Hypertonic and Hypertensive: Navigating Treatment Challenges
Hypertension Background
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition characterized by persistently elevated pressure within the blood vessels. This condition has been recognized as a significant health concern for centuries, with the first recorded description dating back to ancient Egyptian medical texts. However, it wasn't until the early 20th century that the importance of blood pressure measurement in clinical practice was fully realized.
The prevalence of hypertension has been steadily increasing worldwide, with an estimated 1.13 billion people affected globally as of 2019. This rise can be attributed to various factors, including population growth, aging, and behavioral risk factors such as unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and excessive alcohol consumption. Hypertension is often referred to as the "silent killer" due to its asymptomatic nature in many cases, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
The classification of hypertension has evolved over time, with current guidelines generally defining it as a systolic blood pressure ≥130 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure ≥80 mmHg. This classification is based on extensive epidemiological studies and clinical trials that have demonstrated the increased risk of cardiovascular events associated with elevated blood pressure levels.
Hypertension is a major risk factor for numerous cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, and peripheral artery disease. It is also closely associated with other health conditions such as chronic kidney disease and cognitive decline. The global burden of hypertension-related morbidity and mortality is substantial, with an estimated 7.5 million deaths annually attributed to this condition.
The etiology of hypertension is complex and multifactorial, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Primary or essential hypertension, which accounts for approximately 90-95% of cases, has no identifiable cause. Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, results from underlying medical conditions such as renal artery stenosis, endocrine disorders, or certain medications.
Over the years, significant advancements have been made in the understanding of hypertension pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. The development of accurate blood pressure measurement techniques, from the mercury sphygmomanometer to modern automated devices, has greatly improved the ability to diagnose and monitor hypertension. Additionally, the introduction of various classes of antihypertensive medications has revolutionized treatment approaches, allowing for more personalized and effective management strategies.
Despite these advancements, hypertension remains a challenging condition to control effectively. Factors such as medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and the presence of comorbidities contribute to the complexity of hypertension management. The ongoing research in this field continues to explore novel therapeutic targets, innovative treatment modalities, and strategies to improve patient outcomes and reduce the global burden of hypertension-related complications.
Market Analysis
The market for hypertonic and hypertensive treatments is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of hypertension and related cardiovascular diseases worldwide. According to recent epidemiological studies, hypertension affects approximately 1.13 billion people globally, with a higher prevalence in low- and middle-income countries. This widespread occurrence has created a substantial demand for effective treatment options, propelling the market forward.
The pharmaceutical industry has responded to this demand by developing a diverse range of antihypertensive medications, including ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics. The market for these drugs has shown steady growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years. This growth is further fueled by the aging population in many developed countries, as the risk of hypertension increases with age.
In addition to traditional pharmaceutical treatments, there is a growing interest in innovative approaches to managing hypertension. These include combination therapies, novel drug delivery systems, and personalized medicine strategies. The market is also seeing an uptick in demand for non-pharmacological interventions, such as lifestyle modification programs and digital health solutions for blood pressure monitoring and management.
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, represent significant growth opportunities for hypertension treatments. The rising middle class in these regions, coupled with increasing awareness of cardiovascular health, is driving demand for both generic and branded antihypertensive medications. However, challenges such as affordability and access to healthcare in these markets remain important considerations for industry players.
The competitive landscape of the hypertonic and hypertensive treatment market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to bring new, more effective treatments to market. There is also a trend towards strategic partnerships and collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and technology firms to develop integrated treatment solutions.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics. Stringent approval processes for new drugs and ongoing safety monitoring requirements influence product development strategies and market entry timelines. Additionally, healthcare policies and reimbursement structures in different countries significantly impact market access and adoption rates for hypertension treatments.
Looking ahead, the market for hypertonic and hypertensive treatments is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing focus on preventive healthcare, advancements in drug discovery technologies, and the potential for precision medicine approaches in hypertension management are likely to drive innovation and market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges
The treatment of hypertonic and hypertensive conditions presents several significant challenges in modern healthcare. One of the primary obstacles is the complex interplay between fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and blood pressure regulation. Clinicians often struggle to achieve optimal management due to the delicate balance required in addressing these interconnected physiological systems.
