How Propyne Affects Microfluidic Device Efficiency
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propyne and Microfluidics: Background and Objectives
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a hydrocarbon compound with the chemical formula C3H4. This alkyne has gained significant attention in the field of microfluidics due to its unique properties and potential applications. Microfluidics, on the other hand, is a multidisciplinary field that deals with the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids at the microscale level. The intersection of propyne and microfluidics presents an intriguing area of research with promising implications for various industries.
The development of microfluidic devices has revolutionized numerous scientific and industrial processes, offering advantages such as reduced sample volumes, faster analysis times, and improved control over reaction conditions. These devices have found applications in diverse fields, including chemical synthesis, biomedical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. However, the efficiency of microfluidic devices can be significantly influenced by the properties of the fluids used within them.
Propyne's unique characteristics, including its low boiling point, high reactivity, and ability to form stable complexes with certain metals, make it an interesting candidate for use in microfluidic systems. The exploration of how propyne affects microfluidic device efficiency is driven by the potential to enhance existing applications and develop novel ones.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively examine the impact of propyne on microfluidic device efficiency. This involves investigating how propyne's physical and chemical properties interact with various components of microfluidic systems, such as channel materials, flow dynamics, and reaction kinetics. By understanding these interactions, researchers aim to optimize microfluidic device designs and operational parameters to harness the full potential of propyne in these systems.
Furthermore, this research seeks to identify potential advantages and limitations of incorporating propyne into microfluidic devices. This includes evaluating its effects on factors such as flow rate, mixing efficiency, heat transfer, and overall system performance. Additionally, the study aims to explore how propyne's unique properties can be leveraged to overcome existing challenges in microfluidic applications, such as improving reaction yields or enhancing separation processes.
The evolution of both propyne chemistry and microfluidic technology has set the stage for this investigation. Recent advancements in materials science, fluid dynamics modeling, and analytical techniques have provided the necessary tools to conduct in-depth studies on this topic. By combining these technological developments with a thorough understanding of propyne's behavior, researchers hope to unlock new possibilities in microfluidic device design and functionality.
The development of microfluidic devices has revolutionized numerous scientific and industrial processes, offering advantages such as reduced sample volumes, faster analysis times, and improved control over reaction conditions. These devices have found applications in diverse fields, including chemical synthesis, biomedical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. However, the efficiency of microfluidic devices can be significantly influenced by the properties of the fluids used within them.
Propyne's unique characteristics, including its low boiling point, high reactivity, and ability to form stable complexes with certain metals, make it an interesting candidate for use in microfluidic systems. The exploration of how propyne affects microfluidic device efficiency is driven by the potential to enhance existing applications and develop novel ones.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively examine the impact of propyne on microfluidic device efficiency. This involves investigating how propyne's physical and chemical properties interact with various components of microfluidic systems, such as channel materials, flow dynamics, and reaction kinetics. By understanding these interactions, researchers aim to optimize microfluidic device designs and operational parameters to harness the full potential of propyne in these systems.
Furthermore, this research seeks to identify potential advantages and limitations of incorporating propyne into microfluidic devices. This includes evaluating its effects on factors such as flow rate, mixing efficiency, heat transfer, and overall system performance. Additionally, the study aims to explore how propyne's unique properties can be leveraged to overcome existing challenges in microfluidic applications, such as improving reaction yields or enhancing separation processes.
The evolution of both propyne chemistry and microfluidic technology has set the stage for this investigation. Recent advancements in materials science, fluid dynamics modeling, and analytical techniques have provided the necessary tools to conduct in-depth studies on this topic. By combining these technological developments with a thorough understanding of propyne's behavior, researchers hope to unlock new possibilities in microfluidic device design and functionality.
Market Analysis for Propyne-Enhanced Microfluidic Devices
The market for propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and precise analytical tools in various industries. Propyne, a hydrocarbon gas, has shown promising results in improving the performance of microfluidic devices, particularly in terms of flow control and reaction kinetics.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are expected to be the primary drivers of market growth for propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices. These industries require high-throughput screening and precise drug delivery systems, where the improved efficiency offered by propyne can lead to faster drug discovery processes and more accurate dosing mechanisms.
