How Propyne is Utilized in Tunable Dielectric Material Research
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propyne in Dielectrics: Background and Objectives
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, has emerged as a significant compound in the field of tunable dielectric material research. This area of study has gained considerable attention due to the growing demand for advanced electronic components with adjustable properties. The evolution of propyne's role in dielectric materials can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring novel organic compounds for their potential in creating materials with variable dielectric constants.
The primary objective of utilizing propyne in tunable dielectric material research is to develop materials that can dynamically alter their dielectric properties in response to external stimuli. This capability is crucial for applications in telecommunications, radar systems, and adaptive electronic devices. Propyne's unique molecular structure, featuring a triple bond and a methyl group, offers intriguing possibilities for manipulating electronic polarizability and, consequently, the dielectric constant of materials.
Over the past two decades, the technological landscape has witnessed significant advancements in the synthesis and characterization of propyne-based dielectric materials. Initial studies focused on incorporating propyne as a functional group in polymer matrices, aiming to exploit its electronic properties. Subsequent research expanded to include propyne-derived compounds and their integration into composite materials, opening up new avenues for tunable dielectric applications.
The progression of propyne utilization in this field has been driven by the increasing need for miniaturization and efficiency in electronic devices. As traditional dielectric materials reached their performance limits, the search for alternatives capable of meeting the demands of emerging technologies intensified. Propyne-based materials have shown promise in addressing these challenges, offering the potential for finer control over dielectric properties and improved response times to external fields.
Recent technological trends have further emphasized the importance of propyne in dielectric research. The advent of 5G networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced sensing technologies has created a surge in demand for materials with precisely controllable dielectric characteristics. Propyne's role in this context extends beyond its direct use as a dielectric material component; it also serves as a model compound for understanding the fundamental principles governing the behavior of organic molecules in electric fields.
As we look towards the future, the objectives of propyne-based dielectric material research are becoming increasingly ambitious. Scientists and engineers are now exploring ways to create "smart" dielectric materials that can autonomously adjust their properties based on environmental conditions or user requirements. This vision aligns with the broader goals of developing adaptive and energy-efficient electronic systems, positioning propyne-derived materials at the forefront of next-generation technology development.
The primary objective of utilizing propyne in tunable dielectric material research is to develop materials that can dynamically alter their dielectric properties in response to external stimuli. This capability is crucial for applications in telecommunications, radar systems, and adaptive electronic devices. Propyne's unique molecular structure, featuring a triple bond and a methyl group, offers intriguing possibilities for manipulating electronic polarizability and, consequently, the dielectric constant of materials.
Over the past two decades, the technological landscape has witnessed significant advancements in the synthesis and characterization of propyne-based dielectric materials. Initial studies focused on incorporating propyne as a functional group in polymer matrices, aiming to exploit its electronic properties. Subsequent research expanded to include propyne-derived compounds and their integration into composite materials, opening up new avenues for tunable dielectric applications.
The progression of propyne utilization in this field has been driven by the increasing need for miniaturization and efficiency in electronic devices. As traditional dielectric materials reached their performance limits, the search for alternatives capable of meeting the demands of emerging technologies intensified. Propyne-based materials have shown promise in addressing these challenges, offering the potential for finer control over dielectric properties and improved response times to external fields.
Recent technological trends have further emphasized the importance of propyne in dielectric research. The advent of 5G networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced sensing technologies has created a surge in demand for materials with precisely controllable dielectric characteristics. Propyne's role in this context extends beyond its direct use as a dielectric material component; it also serves as a model compound for understanding the fundamental principles governing the behavior of organic molecules in electric fields.
As we look towards the future, the objectives of propyne-based dielectric material research are becoming increasingly ambitious. Scientists and engineers are now exploring ways to create "smart" dielectric materials that can autonomously adjust their properties based on environmental conditions or user requirements. This vision aligns with the broader goals of developing adaptive and energy-efficient electronic systems, positioning propyne-derived materials at the forefront of next-generation technology development.
Market Analysis for Tunable Dielectric Materials
The market for tunable dielectric materials has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced electronic devices and systems across various industries. These materials, which can alter their dielectric properties in response to external stimuli such as electric fields, temperature, or mechanical stress, are finding applications in a wide range of sectors including telecommunications, aerospace, defense, and consumer electronics.