A major challenge lies in the accurate diagnosis and differentiation between hypertonic and hypertensive states. These conditions can present with similar symptoms, making it difficult to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment approach. The lack of specific diagnostic markers further complicates this process, potentially leading to delays in initiating targeted therapies.
Another significant hurdle is the limited effectiveness of current pharmacological interventions. While various medications exist to address hypertension and fluid imbalances, their efficacy can be inconsistent across patient populations. Additionally, many of these drugs come with substantial side effects, which can impact patient compliance and quality of life. The development of more targeted and well-tolerated treatments remains an ongoing challenge in this field.
The management of comorbidities presents yet another layer of complexity. Patients with hypertonic and hypertensive conditions often have concurrent medical issues, such as diabetes, kidney disease, or cardiovascular disorders. Balancing the treatment of these multiple conditions while avoiding adverse interactions and maintaining overall health is a formidable task for healthcare providers.
Patient adherence to treatment regimens is a persistent challenge in managing these conditions. The chronic nature of hypertension and related disorders requires long-term commitment to medication schedules and lifestyle modifications. However, many patients struggle with maintaining these changes over extended periods, leading to suboptimal outcomes and increased risk of complications.
The impact of environmental and lifestyle factors on hypertonic and hypertensive states is another area of concern. Factors such as diet, stress, and physical activity can significantly influence fluid balance and blood pressure. Developing effective strategies to address these modifiable risk factors and integrate them into comprehensive treatment plans remains a challenge for healthcare professionals.
Lastly, the need for personalized treatment approaches poses a significant hurdle. Given the variability in patient responses to different interventions, tailoring therapies to individual physiological profiles and genetic predispositions is crucial. However, the current understanding of personalized medicine in this field is still evolving, and implementing such approaches on a large scale remains a challenge.
Existing Therapies
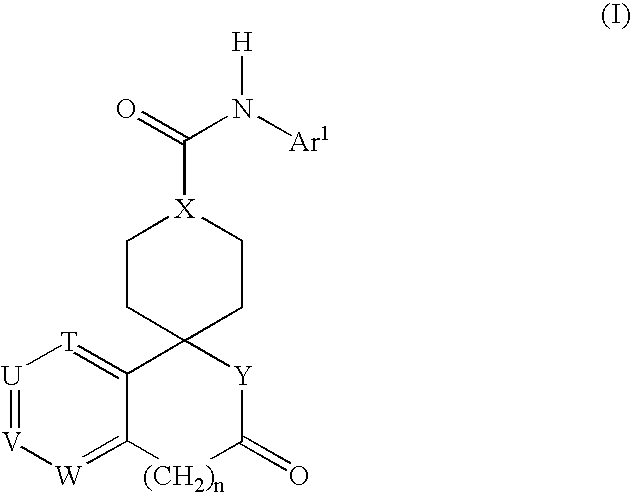
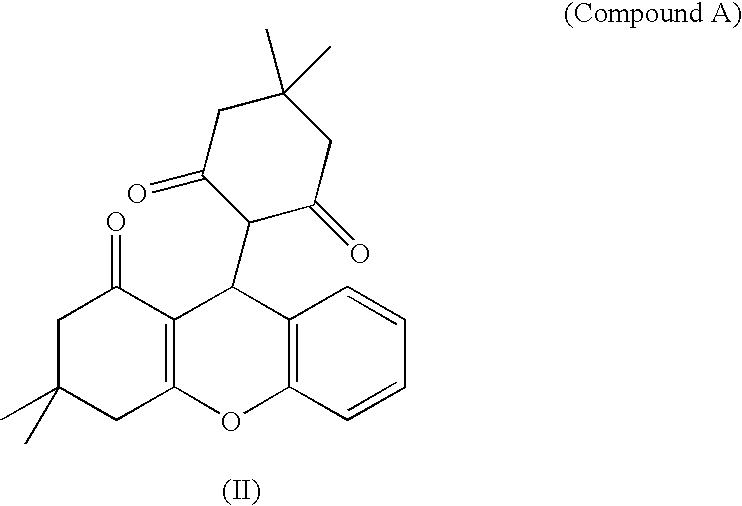
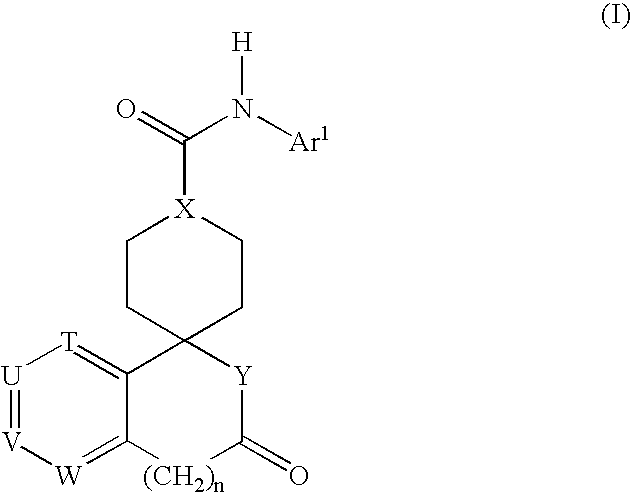
01 Pharmaceutical compositions for treating hypertension
Various pharmaceutical compositions have been developed to treat hypertensive conditions. These may include novel compounds, drug combinations, or formulations designed to effectively lower blood pressure and manage hypertension. The compositions can be administered through different routes and may have improved efficacy or reduced side effects compared to existing treatments.- Pharmaceutical compositions for treating hypertension: Various pharmaceutical compositions have been developed to treat hypertension and hypertonic conditions. These compositions may include active ingredients such as antihypertensive drugs, diuretics, or combinations thereof. The formulations are designed to effectively lower blood pressure and manage hypertensive conditions through different mechanisms of action.
- Medical devices for hypertension treatment: Innovative medical devices have been created to address hypertension and hypertonic conditions. These devices may include specialized catheters, implantable systems, or external apparatus designed to regulate blood pressure or remove excess fluid. Some devices utilize novel technologies to provide targeted treatment for hypertensive patients.
