How to Implement Efficient Hypertonic Protocols in Emergency Care?
Hypertonic Protocols Evolution and Objectives
Hypertonic protocols in emergency care have evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by advancements in medical research and a growing understanding of fluid resuscitation in critical care settings. The primary objective of these protocols is to rapidly restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion in patients experiencing severe hypovolemia, shock, or traumatic brain injury.
The evolution of hypertonic protocols can be traced back to the 1980s when researchers first proposed using small-volume hypertonic saline solutions for fluid resuscitation. This approach aimed to address the limitations of traditional large-volume isotonic fluid administration, which often led to fluid overload and associated complications. The initial focus was on 7.5% hypertonic saline solutions, which demonstrated promising results in animal studies and early clinical trials.
As research progressed, the objectives of hypertonic protocols expanded beyond simple volume expansion. Scientists discovered that hypertonic solutions could also modulate the inflammatory response, reduce intracranial pressure, and improve microcirculatory blood flow. These findings led to the development of more sophisticated protocols combining hypertonic saline with colloids, such as dextran or hydroxyethyl starch, to prolong the volume-expanding effects and enhance the overall resuscitation efficacy.
In recent years, the goals of hypertonic protocols have further evolved to address specific clinical scenarios. For traumatic brain injury, the objective has shifted towards optimizing cerebral perfusion pressure while minimizing secondary brain injury. In septic shock, hypertonic solutions are being explored for their potential immunomodulatory effects and ability to restore endothelial glycocalyx integrity.
The current objectives of implementing efficient hypertonic protocols in emergency care are multifaceted. They aim to achieve rapid hemodynamic stabilization, improve tissue oxygenation, and reduce the overall fluid volume required for resuscitation. Additionally, these protocols seek to mitigate the adverse effects associated with large-volume fluid administration, such as tissue edema and compartment syndrome.
Furthermore, researchers are working towards developing personalized hypertonic protocols that can be tailored to individual patient characteristics and specific disease states. This approach recognizes the heterogeneity of critical illness and aims to optimize outcomes by considering factors such as underlying comorbidities, injury severity, and baseline fluid status.
As the field continues to advance, future objectives for hypertonic protocols include refining dosing strategies, identifying optimal timing for administration, and developing novel formulations that can provide sustained benefits with minimal side effects. The ultimate goal remains to improve patient outcomes in emergency care settings by leveraging the unique properties of hypertonic solutions in a safe and effective manner.
Emergency Care Market Analysis
The emergency care market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by factors such as an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology. The global emergency care market size was valued at approximately $27.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $38.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period.
One of the key segments within the emergency care market is the management of critical conditions, including those requiring hypertonic solutions. The demand for efficient hypertonic protocols in emergency care has been steadily increasing, particularly in the treatment of severe hypovolemia, traumatic brain injury, and other conditions where rapid fluid resuscitation is crucial.
The North American region dominates the emergency care market, accounting for the largest share of global revenue. This can be attributed to well-established healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and the presence of major market players. Europe follows closely, with countries like Germany, France, and the UK leading in emergency care advancements. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare systems and increasing awareness of emergency medical services.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the emergency care market, highlighting the need for robust and efficient protocols in crisis situations. This has led to increased investments in emergency care infrastructure and technologies, including those related to hypertonic solutions and their administration.
Key market trends include the integration of telemedicine in emergency care, the development of portable and user-friendly medical devices, and the adoption of artificial intelligence for rapid diagnosis and treatment decision-making. These trends are expected to shape the future of emergency care delivery, including the implementation of hypertonic protocols.
The market for hypertonic solutions in emergency care is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups. Major players are focusing on developing advanced formulations and delivery systems to improve the efficacy and safety of hypertonic treatments. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on education and training programs for healthcare professionals to ensure the proper implementation of hypertonic protocols in emergency settings.
Challenges in the market include regulatory hurdles, the need for standardized protocols across different healthcare systems, and concerns about potential side effects of hypertonic solutions. However, ongoing research and clinical trials are addressing these challenges, paving the way for more widespread adoption of efficient hypertonic protocols in emergency care.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Therapy
Despite the potential benefits of hypertonic therapy in emergency care, several significant challenges hinder its widespread implementation and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols for hypertonic solution administration. The optimal concentration, volume, and infusion rate of hypertonic solutions vary depending on the specific clinical scenario, patient characteristics, and underlying pathophysiology. This variability makes it difficult for healthcare providers to establish consistent and evidence-based guidelines for hypertonic therapy.