In the telecommunications industry, tunable dielectric materials are being utilized in the development of smart antennas, phase shifters, and tunable filters for 5G and future 6G networks. The ability to dynamically adjust the dielectric properties allows for improved signal quality, increased bandwidth, and enhanced network performance. This application alone is expected to drive substantial market growth as the global rollout of 5G networks continues and research into 6G technologies accelerates.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also significant contributors to the market demand for tunable dielectric materials. These materials are being incorporated into radar systems, electronic warfare equipment, and satellite communications, where adaptability and precision in signal processing are crucial. The increasing focus on modernizing military communications and surveillance systems is likely to further boost the demand for tunable dielectric materials in these sectors.
In the consumer electronics market, tunable dielectric materials are finding applications in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. They are being used to develop tunable capacitors and resonators, which can improve the performance and efficiency of RF front-end modules. As consumers demand more compact devices with enhanced functionality, the market for tunable dielectric materials in this sector is expected to grow steadily.
The automotive industry is emerging as a new frontier for tunable dielectric materials, particularly in the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. These materials are being explored for use in automotive radar systems and sensors, where their tunable properties can enhance detection accuracy and range.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for tunable dielectric materials, owing to their strong presence in telecommunications, aerospace, and defense industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid technological advancements and increasing investments in 5G infrastructure and consumer electronics manufacturing.
As research into the utilization of propyne in tunable dielectric materials progresses, it is likely to open up new opportunities and potentially disrupt existing market dynamics. The unique properties of propyne-based materials could lead to the development of more efficient and versatile tunable dielectric solutions, potentially expanding the market into new application areas and industries.
In the telecommunications industry, tunable dielectric materials are being utilized in the development of smart antennas, phase shifters, and tunable filters for 5G and future 6G networks. The ability to dynamically adjust the dielectric properties allows for improved signal quality, increased bandwidth, and enhanced network performance. This application alone is expected to drive substantial market growth as the global rollout of 5G networks continues and research into 6G technologies accelerates.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also significant contributors to the market demand for tunable dielectric materials. These materials are being incorporated into radar systems, electronic warfare equipment, and satellite communications, where adaptability and precision in signal processing are crucial. The increasing focus on modernizing military communications and surveillance systems is likely to further boost the demand for tunable dielectric materials in these sectors.
In the consumer electronics market, tunable dielectric materials are finding applications in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. They are being used to develop tunable capacitors and resonators, which can improve the performance and efficiency of RF front-end modules. As consumers demand more compact devices with enhanced functionality, the market for tunable dielectric materials in this sector is expected to grow steadily.
The automotive industry is emerging as a new frontier for tunable dielectric materials, particularly in the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. These materials are being explored for use in automotive radar systems and sensors, where their tunable properties can enhance detection accuracy and range.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for tunable dielectric materials, owing to their strong presence in telecommunications, aerospace, and defense industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid technological advancements and increasing investments in 5G infrastructure and consumer electronics manufacturing.
As research into the utilization of propyne in tunable dielectric materials progresses, it is likely to open up new opportunities and potentially disrupt existing market dynamics. The unique properties of propyne-based materials could lead to the development of more efficient and versatile tunable dielectric solutions, potentially expanding the market into new application areas and industries.
Current Challenges in Propyne-Based Dielectric Research
The utilization of propyne in tunable dielectric material research faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and practical application. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of propyne-based dielectric materials under varying environmental conditions. These materials often exhibit sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, and exposure to ultraviolet radiation, which can lead to degradation of their dielectric properties over time.
Another critical challenge lies in the precise control of propyne's molecular structure and orientation within the dielectric matrix. Achieving uniform dispersion and alignment of propyne molecules is crucial for optimizing the material's dielectric performance. However, current fabrication techniques struggle to maintain consistent molecular arrangements across large-scale production, resulting in variations in dielectric properties and reduced reliability.
The integration of propyne-based dielectric materials into existing electronic devices and systems poses additional difficulties. Compatibility issues with other materials used in device fabrication, such as electrodes and substrates, can arise due to chemical interactions or physical mismatches. This compatibility challenge often necessitates the development of new interface materials or modification of existing manufacturing processes, adding complexity and cost to the production pipeline.
Furthermore, the tunability range of propyne-based dielectric materials, while promising, still falls short of the requirements for certain advanced applications. Expanding the range of achievable dielectric constants and improving the response time to external stimuli remain active areas of research. Scientists are exploring various approaches, including the use of composite materials and novel molecular designs, to enhance the tunability and responsiveness of these dielectric systems.