In the healthcare sector, the adoption of propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices is anticipated to rise due to the growing need for point-of-care diagnostics and personalized medicine. The enhanced sensitivity and speed of analysis provided by these devices can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
The chemical and petrochemical industries are also showing interest in propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices for process optimization and quality control applications. The ability to manipulate small volumes of fluids with greater precision can lead to more efficient chemical reactions and improved product quality.
Environmental monitoring and water quality assessment represent another promising market segment for propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices. The increased sensitivity and faster analysis times can enable more frequent and accurate monitoring of pollutants and contaminants in water sources.
The global market for microfluidic devices is projected to grow substantially in the coming years, with propyne-enhanced devices expected to capture a significant portion of this growth. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, but Asia-Pacific is anticipated to show the highest growth rate due to increasing investments in research and development and the rapid expansion of healthcare infrastructure.
Key market players are investing heavily in research and development to further improve the efficiency and applicability of propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are becoming more common, driving innovation and accelerating the commercialization of new technologies.
However, challenges such as high initial costs and the need for specialized expertise in handling propyne may hinder market growth in some regions. Regulatory hurdles related to the use of propyne in medical devices could also impact market expansion in certain countries.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are expected to be the primary drivers of market growth for propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices. These industries require high-throughput screening and precise drug delivery systems, where the improved efficiency offered by propyne can lead to faster drug discovery processes and more accurate dosing mechanisms.
In the healthcare sector, the adoption of propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices is anticipated to rise due to the growing need for point-of-care diagnostics and personalized medicine. The enhanced sensitivity and speed of analysis provided by these devices can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
The chemical and petrochemical industries are also showing interest in propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices for process optimization and quality control applications. The ability to manipulate small volumes of fluids with greater precision can lead to more efficient chemical reactions and improved product quality.
Environmental monitoring and water quality assessment represent another promising market segment for propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices. The increased sensitivity and faster analysis times can enable more frequent and accurate monitoring of pollutants and contaminants in water sources.
The global market for microfluidic devices is projected to grow substantially in the coming years, with propyne-enhanced devices expected to capture a significant portion of this growth. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, but Asia-Pacific is anticipated to show the highest growth rate due to increasing investments in research and development and the rapid expansion of healthcare infrastructure.
Key market players are investing heavily in research and development to further improve the efficiency and applicability of propyne-enhanced microfluidic devices. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are becoming more common, driving innovation and accelerating the commercialization of new technologies.
However, challenges such as high initial costs and the need for specialized expertise in handling propyne may hinder market growth in some regions. Regulatory hurdles related to the use of propyne in medical devices could also impact market expansion in certain countries.
Current Challenges in Propyne-Microfluidic Integration
The integration of propyne into microfluidic devices presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is the chemical compatibility between propyne and the materials commonly used in microfluidic device fabrication. Propyne, being a highly reactive alkyne, can potentially interact with or degrade certain polymers and elastomers used in microfluidic chip construction, such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). This chemical incompatibility may lead to device failure or altered performance over time.
Another critical challenge lies in the precise control and manipulation of propyne within the microfluidic channels. Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, propyne can easily transition from liquid to gas phase, causing unpredictable flow behavior and potential disruption of microfluidic operations. This phase instability complicates the design of reliable and reproducible microfluidic experiments involving propyne.
The safety considerations associated with handling propyne in microfluidic devices also pose significant challenges. Propyne is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air, necessitating stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment for its use in laboratory settings. This not only increases the complexity of experimental setups but also limits the widespread adoption of propyne-based microfluidic applications.
Furthermore, the integration of propyne into microfluidic systems raises concerns about seal integrity and leak prevention. The small molecule size of propyne makes it prone to permeation through conventional microfluidic seals, potentially compromising the containment of the chemical within the device. This necessitates the development of advanced sealing technologies and materials specifically designed to withstand propyne exposure.
