How to Ensure Long-Term Viability of V2G Projects?
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V2G Technology Evolution and Objectives
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 1990s. Initially conceptualized as a means to stabilize the power grid using electric vehicle (EV) batteries, V2G has grown into a complex ecosystem integrating renewable energy sources, smart grid technologies, and advanced energy management systems.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a bidirectional flow of electricity between EVs and the power grid. This allows EVs to not only consume electricity but also feed it back into the grid when needed. The long-term goals of V2G projects include grid stabilization, peak load reduction, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
Over the past two decades, V2G technology has progressed through several key stages. The early 2000s saw the development of basic V2G concepts and pilot projects. By the 2010s, advancements in battery technology and power electronics enabled more efficient bidirectional power flow. Currently, V2G is moving towards large-scale implementation and standardization.
The evolution of V2G technology is closely tied to advancements in EV battery capacity and longevity. As battery technology improves, the potential for V2G to provide significant grid services increases. Concurrently, the development of smart charging algorithms and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication protocols has expanded the capabilities of V2G systems.
Looking forward, the objectives of V2G technology are multifaceted. One key goal is to enhance grid resilience by using EV batteries as distributed energy storage units. This can help mitigate the intermittency issues associated with renewable energy sources. Another objective is to create new revenue streams for EV owners, incentivizing V2G participation and accelerating EV adoption.
The long-term viability of V2G projects hinges on overcoming several technical and regulatory challenges. These include minimizing battery degradation from frequent charging and discharging cycles, developing standardized communication protocols, and creating regulatory frameworks that support V2G implementation.
As V2G technology continues to mature, its objectives are expanding beyond grid services. Future goals include integrating V2G with smart home systems, utilizing EVs for emergency power supply during outages, and leveraging V2G as a key component in smart city infrastructure. The ultimate aim is to create a more flexible, efficient, and sustainable energy ecosystem that seamlessly integrates transportation and power systems.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a bidirectional flow of electricity between EVs and the power grid. This allows EVs to not only consume electricity but also feed it back into the grid when needed. The long-term goals of V2G projects include grid stabilization, peak load reduction, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
Over the past two decades, V2G technology has progressed through several key stages. The early 2000s saw the development of basic V2G concepts and pilot projects. By the 2010s, advancements in battery technology and power electronics enabled more efficient bidirectional power flow. Currently, V2G is moving towards large-scale implementation and standardization.
The evolution of V2G technology is closely tied to advancements in EV battery capacity and longevity. As battery technology improves, the potential for V2G to provide significant grid services increases. Concurrently, the development of smart charging algorithms and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication protocols has expanded the capabilities of V2G systems.
Looking forward, the objectives of V2G technology are multifaceted. One key goal is to enhance grid resilience by using EV batteries as distributed energy storage units. This can help mitigate the intermittency issues associated with renewable energy sources. Another objective is to create new revenue streams for EV owners, incentivizing V2G participation and accelerating EV adoption.
The long-term viability of V2G projects hinges on overcoming several technical and regulatory challenges. These include minimizing battery degradation from frequent charging and discharging cycles, developing standardized communication protocols, and creating regulatory frameworks that support V2G implementation.
As V2G technology continues to mature, its objectives are expanding beyond grid services. Future goals include integrating V2G with smart home systems, utilizing EVs for emergency power supply during outages, and leveraging V2G as a key component in smart city infrastructure. The ultimate aim is to create a more flexible, efficient, and sustainable energy ecosystem that seamlessly integrates transportation and power systems.
V2G Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the growing need for grid flexibility. As the global EV market expands, with sales reaching 10.5 million units in 2022, the potential for V2G integration becomes more significant. This growth is further supported by government initiatives and regulations promoting clean energy and grid stability.
V2G technology offers a unique value proposition by enabling bidirectional power flow between EVs and the electrical grid. This capability addresses several critical market needs. Firstly, it provides grid operators with additional resources for load balancing and frequency regulation, enhancing overall grid stability. Secondly, it offers EV owners the opportunity to monetize their vehicle's battery capacity when not in use, creating a new revenue stream.
