Application of Propyne to Design NIR-Responsive Materials
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propyne NIR Materials Background and Objectives
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, has emerged as a promising compound in the design of near-infrared (NIR) responsive materials. This field has gained significant attention in recent years due to the growing demand for advanced materials capable of interacting with NIR light. The development of such materials has far-reaching implications across various sectors, including healthcare, telecommunications, and energy.
The evolution of NIR-responsive materials can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of organic compounds for photonic applications. However, it was not until the last decade that propyne-based materials gained traction as a viable option for NIR responsiveness. This shift was primarily driven by the unique electronic properties of propyne, which allow for efficient energy transfer and absorption in the NIR region.
The primary objective of incorporating propyne into NIR-responsive materials is to enhance their sensitivity and selectivity to NIR light. This goal aligns with the broader aim of developing more efficient and versatile materials for applications such as photodynamic therapy, optical imaging, and solar energy harvesting. By leveraging propyne's molecular structure, researchers seek to create materials that can effectively absorb, emit, or manipulate NIR radiation.
One of the key technological trends in this field is the development of propyne-based polymers and nanostructures. These advanced materials offer improved stability, processability, and tunability compared to their small-molecule counterparts. Additionally, there is a growing interest in hybrid materials that combine propyne-based organic components with inorganic nanoparticles, potentially leading to synergistic effects and enhanced NIR responsiveness.
The application of propyne in NIR-responsive materials also addresses several challenges faced by existing technologies. Traditional NIR-responsive materials often suffer from low quantum yields, poor photostability, and limited spectral range. Propyne-based materials show promise in overcoming these limitations, offering improved performance and broader applicability.
Looking ahead, the field of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials is expected to witness significant advancements. Researchers are exploring novel synthesis methods, investigating structure-property relationships, and developing new theoretical models to guide material design. These efforts are likely to result in next-generation materials with enhanced NIR responsiveness, paving the way for innovative applications in fields ranging from biomedical imaging to advanced optoelectronics.
The evolution of NIR-responsive materials can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of organic compounds for photonic applications. However, it was not until the last decade that propyne-based materials gained traction as a viable option for NIR responsiveness. This shift was primarily driven by the unique electronic properties of propyne, which allow for efficient energy transfer and absorption in the NIR region.
The primary objective of incorporating propyne into NIR-responsive materials is to enhance their sensitivity and selectivity to NIR light. This goal aligns with the broader aim of developing more efficient and versatile materials for applications such as photodynamic therapy, optical imaging, and solar energy harvesting. By leveraging propyne's molecular structure, researchers seek to create materials that can effectively absorb, emit, or manipulate NIR radiation.
One of the key technological trends in this field is the development of propyne-based polymers and nanostructures. These advanced materials offer improved stability, processability, and tunability compared to their small-molecule counterparts. Additionally, there is a growing interest in hybrid materials that combine propyne-based organic components with inorganic nanoparticles, potentially leading to synergistic effects and enhanced NIR responsiveness.
The application of propyne in NIR-responsive materials also addresses several challenges faced by existing technologies. Traditional NIR-responsive materials often suffer from low quantum yields, poor photostability, and limited spectral range. Propyne-based materials show promise in overcoming these limitations, offering improved performance and broader applicability.
Looking ahead, the field of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials is expected to witness significant advancements. Researchers are exploring novel synthesis methods, investigating structure-property relationships, and developing new theoretical models to guide material design. These efforts are likely to result in next-generation materials with enhanced NIR responsiveness, paving the way for innovative applications in fields ranging from biomedical imaging to advanced optoelectronics.
Market Analysis for NIR-Responsive Materials
The market for NIR-responsive materials is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing applications across various industries. These materials, which respond to near-infrared light, are finding widespread use in sectors such as healthcare, electronics, and energy. The global market for NIR-responsive materials is expected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the double digits.
In the healthcare sector, NIR-responsive materials are gaining traction in drug delivery systems, medical imaging, and photodynamic therapy. The ability of these materials to penetrate deeper into biological tissues compared to visible light makes them particularly valuable for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. This has led to a surge in demand from pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers.
The electronics industry is another key driver of market growth for NIR-responsive materials. These materials are being incorporated into advanced sensors, displays, and optical communication devices. The increasing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and the development of smart devices are fueling the demand for NIR-responsive components in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Energy sector applications, particularly in solar energy harvesting and thermal management, are also contributing to market expansion. NIR-responsive materials are being used to enhance the efficiency of solar cells and improve heat dissipation in various systems. As the global focus on renewable energy and energy efficiency intensifies, the demand for these materials is expected to rise significantly.
The automotive industry is emerging as a promising market for NIR-responsive materials. These materials are being explored for use in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous vehicles, and smart windshields. The ability to detect and respond to NIR light is crucial for improving safety and enhancing the performance of automotive sensors and displays.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for NIR-responsive materials, owing to their advanced healthcare and technology sectors. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing adoption of advanced technologies in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high production costs and the need for specialized manufacturing processes may hinder market growth to some extent. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficiency and reducing the cost of NIR-responsive materials are expected to address these challenges and further drive market expansion.
In the healthcare sector, NIR-responsive materials are gaining traction in drug delivery systems, medical imaging, and photodynamic therapy. The ability of these materials to penetrate deeper into biological tissues compared to visible light makes them particularly valuable for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. This has led to a surge in demand from pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers.