Safety concerns also present a significant hurdle in propyne-based dielectric research. Propyne is a highly flammable gas, and its handling requires stringent safety protocols. Developing safe storage, transportation, and handling methods for propyne and its derivatives in both research and industrial settings is crucial for the widespread adoption of these materials.
Lastly, the scalability of propyne-based dielectric material production presents a considerable challenge. Current synthesis methods often involve complex procedures that are difficult to scale up for industrial production. Developing cost-effective, large-scale manufacturing processes that maintain the desired material properties is essential for the commercial viability of these advanced dielectric materials.
Another critical challenge lies in the precise control of propyne's molecular structure and orientation within the dielectric matrix. Achieving uniform dispersion and alignment of propyne molecules is crucial for optimizing the material's dielectric performance. However, current fabrication techniques struggle to maintain consistent molecular arrangements across large-scale production, resulting in variations in dielectric properties and reduced reliability.
The integration of propyne-based dielectric materials into existing electronic devices and systems poses additional difficulties. Compatibility issues with other materials used in device fabrication, such as electrodes and substrates, can arise due to chemical interactions or physical mismatches. This compatibility challenge often necessitates the development of new interface materials or modification of existing manufacturing processes, adding complexity and cost to the production pipeline.
Furthermore, the tunability range of propyne-based dielectric materials, while promising, still falls short of the requirements for certain advanced applications. Expanding the range of achievable dielectric constants and improving the response time to external stimuli remain active areas of research. Scientists are exploring various approaches, including the use of composite materials and novel molecular designs, to enhance the tunability and responsiveness of these dielectric systems.
Safety concerns also present a significant hurdle in propyne-based dielectric research. Propyne is a highly flammable gas, and its handling requires stringent safety protocols. Developing safe storage, transportation, and handling methods for propyne and its derivatives in both research and industrial settings is crucial for the widespread adoption of these materials.
Lastly, the scalability of propyne-based dielectric material production presents a considerable challenge. Current synthesis methods often involve complex procedures that are difficult to scale up for industrial production. Developing cost-effective, large-scale manufacturing processes that maintain the desired material properties is essential for the commercial viability of these advanced dielectric materials.
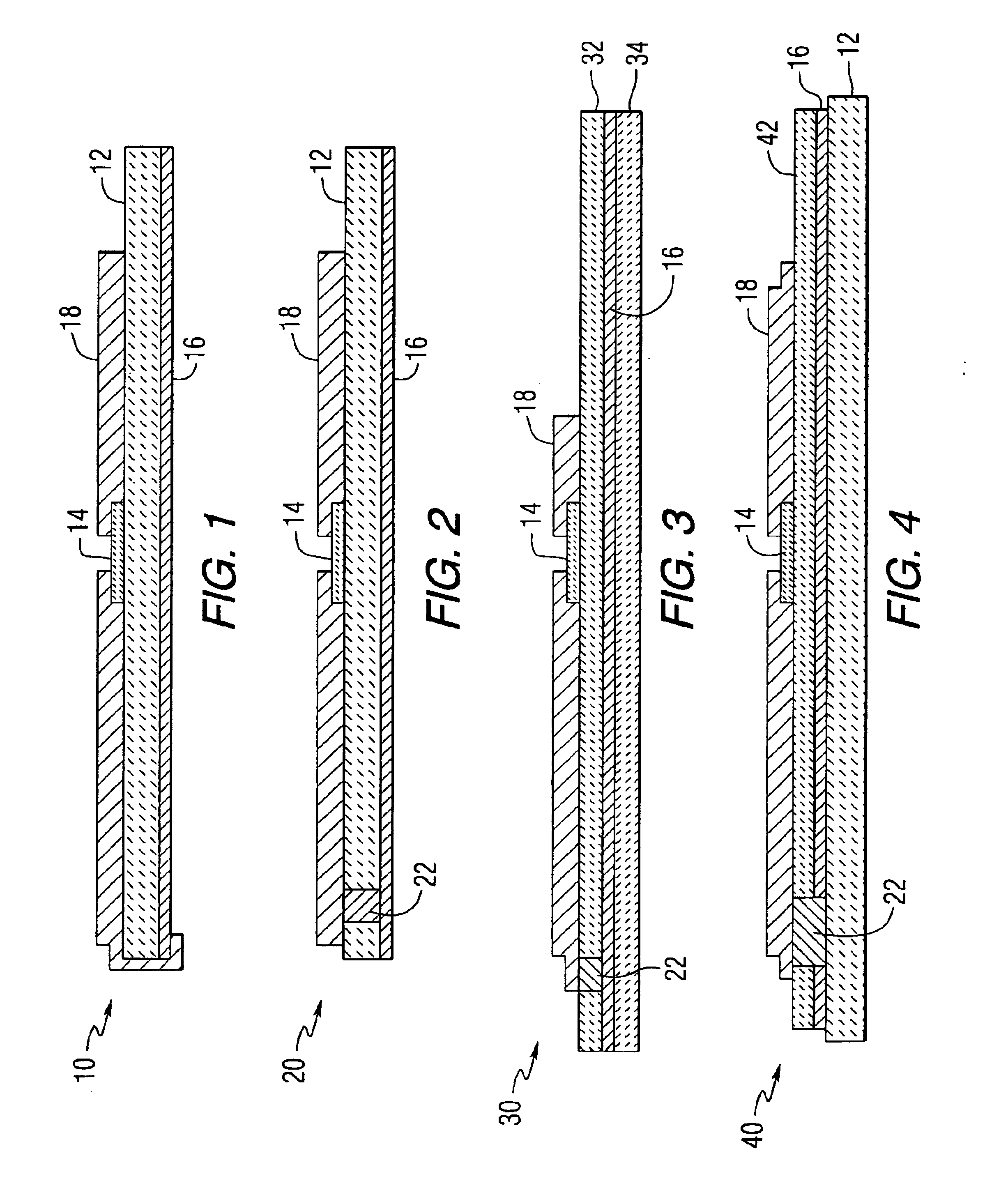
Existing Propyne Utilization Methods in Dielectrics
01 Measurement of dielectric properties of propyne
Various methods and apparatus are used to measure the dielectric properties of propyne, including its permittivity and dielectric constant. These measurements are crucial for understanding the electrical behavior of propyne in different applications and conditions.- Measurement of dielectric properties of propyne: Various methods and apparatus are used to measure the dielectric properties of propyne, including its permittivity and dielectric constant. These measurements are crucial for understanding the electrical behavior of propyne in different applications and conditions.
- Propyne as a component in dielectric materials: Propyne is utilized as a component in the development of novel dielectric materials. Its unique properties contribute to the creation of materials with specific dielectric characteristics, which can be tailored for various electronic and electrical applications.