- Biological therapies for hypertension: Biological approaches have been explored for treating hypertension and hypertonic conditions. These may include gene therapies, stem cell treatments, or immunotherapies targeting specific pathways involved in blood pressure regulation. Such therapies aim to provide long-term solutions by addressing the underlying biological mechanisms of hypertension.
- Natural and herbal remedies for hypertension: Various natural and herbal remedies have been investigated for their potential in treating hypertension and hypertonic conditions. These may include plant extracts, traditional medicines, or dietary supplements that have shown promise in lowering blood pressure or improving cardiovascular health. Such approaches often aim to provide alternative or complementary treatments with fewer side effects.
- Combination therapies for hypertension management: Combination therapies have been developed to enhance the effectiveness of hypertension treatment. These may involve combining different classes of antihypertensive drugs, integrating pharmaceutical treatments with lifestyle modifications, or combining medical devices with drug therapies. Such approaches aim to provide comprehensive management of hypertensive conditions and improve patient outcomes.
02 Medical devices for hypertension management
Innovative medical devices have been created to assist in the treatment and monitoring of hypertonic and hypertensive conditions. These may include implantable devices, wearable monitors, or specialized equipment for blood pressure control. Such devices can provide continuous monitoring, targeted therapy, or novel approaches to managing hypertension.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biological therapies for hypertension
Biological approaches to treating hypertension involve the use of proteins, antibodies, or gene therapies. These treatments may target specific pathways involved in blood pressure regulation or address underlying causes of hypertension at a molecular level. Such therapies could offer more personalized and potentially more effective treatment options for patients with hypertonic conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Natural and herbal remedies for hypertension
Various natural and herbal preparations have been developed for the treatment of hypertensive conditions. These may include plant extracts, traditional medicines, or dietary supplements that have shown potential in managing blood pressure. Such remedies may offer alternative or complementary approaches to conventional hypertension treatments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Methods for treating hypertension-related complications
Specialized methods have been developed to address complications associated with hypertonic and hypertensive conditions. These may include treatments for organ damage, vascular issues, or other health problems that arise from chronic hypertension. Such methods aim to improve overall patient outcomes and quality of life for those with hypertension-related complications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Pharmaceutical Players
The treatment landscape for hypertonic and hypertensive conditions is in a mature stage, with a substantial global market size driven by the high prevalence of hypertension. The technological maturity varies across different approaches, from well-established pharmacological interventions to emerging device-based therapies. Companies like Merck & Co., Novartis AG, and AstraZeneca PLC lead in traditional pharmaceutical solutions, while CVRx, Inc. and Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corp. are advancing in neuromodulation technologies. Innovative approaches are being explored by Theravance Biopharma R&D IP LLC and Quantum Genomics SA, focusing on novel drug targets. The field is characterized by a mix of established players and newer entrants, reflecting ongoing efforts to address unmet needs in hypertension management.
