Hypertonic Safety: Ensuring Best Practices in Use and Development
Hypertonic Safety Background and Objectives
Hypertonic solutions have been a subject of interest in medical and scientific fields for decades, with their applications ranging from treating various medical conditions to enhancing athletic performance. The concept of hypertonicity refers to a solution having a higher solute concentration than another solution, typically compared to human body fluids. This property makes hypertonic solutions particularly useful in certain medical treatments and research applications.
The evolution of hypertonic solutions in medical practice can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers began to understand the principles of osmosis and its effects on biological systems. Since then, the use of hypertonic solutions has expanded significantly, finding applications in areas such as treating cerebral edema, managing severe dehydration, and improving wound healing.
However, with the increased use of hypertonic solutions comes a growing concern for safety. The potential risks associated with improper use or development of hypertonic solutions include electrolyte imbalances, cellular dehydration, and tissue damage. These concerns have led to a heightened focus on establishing and maintaining best practices in the use and development of hypertonic solutions.
The primary objective of hypertonic safety research is to ensure the efficacy of treatments while minimizing potential adverse effects. This involves a multifaceted approach, including the development of standardized protocols for administration, ongoing research into the physiological effects of hypertonic solutions, and the establishment of safety guidelines for different applications.
Current technological trends in hypertonic safety focus on precision medicine approaches, where the composition and concentration of hypertonic solutions are tailored to individual patient needs. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing novel delivery systems that can provide controlled release of hypertonic solutions, potentially reducing the risk of adverse effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
The future of hypertonic safety research is likely to involve advanced monitoring techniques, such as real-time osmolality sensors and personalized predictive models based on patient data. These innovations aim to enhance the safety profile of hypertonic solutions by allowing for more precise and responsive administration.
As we move forward, the goal is to establish a comprehensive framework for hypertonic safety that encompasses all aspects of use and development. This includes not only medical applications but also extends to other fields where hypertonic solutions play a role, such as food preservation and industrial processes. By addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging technologies, we can ensure that the benefits of hypertonic solutions are maximized while minimizing potential risks.
Market Analysis for Hypertonic Solutions
The market for hypertonic solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing applications in medical treatments, pharmaceutical research, and industrial processes. The global hypertonic solutions market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2021 to 2028, reaching a market value of $3.2 billion by the end of the forecast period.
In the healthcare sector, hypertonic solutions are widely used in various medical applications, including the treatment of edema, intracranial pressure management, and as a component in intravenous fluids. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing aging population are key factors contributing to the increased demand for hypertonic solutions in medical settings.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another major market segment for hypertonic solutions. These solutions play a crucial role in drug formulation, stability testing, and as excipients in various pharmaceutical products. The continuous growth of the pharmaceutical sector, coupled with ongoing research and development activities, is expected to drive the demand for hypertonic solutions in this segment.
Industrial applications of hypertonic solutions, particularly in food processing and biotechnology, are also contributing to market growth. In the food industry, hypertonic solutions are used for preservation, dehydration, and flavor enhancement. The biotechnology sector utilizes these solutions in cell culture media and bioprocessing applications.
Geographically, North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The dominance of North America can be attributed to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and presence of major pharmaceutical companies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period, driven by improving healthcare facilities, increasing investments in pharmaceutical research, and growing industrial applications.
Key players in the hypertonic solutions market include Baxter International Inc., B. Braun Melsungen AG, Fresenius Kabi AG, and Hospira Inc. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to maintain their market positions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements and potential side effects associated with the use of hypertonic solutions in medical applications may hinder market growth. Addressing these concerns through improved safety protocols and continued research into best practices for hypertonic solution use and development will be crucial for sustained market expansion.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Safety
Hypertonic safety presents several significant challenges in both its use and development. One of the primary concerns is the potential for adverse effects on patients due to rapid shifts in fluid balance. When hypertonic solutions are administered, they can cause a sudden increase in serum osmolality, leading to cellular dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. This rapid change can be particularly dangerous for patients with pre-existing cardiovascular or renal conditions.
Another challenge lies in determining the optimal concentration and administration rate for hypertonic solutions. The therapeutic window for these solutions is often narrow, requiring precise dosing to achieve the desired clinical effect without causing harm. Clinicians must carefully balance the benefits of increased intravascular volume and reduced intracranial pressure against the risks of hypernatremia and other electrolyte disturbances.
The development of standardized protocols for hypertonic solution use across different clinical scenarios poses an additional challenge. While hypertonic saline has shown efficacy in treating certain conditions, such as cerebral edema and hyponatremia, its use in other areas remains controversial. The lack of consensus guidelines makes it difficult for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about when and how to use hypertonic solutions safely.
Monitoring patients receiving hypertonic therapy presents its own set of challenges. Frequent laboratory tests are necessary to track serum electrolyte levels, osmolality, and fluid balance. However, the resources required for this close monitoring may not be available in all healthcare settings, potentially limiting the safe use of hypertonic solutions in some facilities.