Another challenge lies in the potential adverse effects associated with hypertonic solutions. Rapid infusion of hypertonic fluids can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypernatremia and hyperchloremia. These electrolyte disturbances may exacerbate existing conditions or create new complications, especially in critically ill patients. Additionally, the risk of central pontine myelinolysis due to rapid osmotic shifts remains a concern, particularly in patients with chronic hyponatremia.
The limited availability of point-of-care testing for serum osmolality and electrolyte levels in emergency settings further complicates the safe administration of hypertonic therapy. Without real-time monitoring capabilities, healthcare providers may struggle to titrate hypertonic solutions effectively and prevent iatrogenic complications.
Furthermore, the heterogeneity of patient populations in emergency care settings poses a significant challenge to implementing standardized hypertonic protocols. Factors such as age, comorbidities, and pre-existing fluid and electrolyte imbalances can significantly impact the response to hypertonic therapy, necessitating individualized approaches that may be difficult to implement in time-sensitive emergency situations.
The lack of large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials comparing hypertonic therapy to standard isotonic resuscitation in various emergency conditions also contributes to the uncertainty surrounding its use. This paucity of high-quality evidence makes it challenging for clinicians to make informed decisions about when and how to incorporate hypertonic solutions into their treatment algorithms.
Logistical and practical considerations also present obstacles to the efficient implementation of hypertonic protocols. The need for specialized equipment, such as infusion pumps capable of delivering precise volumes of hypertonic solutions, may not be universally available in all emergency care settings. Additionally, the higher cost of hypertonic solutions compared to standard isotonic fluids may limit their availability in resource-constrained environments.
Existing Hypertonic Protocol Implementations
01 Hypertonic solutions for medical treatments
Hypertonic solutions are used in various medical treatments to improve efficiency. These solutions have a higher concentration of solutes compared to body fluids, which can help in drawing out excess fluid from tissues or creating osmotic gradients for therapeutic purposes. Applications include treating edema, reducing intracranial pressure, and improving wound healing.- Hypertonic solutions for medical treatments: Hypertonic solutions are used in various medical treatments to improve efficiency. These solutions have a higher concentration of solutes compared to body fluids, which can help in drawing out excess fluid from tissues or creating osmotic gradients for therapeutic purposes. Applications include treating edema, reducing intracranial pressure, and improving wound healing.
- Hypertonic protocols in cellular and molecular biology: Hypertonic protocols are employed in cellular and molecular biology research to enhance efficiency in various procedures. These protocols can be used for cell preservation, DNA extraction, and protein isolation. The hypertonic environment created by these protocols can help in maintaining cell integrity, improving yield in nucleic acid extractions, and increasing the purity of isolated biomolecules.
- Hypertonic solutions in dialysis and fluid management: Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in dialysis and fluid management protocols. These solutions can help in achieving more efficient fluid removal during dialysis, managing electrolyte imbalances, and improving overall treatment outcomes for patients with kidney disorders. The use of hypertonic solutions in these protocols can lead to better control of fluid status and reduced treatment times.
- Hypertonic protocols in sports medicine and performance: Hypertonic protocols are utilized in sports medicine to enhance athletic performance and recovery. These protocols may involve the use of hypertonic drinks or solutions to improve hydration, maintain electrolyte balance, and potentially boost endurance. The efficiency of these protocols in improving athletic performance and reducing recovery time is an area of ongoing research and development.
- Hypertonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations: Hypertonic solutions are incorporated into pharmaceutical formulations to enhance the efficiency of drug delivery and absorption. These formulations can improve the solubility and bioavailability of certain drugs, leading to more effective treatments. The use of hypertonic solutions in topical, oral, and injectable formulations is being explored to optimize drug efficacy and patient outcomes.