- Effect of temperature and pressure on propyne's dielectric properties: Research has been conducted to investigate how temperature and pressure affect the dielectric properties of propyne. Understanding these relationships is important for predicting the behavior of propyne in different environmental conditions and for optimizing its use in various applications.
- Propyne in gas mixture analysis: The dielectric properties of propyne are utilized in gas mixture analysis techniques. These methods exploit the unique dielectric characteristics of propyne to detect and quantify its presence in complex gas mixtures, which is valuable for industrial and environmental monitoring applications.
- Applications of propyne's dielectric properties: The dielectric properties of propyne are exploited in various applications, including the development of sensors, capacitors, and other electronic components. Its unique characteristics make it suitable for use in specific industrial processes and in the design of specialized equipment.
02 Propyne as a component in dielectric materials
Propyne is utilized as a component in the development of new dielectric materials. Its unique properties contribute to the creation of materials with specific dielectric characteristics, which can be used in various electronic and electrical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Effect of temperature and pressure on propyne's dielectric properties
Research has been conducted to study the influence of temperature and pressure on the dielectric properties of propyne. Understanding these relationships is important for predicting and controlling the behavior of propyne in different environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propyne in gas mixture analysis
The dielectric properties of propyne are utilized in gas mixture analysis techniques. These methods can detect and quantify propyne in complex gas mixtures, which is valuable for industrial processes and environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of propyne's dielectric properties
The dielectric properties of propyne are exploited in various applications, including the development of sensors, capacitors, and other electronic components. These applications take advantage of propyne's unique electrical characteristics to enhance performance or enable new functionalities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propyne Dielectric Material Development
The utilization of propyne in tunable dielectric material research is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential driven by increasing demand for advanced electronic components. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like NXP USA, Inc., Dow Global Technologies LLC, and GLOBALFOUNDRIES, Inc. leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University and Sichuan University are also contributing significantly to the field. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established semiconductor companies and research institutions, indicating a collaborative approach to advancing this technology. As the potential applications in electronics and telecommunications expand, we can expect increased investment and rapid technological progress in this area.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed a novel approach to utilizing propyne in tunable dielectric materials research. Their method involves incorporating propyne-based monomers into polymer matrices to create highly responsive dielectric materials. The company has engineered a process to synthesize propyne-derived polymers with controlled molecular weight and architecture, allowing for precise tuning of dielectric properties[1]. These materials exhibit a wide range of dielectric constants (2-20) and low dielectric loss, making them suitable for various electronic applications. Dow's research also focuses on enhancing the thermal stability and mechanical properties of these propyne-based dielectric materials, addressing key challenges in their practical implementation[3].