The optimization of propyne flow dynamics within microfluidic channels represents another significant challenge. The unique physical properties of propyne, including its low viscosity and high diffusivity, can lead to unexpected flow patterns and mixing behaviors that differ from those observed with more commonly used fluids in microfluidics. This requires a reevaluation and potential redesign of channel geometries and flow control mechanisms to achieve desired performance metrics.
Lastly, the analytical challenges associated with real-time monitoring and quantification of propyne in microfluidic devices cannot be overlooked. The development of sensitive and selective detection methods compatible with the microscale dimensions of these devices is crucial for understanding and optimizing propyne-based microfluidic processes. This may involve the adaptation of existing analytical techniques or the creation of novel sensing modalities tailored to the unique properties of propyne in microfluidic environments.
Another critical challenge lies in the precise control and manipulation of propyne within the microfluidic channels. Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, propyne can easily transition from liquid to gas phase, causing unpredictable flow behavior and potential disruption of microfluidic operations. This phase instability complicates the design of reliable and reproducible microfluidic experiments involving propyne.
The safety considerations associated with handling propyne in microfluidic devices also pose significant challenges. Propyne is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air, necessitating stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment for its use in laboratory settings. This not only increases the complexity of experimental setups but also limits the widespread adoption of propyne-based microfluidic applications.
Furthermore, the integration of propyne into microfluidic systems raises concerns about seal integrity and leak prevention. The small molecule size of propyne makes it prone to permeation through conventional microfluidic seals, potentially compromising the containment of the chemical within the device. This necessitates the development of advanced sealing technologies and materials specifically designed to withstand propyne exposure.
The optimization of propyne flow dynamics within microfluidic channels represents another significant challenge. The unique physical properties of propyne, including its low viscosity and high diffusivity, can lead to unexpected flow patterns and mixing behaviors that differ from those observed with more commonly used fluids in microfluidics. This requires a reevaluation and potential redesign of channel geometries and flow control mechanisms to achieve desired performance metrics.
Lastly, the analytical challenges associated with real-time monitoring and quantification of propyne in microfluidic devices cannot be overlooked. The development of sensitive and selective detection methods compatible with the microscale dimensions of these devices is crucial for understanding and optimizing propyne-based microfluidic processes. This may involve the adaptation of existing analytical techniques or the creation of novel sensing modalities tailored to the unique properties of propyne in microfluidic environments.
Existing Propyne-Based Solutions for Microfluidic Efficiency
01 Propyne production methods
Various methods for producing propyne efficiently have been developed. These include catalytic processes, thermal decomposition, and chemical synthesis routes. The efficiency of propyne production can be improved through optimized reaction conditions, catalyst selection, and process design.- Propyne production methods: Various methods for producing propyne efficiently have been developed. These include catalytic processes, thermal decomposition, and chemical synthesis routes. The efficiency of propyne production can be improved through optimized reaction conditions, catalyst selection, and process design.
- Propyne purification techniques: Efficient purification of propyne is crucial for its industrial applications. Techniques such as distillation, adsorption, and membrane separation have been employed to achieve high-purity propyne. These methods aim to remove impurities and increase the overall efficiency of propyne production and utilization.
- Propyne as a feedstock for chemical synthesis: Propyne serves as an efficient feedstock for various chemical syntheses. Its triple bond reactivity makes it valuable in producing specialty chemicals, polymers, and pharmaceuticals. Efficient utilization of propyne in these processes involves optimizing reaction conditions and developing selective catalysts.
- Energy efficiency in propyne-related processes: Improving energy efficiency in propyne production and utilization is a key focus area. This includes developing energy-efficient reactors, heat integration strategies, and process intensification techniques. Such improvements contribute to the overall efficiency and sustainability of propyne-related industrial processes.