02 Hypertonic protocols in cell preservation and cryopreservation
Hypertonic protocols are employed in cell preservation and cryopreservation techniques to enhance efficiency. These methods involve using hypertonic solutions to dehydrate cells before freezing, which helps prevent intracellular ice formation and improves cell viability upon thawing. This approach is particularly useful in preserving various cell types and tissues for research and medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypertonic solutions in drug delivery systems
Hypertonic solutions are utilized in drug delivery systems to enhance the efficiency of pharmaceutical administration. These solutions can improve drug absorption, penetration, and distribution in target tissues. The hypertonic environment created by these solutions can also help in overcoming certain biological barriers, leading to more effective drug delivery and improved therapeutic outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypertonic protocols in diagnostic procedures
Hypertonic protocols are employed in various diagnostic procedures to improve efficiency and accuracy. These protocols may involve the use of hypertonic contrast agents or solutions to enhance imaging quality, improve tissue differentiation, or facilitate the detection of specific physiological conditions. The hypertonic nature of these solutions can create temporary changes in fluid dynamics, allowing for better visualization or measurement of certain parameters.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hypertonic solutions in biotechnology and fermentation processes
Hypertonic solutions play a role in improving the efficiency of biotechnology and fermentation processes. These solutions can be used to create osmotic stress in microorganisms, which can lead to increased production of certain metabolites or enhance the expression of specific genes. Additionally, hypertonic environments can be utilized in the purification and concentration of biological products, improving overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Emergency Care Solution Providers
The implementation of efficient hypertonic protocols in emergency care is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global emergency care market is expanding rapidly, driven by rising demand for advanced treatment methods. Technologically, the field is progressing, with companies like ZOLL Medical Corp., Medtronic, and Philips leading innovation. These firms are developing sophisticated solutions, integrating hypertonic protocols with advanced monitoring systems. However, the technology is not yet fully mature, as evidenced by ongoing research from institutions like the University of California and University of Southern California. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established medical device manufacturers and emerging specialized companies contributing to the field's evolution.
ZOLL Medical Corp.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Innovative Hypertonic Therapy Approaches
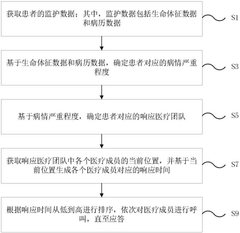
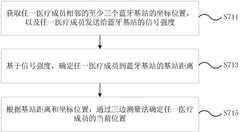
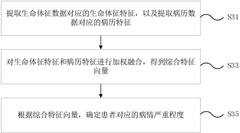
- By collecting patient vital sign data and medical record data in real time, intelligently assess the severity of the disease, automatically match the most suitable medical team, and optimize resource allocation. At the same time, Bluetooth positioning technology is used to track the location of medical team members in real time, calculate the response time, and sort it from low to high according to the response time, and call medical members in turn.
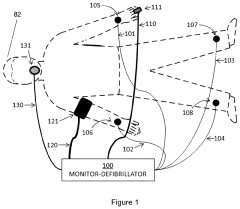
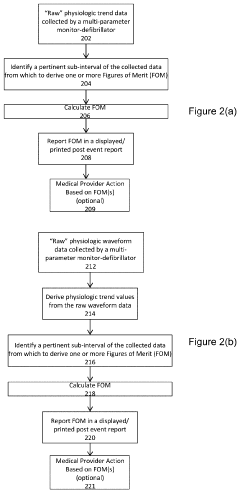
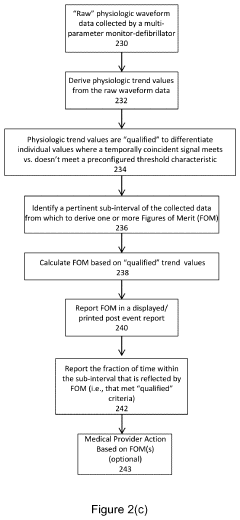
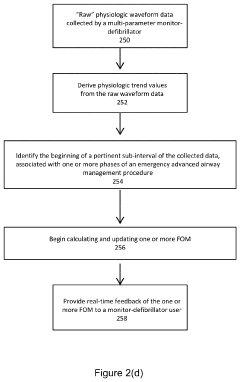
- The implementation of a system that calculates indices like the hypoxemia dose index and ventilation abnormality index based on real-time physiological parameters during a specific time interval relevant to the airway management procedure, using a multi-parameter monitor-defibrillator to generate a summary report that provides actionable insights for quality improvement and patient safety.
