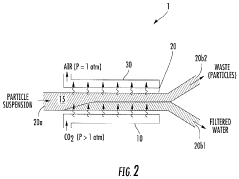
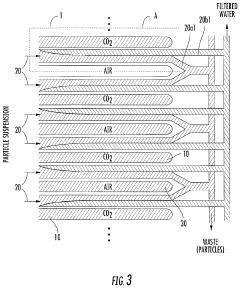
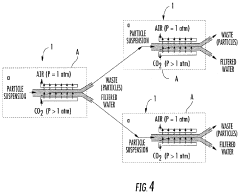
How Propyne-Based Techniques Enhance Filtration Systems
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propyne Filtration Evolution
The evolution of propyne-based filtration techniques has been marked by significant advancements in material science and engineering. Initially, propyne was primarily used in industrial processes as a precursor for various chemical syntheses. However, researchers began to explore its potential in filtration systems due to its unique molecular structure and reactivity.
In the early stages of development, propyne-based filtration focused on simple adsorption mechanisms. Scientists discovered that propyne molecules could be effectively captured by certain porous materials, leading to the creation of basic filtration systems. These early systems were primarily used in laboratory settings for gas purification and separation processes.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards developing more sophisticated filtration membranes incorporating propyne-derived compounds. The introduction of propyne-based polymers marked a significant milestone in this evolution. These polymers exhibited excellent selectivity and permeability, making them ideal for advanced filtration applications.
The next phase of evolution saw the integration of propyne-based materials with nanotechnology. This combination resulted in the creation of nanocomposite membranes with enhanced filtration properties. These membranes demonstrated superior performance in terms of flux, selectivity, and fouling resistance compared to conventional filtration systems.
Recent advancements have led to the development of smart filtration systems utilizing propyne-based materials. These systems incorporate responsive elements that can adapt to changing environmental conditions or contaminant profiles. For instance, some membranes can alter their pore size or surface chemistry in response to specific stimuli, allowing for dynamic filtration processes.
The latest frontier in propyne-based filtration involves the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies are being used to optimize the design and operation of filtration systems, predicting membrane performance and suggesting improvements in real-time. This integration of digital technologies with propyne-based materials represents a significant leap forward in filtration efficiency and effectiveness.
Throughout this evolution, propyne-based filtration techniques have found applications in various industries, including water treatment, air purification, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The continuous improvement in these techniques has led to more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly filtration solutions, addressing critical challenges in resource management and environmental protection.
In the early stages of development, propyne-based filtration focused on simple adsorption mechanisms. Scientists discovered that propyne molecules could be effectively captured by certain porous materials, leading to the creation of basic filtration systems. These early systems were primarily used in laboratory settings for gas purification and separation processes.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards developing more sophisticated filtration membranes incorporating propyne-derived compounds. The introduction of propyne-based polymers marked a significant milestone in this evolution. These polymers exhibited excellent selectivity and permeability, making them ideal for advanced filtration applications.
The next phase of evolution saw the integration of propyne-based materials with nanotechnology. This combination resulted in the creation of nanocomposite membranes with enhanced filtration properties. These membranes demonstrated superior performance in terms of flux, selectivity, and fouling resistance compared to conventional filtration systems.
Recent advancements have led to the development of smart filtration systems utilizing propyne-based materials. These systems incorporate responsive elements that can adapt to changing environmental conditions or contaminant profiles. For instance, some membranes can alter their pore size or surface chemistry in response to specific stimuli, allowing for dynamic filtration processes.
The latest frontier in propyne-based filtration involves the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies are being used to optimize the design and operation of filtration systems, predicting membrane performance and suggesting improvements in real-time. This integration of digital technologies with propyne-based materials represents a significant leap forward in filtration efficiency and effectiveness.
Throughout this evolution, propyne-based filtration techniques have found applications in various industries, including water treatment, air purification, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The continuous improvement in these techniques has led to more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly filtration solutions, addressing critical challenges in resource management and environmental protection.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for propyne-based filtration systems has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing concerns over air and water quality across various industries. This technology offers significant advantages in terms of filtration efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making it particularly attractive for both industrial and consumer applications.
In the industrial sector, propyne-based filtration systems are gaining traction in manufacturing, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries. These sectors require high-performance filtration solutions to meet stringent environmental regulations and improve operational efficiency. The ability of propyne-based techniques to remove fine particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) with greater effectiveness than traditional methods has led to increased adoption rates.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for propyne-based filtration systems. As emission standards become more stringent globally, automakers are seeking advanced filtration technologies to reduce harmful exhaust emissions. Propyne-based filters have shown promise in capturing a wider range of pollutants, potentially revolutionizing automotive emission control systems.
