Propyne's Applications in High-Throughput Process Screening
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propyne Overview and Research Objectives
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a highly reactive alkyne with the chemical formula C3H4. This colorless gas has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in high-throughput process screening. The evolution of propyne's utilization has been driven by advancements in chemical engineering and the increasing demand for efficient and sustainable industrial processes.
The development of propyne-based technologies can be traced back to the early 20th century when it was first isolated and characterized. However, its applications in high-throughput screening have only emerged in the past few decades, coinciding with the rise of combinatorial chemistry and automated synthesis platforms. This technological progression has opened up new possibilities for utilizing propyne as a versatile building block in various chemical processes.
In the context of high-throughput process screening, propyne serves as an ideal candidate due to its unique chemical properties. Its triple bond structure allows for a wide range of reactions, including cycloadditions, hydrogenations, and polymerizations. These characteristics make propyne an excellent probe molecule for rapidly assessing the performance of catalysts, reaction conditions, and process parameters across multiple experimental setups simultaneously.
The primary objective of researching propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening is to accelerate the discovery and optimization of novel chemical processes. By leveraging propyne's reactivity, researchers aim to develop more efficient methodologies for screening large numbers of reaction conditions and catalysts in parallel. This approach has the potential to significantly reduce the time and resources required for process development in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and petrochemicals.
Another key research goal is to explore the potential of propyne as a sustainable feedstock for the production of value-added chemicals. High-throughput screening techniques can be employed to identify innovative catalytic systems and reaction pathways that enable the conversion of propyne into a diverse array of useful products. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green chemistry and the need to develop more environmentally friendly industrial processes.
Furthermore, the integration of propyne-based high-throughput screening with advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms represents a promising frontier in this field. Researchers are working towards developing predictive models that can accelerate the optimization of reaction conditions and guide the design of new catalysts. This synergy between experimental techniques and computational methods has the potential to revolutionize the way chemical processes are developed and scaled up.
As we look towards the future, the continued exploration of propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening is expected to yield significant advancements in chemical manufacturing and process intensification. The insights gained from these studies will not only contribute to more efficient and sustainable industrial practices but also pave the way for the discovery of novel materials and pharmaceutical compounds.
The development of propyne-based technologies can be traced back to the early 20th century when it was first isolated and characterized. However, its applications in high-throughput screening have only emerged in the past few decades, coinciding with the rise of combinatorial chemistry and automated synthesis platforms. This technological progression has opened up new possibilities for utilizing propyne as a versatile building block in various chemical processes.
In the context of high-throughput process screening, propyne serves as an ideal candidate due to its unique chemical properties. Its triple bond structure allows for a wide range of reactions, including cycloadditions, hydrogenations, and polymerizations. These characteristics make propyne an excellent probe molecule for rapidly assessing the performance of catalysts, reaction conditions, and process parameters across multiple experimental setups simultaneously.
The primary objective of researching propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening is to accelerate the discovery and optimization of novel chemical processes. By leveraging propyne's reactivity, researchers aim to develop more efficient methodologies for screening large numbers of reaction conditions and catalysts in parallel. This approach has the potential to significantly reduce the time and resources required for process development in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and petrochemicals.
Another key research goal is to explore the potential of propyne as a sustainable feedstock for the production of value-added chemicals. High-throughput screening techniques can be employed to identify innovative catalytic systems and reaction pathways that enable the conversion of propyne into a diverse array of useful products. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green chemistry and the need to develop more environmentally friendly industrial processes.
Furthermore, the integration of propyne-based high-throughput screening with advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms represents a promising frontier in this field. Researchers are working towards developing predictive models that can accelerate the optimization of reaction conditions and guide the design of new catalysts. This synergy between experimental techniques and computational methods has the potential to revolutionize the way chemical processes are developed and scaled up.
As we look towards the future, the continued exploration of propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening is expected to yield significant advancements in chemical manufacturing and process intensification. The insights gained from these studies will not only contribute to more efficient and sustainable industrial practices but also pave the way for the discovery of novel materials and pharmaceutical compounds.
Market Analysis for Propyne-Based Processes
The market for propyne-based processes is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-throughput screening methodologies in various industries. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, has emerged as a versatile compound with applications in pharmaceutical research, materials science, and chemical manufacturing. Its unique properties make it an ideal candidate for high-throughput process screening, enabling rapid and efficient evaluation of reaction conditions and catalysts.
