240201974A1
Innovation
- A method to locally configure existing standard AC EV chargers with ISO15118 capabilities for V2G operation by loading V2G compatible firmware, authorizing via the cloud, and configuring maximum current, allowing bi-directional charging/discharging through a communication interface.
Directed energy distribution
PatentPendingUS20250231541A1
Innovation
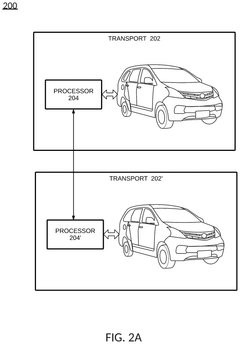
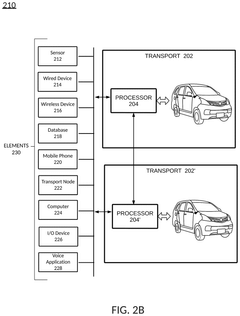
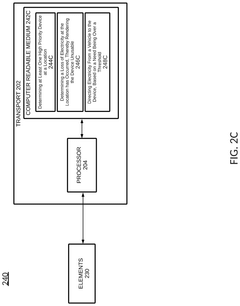
- A system that utilizes vehicle-to-grid technology (V2G) to redirect electricity from connected vehicles to high-priority devices using smart meter processors and vehicle processors, ensuring critical devices receive power by rerouting energy from available sources, including vehicles, backup batteries, and other energy sources.
Grid Integration and Infrastructure Requirements
The integration of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology into existing power infrastructure requires significant modifications and upgrades to the electrical grid. To support emergency power during outages effectively, several key infrastructure components and integration strategies must be implemented.
Firstly, bidirectional charging stations are essential for enabling V2G functionality. These stations must be capable of both charging electric vehicles (EVs) and drawing power from them when needed. The widespread deployment of such charging stations is crucial for creating a robust V2G network that can provide emergency power during outages.
Smart grid technologies play a vital role in facilitating V2G integration. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and smart inverters are necessary to manage the bidirectional flow of electricity between EVs and the grid. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of power flow, ensuring efficient utilization of EV batteries during emergencies.
Grid stability and power quality management systems must be enhanced to handle the intermittent nature of V2G power supply. This includes implementing advanced voltage and frequency regulation mechanisms to maintain grid stability when drawing power from multiple EVs simultaneously.
Communication infrastructure is another critical component for successful V2G integration. Robust, low-latency communication networks are required to enable real-time coordination between EVs, charging stations, and grid operators. This infrastructure ensures rapid response times during power outages and efficient allocation of available EV battery resources.
Energy management systems (EMS) need to be upgraded to incorporate V2G capabilities. These systems must be able to forecast power demand, manage EV charging schedules, and optimize the use of EV batteries as distributed energy resources during emergencies.
Grid operators must also implement advanced control systems capable of seamlessly integrating V2G resources into their existing power distribution networks. This includes developing algorithms for optimal dispatch of EV power during outages and ensuring proper load balancing across the grid.
Lastly, the physical infrastructure of the power grid may require reinforcement to handle increased power flows and bidirectional energy transfer. This could involve upgrading transformers, power lines, and substations to accommodate the additional stress placed on the system by V2G operations during emergency situations.
Firstly, bidirectional charging stations are essential for enabling V2G functionality. These stations must be capable of both charging electric vehicles (EVs) and drawing power from them when needed. The widespread deployment of such charging stations is crucial for creating a robust V2G network that can provide emergency power during outages.
Smart grid technologies play a vital role in facilitating V2G integration. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and smart inverters are necessary to manage the bidirectional flow of electricity between EVs and the grid. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of power flow, ensuring efficient utilization of EV batteries during emergencies.
Grid stability and power quality management systems must be enhanced to handle the intermittent nature of V2G power supply. This includes implementing advanced voltage and frequency regulation mechanisms to maintain grid stability when drawing power from multiple EVs simultaneously.
Communication infrastructure is another critical component for successful V2G integration. Robust, low-latency communication networks are required to enable real-time coordination between EVs, charging stations, and grid operators. This infrastructure ensures rapid response times during power outages and efficient allocation of available EV battery resources.