Strengths: Wide range of tunable dielectric properties, low dielectric loss, and potential for diverse applications. Weaknesses: May face challenges in scaling up production and ensuring long-term stability in harsh environments.
Zhejiang University
Technical Solution: Zhejiang University has made significant strides in propyne-based tunable dielectric material research. Their approach focuses on developing nanocomposite materials that incorporate propyne-functionalized nanoparticles into polymer matrices. By controlling the degree of propyne functionalization and nanoparticle dispersion, researchers have achieved a high degree of tunability in dielectric properties[2]. The university's team has also explored the use of propyne as a precursor for creating carbon-rich dielectric films through chemical vapor deposition techniques. These films demonstrate excellent voltage-dependent capacitance, making them promising for applications in tunable capacitors and phase shifters[4].
Strengths: Innovative nanocomposite approach, high tunability, and potential for integration in advanced electronic devices. Weaknesses: Complexity in manufacturing processes and potential high costs for large-scale production.
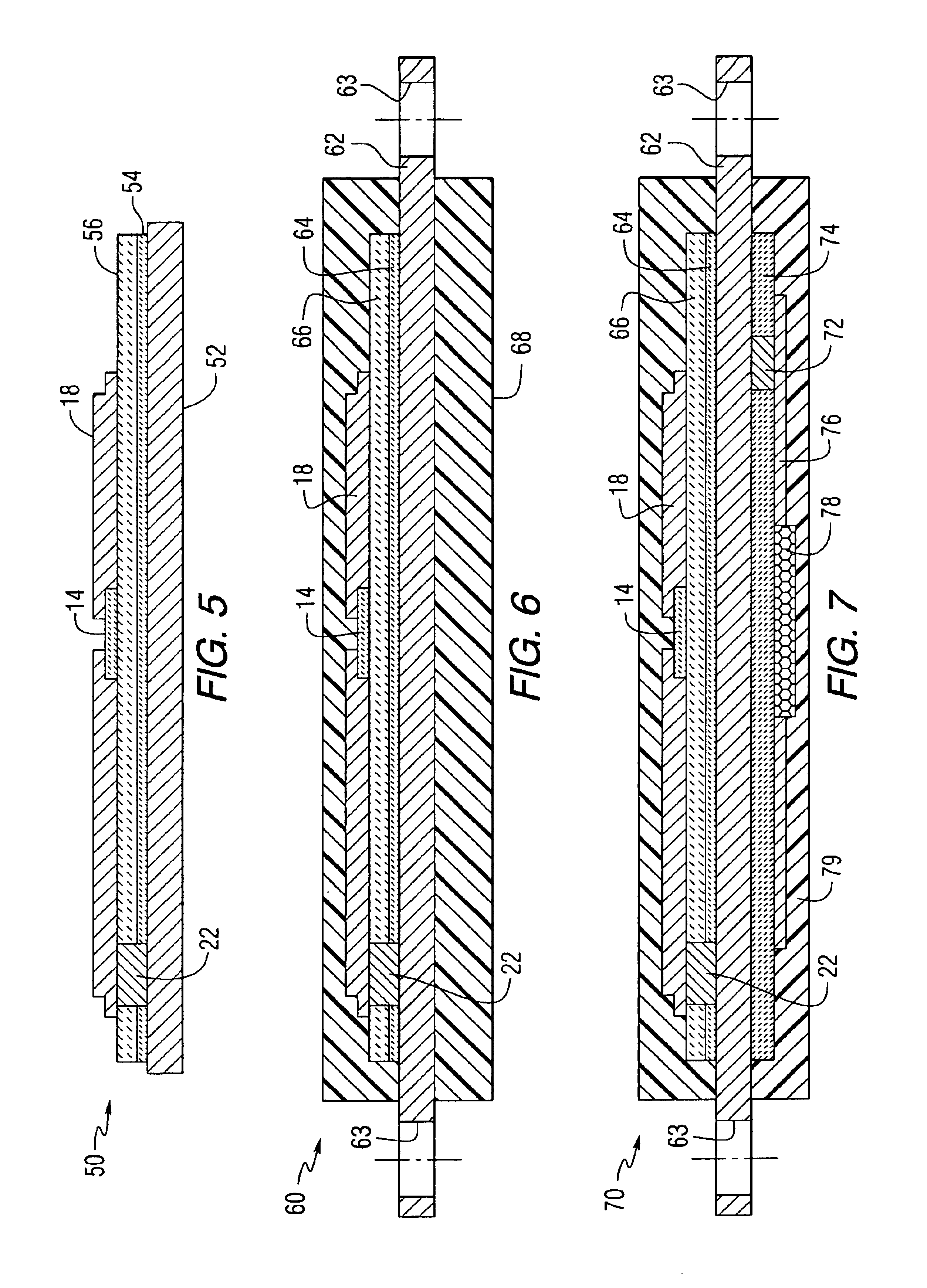
Innovative Propyne Applications in Dielectric Tuning
Tunable dielectric compositions including low loss glass
PatentInactiveUS6905989B2
Innovation
- Development of tunable dielectric materials comprising an electronically tunable ceramic and a low loss glass additive, allowing for sintering at relatively low temperatures (less than 1,300°C) and enabling the use of standard thick film substrate materials and noble metal metallization, resulting in materials with improved breakdown strength, low losses, and high tunability.
Environmental Impact of Propyne in Dielectric Materials
The environmental impact of propyne in dielectric materials research is a critical consideration as this field advances. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a hydrocarbon gas that plays a significant role in the development of tunable dielectric materials. While its use offers promising technological advancements, it is essential to assess its potential environmental implications.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with propyne is its contribution to air pollution. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), propyne can react with other atmospheric pollutants to form ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems in urban areas where research facilities are often located. Additionally, propyne has a high global warming potential, contributing to climate change when released into the atmosphere.
The production and handling of propyne also pose environmental risks. Industrial processes used to synthesize propyne often involve energy-intensive methods and may result in the release of greenhouse gases. Proper containment and handling procedures are crucial to prevent accidental releases, which could have localized environmental impacts on soil and water resources.
