Hypertonic Therapy: Innovative Approaches in Healthcare
Hypertonic Therapy Evolution and Objectives
Hypertonic therapy has emerged as a promising approach in healthcare, evolving from its initial applications in treating edema to a wide range of innovative uses. The concept of using hypertonic solutions to manipulate osmotic gradients dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in recent decades. This therapy leverages the principle of osmosis, where fluid moves from areas of lower solute concentration to higher concentration, allowing for targeted fluid removal or delivery of therapeutic agents.
The evolution of hypertonic therapy has been marked by several key milestones. Initially used primarily in the treatment of cerebral edema, its applications have expanded to include management of various conditions such as hyponatremia, traumatic brain injury, and sepsis. The development of specialized hypertonic solutions, including hypertonic saline and mannitol, has played a crucial role in enhancing the efficacy and safety of these treatments.
Recent years have seen a surge in research exploring novel applications of hypertonic therapy. One significant area of focus has been its potential in improving outcomes in resuscitation for trauma patients. Studies have shown that small-volume hypertonic saline solutions can effectively restore blood volume while minimizing the risk of fluid overload, a common concern with traditional isotonic fluid resuscitation.
Another innovative direction in hypertonic therapy research is its application in drug delivery systems. The use of hypertonic solutions as carriers for medications has shown promise in enhancing drug penetration across biological barriers, potentially improving the efficacy of treatments for conditions ranging from ocular diseases to cancer.
The objectives of current hypertonic therapy research and development are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a focus on optimizing the composition and concentration of hypertonic solutions to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing side effects. This includes exploring combinations of hypertonic agents with other therapeutic compounds to create synergistic effects.
Additionally, researchers are working on developing novel delivery methods for hypertonic solutions, such as targeted delivery systems that can localize the effects of the therapy to specific tissues or organs. This approach aims to enhance the precision of treatments and reduce systemic side effects.
Another key objective is to expand the application of hypertonic therapy to new medical fields. For instance, its potential in neurodegenerative diseases, where osmotic regulation plays a crucial role, is being actively investigated. Similarly, its use in managing inflammatory conditions and improving wound healing is an area of growing interest.
As the field progresses, a significant goal is to establish standardized protocols for the use of hypertonic therapy across various medical conditions. This includes determining optimal dosing regimens, treatment durations, and monitoring parameters to ensure safe and effective implementation in clinical practice.
Market Analysis for Hypertonic Solutions
The global market for hypertonic solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, rising geriatric population, and growing awareness about the therapeutic benefits of hypertonic therapy. The market is segmented based on product types, including hypertonic saline solutions, dextrose solutions, and mannitol solutions, each catering to specific medical needs.
Hypertonic saline solutions dominate the market share due to their widespread use in treating various conditions such as hyponatremia, cerebral edema, and cystic fibrosis. The dextrose solutions segment is also witnessing substantial growth, particularly in the management of hypoglycemia and as a source of calories in parenteral nutrition.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, attributed to advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and the presence of key market players. Europe follows closely, with a growing emphasis on innovative healthcare solutions. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of advanced medical treatments.
The hospital segment remains the primary end-user of hypertonic solutions, accounting for the majority of market revenue. However, the homecare segment is projected to grow at a faster rate due to the increasing trend of home-based healthcare services and the rising demand for self-administered treatments.
Key market trends include the development of novel formulations with enhanced efficacy and safety profiles, increasing focus on personalized medicine, and the integration of smart packaging technologies for improved drug delivery and patient compliance. The market is also witnessing a surge in research and development activities aimed at exploring new therapeutic applications of hypertonic solutions, particularly in areas such as wound healing, oncology, and neurology.
Challenges facing the market include stringent regulatory requirements, potential side effects associated with hypertonic therapies, and the need for skilled healthcare professionals to administer these treatments effectively. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure are expected to mitigate these challenges and drive market growth.
The competitive landscape of the hypertonic solutions market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging players. Key strategies adopted by market participants include product innovations, strategic collaborations, and geographical expansions to strengthen their market position and cater to evolving customer needs.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Therapy
Hypertonic therapy, while promising in various medical applications, faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in maintaining consistent osmotic gradients over extended periods. The human body's natural homeostatic mechanisms tend to counteract the effects of hypertonic solutions, potentially reducing their therapeutic impact over time.
Another challenge lies in the potential side effects associated with hypertonic therapy. The rapid shift in fluid balance can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal or cardiovascular conditions. This necessitates careful monitoring and individualized treatment protocols, which can be resource-intensive and complex to implement in clinical settings.
The optimal composition and concentration of hypertonic solutions remain subjects of ongoing debate and research. Different medical conditions may require varying levels of hypertonicity, and finding the right balance between efficacy and safety is a delicate process. This variability makes it challenging to develop standardized treatment protocols across different patient populations and medical conditions.