In the consumer market, there is a growing demand for high-efficiency air purifiers and water filtration systems. Heightened awareness of indoor air quality and water contamination issues has driven consumers to seek more effective filtration solutions for their homes and offices. Propyne-based filters offer superior performance in removing allergens, bacteria, and other microscopic contaminants, addressing these consumer concerns.
The healthcare sector presents a substantial growth opportunity for propyne-based filtration systems. Hospitals, laboratories, and pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities require ultra-clean environments to prevent contamination and ensure product quality. The enhanced filtration capabilities of propyne-based techniques make them well-suited for these critical applications, potentially driving significant market growth in this sector.
Geographically, developed regions such as North America and Europe currently lead the market for propyne-based filtration systems due to stringent environmental regulations and higher consumer awareness. However, rapid industrialization and urbanization in emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are expected to create substantial market opportunities in the coming years.
The global trend towards sustainability and circular economy principles is also likely to boost the demand for propyne-based filtration systems. As industries seek to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency, advanced filtration technologies that can recover valuable materials from waste streams become increasingly attractive.
In the industrial sector, propyne-based filtration systems are gaining traction in manufacturing, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries. These sectors require high-performance filtration solutions to meet stringent environmental regulations and improve operational efficiency. The ability of propyne-based techniques to remove fine particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) with greater effectiveness than traditional methods has led to increased adoption rates.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for propyne-based filtration systems. As emission standards become more stringent globally, automakers are seeking advanced filtration technologies to reduce harmful exhaust emissions. Propyne-based filters have shown promise in capturing a wider range of pollutants, potentially revolutionizing automotive emission control systems.
In the consumer market, there is a growing demand for high-efficiency air purifiers and water filtration systems. Heightened awareness of indoor air quality and water contamination issues has driven consumers to seek more effective filtration solutions for their homes and offices. Propyne-based filters offer superior performance in removing allergens, bacteria, and other microscopic contaminants, addressing these consumer concerns.
The healthcare sector presents a substantial growth opportunity for propyne-based filtration systems. Hospitals, laboratories, and pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities require ultra-clean environments to prevent contamination and ensure product quality. The enhanced filtration capabilities of propyne-based techniques make them well-suited for these critical applications, potentially driving significant market growth in this sector.
Geographically, developed regions such as North America and Europe currently lead the market for propyne-based filtration systems due to stringent environmental regulations and higher consumer awareness. However, rapid industrialization and urbanization in emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are expected to create substantial market opportunities in the coming years.
The global trend towards sustainability and circular economy principles is also likely to boost the demand for propyne-based filtration systems. As industries seek to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency, advanced filtration technologies that can recover valuable materials from waste streams become increasingly attractive.
Technical Challenges
Propyne-based filtration techniques represent a promising frontier in advanced filtration systems, yet they face several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of synthesizing and stabilizing propyne-based materials at scale. The highly reactive nature of propyne molecules makes them difficult to handle and incorporate into filtration membranes without compromising their unique properties.
Another major challenge lies in optimizing the pore size and distribution of propyne-based filters. While the small molecular structure of propyne allows for potentially high selectivity, achieving consistent and controllable pore sizes across large membrane areas remains a significant hurdle. This inconsistency can lead to variations in filtration performance and reduced overall efficiency.
The long-term stability of propyne-based filtration systems under various operational conditions poses another critical challenge. Exposure to different pH levels, temperatures, and chemical environments can potentially degrade the propyne structures, affecting the longevity and reliability of the filtration system. Developing robust propyne-based materials that maintain their performance over extended periods and under diverse conditions is crucial for practical applications.
Energy efficiency in propyne-based filtration systems is another area requiring significant improvement. While these systems show promise in terms of selectivity and throughput, they often require higher energy inputs compared to conventional filtration methods. Reducing the energy demand without compromising filtration efficiency is a key challenge that researchers and engineers must address.
The integration of propyne-based techniques with existing filtration infrastructure presents both technical and economic challenges. Retrofitting current systems or designing entirely new setups to accommodate propyne-based filters requires substantial investment and engineering expertise. Ensuring compatibility with various industrial processes and scaling up production to meet potential demand are additional hurdles that need to be overcome.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with propyne-based filtration systems require careful consideration. The potential release of propyne or its derivatives during the manufacturing or operational phases could have environmental implications. Developing safe handling protocols and environmentally friendly production methods are essential for the sustainable implementation of this technology.