The long-term effects of repeated or prolonged hypertonic therapy are not fully understood, creating uncertainty in its use for chronic conditions. There is a need for more comprehensive longitudinal studies to assess the safety profile of hypertonic solutions over extended periods, particularly in patients who may require repeated treatments.
Manufacturing and storage of hypertonic solutions also present challenges. Ensuring consistent concentration and sterility is crucial, as even small variations can have significant clinical implications. Additionally, the shelf life and stability of these solutions under various storage conditions must be carefully evaluated to maintain their safety and efficacy.
Lastly, there is a growing concern about the potential for hypertonic solutions to exacerbate underlying tissue damage in certain conditions, such as traumatic brain injury. The complex interplay between increased osmolality, blood-brain barrier function, and cellular responses to injury requires further investigation to optimize the use of hypertonic therapy in these critical situations.
Existing Safety Protocols for Hypertonics
01 Safety considerations for hypertonic solutions in medical applications
Hypertonic solutions require careful consideration in medical applications due to their potential effects on osmotic balance. Safety measures include monitoring patient response, adjusting concentrations, and controlling administration rates to prevent adverse effects such as dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.- Safety considerations for hypertonic solutions in medical applications: Hypertonic solutions require careful consideration in medical applications due to their potential effects on osmotic balance. Safety measures include proper dosing, monitoring of patient response, and appropriate administration techniques to prevent adverse effects such as dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
- Formulation and stability of hypertonic solutions: The formulation of hypertonic solutions involves careful selection of ingredients and stabilizers to ensure product safety and efficacy. Considerations include pH adjustment, use of preservatives, and packaging to maintain stability and prevent contamination during storage and use.
- Safety protocols for hypertonic solution administration: Implementing safety protocols for the administration of hypertonic solutions is crucial to minimize risks. This includes proper training of healthcare professionals, use of appropriate infusion devices, and monitoring of vital signs during administration to ensure patient safety.
- Hypertonic solutions in specific medical treatments: The use of hypertonic solutions in specific medical treatments, such as wound care or ophthalmic applications, requires tailored safety measures. This includes consideration of the target tissue, potential interactions with other medications, and appropriate concentration levels to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks.
- Quality control and testing of hypertonic solutions: Ensuring the safety of hypertonic solutions involves rigorous quality control measures and testing protocols. This includes assessing osmolality, sterility testing, and evaluation of potential contaminants to guarantee product safety before use in clinical settings.
02 Formulation techniques for safe hypertonic solutions
Developing safe hypertonic solutions involves precise formulation techniques. This includes selecting appropriate solutes, optimizing concentrations, and incorporating stabilizing agents to ensure product safety and efficacy while minimizing potential risks associated with hypertonicity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety testing protocols for hypertonic solutions
Rigorous safety testing protocols are essential for hypertonic solutions. These may include in vitro and in vivo studies to assess toxicity, osmotic effects, and potential interactions with biological systems. Standardized testing methods help ensure consistent safety evaluations across different formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Packaging and storage considerations for hypertonic solution safety
Proper packaging and storage are crucial for maintaining the safety of hypertonic solutions. This includes using appropriate container materials, implementing effective sealing methods, and establishing storage conditions that preserve solution integrity and prevent contamination or degradation over time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Patient-specific safety considerations for hypertonic solutions
Ensuring the safe use of hypertonic solutions requires consideration of individual patient factors. This includes assessing patient health status, potential contraindications, and tailoring administration protocols to minimize risks and optimize therapeutic outcomes in diverse patient populations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Solution Industry
The hypertonic safety landscape is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by rising awareness of its importance in medical and industrial applications. The technology maturity varies across different sectors, with some areas more advanced than others. Key players like Medtronic, Inc., Novartis AG, and Koninklijke Philips NV are leading innovation in medical applications, while companies such as Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. and Honeywell Safety Products USA, Inc. are focusing on industrial safety solutions. The market is characterized by a mix of established healthcare giants and emerging specialized firms like Reveal Biosensors, Inc., indicating a dynamic and competitive environment with potential for further technological advancements and market expansion.
Novartis AG
Koninklijke Philips NV
Innovative Approaches to Hypertonic Safety
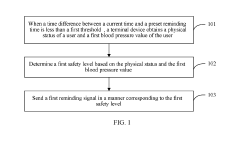
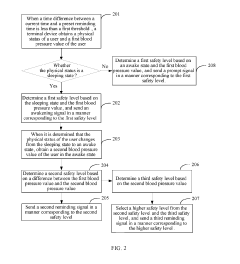
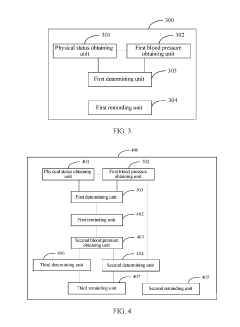
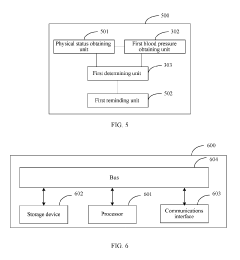
- A user reminding method and apparatus that determines a safety level based on the user's physical status and blood pressure value, sending customized reminding signals to gradually wake users, thereby avoiding health risks and reducing blood pressure burden.