Merck & Co., Inc.
Novartis AG
Innovative Approaches
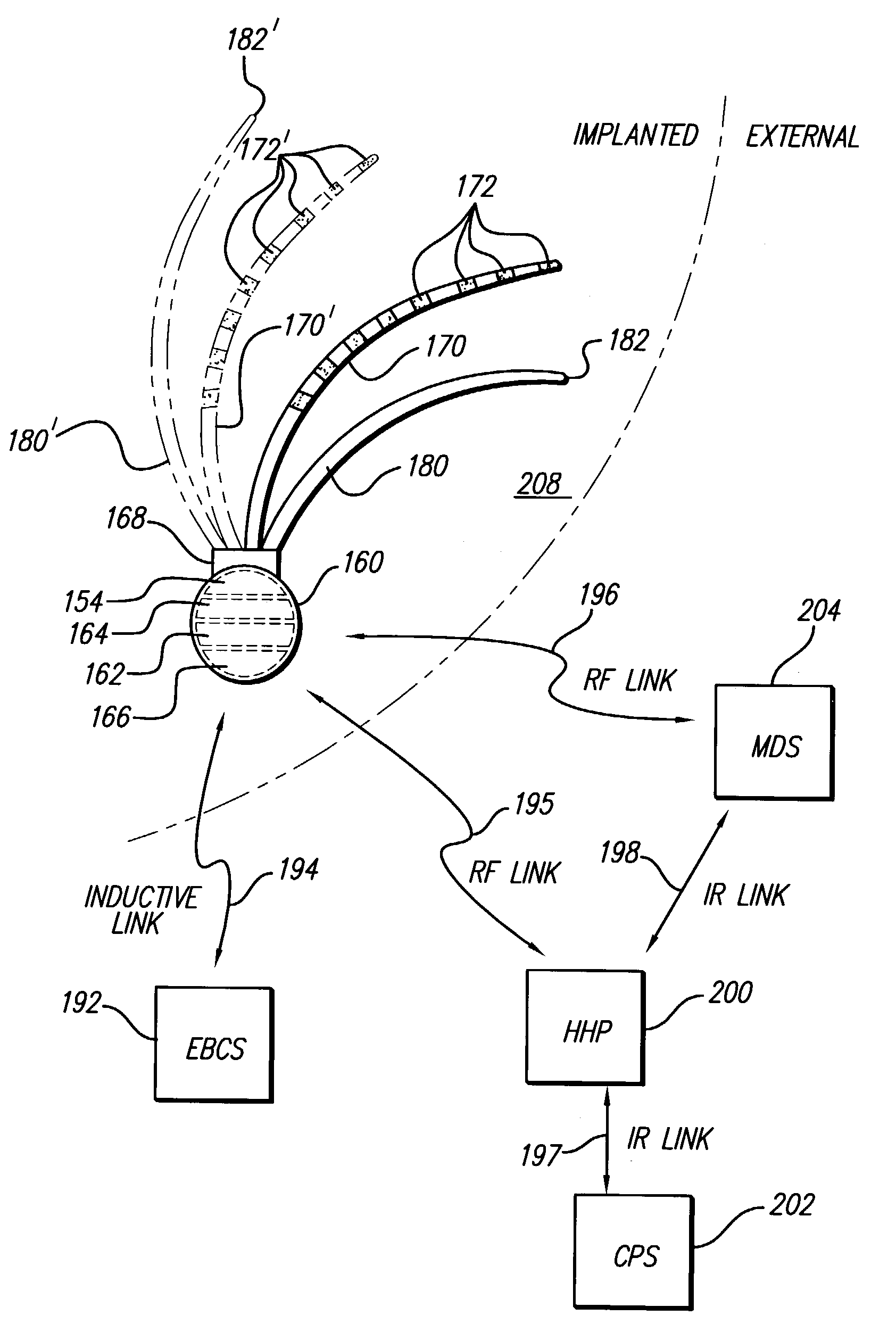
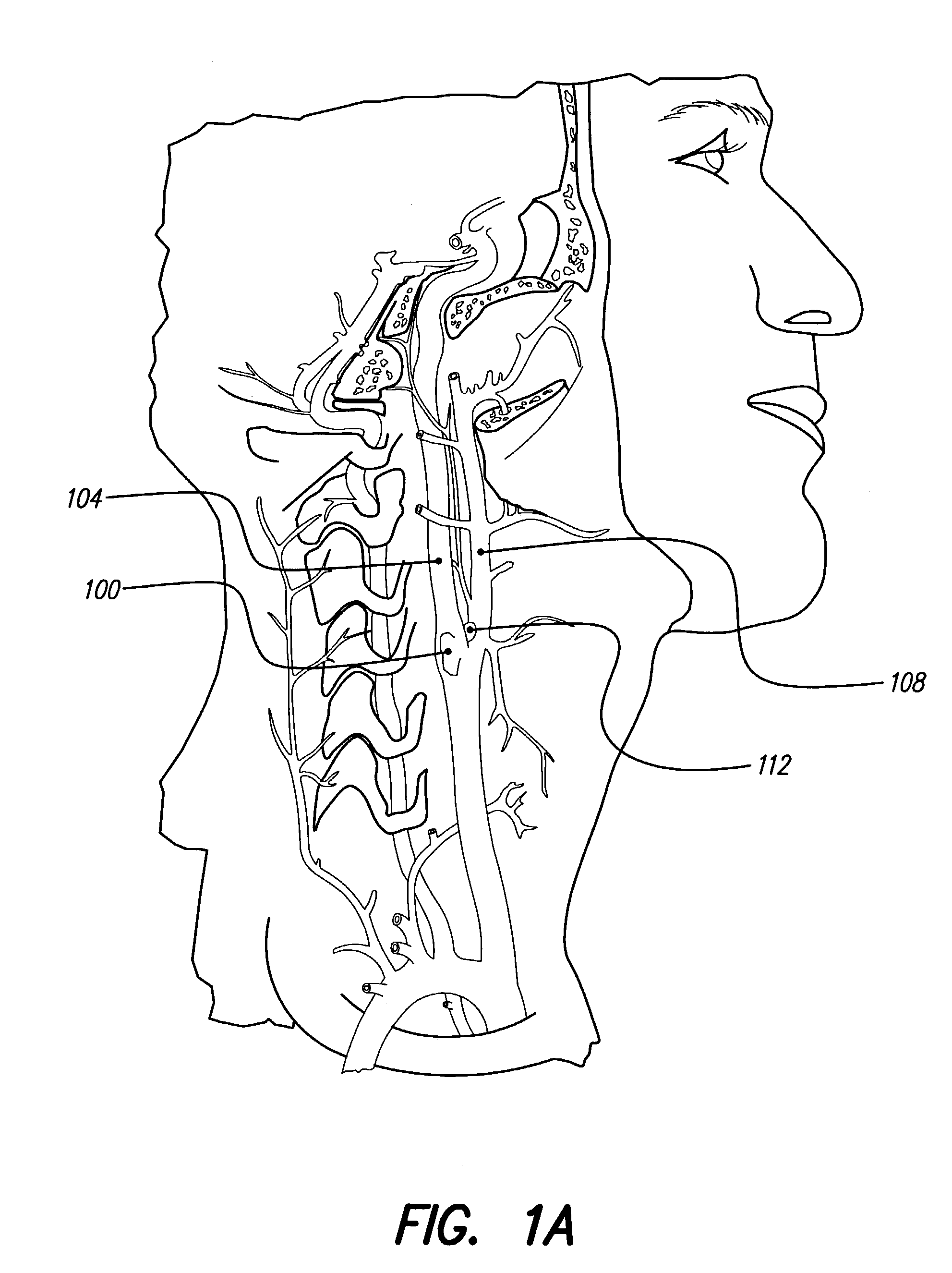
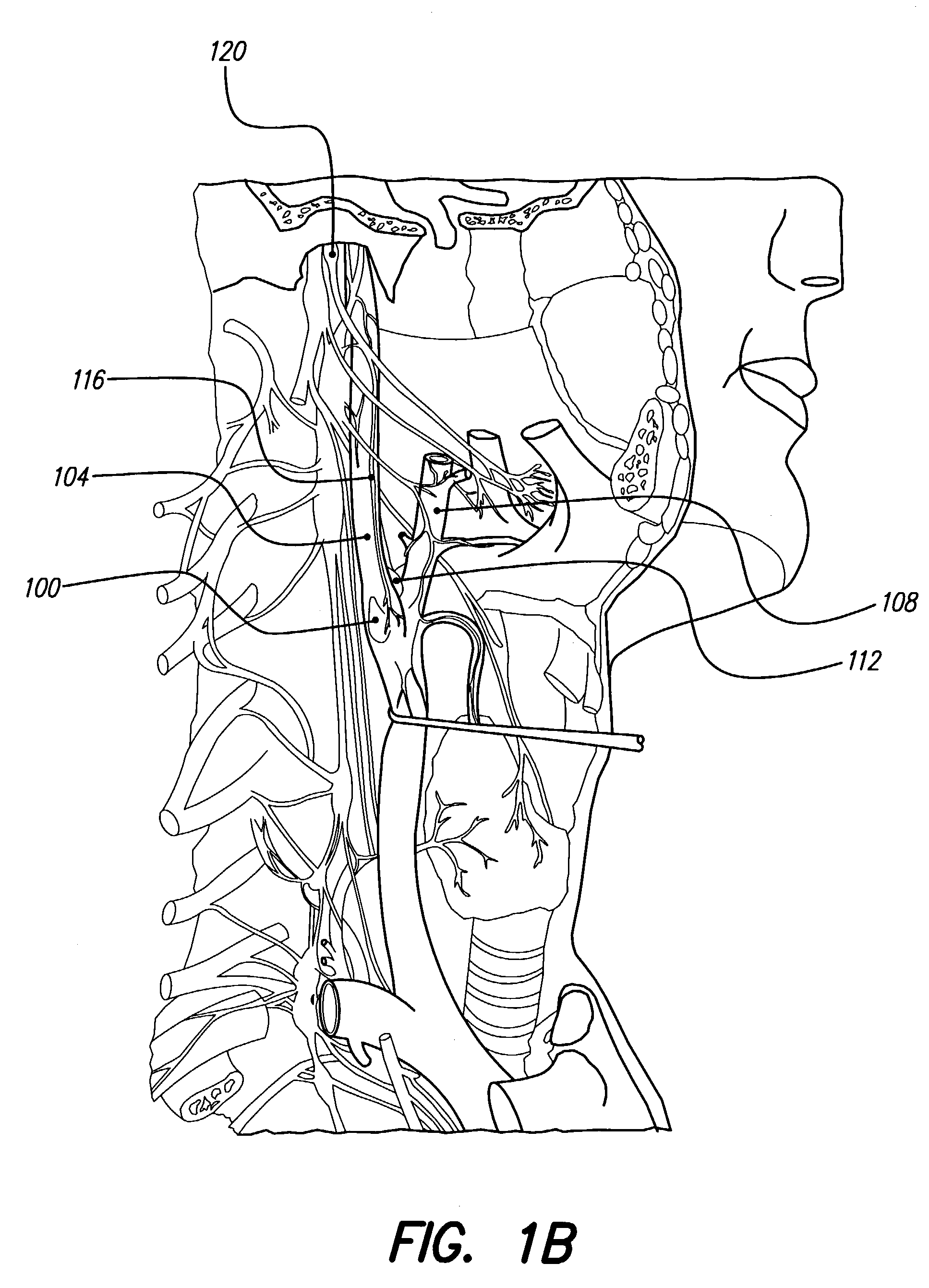
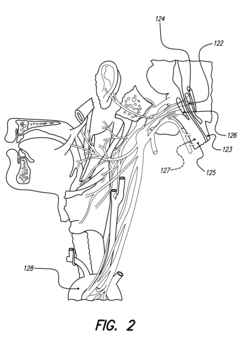
- An implantable system comprising a pump and catheter for drug delivery and an implantable signal generator and electrode for electrical stimulation, allowing for chronic and acute treatment of hypertension through basal or periodic drug infusion and electrical stimulation, respectively, with parameters modulated by sensed data or caregivers.