In the context of dielectric material research, the use of propyne may involve specialized equipment and processes that consume significant amounts of energy. This indirect environmental impact should be considered when evaluating the overall sustainability of propyne-based dielectric materials. Researchers are increasingly focusing on developing energy-efficient synthesis and application methods to mitigate these effects.
Waste management is another important aspect of propyne's environmental impact in dielectric research. Unused or contaminated propyne must be disposed of properly to prevent environmental contamination. This often involves specialized treatment processes that can be resource-intensive and potentially generate additional waste streams.
On the positive side, the development of tunable dielectric materials using propyne could lead to more efficient electronic devices, potentially reducing overall energy consumption in various applications. This long-term benefit may offset some of the immediate environmental concerns associated with propyne use in research settings.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles in dielectric material research. Scientists are exploring alternative compounds and methodologies that could provide similar tunable properties with reduced environmental impact. This includes investigating bio-based precursors and developing closed-loop systems to minimize waste and emissions.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with propyne is its contribution to air pollution. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), propyne can react with other atmospheric pollutants to form ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems in urban areas where research facilities are often located. Additionally, propyne has a high global warming potential, contributing to climate change when released into the atmosphere.
The production and handling of propyne also pose environmental risks. Industrial processes used to synthesize propyne often involve energy-intensive methods and may result in the release of greenhouse gases. Proper containment and handling procedures are crucial to prevent accidental releases, which could have localized environmental impacts on soil and water resources.
In the context of dielectric material research, the use of propyne may involve specialized equipment and processes that consume significant amounts of energy. This indirect environmental impact should be considered when evaluating the overall sustainability of propyne-based dielectric materials. Researchers are increasingly focusing on developing energy-efficient synthesis and application methods to mitigate these effects.