The demand for V2G services is particularly strong in regions with high renewable energy penetration. As countries strive to increase their reliance on intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind, the need for flexible energy storage solutions grows. V2G can help mitigate the challenges associated with renewable energy integration by providing short-term energy storage and demand response capabilities.
In the commercial and fleet sectors, V2G presents significant opportunities. Fleet operators can leverage V2G to optimize their energy costs and potentially generate additional income. This is especially attractive for businesses with large EV fleets that have predictable usage patterns, allowing for strategic participation in energy markets.
However, the market demand for V2G is not without challenges. Consumer awareness and acceptance of the technology remain limited, with concerns about battery degradation and range anxiety potentially hindering adoption. Additionally, the lack of standardized V2G protocols and infrastructure across different regions creates barriers to widespread implementation.
Despite these challenges, market projections for V2G are optimistic. The global V2G market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, supportive policies, and increasing recognition of its benefits. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, its integration into smart grid systems is likely to accelerate, further boosting demand.
To ensure the long-term viability of V2G projects, addressing these market demands is crucial. This involves developing robust business models that clearly demonstrate the value proposition to all stakeholders, including EV owners, utilities, and grid operators. Furthermore, continued investment in research and development is essential to improve V2G technology, enhance its efficiency, and mitigate concerns about battery life impact.
V2G technology offers a unique value proposition by enabling bidirectional power flow between EVs and the electrical grid. This capability addresses several critical market needs. Firstly, it provides grid operators with additional resources for load balancing and frequency regulation, enhancing overall grid stability. Secondly, it offers EV owners the opportunity to monetize their vehicle's battery capacity when not in use, creating a new revenue stream.
The demand for V2G services is particularly strong in regions with high renewable energy penetration. As countries strive to increase their reliance on intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind, the need for flexible energy storage solutions grows. V2G can help mitigate the challenges associated with renewable energy integration by providing short-term energy storage and demand response capabilities.
In the commercial and fleet sectors, V2G presents significant opportunities. Fleet operators can leverage V2G to optimize their energy costs and potentially generate additional income. This is especially attractive for businesses with large EV fleets that have predictable usage patterns, allowing for strategic participation in energy markets.
However, the market demand for V2G is not without challenges. Consumer awareness and acceptance of the technology remain limited, with concerns about battery degradation and range anxiety potentially hindering adoption. Additionally, the lack of standardized V2G protocols and infrastructure across different regions creates barriers to widespread implementation.
Despite these challenges, market projections for V2G are optimistic. The global V2G market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, supportive policies, and increasing recognition of its benefits. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, its integration into smart grid systems is likely to accelerate, further boosting demand.
To ensure the long-term viability of V2G projects, addressing these market demands is crucial. This involves developing robust business models that clearly demonstrate the value proposition to all stakeholders, including EV owners, utilities, and grid operators. Furthermore, continued investment in research and development is essential to improve V2G technology, enhance its efficiency, and mitigate concerns about battery life impact.
V2G Implementation Challenges
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology holds immense potential for revolutionizing energy management and grid stability. However, its implementation faces several significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure long-term viability. One of the primary obstacles is the high initial investment required for V2G infrastructure. This includes the cost of bidirectional chargers, grid upgrades, and vehicle modifications, which can be prohibitively expensive for many stakeholders.
Another major challenge is the complex regulatory landscape surrounding V2G implementation. Many regions lack clear policies and regulations governing the integration of electric vehicles into the grid. This regulatory uncertainty can deter potential investors and slow down the adoption of V2G technology. Additionally, there are concerns about data privacy and security, as V2G systems involve the exchange of sensitive information between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators.
Technical challenges also pose significant hurdles to V2G implementation. Battery degradation is a key concern, as frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can potentially reduce battery lifespan. This issue needs to be carefully managed to ensure that vehicle owners are not disadvantaged by participating in V2G programs. Furthermore, the development of robust communication protocols and control systems is crucial for seamless integration of vehicles with the grid.
Consumer acceptance and engagement represent another critical challenge. Many vehicle owners may be hesitant to participate in V2G programs due to concerns about battery life, vehicle availability, and perceived inconvenience. Overcoming these reservations requires extensive education and awareness campaigns, as well as the development of user-friendly interfaces and incentive structures that make V2G participation attractive to consumers.