In the pharmaceutical sector, propyne-based processes are gaining traction for drug discovery and development. The ability to quickly screen multiple reaction conditions and catalysts allows researchers to optimize synthetic routes for potential drug candidates more efficiently. This has led to a reduction in time-to-market for new pharmaceuticals and has attracted substantial investment from major pharmaceutical companies.
The materials science industry has also recognized the potential of propyne in high-throughput screening applications. Researchers are utilizing propyne-based processes to develop novel materials with enhanced properties, such as advanced polymers and composites. This has opened up new opportunities in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where there is a constant demand for innovative materials with improved performance characteristics.
Chemical manufacturers are increasingly adopting propyne-based high-throughput screening techniques to optimize their production processes. By rapidly evaluating different reaction parameters, companies can identify more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing routes. This has resulted in improved product yields, reduced energy consumption, and minimized waste generation, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
The market for propyne-based processes in high-throughput screening is characterized by a growing number of specialized equipment and software providers. These companies offer integrated solutions that combine automated liquid handling systems, spectroscopic analysis tools, and data management platforms. The increasing sophistication of these systems has expanded the potential applications of propyne-based screening, attracting interest from a broader range of industries.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for propyne-based high-throughput screening processes, primarily due to their well-established pharmaceutical and chemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing R&D investments and the rapid expansion of manufacturing capabilities in countries like China and India.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high initial investment required for advanced screening equipment and the need for specialized expertise to interpret complex data sets. However, these barriers are gradually being addressed through collaborations between industry and academia, as well as the development of more user-friendly software interfaces.
In the pharmaceutical sector, propyne-based processes are gaining traction for drug discovery and development. The ability to quickly screen multiple reaction conditions and catalysts allows researchers to optimize synthetic routes for potential drug candidates more efficiently. This has led to a reduction in time-to-market for new pharmaceuticals and has attracted substantial investment from major pharmaceutical companies.
The materials science industry has also recognized the potential of propyne in high-throughput screening applications. Researchers are utilizing propyne-based processes to develop novel materials with enhanced properties, such as advanced polymers and composites. This has opened up new opportunities in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where there is a constant demand for innovative materials with improved performance characteristics.
Chemical manufacturers are increasingly adopting propyne-based high-throughput screening techniques to optimize their production processes. By rapidly evaluating different reaction parameters, companies can identify more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing routes. This has resulted in improved product yields, reduced energy consumption, and minimized waste generation, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
The market for propyne-based processes in high-throughput screening is characterized by a growing number of specialized equipment and software providers. These companies offer integrated solutions that combine automated liquid handling systems, spectroscopic analysis tools, and data management platforms. The increasing sophistication of these systems has expanded the potential applications of propyne-based screening, attracting interest from a broader range of industries.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for propyne-based high-throughput screening processes, primarily due to their well-established pharmaceutical and chemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing R&D investments and the rapid expansion of manufacturing capabilities in countries like China and India.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high initial investment required for advanced screening equipment and the need for specialized expertise to interpret complex data sets. However, these barriers are gradually being addressed through collaborations between industry and academia, as well as the development of more user-friendly software interfaces.
Current Challenges in Propyne Utilization
Despite the potential of propyne in high-throughput process screening, several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the limited availability and high cost of propyne. As a byproduct of petroleum refining, its production is not easily scalable, making it difficult to obtain in large quantities for industrial applications. This scarcity often leads to price volatility, which can impact the economic viability of propyne-based processes.
Another major challenge lies in the handling and storage of propyne. Due to its high reactivity and flammability, propyne requires specialized equipment and safety measures. This not only increases the operational costs but also poses potential safety risks in industrial settings. The need for stringent safety protocols can sometimes slow down the screening process, reducing the overall efficiency of high-throughput operations.
The reactivity of propyne, while beneficial in many applications, also presents challenges in terms of selectivity and control. In high-throughput screening processes, achieving precise control over propyne reactions can be difficult, often leading to unwanted side products or reduced yields. This issue is particularly pronounced when dealing with complex reaction systems or when attempting to optimize multiple parameters simultaneously.
Furthermore, the integration of propyne into existing high-throughput screening platforms poses technical challenges. Many current systems are not designed to handle highly reactive gases, requiring significant modifications or the development of new equipment. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and costly, potentially deterring some researchers or industries from exploring propyne-based applications.
Environmental concerns also play a role in the challenges facing propyne utilization. As a hydrocarbon, propyne contributes to carbon emissions, and its production from fossil fuel sources raises sustainability questions. This aspect becomes increasingly important as industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and align with global environmental goals.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the full potential of propyne in various high-throughput applications. While its reactivity is well-known, the exploration of its use in diverse chemical processes and material syntheses is still ongoing. This lack of comprehensive data and case studies makes it challenging for researchers and industries to fully leverage propyne's capabilities in high-throughput screening processes.
