Polyvinyl Acetate: Technical Analysis for Industry Breakthroughs
JUL 30, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PVAc Evolution and Objectives
Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) has a rich history dating back to its discovery in 1912 by Fritz Klatte. Initially developed as a potential substitute for celluloid, PVAc's evolution has been marked by continuous improvements in synthesis methods and applications. The technology has progressed from basic polymerization techniques to more sophisticated processes that allow for precise control over molecular weight, particle size, and copolymerization with other monomers.
The primary objective in PVAc research and development has been to enhance its properties for diverse applications. Key goals include improving adhesion strength, water resistance, and thermal stability. These advancements have led to PVAc's widespread use in adhesives, paints, coatings, and textiles. The focus has also shifted towards developing environmentally friendly formulations, aligning with global sustainability trends.
Recent technological trends in PVAc development include the exploration of nanocomposites to enhance mechanical properties and barrier characteristics. Researchers are investigating the incorporation of nanoparticles such as silica, clay, and carbon nanotubes to create high-performance PVAc materials. Another significant trend is the development of bio-based PVAc, utilizing renewable resources to reduce environmental impact.
The evolution of PVAc technology has been driven by industry demands for improved performance in specific applications. For instance, in the adhesives sector, there's a push for PVAc formulations with faster setting times and higher bond strength. In the construction industry, water-resistant PVAc is being developed for exterior applications. The packaging industry is seeking PVAc with enhanced barrier properties against oxygen and moisture.
Looking ahead, the objectives for PVAc technology include developing smart and responsive materials. This involves creating PVAc formulations that can change properties in response to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, or light. Another key goal is to improve the biodegradability of PVAc products while maintaining their performance characteristics, addressing growing environmental concerns.
The integration of PVAc with other emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and flexible electronics, represents another frontier. Researchers are exploring ways to utilize PVAc's unique properties in these cutting-edge fields, potentially opening up new markets and applications. Additionally, there's a focus on developing PVAc-based materials with antimicrobial properties, responding to increased demand for hygienic surfaces in various sectors.
The primary objective in PVAc research and development has been to enhance its properties for diverse applications. Key goals include improving adhesion strength, water resistance, and thermal stability. These advancements have led to PVAc's widespread use in adhesives, paints, coatings, and textiles. The focus has also shifted towards developing environmentally friendly formulations, aligning with global sustainability trends.
Recent technological trends in PVAc development include the exploration of nanocomposites to enhance mechanical properties and barrier characteristics. Researchers are investigating the incorporation of nanoparticles such as silica, clay, and carbon nanotubes to create high-performance PVAc materials. Another significant trend is the development of bio-based PVAc, utilizing renewable resources to reduce environmental impact.
The evolution of PVAc technology has been driven by industry demands for improved performance in specific applications. For instance, in the adhesives sector, there's a push for PVAc formulations with faster setting times and higher bond strength. In the construction industry, water-resistant PVAc is being developed for exterior applications. The packaging industry is seeking PVAc with enhanced barrier properties against oxygen and moisture.
Looking ahead, the objectives for PVAc technology include developing smart and responsive materials. This involves creating PVAc formulations that can change properties in response to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, or light. Another key goal is to improve the biodegradability of PVAc products while maintaining their performance characteristics, addressing growing environmental concerns.
The integration of PVAc with other emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and flexible electronics, represents another frontier. Researchers are exploring ways to utilize PVAc's unique properties in these cutting-edge fields, potentially opening up new markets and applications. Additionally, there's a focus on developing PVAc-based materials with antimicrobial properties, responding to increased demand for hygienic surfaces in various sectors.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polyvinyl acetate (PVA) continues to grow steadily, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. The global PVA market is experiencing significant expansion, with projections indicating sustained growth in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing use of PVA in adhesives, paints, coatings, textiles, and paper industries.
In the adhesives sector, PVA-based products are witnessing heightened demand due to their excellent bonding properties, low toxicity, and environmental friendliness. The construction industry, in particular, is a major consumer of PVA adhesives for wood bonding, lamination, and general-purpose applications. As urbanization and infrastructure development accelerate worldwide, the demand for PVA in construction-related applications is expected to surge.
The paints and coatings industry represents another significant market for PVA. The growing emphasis on eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) products has led to increased adoption of PVA-based formulations. These water-based paints and coatings offer improved durability, quick drying times, and reduced environmental impact, aligning with stringent regulations and consumer preferences for sustainable products.