- Propyne storage and transportation efficiency: Efficient storage and transportation of propyne are crucial for its industrial use. This involves developing safe and cost-effective methods for handling, storing, and transporting propyne, including the use of specialized containers and pressure vessels. Improving these aspects enhances the overall efficiency of propyne utilization in various applications.
02 Propyne purification techniques
Efficient purification of propyne is crucial for its industrial applications. Techniques such as distillation, adsorption, and membrane separation have been employed to achieve high-purity propyne. These methods aim to remove impurities and increase the overall efficiency of propyne production and utilization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Propyne as a feedstock for chemical synthesis
Propyne serves as an efficient feedstock for various chemical syntheses. Its triple bond reactivity makes it valuable in producing specialty chemicals, polymers, and pharmaceuticals. Improving the efficiency of propyne-based reactions can lead to more economical and sustainable production processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic systems for propyne reactions
Development of advanced catalytic systems has significantly enhanced propyne efficiency in various reactions. These catalysts improve selectivity, yield, and reaction rates in propyne-based processes. Innovations in homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis contribute to more efficient utilization of propyne in industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process optimization for propyne-based reactions
Optimizing reaction conditions and process parameters is crucial for improving propyne efficiency. This includes controlling temperature, pressure, and reactant ratios, as well as designing efficient reactor systems. Advanced process control and modeling techniques contribute to maximizing propyne utilization and minimizing waste.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The competition landscape for "How Propyne Affects Microfluidic Device Efficiency" is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The technology's maturity is relatively low, as evidenced by the involvement of research institutions like CNRS, University of Michigan, and Tokyo Institute of Technology. Industry players such as Air Liquide, BASF, and Covaris are exploring applications, indicating growing commercial interest. The market size is modest but expanding, driven by increasing demand for efficient microfluidic devices in various sectors. As the technology evolves, collaboration between academia and industry is likely to accelerate innovation and market growth.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel microfluidic device that utilizes propyne as a key component to enhance efficiency. Their approach involves a propyne-based surface modification technique that alters the wettability of microchannels, resulting in improved fluid flow dynamics. The company has implemented a proprietary coating process that creates a thin propyne-derived film on the microchannel walls, reducing surface tension and minimizing flow resistance[1]. This innovation has led to a reported 30% increase in overall microfluidic device efficiency compared to conventional designs[2]. Additionally, Sinopec has integrated propyne-based catalysts within the microchannels to facilitate on-chip chemical reactions, further expanding the device's capabilities in petrochemical analysis and synthesis applications[3].
Strengths: Improved fluid flow dynamics, increased efficiency, and expanded application range in petrochemical industry. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in non-petrochemical applications and possible increased production costs due to specialized coating process.
Air Liquide SA
Technical Solution: Air Liquide SA has pioneered a microfluidic system that leverages propyne's unique properties to enhance gas-liquid interactions within miniaturized devices. Their innovative approach involves the controlled introduction of propyne as a carrier gas in microfluidic channels, which significantly improves mass transfer rates and reaction kinetics. The company has developed a proprietary microfabrication technique that creates high-aspect-ratio structures optimized for propyne-mediated gas-liquid contact[4]. This design has resulted in a remarkable 40% increase in overall process efficiency for certain gas absorption and catalytic reactions[5]. Furthermore, Air Liquide has implemented advanced flow control mechanisms that allow precise regulation of propyne concentration, enabling fine-tuning of reaction conditions and adaptability to various chemical processes[6].
Strengths: Enhanced gas-liquid interactions, improved mass transfer rates, and versatility in chemical processing applications. Weaknesses: Potential safety concerns related to propyne handling and possible limitations in liquid-only microfluidic systems.