Another major challenge lies in the handling and storage of propyne. Due to its high reactivity and flammability, propyne requires specialized equipment and safety measures. This not only increases the operational costs but also poses potential safety risks in industrial settings. The need for stringent safety protocols can sometimes slow down the screening process, reducing the overall efficiency of high-throughput operations.
The reactivity of propyne, while beneficial in many applications, also presents challenges in terms of selectivity and control. In high-throughput screening processes, achieving precise control over propyne reactions can be difficult, often leading to unwanted side products or reduced yields. This issue is particularly pronounced when dealing with complex reaction systems or when attempting to optimize multiple parameters simultaneously.
Furthermore, the integration of propyne into existing high-throughput screening platforms poses technical challenges. Many current systems are not designed to handle highly reactive gases, requiring significant modifications or the development of new equipment. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and costly, potentially deterring some researchers or industries from exploring propyne-based applications.
Environmental concerns also play a role in the challenges facing propyne utilization. As a hydrocarbon, propyne contributes to carbon emissions, and its production from fossil fuel sources raises sustainability questions. This aspect becomes increasingly important as industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and align with global environmental goals.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the full potential of propyne in various high-throughput applications. While its reactivity is well-known, the exploration of its use in diverse chemical processes and material syntheses is still ongoing. This lack of comprehensive data and case studies makes it challenging for researchers and industries to fully leverage propyne's capabilities in high-throughput screening processes.
High-Throughput Screening Methodologies
01 Synthesis and production methods of propyne
Various methods for synthesizing and producing propyne are described, including catalytic processes, thermal cracking, and dehydrogenation reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, selectivity, and efficiency in propyne production.- Synthesis and production of propyne: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing propyne, including catalytic reactions, thermal decomposition, and chemical transformations. These techniques aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propyne production for industrial applications.
- Propyne as a raw material in chemical processes: Utilization of propyne as a key intermediate or starting material in the synthesis of various organic compounds, polymers, and specialty chemicals. This includes its role in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials.
- Purification and separation of propyne: Techniques and systems for purifying and separating propyne from mixtures or by-products. This includes distillation, adsorption, membrane separation, and other methods to obtain high-purity propyne for industrial use.
- Propyne in fuel and energy applications: Research and development of propyne-based fuels, fuel additives, and energy storage systems. This includes studies on combustion properties, energy efficiency, and potential use in alternative energy technologies.
- Safety and handling of propyne: Methods and equipment for safe storage, transportation, and handling of propyne, considering its flammable and potentially explosive nature. This includes the development of specialized containers, monitoring systems, and safety protocols for industrial use.
02 Purification and separation of propyne
Techniques for purifying and separating propyne from other hydrocarbons or reaction mixtures are outlined. These may include distillation, adsorption, membrane separation, or other physical and chemical separation processes to obtain high-purity propyne.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of propyne in chemical synthesis
Propyne is used as a versatile building block in various chemical syntheses, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its triple bond reactivity makes it valuable in organic synthesis and materials science.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propyne in fuel and energy applications
Research on the use of propyne in fuel blends, combustion processes, and energy storage systems is discussed. This includes studies on its potential as an alternative fuel or fuel additive to improve engine performance and reduce emissions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling of propyne
Guidelines and technologies for the safe handling, storage, and transportation of propyne are presented. This includes risk assessment, containment strategies, and safety equipment design to mitigate the hazards associated with this flammable gas.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The competitive landscape for propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening is evolving rapidly, with the industry in a growth phase. The market size is expanding as more companies recognize the potential of propyne in accelerating chemical process development. Technologically, the field is advancing, with key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Zhejiang University, and Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing leading innovation. These organizations are developing sophisticated screening methods and catalysts to optimize propyne utilization. While the technology is not yet fully mature, significant progress is being made in areas such as catalyst design and process efficiency, indicating a promising future for propyne in high-throughput applications.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a high-throughput process screening system for propyne applications, focusing on catalytic conversion to high-value chemicals. Their approach utilizes parallel microreactors with automated sampling and analysis, enabling rapid evaluation of multiple catalysts and reaction conditions simultaneously. The system incorporates advanced in-situ spectroscopic techniques for real-time monitoring of reaction progress[1]. Sinopec's method integrates machine learning algorithms to predict optimal reaction parameters and catalyst compositions, significantly reducing the time and resources required for process development[2]. The company has successfully applied this technology to optimize propyne conversion to acrylonitrile, achieving yields up to 85% with novel catalyst formulations[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive integration of automation and AI for efficient screening. Large-scale industrial application potential. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs. Potential limitations in screening very complex reaction systems.