Delivery methods pose another significant hurdle in hypertonic therapy. Intravenous administration, while effective, requires careful management to prevent complications such as thrombophlebitis or extravasation. Alternative delivery routes, such as oral or topical applications, often struggle with bioavailability issues, limiting their effectiveness in certain therapeutic contexts.
The long-term effects of repeated hypertonic therapy sessions are not fully understood, particularly in chronic conditions that may require ongoing treatment. There are concerns about potential cumulative effects on organ systems, especially the kidneys and cardiovascular system, which necessitate further longitudinal studies to establish safety profiles for extended use.
From a practical standpoint, the preparation and storage of hypertonic solutions can be challenging, especially in resource-limited settings. Maintaining sterility and stability of these solutions over time requires specialized equipment and protocols, which may not be readily available in all healthcare facilities.
Lastly, there is a need for more robust clinical evidence supporting the use of hypertonic therapy across various medical conditions. While some applications, such as in traumatic brain injury management, have shown promise, many potential uses remain under-researched. This lack of comprehensive clinical data makes it difficult for healthcare providers to confidently incorporate hypertonic therapy into standard treatment regimens for a broader range of conditions.
Existing Hypertonic Therapy Protocols
01 Hypertonic solutions for medical treatments
Hypertonic solutions are used in various medical treatments, including wound healing, reducing edema, and treating intracranial pressure. These solutions have a higher solute concentration than body fluids, which can draw excess fluid from tissues and promote healing.- Hypertonic solutions for medical treatments: Hypertonic solutions are used in various medical treatments, including wound healing, reducing edema, and treating certain respiratory conditions. These solutions have a higher solute concentration than body fluids, which can help draw excess fluid from tissues and improve healing processes.
- Hypertonic therapy for neurological disorders: Hypertonic therapy is being explored for the treatment of neurological disorders, such as traumatic brain injury and stroke. The use of hypertonic solutions may help reduce intracranial pressure and improve cerebral blood flow, potentially leading to better outcomes for patients with these conditions.
- Hypertonic solutions in ophthalmic applications: Hypertonic solutions are utilized in various ophthalmic applications, including the treatment of dry eye syndrome and corneal edema. These solutions can help reduce ocular surface inflammation and improve tear film stability, providing relief for patients with eye-related conditions.
- Hypertonic therapy for respiratory conditions: Hypertonic saline solutions are used in the treatment of respiratory conditions, particularly in patients with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis. Inhalation of hypertonic solutions can help improve mucociliary clearance, reduce sputum viscosity, and enhance lung function in these patients.
- Hypertonic solutions in cell and tissue preservation: Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in cell and tissue preservation techniques, including cryopreservation and organ transplantation. These solutions help protect cells from damage during freezing and thawing processes, and can improve the viability of preserved tissues for various medical and research applications.
02 Hypertonic therapy for respiratory conditions
Hypertonic saline solutions are employed in the treatment of respiratory conditions such as cystic fibrosis and bronchiolitis. These solutions help to thin mucus, improve airway hydration, and enhance mucociliary clearance, leading to better respiratory function.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypertonic solutions in ophthalmology
Hypertonic solutions are used in ophthalmology for treating various eye conditions, including corneal edema and glaucoma. These solutions help reduce intraocular pressure and improve visual acuity by drawing excess fluid from the eye tissues.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypertonic therapy in dermatology
Hypertonic solutions and preparations are utilized in dermatology for treating skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and wound healing. These therapies help to reduce inflammation, promote skin hydration, and enhance the skin's barrier function.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hypertonic solutions in cell preservation and cryopreservation
Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in cell preservation and cryopreservation techniques. These solutions help protect cells from damage during freezing and thawing processes, maintaining cell viability and function for various research and medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Therapy
Hypertonic therapy is emerging as an innovative approach in healthcare, currently in its early development stage. The market size is growing, driven by increasing applications in treating various medical conditions. While the technology is still evolving, it shows promise in areas such as wound healing, edema management, and neurological disorders. Companies like Medtronic, Novartis AG, and Bayer AG are at the forefront of research and development in this field, investing in clinical trials and product development. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with some areas more advanced than others. As the field progresses, we can expect to see more targeted therapies and improved delivery methods, potentially revolutionizing treatment approaches in several medical specialties.