Textile manufacturing is also contributing to the rising demand for PVA. Its use as a sizing agent in textile production enhances fabric strength and reduces fiber breakage during weaving. As the global textile industry expands, particularly in developing economies, the demand for PVA in this sector is projected to grow substantially.
The paper industry represents another key market for PVA, where it is used as a coating agent to improve paper quality, printability, and water resistance. With the increasing demand for high-quality packaging materials and specialty papers, the consumption of PVA in this sector is expected to rise.
Emerging applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries are opening new avenues for PVA market growth. Its use in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and cosmetic formulations is gaining traction, driven by its biocompatibility and film-forming properties.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest and fastest-growing market for PVA, fueled by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and the presence of major manufacturing hubs. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and increasing focus on sustainable products.
However, the market faces challenges such as raw material price volatility and competition from alternative materials. Manufacturers are focusing on developing advanced PVA formulations with enhanced properties to maintain their competitive edge and meet evolving industry requirements.
In the adhesives sector, PVA-based products are witnessing heightened demand due to their excellent bonding properties, low toxicity, and environmental friendliness. The construction industry, in particular, is a major consumer of PVA adhesives for wood bonding, lamination, and general-purpose applications. As urbanization and infrastructure development accelerate worldwide, the demand for PVA in construction-related applications is expected to surge.
The paints and coatings industry represents another significant market for PVA. The growing emphasis on eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) products has led to increased adoption of PVA-based formulations. These water-based paints and coatings offer improved durability, quick drying times, and reduced environmental impact, aligning with stringent regulations and consumer preferences for sustainable products.
Textile manufacturing is also contributing to the rising demand for PVA. Its use as a sizing agent in textile production enhances fabric strength and reduces fiber breakage during weaving. As the global textile industry expands, particularly in developing economies, the demand for PVA in this sector is projected to grow substantially.
The paper industry represents another key market for PVA, where it is used as a coating agent to improve paper quality, printability, and water resistance. With the increasing demand for high-quality packaging materials and specialty papers, the consumption of PVA in this sector is expected to rise.
Emerging applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries are opening new avenues for PVA market growth. Its use in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and cosmetic formulations is gaining traction, driven by its biocompatibility and film-forming properties.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest and fastest-growing market for PVA, fueled by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and the presence of major manufacturing hubs. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and increasing focus on sustainable products.
However, the market faces challenges such as raw material price volatility and competition from alternative materials. Manufacturers are focusing on developing advanced PVA formulations with enhanced properties to maintain their competitive edge and meet evolving industry requirements.
PVAc Technical Challenges
Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) faces several technical challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and limit its potential applications in various industries. One of the primary issues is its poor water resistance, which restricts its use in outdoor or high-humidity environments. When exposed to moisture, PVAc tends to soften and lose its adhesive properties, leading to reduced durability and performance in end products.
Another significant challenge is the relatively low heat resistance of PVAc. The material begins to soften at temperatures around 30-50°C, which limits its use in applications that require thermal stability. This characteristic makes PVAc unsuitable for certain industrial processes and products that may be exposed to elevated temperatures during manufacturing or use.
The mechanical properties of PVAc also present challenges in some applications. While it exhibits good flexibility, its tensile strength and impact resistance are lower compared to some other polymers. This can result in limitations when PVAc is used in structural or load-bearing applications, requiring reinforcement or alternative materials in such cases.
Biodegradability is another area where PVAc faces technical hurdles. Although it is not considered harmful to the environment, PVAc is not readily biodegradable. This characteristic poses challenges in terms of waste management and sustainability, particularly in an era where eco-friendly materials are increasingly in demand.
The synthesis and processing of PVAc also present technical challenges. Controlling the molecular weight distribution and degree of polymerization during production can be difficult, affecting the final properties of the material. Additionally, the presence of residual monomers in the final product can impact its performance and safety, necessitating careful control and purification processes.
Compatibility with other materials is another area of concern for PVAc. While it adheres well to many substrates, its compatibility with certain plastics and metals can be limited. This restricts its use in multi-material composites and certain bonding applications, requiring the development of specialized formulations or surface treatments to improve adhesion.
Lastly, the long-term stability of PVAc under various environmental conditions remains a challenge. Factors such as UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure can lead to degradation over time, affecting the material's performance and lifespan in certain applications. Addressing these stability issues is crucial for expanding the use of PVAc in more demanding and long-lasting products.