Shanghai Petrochemical Research Institute of China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation
Technical Solution: The Shanghai Petrochemical Research Institute has developed a novel high-throughput screening platform specifically tailored for propyne-based processes. Their system employs a combination of microfluidic reactors and rapid analytical techniques, allowing for the simultaneous evaluation of hundreds of reaction conditions. The institute has pioneered the use of in-line Raman spectroscopy for real-time monitoring of propyne conversion and product formation[4]. Their approach also incorporates a unique catalyst library system, enabling rapid screening of diverse metal and support combinations for propyne functionalization reactions. The institute has successfully applied this technology to develop new processes for propyne oligomerization, achieving selectivities over 90% for valuable C6 and C9 products[5].
Strengths: Highly specialized for propyne chemistry. Rapid screening capabilities. Weaknesses: May be less versatile for other chemical processes. Potential scalability challenges for some discovered processes.
Innovative Propyne Process Technologies
Electromotive system for high-throughput screening
PatentWO2012178095A1
Innovation
- A system utilizing electrokinetic properties, including electrodes and a function generator, is employed to dynamically manipulate fluids and particles within microplates, microslides, and microarrays by applying different amplitude, frequencies, and signal shapes to induce forces for mixing, separation, concentration, and transport.
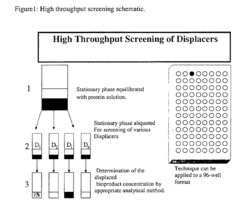
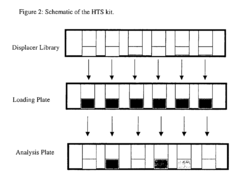
High throughtput screening of potential displacer molecules
PatentInactiveUS6881540B2
Innovation
- A method for rapidly screening a large number of displacer candidates by determining their efficacy in separating bioproducts from impurities using a displacement chromatography system, involving the determination of equilibrium concentrations and relative amounts displaced from the stationary phase, allowing for parallel assessment and rating of candidates.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening is a critical aspect that requires thorough evaluation. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a highly flammable and reactive gas that poses potential risks to the environment if not handled properly. In the context of high-throughput process screening, the use of propyne may lead to increased emissions and waste generation, necessitating careful consideration of its environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with propyne usage is its contribution to air pollution. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), propyne can react with other atmospheric pollutants to form ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This can have detrimental effects on air quality, particularly in urban areas where industrial activities are concentrated. Additionally, propyne's high reactivity may lead to the formation of secondary pollutants, further exacerbating air quality issues.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact that must be addressed. In high-throughput process screening, propyne may come into contact with various solvents and reagents, potentially resulting in contaminated wastewater. Proper treatment and disposal of this wastewater are essential to prevent the release of harmful substances into aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, accidental spills or leaks of propyne-containing solutions could have severe consequences for local water bodies and groundwater resources.
The energy-intensive nature of high-throughput process screening using propyne also contributes to its environmental impact. The production, storage, and handling of propyne require significant energy inputs, potentially leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions if not managed efficiently. Implementing energy-saving measures and exploring alternative energy sources for these processes could help mitigate this impact.
Waste management is a crucial consideration in the environmental assessment of propyne applications. High-throughput screening generates substantial amounts of chemical waste, including unreacted propyne and its byproducts. Proper disposal and recycling strategies must be developed to minimize the environmental burden of these waste streams. This may include implementing closed-loop systems, exploring catalytic conversion techniques, or developing novel waste treatment methods specific to propyne-containing mixtures.
Biodiversity and ecosystem health are also potential areas of concern when assessing the environmental impact of propyne usage in high-throughput screening. Accidental releases or long-term exposure to propyne and its derivatives could have adverse effects on local flora and fauna. Conducting comprehensive ecological risk assessments and establishing robust safety protocols are essential steps in safeguarding biodiversity in areas where propyne-based processes are employed.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening reveals several areas of concern that require careful management and mitigation strategies. By addressing air and water pollution, energy consumption, waste management, and ecological risks, researchers and industry professionals can work towards minimizing the environmental footprint of propyne-based screening processes while maximizing their scientific and industrial benefits.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with propyne usage is its contribution to air pollution. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), propyne can react with other atmospheric pollutants to form ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This can have detrimental effects on air quality, particularly in urban areas where industrial activities are concentrated. Additionally, propyne's high reactivity may lead to the formation of secondary pollutants, further exacerbating air quality issues.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact that must be addressed. In high-throughput process screening, propyne may come into contact with various solvents and reagents, potentially resulting in contaminated wastewater. Proper treatment and disposal of this wastewater are essential to prevent the release of harmful substances into aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, accidental spills or leaks of propyne-containing solutions could have severe consequences for local water bodies and groundwater resources.