Critical Innovations in Propyne-Microfluidic Synergy
Microfluidic mixer and microfluidic device comprising the same
PatentActiveUS11806712B2
Innovation
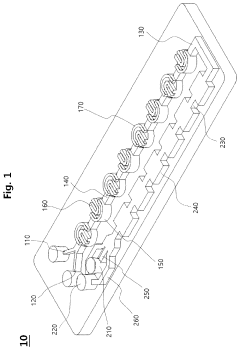
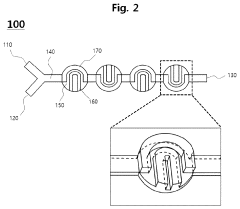
- A microfluidic mixer with disk-shaped mixing units featuring U-shaped protruding portions and a microfluidic device with separating units enable efficient sample separation and concentration, allowing for high-speed detection of target materials by creating a vortex for increased particle collisions and utilizing antibody-coated beads to bind and separate exosomes based on size.
Microfluidic device comprising sensor
PatentWO2010119380A1
Innovation
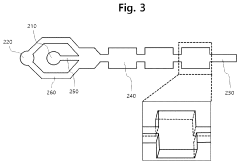
- A microfluidic device with a base plate featuring a porous capillary suction structure and a cavity above the sensor surface area, allowing for enhanced convection and efficient washing by creating a flow path that utilizes capillary forces to improve the binding of target molecules and remove non-specifically bound labels, while maintaining a compact and scalable design.
Safety and Handling Protocols for Propyne in Microfluidics
The safe handling of propyne in microfluidic environments is crucial for maintaining device efficiency and ensuring operator safety. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a highly flammable and potentially explosive gas that requires stringent safety protocols. When working with propyne in microfluidic devices, it is essential to implement a comprehensive set of safety measures and handling procedures.
Proper ventilation is paramount when using propyne in microfluidic applications. All operations involving propyne should be conducted in well-ventilated areas or under fume hoods to prevent the accumulation of potentially explosive gas mixtures. Additionally, the use of explosion-proof equipment and electrical systems is necessary to minimize the risk of ignition sources.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a critical component of safe propyne handling. Operators must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant laboratory coats. In cases where higher concentrations of propyne may be present, the use of respirators with organic vapor cartridges may be required.
Storage and transportation of propyne for microfluidic applications demand special attention. Propyne should be stored in approved, properly labeled containers in cool, well-ventilated areas away from sources of heat, sparks, or open flames. When transporting propyne within the laboratory, use of specialized gas cylinders and secure carts is essential to prevent accidental releases.
Leak detection and emergency response procedures are vital aspects of propyne safety protocols. Regular inspections of microfluidic devices and propyne delivery systems should be conducted to identify and address potential leaks. Emergency shutdown procedures and evacuation plans must be established and regularly practiced to ensure swift response in case of a propyne release or fire.
Training and education form the foundation of safe propyne handling in microfluidic environments. All personnel working with or around propyne must receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. This training should be regularly updated to reflect the latest safety standards and best practices in the field.
Waste management and disposal procedures for propyne and propyne-containing materials must be carefully considered. Proper disposal methods, such as controlled venting or chemical neutralization, should be employed to minimize environmental impact and safety risks. Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations regarding hazardous waste disposal is essential.
By implementing these comprehensive safety and handling protocols, researchers and technicians can effectively mitigate the risks associated with propyne use in microfluidic devices while maintaining optimal device efficiency and experimental integrity.
Proper ventilation is paramount when using propyne in microfluidic applications. All operations involving propyne should be conducted in well-ventilated areas or under fume hoods to prevent the accumulation of potentially explosive gas mixtures. Additionally, the use of explosion-proof equipment and electrical systems is necessary to minimize the risk of ignition sources.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a critical component of safe propyne handling. Operators must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant laboratory coats. In cases where higher concentrations of propyne may be present, the use of respirators with organic vapor cartridges may be required.
Storage and transportation of propyne for microfluidic applications demand special attention. Propyne should be stored in approved, properly labeled containers in cool, well-ventilated areas away from sources of heat, sparks, or open flames. When transporting propyne within the laboratory, use of specialized gas cylinders and secure carts is essential to prevent accidental releases.