Grid integration challenges also need to be addressed. The existing power infrastructure in many areas may not be equipped to handle the bidirectional flow of electricity required for V2G operations. Upgrading the grid to accommodate this new technology can be a time-consuming and expensive process. Additionally, grid operators must develop sophisticated management systems to effectively coordinate the charging and discharging of large numbers of electric vehicles while maintaining grid stability.
Lastly, the development of sustainable business models for V2G projects remains a significant challenge. Stakeholders need to find ways to fairly distribute the costs and benefits of V2G implementation among vehicle owners, utilities, and other participants. This requires careful consideration of pricing structures, revenue sharing mechanisms, and incentive programs to ensure that all parties can derive value from V2G participation.
Another major challenge is the complex regulatory landscape surrounding V2G implementation. Many regions lack clear policies and regulations governing the integration of electric vehicles into the grid. This regulatory uncertainty can deter potential investors and slow down the adoption of V2G technology. Additionally, there are concerns about data privacy and security, as V2G systems involve the exchange of sensitive information between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators.
Technical challenges also pose significant hurdles to V2G implementation. Battery degradation is a key concern, as frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can potentially reduce battery lifespan. This issue needs to be carefully managed to ensure that vehicle owners are not disadvantaged by participating in V2G programs. Furthermore, the development of robust communication protocols and control systems is crucial for seamless integration of vehicles with the grid.
Consumer acceptance and engagement represent another critical challenge. Many vehicle owners may be hesitant to participate in V2G programs due to concerns about battery life, vehicle availability, and perceived inconvenience. Overcoming these reservations requires extensive education and awareness campaigns, as well as the development of user-friendly interfaces and incentive structures that make V2G participation attractive to consumers.
Grid integration challenges also need to be addressed. The existing power infrastructure in many areas may not be equipped to handle the bidirectional flow of electricity required for V2G operations. Upgrading the grid to accommodate this new technology can be a time-consuming and expensive process. Additionally, grid operators must develop sophisticated management systems to effectively coordinate the charging and discharging of large numbers of electric vehicles while maintaining grid stability.
Lastly, the development of sustainable business models for V2G projects remains a significant challenge. Stakeholders need to find ways to fairly distribute the costs and benefits of V2G implementation among vehicle owners, utilities, and other participants. This requires careful consideration of pricing structures, revenue sharing mechanisms, and incentive programs to ensure that all parties can derive value from V2G participation.
Current V2G Solutions
01 Grid integration and energy management
V2G projects focus on integrating electric vehicles into the power grid, enabling bidirectional energy flow. This involves developing advanced energy management systems to optimize power distribution, balance load, and enhance grid stability. These systems coordinate charging and discharging of vehicles based on grid demand and electricity prices.- Grid integration and energy management: V2G projects focus on integrating electric vehicles into the power grid, enabling bidirectional energy flow. This involves developing advanced energy management systems to optimize power distribution, balance load, and enhance grid stability. These systems coordinate charging and discharging of vehicles based on grid demand and energy prices.
- Economic viability and incentive models: The economic feasibility of V2G projects depends on developing effective incentive models for vehicle owners. This includes designing pricing structures, rewards programs, and financial benefits to encourage participation. Researchers are exploring various business models to ensure profitability for both grid operators and vehicle owners.
- Battery life and degradation management: A critical aspect of V2G viability is managing battery degradation caused by frequent charging and discharging cycles. Research focuses on developing algorithms and control strategies to minimize battery wear, optimize charging patterns, and extend overall battery lifespan. This includes adaptive charging techniques and predictive maintenance systems.
- Communication and cybersecurity protocols: Implementing secure and efficient communication protocols between vehicles, charging stations, and the grid is crucial for V2G project viability. This involves developing robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential threats and ensure data privacy. Standardization efforts are underway to create interoperable systems across different vehicle models and grid infrastructures.
- Regulatory framework and policy support: The success of V2G projects heavily relies on supportive regulatory frameworks and policies. This includes developing guidelines for grid integration, standardizing V2G technologies, and creating favorable market conditions. Policymakers are working on incentives, tax benefits, and regulations to promote widespread adoption of V2G technologies and ensure their long-term viability.