Another significant challenge is the relatively low heat resistance of PVAc. The material begins to soften at temperatures around 30-50°C, which limits its use in applications that require thermal stability. This characteristic makes PVAc unsuitable for certain industrial processes and products that may be exposed to elevated temperatures during manufacturing or use.
The mechanical properties of PVAc also present challenges in some applications. While it exhibits good flexibility, its tensile strength and impact resistance are lower compared to some other polymers. This can result in limitations when PVAc is used in structural or load-bearing applications, requiring reinforcement or alternative materials in such cases.
Biodegradability is another area where PVAc faces technical hurdles. Although it is not considered harmful to the environment, PVAc is not readily biodegradable. This characteristic poses challenges in terms of waste management and sustainability, particularly in an era where eco-friendly materials are increasingly in demand.
The synthesis and processing of PVAc also present technical challenges. Controlling the molecular weight distribution and degree of polymerization during production can be difficult, affecting the final properties of the material. Additionally, the presence of residual monomers in the final product can impact its performance and safety, necessitating careful control and purification processes.
Compatibility with other materials is another area of concern for PVAc. While it adheres well to many substrates, its compatibility with certain plastics and metals can be limited. This restricts its use in multi-material composites and certain bonding applications, requiring the development of specialized formulations or surface treatments to improve adhesion.
Lastly, the long-term stability of PVAc under various environmental conditions remains a challenge. Factors such as UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure can lead to degradation over time, affecting the material's performance and lifespan in certain applications. Addressing these stability issues is crucial for expanding the use of PVAc in more demanding and long-lasting products.
Current PVAc Solutions
01 Synthesis and polymerization of polyvinyl acetate
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and polymerizing polyvinyl acetate, including emulsion polymerization, suspension polymerization, and bulk polymerization techniques. These processes often involve the use of initiators, stabilizers, and other additives to control the molecular weight and properties of the resulting polymer.- Synthesis and polymerization of polyvinyl acetate: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and polymerizing polyvinyl acetate, including different catalysts, reaction conditions, and techniques to control molecular weight and properties of the resulting polymer.
- Polyvinyl acetate compositions and applications: Formulations and applications of polyvinyl acetate in various industries, such as adhesives, coatings, films, and construction materials. These compositions often include additives or modifications to enhance specific properties for targeted uses.
- Emulsion polymerization of vinyl acetate: Techniques and processes for emulsion polymerization of vinyl acetate, including the use of specific emulsifiers, stabilizers, and reaction conditions to produce polyvinyl acetate with desired characteristics for various applications.
- Copolymerization of vinyl acetate with other monomers: Methods for copolymerizing vinyl acetate with other monomers to produce copolymers with enhanced properties, such as improved adhesion, flexibility, or water resistance. This includes the selection of comonomers and optimization of reaction conditions.
- Modifications and treatments of polyvinyl acetate: Post-polymerization modifications and treatments of polyvinyl acetate to alter its properties, such as hydrolysis to produce polyvinyl alcohol, crosslinking for improved strength, or grafting with other polymers for specific applications.
02 Modifications and copolymers of polyvinyl acetate
Development of modified polyvinyl acetate and copolymers to enhance specific properties or functionalities. This includes grafting, crosslinking, and copolymerization with other monomers to create materials with improved adhesion, water resistance, or thermal properties for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in adhesives and coatings
Utilization of polyvinyl acetate in adhesive formulations and coating materials. This includes water-based and solvent-based adhesives for wood, paper, and packaging industries, as well as coatings for various substrates to provide protection, gloss, or specific surface properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polyvinyl acetate in composite materials
Incorporation of polyvinyl acetate into composite materials to improve binding, flexibility, or other physical properties. This includes use in wood-plastic composites, cement-based materials, and other multi-component systems where polyvinyl acetate acts as a binder or modifier.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Development of eco-friendly polyvinyl acetate formulations and processes, focusing on reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), improving biodegradability, and ensuring safety in various applications. This includes water-based systems, bio-based alternatives, and methods to reduce environmental impact during production and use.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polyvinyl acetate market is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to reach $5.5 billion by 2027. The technology is well-established, with key players like Kuraray, Wacker Chemie, and Celanese dominating the industry. These companies have advanced manufacturing capabilities and extensive R&D efforts focused on product innovations and applications in adhesives, coatings, and textiles. Emerging players such as Sinopec and PetroChina are also making significant investments in production capacity and technology development, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing efforts to improve product performance, reduce costs, and expand into new application areas.