Energy management systems (EMS) need to be upgraded to incorporate V2G capabilities. These systems must be able to forecast power demand, manage EV charging schedules, and optimize the use of EV batteries as distributed energy resources during emergencies.
Grid operators must also implement advanced control systems capable of seamlessly integrating V2G resources into their existing power distribution networks. This includes developing algorithms for optimal dispatch of EV power during outages and ensuring proper load balancing across the grid.
Lastly, the physical infrastructure of the power grid may require reinforcement to handle increased power flows and bidirectional energy transfer. This could involve upgrading transformers, power lines, and substations to accommodate the additional stress placed on the system by V2G operations during emergency situations.
Regulatory Framework for V2G Emergency Power
The regulatory framework for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) emergency power is a critical component in enabling the widespread adoption and implementation of this technology during power outages. As V2G systems become increasingly integrated into emergency response strategies, governments and regulatory bodies are developing comprehensive guidelines to ensure safe, efficient, and equitable use of electric vehicles as power sources.
At the federal level, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has issued orders to remove barriers for distributed energy resources, including V2G, to participate in wholesale electricity markets. These orders provide a foundation for states to develop their own regulatory frameworks that support V2G integration into emergency power systems.
State-level regulations play a crucial role in shaping the V2G landscape for emergency power. California, for instance, has been at the forefront of V2G policy development. The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has established rules for V2G participation in demand response programs and is working on regulations to facilitate V2G integration into the state's emergency preparedness plans.
Many states are following suit, developing regulations that address key aspects of V2G emergency power deployment. These include safety standards for bidirectional charging equipment, protocols for grid interconnection during emergencies, and guidelines for compensating EV owners who provide power during outages.
Regulatory frameworks also focus on ensuring equitable access to V2G emergency power services. This includes provisions for low-income communities and areas prone to frequent power outages. Some states are implementing incentive programs to encourage EV owners to participate in V2G emergency power schemes, offering benefits such as reduced electricity rates or tax credits.
Cybersecurity is another critical area addressed in V2G regulatory frameworks. As V2G systems involve complex interactions between vehicles, charging infrastructure, and the grid, regulations are being developed to protect against potential cyber threats and ensure the resilience of emergency power systems.
Interoperability standards are also a key focus of regulatory efforts. These standards aim to ensure that V2G systems from different manufacturers can work seamlessly together during emergency situations, maximizing the potential power available during outages.
As the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks are being designed with flexibility in mind, allowing for updates and adaptations to accommodate new technological advancements and changing grid requirements. This adaptive approach ensures that regulations remain relevant and effective in supporting V2G as a reliable emergency power source.
At the federal level, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has issued orders to remove barriers for distributed energy resources, including V2G, to participate in wholesale electricity markets. These orders provide a foundation for states to develop their own regulatory frameworks that support V2G integration into emergency power systems.
State-level regulations play a crucial role in shaping the V2G landscape for emergency power. California, for instance, has been at the forefront of V2G policy development. The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has established rules for V2G participation in demand response programs and is working on regulations to facilitate V2G integration into the state's emergency preparedness plans.
Many states are following suit, developing regulations that address key aspects of V2G emergency power deployment. These include safety standards for bidirectional charging equipment, protocols for grid interconnection during emergencies, and guidelines for compensating EV owners who provide power during outages.
Regulatory frameworks also focus on ensuring equitable access to V2G emergency power services. This includes provisions for low-income communities and areas prone to frequent power outages. Some states are implementing incentive programs to encourage EV owners to participate in V2G emergency power schemes, offering benefits such as reduced electricity rates or tax credits.
Cybersecurity is another critical area addressed in V2G regulatory frameworks. As V2G systems involve complex interactions between vehicles, charging infrastructure, and the grid, regulations are being developed to protect against potential cyber threats and ensure the resilience of emergency power systems.
Interoperability standards are also a key focus of regulatory efforts. These standards aim to ensure that V2G systems from different manufacturers can work seamlessly together during emergency situations, maximizing the potential power available during outages.
As the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks are being designed with flexibility in mind, allowing for updates and adaptations to accommodate new technological advancements and changing grid requirements. This adaptive approach ensures that regulations remain relevant and effective in supporting V2G as a reliable emergency power source.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!