02 Economic viability and incentive structures
The economic feasibility of V2G projects depends on creating effective incentive structures for vehicle owners. This includes developing pricing models, reward systems, and financial benefits to encourage participation. Factors such as battery degradation costs, electricity price differentials, and regulatory support are considered in assessing the economic viability of V2G implementations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Technical infrastructure and communication protocols
Successful V2G projects require robust technical infrastructure and standardized communication protocols. This involves developing charging stations capable of bidirectional power flow, implementing secure data exchange systems between vehicles and the grid, and ensuring interoperability across different vehicle models and grid systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Battery management and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) applications
Effective battery management is crucial for V2G viability, focusing on minimizing battery degradation and optimizing charging/discharging cycles. Additionally, V2G technology is expanding into V2X applications, allowing vehicles to power homes, buildings, or other electric vehicles, increasing the potential use cases and value proposition of the technology.Expand Specific Solutions05 Regulatory framework and policy support
The viability of V2G projects heavily depends on supportive regulatory frameworks and policies. This includes developing standards for grid integration, addressing legal and liability issues, and creating policies that incentivize V2G adoption. Governments and utilities play a crucial role in establishing these frameworks to enable widespread implementation of V2G technology.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V2G Industry Players
The V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) market is in its early growth stage, characterized by increasing pilot projects and technological advancements. The global V2G market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by the rising adoption of electric vehicles and the need for grid stability. While the technology is still evolving, several key players are making strides in its development. Companies like Huawei Technologies, LG Electronics, and Hyundai Mobis are investing in V2G solutions, leveraging their expertise in electronics and automotive systems. Power grid operators such as State Grid Corporation of China and its subsidiaries are also actively exploring V2G applications to enhance grid flexibility and efficiency. As the technology matures, collaboration between automakers, energy companies, and technology providers will be crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of V2G projects.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei's V2G solution integrates advanced power electronics and intelligent energy management systems. Their approach focuses on bidirectional charging stations equipped with high-efficiency inverters, capable of managing both AC and DC charging. The system incorporates real-time grid monitoring and predictive algorithms to optimize energy flow between vehicles and the grid. Huawei's solution also includes a cloud-based platform for remote management and data analytics, enabling grid operators to forecast demand and adjust accordingly[1][3]. To ensure long-term viability, Huawei emphasizes scalability and interoperability, allowing their V2G infrastructure to adapt to evolving vehicle technologies and grid requirements.
Strengths: Strong technological expertise, comprehensive system integration, and global market presence. Weaknesses: Potential geopolitical challenges in some markets, and reliance on partnerships for automotive integration.
State Grid Corp. of China
Technical Solution: State Grid's V2G strategy focuses on large-scale implementation and grid integration. Their approach involves developing a nationwide network of V2G-capable charging stations, integrated with their existing smart grid infrastructure. The company has invested in advanced power management systems that can handle bidirectional power flow at scale. State Grid's solution includes dynamic pricing mechanisms to incentivize V2G participation during peak demand periods[2]. To ensure long-term viability, they are working on standardizing V2G protocols across their network and collaborating with automakers to increase the number of V2G-compatible vehicles. The company is also exploring the use of blockchain technology for secure and transparent energy transactions in V2G systems[4].
Strengths: Extensive grid infrastructure, strong government support, and ability to implement at a national scale. Weaknesses: Potential bureaucratic challenges in rapid innovation and adaptation to new technologies.
V2G Core Innovations
V2G service recommendation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PatentActiveCN118037360A
Innovation
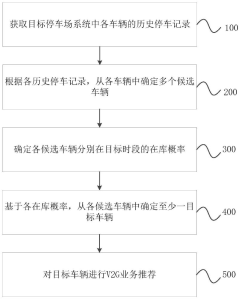
- By obtaining the historical parking records in the target parking lot system, vehicles with a high probability of being in the parking lot during peak power consumption periods are screened out as candidate vehicles, and the target vehicles are determined based on their parking habits to make targeted V2G service recommendations.