Kuraray Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kuraray has developed advanced polyvinyl acetate (PVA) technologies, focusing on high-performance grades for various applications. Their POVAL™ and EXCEVAL™ product lines showcase innovations in water-soluble PVA films and resins. Kuraray's approach includes modifying PVA's molecular structure to enhance properties such as water solubility, adhesion strength, and film-forming capabilities[1]. They have also made strides in developing eco-friendly PVA grades with improved biodegradability, addressing growing environmental concerns in the industry[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, diverse product portfolio, and focus on sustainable solutions. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs due to specialized grades and environmental considerations.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: Sinopec has invested heavily in PVA research and production, focusing on large-scale manufacturing processes and cost-effective solutions. Their approach includes optimizing polymerization techniques to improve product quality and consistency. Sinopec has developed a proprietary catalytic system that enhances the efficiency of vinyl acetate monomer conversion, resulting in higher-quality PVA with controlled molecular weight distribution[5]. They have also made significant progress in recycling and reusing process water, reducing environmental impact and production costs[7].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, cost-effective manufacturing, and vertical integration. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in developing highly specialized grades compared to smaller, more focused competitors.
Core PVAc Innovations
POLYVINYL ACETATE latex
PatentInactiveBR102015030874A2
Innovation
- Polymerizing vinyl acetate under emulsion polymerization conditions with a chain transfer agent such as hypophosphite salts or X-R2SH, where R1 is a C1-C4 alkyl group and X is sulfonate, hydroxyl, sulfate, phosphate, phosphonate, or carboxylic acid, to produce vinyl acetate homopolymers or copolymers with reduced viscosities.
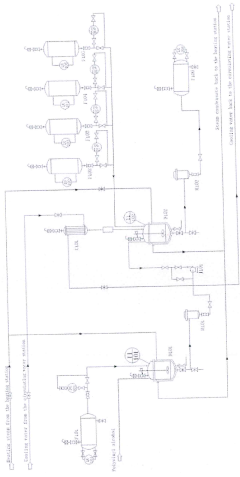
Polyvinyl acetate production plant
PatentUndeterminedIES20180484A2
Innovation
- A polyvinyl acetate production plant design incorporating specific tanks, a stirring vessel, filter, condenser, feedstock pump, polymerizer, and emulsion tank, with controlled temperature and chemical additions to optimize polymerization reaction conditions, including the use of deionized water, dibutyl phthalate, vinyl acetate, sodium bicarbonate, and ammonium persulfate, to streamline the production process and enhance reaction efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) has become a ubiquitous material in various industries, but its environmental impact is a growing concern. The production and disposal of PVA-based products have significant implications for ecosystems and human health. During the manufacturing process, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are released, contributing to air pollution and potentially causing respiratory issues in workers and nearby communities.
The disposal of PVA products presents another environmental challenge. While PVA is biodegradable under certain conditions, its degradation rate in natural environments can be slow, leading to accumulation in landfills and water bodies. This accumulation can disrupt aquatic ecosystems and potentially enter the food chain. Moreover, the additives and plasticizers used in PVA formulations may leach into the environment, causing further contamination.
Water pollution is a particular concern with PVA. When PVA-containing products are washed or disposed of in water systems, they can increase the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) of water bodies. This can lead to oxygen depletion, harming aquatic life and altering ecosystem balance. Additionally, PVA can form films on water surfaces, interfering with gas exchange and light penetration essential for aquatic organisms.
Recent studies have focused on developing more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional PVA. Bio-based and biodegradable versions of PVA are being researched, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint and improve end-of-life biodegradability. These innovations include the use of renewable resources in PVA production and the incorporation of enzymes or other additives to enhance biodegradation rates.
The recycling of PVA-based products is another area of focus for reducing environmental impact. While challenging due to the water-soluble nature of PVA, advancements in recycling technologies are being made. These include chemical recycling methods that break down PVA into its monomers for reuse, and mechanical recycling processes that repurpose PVA waste into new products.
Industry efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of PVA are also focusing on improving production efficiency and reducing waste. This includes optimizing manufacturing processes to minimize VOC emissions and developing closed-loop systems that recycle water and chemicals used in PVA production. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on life cycle assessments to comprehensively evaluate the environmental footprint of PVA products from cradle to grave.