Another major challenge lies in optimizing the pore size and distribution of propyne-based filters. While the small molecular structure of propyne allows for potentially high selectivity, achieving consistent and controllable pore sizes across large membrane areas remains a significant hurdle. This inconsistency can lead to variations in filtration performance and reduced overall efficiency.
The long-term stability of propyne-based filtration systems under various operational conditions poses another critical challenge. Exposure to different pH levels, temperatures, and chemical environments can potentially degrade the propyne structures, affecting the longevity and reliability of the filtration system. Developing robust propyne-based materials that maintain their performance over extended periods and under diverse conditions is crucial for practical applications.
Energy efficiency in propyne-based filtration systems is another area requiring significant improvement. While these systems show promise in terms of selectivity and throughput, they often require higher energy inputs compared to conventional filtration methods. Reducing the energy demand without compromising filtration efficiency is a key challenge that researchers and engineers must address.
The integration of propyne-based techniques with existing filtration infrastructure presents both technical and economic challenges. Retrofitting current systems or designing entirely new setups to accommodate propyne-based filters requires substantial investment and engineering expertise. Ensuring compatibility with various industrial processes and scaling up production to meet potential demand are additional hurdles that need to be overcome.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with propyne-based filtration systems require careful consideration. The potential release of propyne or its derivatives during the manufacturing or operational phases could have environmental implications. Developing safe handling protocols and environmentally friendly production methods are essential for the sustainable implementation of this technology.
Current Propyne Solutions
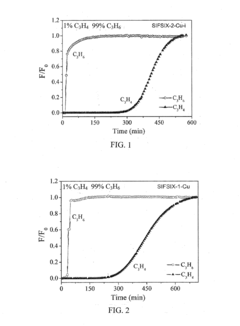
01 Propyne-based filtration membranes
Development of filtration membranes using propyne-based materials. These membranes offer improved selectivity and permeability for various separation processes, including gas separation and water purification. The propyne-based structure allows for precise control of pore size and surface properties, enhancing filtration efficiency.- Propyne-based filtration membranes: Development of filtration membranes using propyne-based polymers or copolymers. These membranes offer improved selectivity and permeability for various separation processes, including gas separation, water purification, and chemical filtration.
- Propyne as a precursor in filter material synthesis: Utilization of propyne as a starting material or intermediate in the synthesis of advanced filter materials. This approach enables the creation of highly specific and efficient filtration media for diverse applications in industrial and environmental sectors.
- Propyne-based catalytic filtration systems: Integration of propyne-derived catalysts into filtration systems to enhance the removal of specific contaminants. These catalytic filtration techniques combine physical separation with chemical transformation, improving overall filtration efficiency.
- Propyne-modified filter media: Modification of existing filter media using propyne-based compounds to impart specific properties such as hydrophobicity, oleophobicity, or antimicrobial activity. This technique enhances the performance and versatility of conventional filtration materials.
- Propyne-based nanofiber filtration technology: Development of nanofiber filtration materials using propyne-based polymers or precursors. These nanofibers offer high surface area and customizable pore sizes, resulting in superior filtration performance for fine particles and molecular separations.
02 Propyne derivatives in filter media
Utilization of propyne derivatives in the production of filter media. These compounds can be incorporated into filter materials to enhance their performance, such as improving particle capture efficiency, chemical resistance, and durability. The propyne-based additives can be applied to various filter types, including air and liquid filters.Expand Specific Solutions03 Propyne-based catalysts for filtration processes
Development of propyne-based catalysts for use in filtration processes. These catalysts can enhance the removal of specific contaminants or facilitate the breakdown of complex molecules during filtration. The propyne-based structure allows for tailored catalytic activity and improved stability in various filtration environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propyne-functionalized adsorbents
Creation of propyne-functionalized adsorbent materials for advanced filtration applications. These materials can be used in various filtration systems to selectively remove contaminants through adsorption. The propyne functional groups provide unique surface properties that enhance adsorption capacity and selectivity for specific target molecules.Expand Specific Solutions05 Propyne-based filter regeneration techniques
Development of methods for regenerating filters using propyne-based compounds. These techniques can extend the lifespan of filtration systems by effectively removing accumulated contaminants and restoring filter performance. The propyne-based regeneration processes offer advantages such as improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional methods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The propyne-based filtration technology market is in its growth phase, with increasing demand for advanced filtration solutions across various industries. The market size is expanding, driven by the need for more efficient and sustainable filtration systems. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with companies like BASF Corp., 3M Innovative Properties Co., and R-Zero Systems, Inc. leading innovation. These firms are developing proprietary propyne-based techniques to enhance filtration performance, focusing on improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and broader application potential. The technology's maturity is progressing, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at optimizing propyne-based filtration for diverse industrial and consumer applications.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed advanced propyne-based filtration systems that utilize innovative polymer chemistry. Their approach involves synthesizing propyne-derived polymers with tailored pore structures and surface properties. These polymers are then incorporated into high-performance filter membranes. The company's proprietary cross-linking technology enhances the mechanical and chemical stability of the membranes, allowing for improved separation of particles and molecules in various industrial processes[1]. BASF's filtration systems demonstrate exceptional selectivity and flux rates, particularly in gas separation and water purification applications[3].