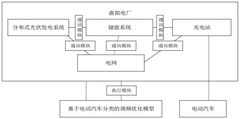
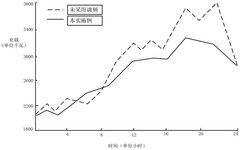
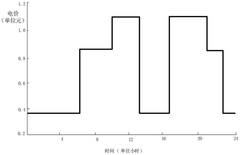
Virtual power plant frequency modulation method and system based on electric vehicle V2G
PatentActiveCN119543229A
Innovation
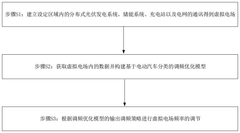
- By establishing a virtual power plant frequency regulation optimization model based on electric vehicle classification, data in the virtual power plant is obtained and frequency regulation optimization model is constructed. The objective function includes the charging cost, network loss cost and peak-to-valley difference of electric private cars and electric operating vehicles, and the frequency regulation of virtual power plant frequency is adjusted according to the frequency regulation strategy output by the model.
V2G Policy and Regulations
The long-term viability of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) projects heavily depends on supportive policy frameworks and well-structured regulations. Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in shaping the V2G landscape through various policy instruments and regulatory mechanisms.
One of the primary policy tools to promote V2G adoption is the implementation of financial incentives. These may include tax credits, rebates, or grants for V2G-enabled vehicles and charging infrastructure. Such incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs for consumers and businesses, making V2G technology more accessible and economically viable.
Regulatory frameworks must also address the integration of V2G systems into existing electricity markets. This involves establishing clear rules for grid participation, defining bidding mechanisms, and ensuring fair compensation for V2G services. Regulators need to create a level playing field that allows V2G to compete with traditional grid resources, such as power plants and stationary energy storage systems.
Standards and protocols are another critical aspect of V2G policy. Governments and industry bodies should collaborate to develop and enforce interoperability standards, ensuring that V2G systems can communicate seamlessly across different vehicle brands, charging stations, and grid operators. This standardization is essential for scaling up V2G deployment and reducing integration costs.
Energy market reforms may be necessary to fully unlock the potential of V2G. This could involve restructuring electricity tariffs to better reflect real-time grid conditions and introducing dynamic pricing mechanisms. Such reforms would create stronger price signals for V2G participation and enhance the economic benefits for vehicle owners.
Policy makers must also address data privacy and cybersecurity concerns associated with V2G systems. Robust regulations should be put in place to protect consumer data and ensure the security of V2G communications. This is crucial for building public trust and preventing potential vulnerabilities in the power grid.
Environmental regulations can further support V2G adoption by recognizing its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and integrating renewable energy sources. Policies that value the environmental benefits of V2G, such as carbon pricing or renewable energy credits, can provide additional revenue streams for V2G projects.
Lastly, regulatory bodies should establish clear guidelines for the measurement and verification of V2G services. This includes defining performance metrics, setting quality standards, and implementing monitoring systems to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of V2G operations.
One of the primary policy tools to promote V2G adoption is the implementation of financial incentives. These may include tax credits, rebates, or grants for V2G-enabled vehicles and charging infrastructure. Such incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs for consumers and businesses, making V2G technology more accessible and economically viable.
Regulatory frameworks must also address the integration of V2G systems into existing electricity markets. This involves establishing clear rules for grid participation, defining bidding mechanisms, and ensuring fair compensation for V2G services. Regulators need to create a level playing field that allows V2G to compete with traditional grid resources, such as power plants and stationary energy storage systems.
Standards and protocols are another critical aspect of V2G policy. Governments and industry bodies should collaborate to develop and enforce interoperability standards, ensuring that V2G systems can communicate seamlessly across different vehicle brands, charging stations, and grid operators. This standardization is essential for scaling up V2G deployment and reducing integration costs.
Energy market reforms may be necessary to fully unlock the potential of V2G. This could involve restructuring electricity tariffs to better reflect real-time grid conditions and introducing dynamic pricing mechanisms. Such reforms would create stronger price signals for V2G participation and enhance the economic benefits for vehicle owners.
Policy makers must also address data privacy and cybersecurity concerns associated with V2G systems. Robust regulations should be put in place to protect consumer data and ensure the security of V2G communications. This is crucial for building public trust and preventing potential vulnerabilities in the power grid.
Environmental regulations can further support V2G adoption by recognizing its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and integrating renewable energy sources. Policies that value the environmental benefits of V2G, such as carbon pricing or renewable energy credits, can provide additional revenue streams for V2G projects.