Novartis AG
Bayer AG
Breakthrough Hypertonic Technologies
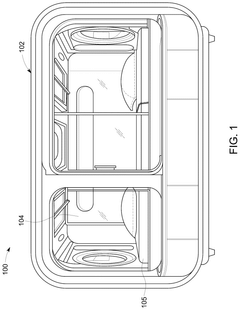
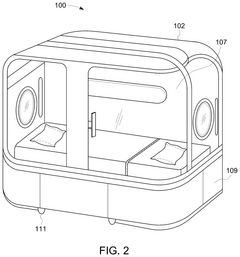
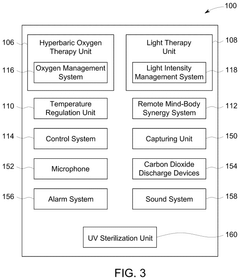
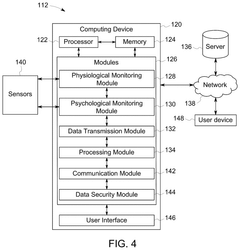
- A multi-functional hyperbaric oxygen device that integrates hyperbaric oxygen therapy, light therapy, sleep assistance, and temperature regulation with a remote mind-body synergy system, allowing for personalized, data-driven therapies and real-time monitoring of physiological and psychological parameters.
- The use of electromagnetic signals applied to specific target neural populations in the brain, either through implanted devices or in conjunction with behavioral therapies, to reduce or eliminate hypertonicity, with signal delivery parameters tailored to address both acute symptoms and promote neuroplasticity.
Regulatory Framework for Hypertonic Therapies
The regulatory framework for hypertonic therapies is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the development, approval, and implementation of these innovative healthcare approaches. As hypertonic therapy continues to gain traction in various medical applications, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to ensure patient safety while fostering innovation.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of hypertonic therapies. These treatments are typically classified as medical devices or drugs, depending on their specific mechanism of action and intended use. The FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) is responsible for regulating hypertonic therapy devices, while the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) handles drug-based hypertonic treatments.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory framework through the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR). These regulations provide stringent guidelines for manufacturers, importers, and distributors of hypertonic therapy products, ensuring their safety and efficacy before market entry. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) also plays a role in regulating hypertonic therapies that fall under the category of medicinal products.
In Asia, countries like Japan and China have their own regulatory bodies overseeing hypertonic therapies. The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan and the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China have established specific pathways for the approval and monitoring of these innovative treatments.
Regulatory requirements for hypertonic therapies typically include extensive preclinical and clinical studies to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the product's composition, manufacturing process, quality control measures, and potential risks. Post-market surveillance is also a critical component of the regulatory framework, ensuring ongoing safety monitoring and prompt reporting of adverse events.
As the field of hypertonic therapy continues to advance, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on personalized medicine approaches. This has led to the development of adaptive regulatory pathways that allow for more flexible and efficient approval processes while maintaining rigorous safety standards. These pathways often involve close collaboration between regulators, manufacturers, and healthcare providers to optimize the development and implementation of hypertonic therapies.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), are working to align regulatory requirements across different regions. This harmonization aims to streamline the approval process for hypertonic therapies, reducing duplicative efforts and accelerating global access to innovative treatments.
Patient Safety and Ethical Considerations
Patient safety and ethical considerations are paramount in the development and implementation of hypertonic therapy as an innovative approach in healthcare. The use of hypertonic solutions, while potentially beneficial, carries inherent risks that must be carefully managed and mitigated.
One of the primary safety concerns is the rapid shift in fluid balance that hypertonic therapy can induce. This sudden change can lead to complications such as electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypernatremia, which may cause neurological symptoms ranging from confusion to seizures. Healthcare providers must closely monitor patients' electrolyte levels and adjust treatment protocols accordingly to prevent adverse effects.
Cardiovascular risks also warrant attention, as hypertonic solutions can increase blood volume and potentially exacerbate heart failure in susceptible patients. Careful patient selection and continuous monitoring of hemodynamic parameters are essential to ensure safe administration of hypertonic therapy.
Renal function is another critical consideration, as hypertonic solutions can impact kidney function and potentially lead to acute kidney injury in some cases. Patients with pre-existing renal impairment require particularly close observation and may need dosage adjustments or alternative treatments.
From an ethical standpoint, the use of hypertonic therapy raises questions about informed consent and patient autonomy. Given the potential risks and the innovative nature of some hypertonic therapies, it is crucial to ensure that patients or their legal representatives fully understand the treatment's benefits, risks, and alternatives before consenting.
The principle of non-maleficence (do no harm) must be carefully balanced against potential benefits, especially when considering hypertonic therapy for off-label uses or in experimental settings. Ethical review boards play a vital role in evaluating research protocols and ensuring that patient safety remains the top priority.
Equity in access to hypertonic therapy is another ethical consideration. As an innovative treatment, it may not be universally available or covered by all insurance plans, potentially creating disparities in healthcare access. Healthcare systems and policymakers must address these issues to ensure fair distribution of medical innovations.
Lastly, the long-term effects of hypertonic therapy are not fully understood in all applications. This uncertainty underscores the importance of ongoing research and post-treatment surveillance. Healthcare providers have an ethical obligation to contribute to the growing body of knowledge by reporting outcomes and participating in clinical studies when appropriate.