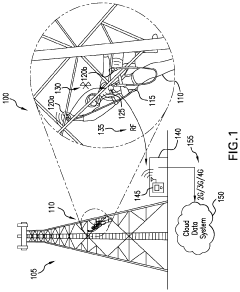
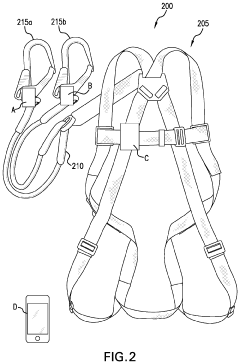
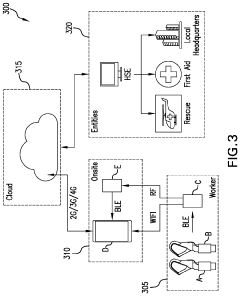
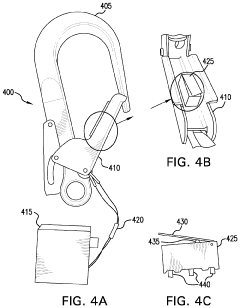
- A smart safety harness system equipped with sensors and electronic components that monitor acceleration, velocity, position, and ambient air pressure, and communicate wirelessly with rebar hooks to detect improper usage and potential falls, sending alerts to supervisors and emergency services as needed.
Regulatory Framework for Hypertonic Solutions
The regulatory framework for hypertonic solutions is a critical aspect of ensuring their safe and effective use in medical and research settings. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards to govern the development, production, and application of hypertonic solutions.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating hypertonic solutions. The FDA classifies these solutions as drugs or medical devices, depending on their intended use. For hypertonic solutions used as drugs, manufacturers must comply with Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations, which ensure consistent quality and safety in production processes.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of hypertonic solutions in the European Union. The EMA has established specific guidelines for the quality, safety, and efficacy of these products. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards and obtain marketing authorization before introducing their products to the market.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidance on the use of hypertonic solutions, particularly in the context of global health initiatives. The WHO's guidelines focus on ensuring access to safe and effective hypertonic solutions in resource-limited settings.
Regulatory frameworks also address the labeling and packaging of hypertonic solutions. Clear and accurate labeling is essential to prevent medication errors and ensure proper use. Manufacturers are required to include information such as concentration, ingredients, storage conditions, and expiration dates on product labels.
Safety monitoring and pharmacovigilance are integral components of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers and healthcare providers are obligated to report adverse events associated with the use of hypertonic solutions. This information is crucial for ongoing safety assessments and potential updates to regulatory guidelines.
Research involving hypertonic solutions is subject to ethical review and approval processes. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or Ethics Committees evaluate research protocols to ensure the protection of human subjects and compliance with regulatory requirements.
As the field of hypertonic solutions continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging challenges and technologies. This includes considerations for novel delivery methods, combination products, and personalized medicine approaches involving hypertonic solutions.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Risk assessment and mitigation strategies are crucial components in ensuring the safe use and development of hypertonic solutions. A comprehensive approach to identifying potential hazards and implementing effective control measures is essential to minimize risks associated with these concentrated solutions.
The first step in risk assessment involves a thorough analysis of the entire lifecycle of hypertonic solutions, from production to disposal. This includes evaluating potential chemical reactions, storage conditions, handling procedures, and administration methods. Factors such as solution concentration, pH levels, and compatibility with other substances must be carefully considered to identify potential sources of harm.
Once potential risks are identified, they should be categorized and prioritized based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential severity of consequences. This prioritization allows for the allocation of resources to address the most critical risks first. Common risks associated with hypertonic solutions include osmotic shock to cells and tissues, electrolyte imbalances, and potential contamination during preparation or administration.
Mitigation strategies should be developed to address each identified risk. These strategies may include engineering controls, such as the use of specialized equipment for preparation and administration, administrative controls like standardized protocols and staff training programs, and personal protective equipment for those handling the solutions. Implementing a robust quality control system is also essential to ensure consistent product quality and safety.
Regular monitoring and review of risk assessment and mitigation strategies are necessary to maintain their effectiveness. This includes conducting periodic audits, analyzing incident reports, and staying updated on new research and regulatory requirements. Continuous improvement of safety measures should be an ongoing process, with feedback from healthcare professionals and researchers incorporated into updated protocols.
Collaboration between various stakeholders, including manufacturers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies, is crucial for developing and implementing effective risk management strategies. Sharing best practices, incident reports, and research findings can contribute to the overall safety of hypertonic solution use and development across the industry.
Education and training play a vital role in risk mitigation. All personnel involved in the handling, preparation, and administration of hypertonic solutions should receive comprehensive training on potential risks, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and competency assessments can help maintain a high level of safety awareness and compliance with established protocols.