Lastly, regulatory bodies should establish clear guidelines for the measurement and verification of V2G services. This includes defining performance metrics, setting quality standards, and implementing monitoring systems to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of V2G operations.
V2G Economic Viability
The economic viability of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) projects is a critical factor in ensuring their long-term success and widespread adoption. To achieve this, several key aspects must be considered and addressed.
Firstly, the cost-benefit analysis of V2G implementation needs to be favorable for all stakeholders involved. This includes vehicle owners, utility companies, and grid operators. For vehicle owners, the financial incentives must outweigh the potential costs associated with increased battery degradation and inconvenience. Utility companies and grid operators should see clear economic benefits in terms of grid stability, peak load reduction, and improved energy management.
The development of robust business models is essential for V2G economic viability. These models should account for various revenue streams, such as frequency regulation, demand response, and energy arbitrage. Additionally, they must consider the unique characteristics of different markets and regulatory environments to maximize economic potential.
Infrastructure investment is another crucial aspect of V2G economic viability. The rollout of bidirectional charging stations and the necessary grid upgrades require significant capital expenditure. To justify these investments, a clear path to profitability must be established, taking into account factors such as utilization rates, maintenance costs, and technology obsolescence.
Regulatory frameworks play a vital role in shaping the economic landscape for V2G projects. Supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and streamlined permitting processes, can significantly enhance the financial attractiveness of V2G initiatives. Conversely, unfavorable regulations or lack of clarity can hinder investment and adoption.
The scalability of V2G projects is crucial for long-term economic viability. As the number of participating vehicles increases, economies of scale can be achieved, reducing per-unit costs and improving overall profitability. This scalability also enhances the value proposition for grid operators by providing a larger, more flexible resource for grid management.
Technological advancements, particularly in battery technology and smart charging systems, can significantly impact the economic viability of V2G projects. Improvements in battery life and efficiency can reduce the costs associated with battery degradation, while more sophisticated charging algorithms can optimize energy flows and maximize economic benefits.
Lastly, consumer acceptance and participation are fundamental to the economic success of V2G projects. Education and awareness campaigns, coupled with user-friendly interfaces and transparent compensation schemes, can drive adoption and ensure a stable base of participants, which is essential for the long-term viability of V2G initiatives.
Firstly, the cost-benefit analysis of V2G implementation needs to be favorable for all stakeholders involved. This includes vehicle owners, utility companies, and grid operators. For vehicle owners, the financial incentives must outweigh the potential costs associated with increased battery degradation and inconvenience. Utility companies and grid operators should see clear economic benefits in terms of grid stability, peak load reduction, and improved energy management.
The development of robust business models is essential for V2G economic viability. These models should account for various revenue streams, such as frequency regulation, demand response, and energy arbitrage. Additionally, they must consider the unique characteristics of different markets and regulatory environments to maximize economic potential.
Infrastructure investment is another crucial aspect of V2G economic viability. The rollout of bidirectional charging stations and the necessary grid upgrades require significant capital expenditure. To justify these investments, a clear path to profitability must be established, taking into account factors such as utilization rates, maintenance costs, and technology obsolescence.
Regulatory frameworks play a vital role in shaping the economic landscape for V2G projects. Supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and streamlined permitting processes, can significantly enhance the financial attractiveness of V2G initiatives. Conversely, unfavorable regulations or lack of clarity can hinder investment and adoption.
The scalability of V2G projects is crucial for long-term economic viability. As the number of participating vehicles increases, economies of scale can be achieved, reducing per-unit costs and improving overall profitability. This scalability also enhances the value proposition for grid operators by providing a larger, more flexible resource for grid management.
Technological advancements, particularly in battery technology and smart charging systems, can significantly impact the economic viability of V2G projects. Improvements in battery life and efficiency can reduce the costs associated with battery degradation, while more sophisticated charging algorithms can optimize energy flows and maximize economic benefits.
Lastly, consumer acceptance and participation are fundamental to the economic success of V2G projects. Education and awareness campaigns, coupled with user-friendly interfaces and transparent compensation schemes, can drive adoption and ensure a stable base of participants, which is essential for the long-term viability of V2G initiatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!