- A combination therapy comprising at least one anti-obesity agent and at least one anti-hypertensive agent is provided, which can be administered together or separately, to treat obesity, hypertension, and related disorders, with the expectation of enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects compared to monotherapy.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding hypertonic and hypertensive treatments is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the critical nature of these conditions and the potential risks associated with their management. Regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe play pivotal roles in overseeing the development, approval, and marketing of medications and therapies for these conditions.
These agencies have established stringent guidelines for clinical trials, safety monitoring, and efficacy assessments of antihypertensive medications. The approval process typically involves multiple phases of clinical trials, with a focus on demonstrating both short-term and long-term safety profiles, as well as significant improvements in blood pressure control compared to existing treatments or placebos.
In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on real-world evidence and post-marketing surveillance to ensure the ongoing safety and effectiveness of approved treatments. This has led to the implementation of risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) for certain medications, particularly those with potential for serious side effects or those used in high-risk populations.
Regulatory bodies have also established guidelines for the development of combination therapies, recognizing the potential benefits of addressing multiple pathways in blood pressure regulation. These guidelines outline specific requirements for demonstrating the additive or synergistic effects of combination treatments, as well as their safety profiles when used together.
The regulatory landscape also extends to medical devices used in the management of hypertension, such as home blood pressure monitors and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring systems. These devices must meet specific accuracy and reliability standards to ensure their suitability for clinical decision-making.
In the context of hypertonic solutions, regulatory oversight focuses on ensuring proper formulation, sterility, and labeling to prevent medication errors and adverse events. This is particularly crucial given the potential for serious complications if hypertonic solutions are administered incorrectly.
Global harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), have sought to streamline regulatory processes across different regions. This has facilitated more efficient drug development and approval processes, potentially accelerating the availability of new treatments for hypertension and related conditions.
As personalized medicine advances, regulatory frameworks are evolving to accommodate novel approaches such as pharmacogenomics and targeted therapies. This includes guidance on the development and validation of companion diagnostics that may be used to identify patients most likely to benefit from specific antihypertensive treatments.
Patient-Centric Care
Patient-centric care is a crucial aspect of managing hypertonic and hypertensive conditions, emphasizing the importance of tailoring treatment approaches to individual patient needs and preferences. This approach recognizes that each patient's experience with hypertension is unique, influenced by factors such as age, lifestyle, comorbidities, and personal values.
One key element of patient-centric care in hypertension management is shared decision-making. This process involves healthcare providers and patients working together to make treatment decisions based on clinical evidence and patient preferences. By engaging patients in their care plans, adherence to treatment regimens can be significantly improved, leading to better health outcomes.
Personalized treatment plans are another cornerstone of patient-centric care for hypertonic and hypertensive patients. These plans take into account not only the patient's blood pressure readings but also their overall health status, risk factors, and lifestyle. For instance, dietary modifications and exercise recommendations may be tailored to fit the patient's cultural background and daily routines, making them more likely to be adopted and maintained.
Technology plays an increasingly important role in patient-centric hypertension care. Mobile health applications and wearable devices enable patients to monitor their blood pressure at home and share data with their healthcare providers in real-time. This continuous monitoring allows for more timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans, empowering patients to take an active role in managing their condition.
Education and support are vital components of patient-centric care for hypertensive individuals. Comprehensive patient education programs help individuals understand their condition, recognize symptoms, and make informed decisions about their health. Support groups, both in-person and online, provide valuable peer support and a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
Addressing barriers to care is another critical aspect of patient-centric hypertension management. This may involve implementing telemedicine services to improve access for patients in remote areas, offering medication assistance programs for those facing financial constraints, or providing language interpretation services to ensure effective communication with diverse patient populations.
Integrating mental health support into hypertension care is gaining recognition as an essential element of patient-centric approaches. Stress management techniques, counseling services, and mindfulness practices are increasingly being incorporated into treatment plans to address the psychological aspects of living with a chronic condition like hypertension.