Strengths: Superior chemical resistance, high selectivity, and improved flux rates. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and limited scalability for certain applications.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has pioneered propyne-based filtration technology through the development of advanced nanofiber membranes. Their approach involves electrospinning propyne-modified polymers to create ultra-fine fibers with diameters in the nanometer range. These nanofibers are then assembled into multi-layered filter media with precisely controlled pore sizes and distributions. The resulting filtration systems exhibit exceptional particle capture efficiency, even for sub-micron particles, while maintaining high air permeability[2]. 3M's propyne-enhanced nanofiber filters have shown particular promise in air filtration applications, including HVAC systems and personal protective equipment[4].
Strengths: High filtration efficiency, low pressure drop, and versatility across various applications. Weaknesses: Potential for higher manufacturing costs and limited durability in harsh chemical environments.
Core Propyne Innovations
Method for adsorption separation of propylene and propyne
PatentActiveUS20190010102A1
Innovation
- The use of anion-containing metal-organic framework materials that selectively adsorb propyne, allowing for deep removal and purification of propylene with ultralow propyne concentrations, utilizing their high specific surface area and tunable pore size for efficient separation.
Device and methods for continuous flow separation of particles by gas dissolution
PatentInactiveUS20200255299A1
Innovation
- A device and method that create an ion concentration gradient in a liquid by dissolving gas, inducing diffusiophoresis to separate charged particles without the need for filter media, allowing for dynamic separation and reduced maintenance.
Environmental Impact
The implementation of propyne-based techniques in filtration systems has significant environmental implications, both positive and negative. On the positive side, these advanced filtration methods can substantially improve air and water quality by removing a wider range of pollutants and contaminants more effectively than traditional systems. This enhanced filtration capability can lead to cleaner industrial emissions, reduced atmospheric pollution, and improved water treatment processes, ultimately contributing to better environmental health and ecosystem preservation.
Propyne-based filtration systems also demonstrate potential for reducing energy consumption in various industrial processes. By improving the efficiency of separation and purification processes, these systems can minimize the need for energy-intensive operations, thereby lowering overall carbon footprints and supporting sustainability goals. Additionally, the increased effectiveness of propyne-based filters may extend their operational lifespan, reducing the frequency of filter replacements and associated waste generation.
However, the environmental impact of propyne-based filtration techniques is not without concerns. The production and disposal of propyne-based materials used in these filtration systems may introduce new environmental challenges. The synthesis of propyne and its derivatives often involves petrochemical processes, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion if not managed sustainably. Furthermore, the end-of-life disposal of spent propyne-based filters requires careful consideration to prevent potential soil or water contamination.
Another environmental consideration is the potential release of propyne or its byproducts during the filtration process. While propyne is generally considered less harmful than many other industrial chemicals, its long-term environmental effects are not fully understood. Proper containment and handling protocols are essential to mitigate any risks associated with accidental releases or long-term exposure.
The scalability of propyne-based filtration systems also plays a crucial role in their overall environmental impact. As these technologies become more widespread, their cumulative effect on resource consumption and waste generation must be carefully monitored and managed. Balancing the environmental benefits of improved filtration against the potential drawbacks of increased propyne production and usage is key to ensuring a net positive environmental outcome.
In conclusion, while propyne-based filtration techniques offer promising environmental benefits through enhanced pollutant removal and potential energy savings, their widespread adoption necessitates a comprehensive assessment of their full lifecycle environmental impact. Ongoing research and development efforts should focus on optimizing the environmental performance of these systems, exploring sustainable production methods for propyne-based materials, and developing effective recycling and disposal strategies to maximize their positive environmental contributions.
Propyne-based filtration systems also demonstrate potential for reducing energy consumption in various industrial processes. By improving the efficiency of separation and purification processes, these systems can minimize the need for energy-intensive operations, thereby lowering overall carbon footprints and supporting sustainability goals. Additionally, the increased effectiveness of propyne-based filters may extend their operational lifespan, reducing the frequency of filter replacements and associated waste generation.