The energy-intensive nature of high-throughput process screening using propyne also contributes to its environmental impact. The production, storage, and handling of propyne require significant energy inputs, potentially leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions if not managed efficiently. Implementing energy-saving measures and exploring alternative energy sources for these processes could help mitigate this impact.
Waste management is a crucial consideration in the environmental assessment of propyne applications. High-throughput screening generates substantial amounts of chemical waste, including unreacted propyne and its byproducts. Proper disposal and recycling strategies must be developed to minimize the environmental burden of these waste streams. This may include implementing closed-loop systems, exploring catalytic conversion techniques, or developing novel waste treatment methods specific to propyne-containing mixtures.
Biodiversity and ecosystem health are also potential areas of concern when assessing the environmental impact of propyne usage in high-throughput screening. Accidental releases or long-term exposure to propyne and its derivatives could have adverse effects on local flora and fauna. Conducting comprehensive ecological risk assessments and establishing robust safety protocols are essential steps in safeguarding biodiversity in areas where propyne-based processes are employed.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of propyne's applications in high-throughput process screening reveals several areas of concern that require careful management and mitigation strategies. By addressing air and water pollution, energy consumption, waste management, and ecological risks, researchers and industry professionals can work towards minimizing the environmental footprint of propyne-based screening processes while maximizing their scientific and industrial benefits.
Regulatory Framework for Propyne Use
The regulatory framework for propyne use in high-throughput process screening is a complex and evolving landscape. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is classified as a highly flammable gas, which necessitates strict safety protocols and handling procedures. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific guidelines for the use of propyne in industrial settings, including requirements for proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and emergency response plans.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates propyne under the Clean Air Act, particularly concerning its potential as a volatile organic compound (VOC) and its impact on air quality. Facilities using propyne in high-throughput screening processes must adhere to emission standards and reporting requirements set forth by the EPA.
Internationally, the transportation and storage of propyne are governed by regulations such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines provide a framework for the safe handling and shipping of propyne across borders, which is crucial for global research and industrial applications.
In the context of high-throughput process screening, regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have established guidelines for the use of chemical compounds in drug discovery and development processes. While propyne itself may not be directly regulated by these agencies, the processes and methodologies employing propyne must comply with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards.
Research institutions and pharmaceutical companies utilizing propyne in high-throughput screening must also adhere to institutional review board (IRB) protocols and obtain necessary approvals for experimental designs involving this compound. This ensures ethical considerations and safety measures are in place for all research activities.
As the applications of propyne in high-throughput screening continue to expand, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Ongoing dialogue between industry stakeholders, regulatory agencies, and scientific communities is essential to develop and refine guidelines that balance innovation with safety and environmental considerations. Future regulatory developments may include more specific protocols for the use of propyne in automated screening systems, as well as updated safety data sheets and handling instructions tailored to high-throughput applications.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates propyne under the Clean Air Act, particularly concerning its potential as a volatile organic compound (VOC) and its impact on air quality. Facilities using propyne in high-throughput screening processes must adhere to emission standards and reporting requirements set forth by the EPA.
Internationally, the transportation and storage of propyne are governed by regulations such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines provide a framework for the safe handling and shipping of propyne across borders, which is crucial for global research and industrial applications.
In the context of high-throughput process screening, regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have established guidelines for the use of chemical compounds in drug discovery and development processes. While propyne itself may not be directly regulated by these agencies, the processes and methodologies employing propyne must comply with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards.
Research institutions and pharmaceutical companies utilizing propyne in high-throughput screening must also adhere to institutional review board (IRB) protocols and obtain necessary approvals for experimental designs involving this compound. This ensures ethical considerations and safety measures are in place for all research activities.
As the applications of propyne in high-throughput screening continue to expand, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Ongoing dialogue between industry stakeholders, regulatory agencies, and scientific communities is essential to develop and refine guidelines that balance innovation with safety and environmental considerations. Future regulatory developments may include more specific protocols for the use of propyne in automated screening systems, as well as updated safety data sheets and handling instructions tailored to high-throughput applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!