Waste management is another important aspect of propyne's environmental impact in dielectric research. Unused or contaminated propyne must be disposed of properly to prevent environmental contamination. This often involves specialized treatment processes that can be resource-intensive and potentially generate additional waste streams.
On the positive side, the development of tunable dielectric materials using propyne could lead to more efficient electronic devices, potentially reducing overall energy consumption in various applications. This long-term benefit may offset some of the immediate environmental concerns associated with propyne use in research settings.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles in dielectric material research. Scientists are exploring alternative compounds and methodologies that could provide similar tunable properties with reduced environmental impact. This includes investigating bio-based precursors and developing closed-loop systems to minimize waste and emissions.
Scalability of Propyne-Based Dielectric Production
The scalability of propyne-based dielectric production is a critical factor in determining the feasibility of large-scale implementation of tunable dielectric materials. As research in this field progresses, it is essential to evaluate the potential for scaling up production processes to meet industrial demands.
One of the primary considerations for scalability is the availability of propyne as a raw material. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is typically produced as a byproduct in the petroleum refining process. While this ensures a steady supply, the quantity may be limited compared to other industrial chemicals. To address this, researchers are exploring alternative synthesis methods for propyne, including catalytic dehydrogenation of propane and selective hydrogenation of propadiene.
The production of propyne-based dielectric materials often involves complex chemical reactions and precise control of reaction conditions. Scaling up these processes requires careful engineering to maintain the desired material properties while increasing production volume. This may involve the development of specialized reactors and process control systems capable of handling larger quantities of reactants and products.
Another crucial aspect of scalability is the uniformity and consistency of the produced dielectric materials. As production scales up, maintaining the same level of quality and performance across larger batches becomes increasingly challenging. Advanced quality control measures and in-line monitoring systems may need to be implemented to ensure that the dielectric properties remain consistent throughout the production process.
The environmental impact of large-scale propyne-based dielectric production must also be considered. As production volumes increase, so does the potential for emissions and waste generation. Developing sustainable production methods and implementing efficient recycling processes for unused materials and byproducts will be essential for long-term scalability.
Cost-effectiveness is another critical factor in scaling up production. While propyne-based dielectric materials may offer superior performance, their widespread adoption will depend on achieving competitive pricing compared to existing alternatives. This may require optimizing production processes, reducing material waste, and exploring economies of scale to lower overall production costs.
Lastly, the scalability of propyne-based dielectric production will also depend on the development of appropriate handling and storage infrastructure. Propyne is a flammable gas, and large-scale production will require robust safety measures and specialized storage facilities. Developing safe and efficient transportation methods for both raw materials and finished products will be crucial for expanding production capabilities beyond local markets.
One of the primary considerations for scalability is the availability of propyne as a raw material. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is typically produced as a byproduct in the petroleum refining process. While this ensures a steady supply, the quantity may be limited compared to other industrial chemicals. To address this, researchers are exploring alternative synthesis methods for propyne, including catalytic dehydrogenation of propane and selective hydrogenation of propadiene.
The production of propyne-based dielectric materials often involves complex chemical reactions and precise control of reaction conditions. Scaling up these processes requires careful engineering to maintain the desired material properties while increasing production volume. This may involve the development of specialized reactors and process control systems capable of handling larger quantities of reactants and products.
Another crucial aspect of scalability is the uniformity and consistency of the produced dielectric materials. As production scales up, maintaining the same level of quality and performance across larger batches becomes increasingly challenging. Advanced quality control measures and in-line monitoring systems may need to be implemented to ensure that the dielectric properties remain consistent throughout the production process.
The environmental impact of large-scale propyne-based dielectric production must also be considered. As production volumes increase, so does the potential for emissions and waste generation. Developing sustainable production methods and implementing efficient recycling processes for unused materials and byproducts will be essential for long-term scalability.
Cost-effectiveness is another critical factor in scaling up production. While propyne-based dielectric materials may offer superior performance, their widespread adoption will depend on achieving competitive pricing compared to existing alternatives. This may require optimizing production processes, reducing material waste, and exploring economies of scale to lower overall production costs.
Lastly, the scalability of propyne-based dielectric production will also depend on the development of appropriate handling and storage infrastructure. Propyne is a flammable gas, and large-scale production will require robust safety measures and specialized storage facilities. Developing safe and efficient transportation methods for both raw materials and finished products will be crucial for expanding production capabilities beyond local markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!