The disposal of PVA products presents another environmental challenge. While PVA is biodegradable under certain conditions, its degradation rate in natural environments can be slow, leading to accumulation in landfills and water bodies. This accumulation can disrupt aquatic ecosystems and potentially enter the food chain. Moreover, the additives and plasticizers used in PVA formulations may leach into the environment, causing further contamination.
Water pollution is a particular concern with PVA. When PVA-containing products are washed or disposed of in water systems, they can increase the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) of water bodies. This can lead to oxygen depletion, harming aquatic life and altering ecosystem balance. Additionally, PVA can form films on water surfaces, interfering with gas exchange and light penetration essential for aquatic organisms.
Recent studies have focused on developing more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional PVA. Bio-based and biodegradable versions of PVA are being researched, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint and improve end-of-life biodegradability. These innovations include the use of renewable resources in PVA production and the incorporation of enzymes or other additives to enhance biodegradation rates.
The recycling of PVA-based products is another area of focus for reducing environmental impact. While challenging due to the water-soluble nature of PVA, advancements in recycling technologies are being made. These include chemical recycling methods that break down PVA into its monomers for reuse, and mechanical recycling processes that repurpose PVA waste into new products.
Industry efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of PVA are also focusing on improving production efficiency and reducing waste. This includes optimizing manufacturing processes to minimize VOC emissions and developing closed-loop systems that recycle water and chemicals used in PVA production. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on life cycle assessments to comprehensively evaluate the environmental footprint of PVA products from cradle to grave.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding polyvinyl acetate (PVA) is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the diverse applications of this versatile polymer across various industries. As a key component in adhesives, coatings, and other consumer products, PVA is subject to a range of regulations that aim to ensure safety, environmental protection, and quality standards.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating PVA, particularly in food contact applications. The FDA has approved PVA for use in food packaging and as an indirect food additive, subject to specific limitations and conditions. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees PVA under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), monitoring its production, use, and potential environmental impacts.
Internationally, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is a significant framework affecting PVA manufacturers and users. REACH requires companies to register chemical substances and provide safety data, ensuring that potential risks to human health and the environment are adequately assessed and managed.
In the construction industry, regulations such as the European Construction Products Regulation (CPR) impact PVA-based products, mandating compliance with harmonized technical specifications and CE marking requirements. Similarly, in the automotive sector, regulations like the End-of-Life Vehicles Directive in the EU influence the use of PVA in vehicle components, promoting recyclability and limiting hazardous substances.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, also apply to PVA manufacturing and handling processes. These regulations set standards for workplace exposure limits, personal protective equipment, and safety protocols.
Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping the PVA industry, with a growing focus on sustainability and biodegradability. Many jurisdictions are implementing stricter waste management and recycling policies, encouraging the development of more environmentally friendly PVA formulations and applications.
As the global regulatory landscape continues to evolve, PVA manufacturers and users must stay abreast of changing requirements across different regions and sectors. This dynamic regulatory environment presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation in PVA technology, driving research into new formulations and applications that meet increasingly stringent regulatory standards while maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating PVA, particularly in food contact applications. The FDA has approved PVA for use in food packaging and as an indirect food additive, subject to specific limitations and conditions. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees PVA under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), monitoring its production, use, and potential environmental impacts.
Internationally, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is a significant framework affecting PVA manufacturers and users. REACH requires companies to register chemical substances and provide safety data, ensuring that potential risks to human health and the environment are adequately assessed and managed.
In the construction industry, regulations such as the European Construction Products Regulation (CPR) impact PVA-based products, mandating compliance with harmonized technical specifications and CE marking requirements. Similarly, in the automotive sector, regulations like the End-of-Life Vehicles Directive in the EU influence the use of PVA in vehicle components, promoting recyclability and limiting hazardous substances.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, also apply to PVA manufacturing and handling processes. These regulations set standards for workplace exposure limits, personal protective equipment, and safety protocols.
Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping the PVA industry, with a growing focus on sustainability and biodegradability. Many jurisdictions are implementing stricter waste management and recycling policies, encouraging the development of more environmentally friendly PVA formulations and applications.
As the global regulatory landscape continues to evolve, PVA manufacturers and users must stay abreast of changing requirements across different regions and sectors. This dynamic regulatory environment presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation in PVA technology, driving research into new formulations and applications that meet increasingly stringent regulatory standards while maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!