Regulatory Framework for Emergency Treatments
The regulatory framework for emergency treatments involving hypertonic protocols is a critical aspect of implementing efficient care in emergency settings. These regulations are designed to ensure patient safety, standardize treatment protocols, and maintain high-quality care across healthcare facilities.
At the federal level, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating hypertonic solutions used in emergency care. The FDA oversees the approval process for these solutions, ensuring they meet safety and efficacy standards before they can be used in clinical practice. Additionally, the agency provides guidelines on proper storage, handling, and administration of hypertonic solutions to minimize risks associated with their use.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) also contribute to the regulatory framework by establishing reimbursement policies for emergency treatments, including those involving hypertonic protocols. These policies influence the adoption and implementation of such treatments in healthcare facilities across the country.
State-level regulations further shape the landscape of emergency care protocols. Each state's Department of Health or equivalent agency may have specific requirements for the use of hypertonic solutions in emergency settings. These regulations often address issues such as staff training, equipment standards, and documentation requirements.
Professional organizations, such as the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), play a significant role in developing clinical practice guidelines for the use of hypertonic protocols in emergency care. While not legally binding, these guidelines often inform regulatory decisions and are widely adopted by healthcare institutions.
The Joint Commission, an independent, non-profit organization that accredits healthcare organizations in the United States, incorporates standards related to emergency care protocols in its accreditation process. Compliance with these standards is often necessary for healthcare facilities to maintain their accreditation status and participate in federal healthcare programs.
Institutional policies and protocols within individual hospitals and emergency departments also form an essential part of the regulatory framework. These policies must align with federal and state regulations while addressing the specific needs and resources of the institution.
As the field of emergency medicine evolves, regulatory bodies continually update their frameworks to incorporate new evidence and best practices. This ongoing process ensures that the regulatory environment remains responsive to advances in hypertonic protocols and other emergency care treatments, ultimately supporting the goal of providing efficient and effective care to patients in critical situations.
Patient Safety and Ethical Considerations
The implementation of hypertonic protocols in emergency care necessitates careful consideration of patient safety and ethical implications. Hypertonic solutions, while effective in certain critical situations, can pose significant risks if not administered properly. Patient safety must be the paramount concern when developing and implementing these protocols.
One of the primary safety considerations is the potential for rapid shifts in electrolyte balance and fluid distribution within the body. Hypertonic solutions can cause rapid changes in serum osmolality, which may lead to complications such as central pontine myelinolysis if not carefully monitored. Healthcare providers must be trained to recognize and manage these potential adverse effects promptly.
Accurate dosing and administration rates are crucial to minimize risks. Protocols should include clear guidelines on dosage calculations based on patient weight, condition, and specific clinical indicators. The use of smart infusion pumps and double-checking procedures can help prevent medication errors and ensure precise delivery of hypertonic solutions.
Ethical considerations come into play when deciding which patients should receive hypertonic therapy. The risk-benefit analysis must be carefully weighed for each individual, taking into account their overall health status, comorbidities, and potential for recovery. Informed consent processes should be established to ensure patients or their legal representatives understand the risks and benefits of hypertonic therapy.
Another ethical aspect is the equitable distribution of resources, particularly in mass casualty situations where hypertonic solutions may be in limited supply. Clear triage protocols must be developed to guide decision-making in such scenarios, balancing individual patient needs with overall public health considerations.
Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential components of patient safety in hypertonic protocols. This includes regular assessments of vital signs, electrolyte levels, and neurological status. Protocols should outline specific criteria for discontinuation or adjustment of therapy based on patient response.
Healthcare providers must also be prepared to manage potential complications promptly. This includes having reversal agents and alternative treatments readily available. Regular training and simulation exercises can help maintain staff competency in managing both routine administration and emergency situations related to hypertonic therapy.
Lastly, the implementation of hypertonic protocols should be accompanied by robust quality assurance measures. This includes systematic data collection, analysis of outcomes, and continuous refinement of protocols based on evidence and clinical experience. Regular audits and peer reviews can help identify areas for improvement and ensure adherence to best practices in patient safety and ethical care delivery.