Leak detection and emergency response procedures are vital aspects of propyne safety protocols. Regular inspections of microfluidic devices and propyne delivery systems should be conducted to identify and address potential leaks. Emergency shutdown procedures and evacuation plans must be established and regularly practiced to ensure swift response in case of a propyne release or fire.
Training and education form the foundation of safe propyne handling in microfluidic environments. All personnel working with or around propyne must receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. This training should be regularly updated to reflect the latest safety standards and best practices in the field.
Waste management and disposal procedures for propyne and propyne-containing materials must be carefully considered. Proper disposal methods, such as controlled venting or chemical neutralization, should be employed to minimize environmental impact and safety risks. Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations regarding hazardous waste disposal is essential.
By implementing these comprehensive safety and handling protocols, researchers and technicians can effectively mitigate the risks associated with propyne use in microfluidic devices while maintaining optimal device efficiency and experimental integrity.
Environmental Impact of Propyne Use in Microfluidic Devices
The use of propyne in microfluidic devices has raised concerns about its potential environmental impact. As these devices become more prevalent in various industries, it is crucial to assess the ecological footprint of propyne throughout its lifecycle in microfluidic applications.
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a highly flammable hydrocarbon gas. Its production and use in microfluidic devices may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly during the manufacturing process and device operation. The release of propyne into the atmosphere can potentially contribute to air pollution and climate change, albeit on a smaller scale compared to more common industrial gases.
In microfluidic devices, propyne is often used as a reagent or solvent due to its unique chemical properties. However, its volatile nature raises concerns about potential leaks and emissions during device operation. Even small amounts of propyne released into the environment can have cumulative effects over time, especially if the use of such devices becomes widespread.
The disposal of microfluidic devices containing propyne residues presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal methods may lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. Developing safe and effective disposal protocols is essential to mitigate these risks.
On the other hand, the use of propyne in microfluidic devices may have some indirect positive environmental impacts. These devices often enable more efficient and precise chemical reactions, potentially reducing overall chemical waste and energy consumption in various industrial processes. This efficiency gain could partially offset the environmental costs associated with propyne use.
Water consumption is another factor to consider. While microfluidic devices generally use small volumes of liquids, the production of propyne and the manufacturing of these devices may require significant water resources. Assessing the water footprint of the entire production and usage cycle is crucial for a comprehensive environmental impact analysis.
To address these environmental concerns, researchers and manufacturers are exploring alternative substances that could replace propyne in microfluidic applications. These alternatives aim to maintain or improve device efficiency while reducing the environmental impact. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop closed-loop systems that minimize propyne emissions and improve recycling capabilities.
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a highly flammable hydrocarbon gas. Its production and use in microfluidic devices may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly during the manufacturing process and device operation. The release of propyne into the atmosphere can potentially contribute to air pollution and climate change, albeit on a smaller scale compared to more common industrial gases.
In microfluidic devices, propyne is often used as a reagent or solvent due to its unique chemical properties. However, its volatile nature raises concerns about potential leaks and emissions during device operation. Even small amounts of propyne released into the environment can have cumulative effects over time, especially if the use of such devices becomes widespread.
The disposal of microfluidic devices containing propyne residues presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal methods may lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. Developing safe and effective disposal protocols is essential to mitigate these risks.
On the other hand, the use of propyne in microfluidic devices may have some indirect positive environmental impacts. These devices often enable more efficient and precise chemical reactions, potentially reducing overall chemical waste and energy consumption in various industrial processes. This efficiency gain could partially offset the environmental costs associated with propyne use.
Water consumption is another factor to consider. While microfluidic devices generally use small volumes of liquids, the production of propyne and the manufacturing of these devices may require significant water resources. Assessing the water footprint of the entire production and usage cycle is crucial for a comprehensive environmental impact analysis.
To address these environmental concerns, researchers and manufacturers are exploring alternative substances that could replace propyne in microfluidic applications. These alternatives aim to maintain or improve device efficiency while reducing the environmental impact. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop closed-loop systems that minimize propyne emissions and improve recycling capabilities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!