However, the environmental impact of propyne-based filtration techniques is not without concerns. The production and disposal of propyne-based materials used in these filtration systems may introduce new environmental challenges. The synthesis of propyne and its derivatives often involves petrochemical processes, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion if not managed sustainably. Furthermore, the end-of-life disposal of spent propyne-based filters requires careful consideration to prevent potential soil or water contamination.
Another environmental consideration is the potential release of propyne or its byproducts during the filtration process. While propyne is generally considered less harmful than many other industrial chemicals, its long-term environmental effects are not fully understood. Proper containment and handling protocols are essential to mitigate any risks associated with accidental releases or long-term exposure.
The scalability of propyne-based filtration systems also plays a crucial role in their overall environmental impact. As these technologies become more widespread, their cumulative effect on resource consumption and waste generation must be carefully monitored and managed. Balancing the environmental benefits of improved filtration against the potential drawbacks of increased propyne production and usage is key to ensuring a net positive environmental outcome.
In conclusion, while propyne-based filtration techniques offer promising environmental benefits through enhanced pollutant removal and potential energy savings, their widespread adoption necessitates a comprehensive assessment of their full lifecycle environmental impact. Ongoing research and development efforts should focus on optimizing the environmental performance of these systems, exploring sustainable production methods for propyne-based materials, and developing effective recycling and disposal strategies to maximize their positive environmental contributions.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the development and implementation of propyne-based filtration techniques. As these innovative systems gain traction in various industries, adherence to established standards and regulations becomes paramount to ensure safety, efficacy, and environmental protection.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the regulation of air and water filtration systems. Propyne-based filtration techniques must comply with the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act, which set stringent standards for emissions and effluent quality. Manufacturers and operators of these systems are required to obtain necessary permits and demonstrate compliance through regular testing and reporting.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also plays a significant role in regulating the use of propyne-based filtration systems in workplace environments. OSHA standards address issues such as exposure limits, personal protective equipment, and proper handling procedures for propyne and related compounds.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks vary, but many countries have adopted similar approaches to the United States. The European Union, for instance, has established the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which impacts the use of propyne and its derivatives in filtration systems. Manufacturers must register these substances and provide detailed safety information to comply with REACH requirements.
In the context of food and beverage industries, propyne-based filtration systems must meet the standards set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and equivalent agencies in other countries. These regulations ensure that filtration processes do not introduce harmful contaminants into food products or compromise food safety.
As propyne-based filtration techniques continue to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines to address emerging concerns and technological advancements. Industry stakeholders must stay informed about these changes and proactively adapt their systems to maintain compliance.
Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in testing, documentation, and quality control measures. However, adherence to these standards not only ensures legal operation but also builds consumer trust and enhances the reputation of companies utilizing propyne-based filtration technologies.
It is worth noting that regulatory compliance extends beyond the operational aspects of filtration systems. The entire lifecycle of these technologies, from research and development to disposal, must be considered. This includes regulations governing the transportation of propyne and related materials, as well as proper disposal methods for spent filtration media.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the regulation of air and water filtration systems. Propyne-based filtration techniques must comply with the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act, which set stringent standards for emissions and effluent quality. Manufacturers and operators of these systems are required to obtain necessary permits and demonstrate compliance through regular testing and reporting.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also plays a significant role in regulating the use of propyne-based filtration systems in workplace environments. OSHA standards address issues such as exposure limits, personal protective equipment, and proper handling procedures for propyne and related compounds.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks vary, but many countries have adopted similar approaches to the United States. The European Union, for instance, has established the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which impacts the use of propyne and its derivatives in filtration systems. Manufacturers must register these substances and provide detailed safety information to comply with REACH requirements.
In the context of food and beverage industries, propyne-based filtration systems must meet the standards set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and equivalent agencies in other countries. These regulations ensure that filtration processes do not introduce harmful contaminants into food products or compromise food safety.
As propyne-based filtration techniques continue to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines to address emerging concerns and technological advancements. Industry stakeholders must stay informed about these changes and proactively adapt their systems to maintain compliance.
Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in testing, documentation, and quality control measures. However, adherence to these standards not only ensures legal operation but also builds consumer trust and enhances the reputation of companies utilizing propyne-based filtration technologies.
It is worth noting that regulatory compliance extends beyond the operational aspects of filtration systems. The entire lifecycle of these technologies, from research and development to disposal, must be considered. This includes regulations governing the transportation of propyne and related materials, as well as proper disposal methods for spent filtration media.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!