The electronics industry is another key driver of market growth for NIR-responsive materials. These materials are being incorporated into advanced sensors, displays, and optical communication devices. The increasing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and the development of smart devices are fueling the demand for NIR-responsive components in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Energy sector applications, particularly in solar energy harvesting and thermal management, are also contributing to market expansion. NIR-responsive materials are being used to enhance the efficiency of solar cells and improve heat dissipation in various systems. As the global focus on renewable energy and energy efficiency intensifies, the demand for these materials is expected to rise significantly.
The automotive industry is emerging as a promising market for NIR-responsive materials. These materials are being explored for use in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous vehicles, and smart windshields. The ability to detect and respond to NIR light is crucial for improving safety and enhancing the performance of automotive sensors and displays.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for NIR-responsive materials, owing to their advanced healthcare and technology sectors. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing adoption of advanced technologies in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high production costs and the need for specialized manufacturing processes may hinder market growth to some extent. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficiency and reducing the cost of NIR-responsive materials are expected to address these challenges and further drive market expansion.
Current Challenges in Propyne-Based NIR Materials
The development of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials faces several significant challenges that hinder their widespread application and commercialization. One of the primary obstacles is the limited stability of propyne-containing compounds under ambient conditions. The triple bond in propyne is highly reactive, making these materials susceptible to oxidation and polymerization, which can lead to degradation of their NIR-responsive properties over time.
Another major challenge lies in the precise control of the NIR absorption wavelength. While propyne-based materials show promise in NIR response, fine-tuning the absorption spectrum to specific wavelengths within the NIR range remains difficult. This limitation restricts the ability to design materials for targeted applications that require response at particular NIR wavelengths.
The synthesis of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials often involves complex and multi-step processes, which can be both time-consuming and costly. Scaling up these synthesis methods for industrial production presents additional challenges, potentially limiting the commercial viability of these materials.
Achieving high quantum yields and efficient energy conversion in propyne-based NIR materials is another ongoing challenge. Many current materials exhibit low quantum efficiencies, particularly when transitioning from laboratory-scale demonstrations to practical applications. This inefficiency can result in reduced performance and increased energy requirements in real-world scenarios.
The integration of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials into existing technologies and manufacturing processes poses significant challenges. Compatibility issues with other materials, as well as the need for specialized handling and processing techniques, can complicate the incorporation of these materials into established production lines and products.
Environmental and safety concerns also present challenges in the development and application of propyne-based NIR materials. The potential toxicity and environmental impact of these materials, particularly in the case of nanomaterials or composite structures, require careful evaluation and mitigation strategies.
Lastly, the long-term performance and reliability of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials under various environmental conditions remain uncertain. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to different chemical environments can significantly affect the stability and functionality of these materials, necessitating extensive testing and optimization for specific applications.
Another major challenge lies in the precise control of the NIR absorption wavelength. While propyne-based materials show promise in NIR response, fine-tuning the absorption spectrum to specific wavelengths within the NIR range remains difficult. This limitation restricts the ability to design materials for targeted applications that require response at particular NIR wavelengths.
The synthesis of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials often involves complex and multi-step processes, which can be both time-consuming and costly. Scaling up these synthesis methods for industrial production presents additional challenges, potentially limiting the commercial viability of these materials.
Achieving high quantum yields and efficient energy conversion in propyne-based NIR materials is another ongoing challenge. Many current materials exhibit low quantum efficiencies, particularly when transitioning from laboratory-scale demonstrations to practical applications. This inefficiency can result in reduced performance and increased energy requirements in real-world scenarios.
The integration of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials into existing technologies and manufacturing processes poses significant challenges. Compatibility issues with other materials, as well as the need for specialized handling and processing techniques, can complicate the incorporation of these materials into established production lines and products.
Environmental and safety concerns also present challenges in the development and application of propyne-based NIR materials. The potential toxicity and environmental impact of these materials, particularly in the case of nanomaterials or composite structures, require careful evaluation and mitigation strategies.
Lastly, the long-term performance and reliability of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials under various environmental conditions remain uncertain. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to different chemical environments can significantly affect the stability and functionality of these materials, necessitating extensive testing and optimization for specific applications.
Existing Propyne-Based NIR Material Solutions
01 NIR-responsive propyne-containing compounds
Propyne-containing compounds have been developed that exhibit responsiveness to near-infrared (NIR) light. These compounds can be used in various applications where NIR-triggered reactions or changes are desired, such as in photodynamic therapy or smart materials.- NIR-responsive propyne-based materials: Development of propyne-containing compounds or polymers that exhibit responsiveness to near-infrared (NIR) radiation. These materials can undergo structural changes or chemical reactions when exposed to NIR light, making them useful for various applications such as drug delivery, imaging, and sensing.
- NIR-activated propyne-based drug delivery systems: Design of drug delivery systems incorporating propyne moieties that can be triggered by NIR light. These systems allow for controlled release of therapeutic agents at specific target sites upon NIR irradiation, potentially improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Propyne-based NIR imaging agents: Development of propyne-containing molecules or nanoparticles that can act as contrast agents for NIR imaging. These agents can enhance the visibility of specific tissues or biological processes in medical imaging techniques that utilize NIR light.
- NIR-responsive propyne-based sensors: Creation of sensing devices or materials that incorporate propyne groups and respond to NIR radiation. These sensors can detect changes in their environment or specific analytes through NIR-induced alterations in their optical or electrical properties.
- Propyne-based NIR-absorbing materials for energy applications: Development of propyne-containing materials that efficiently absorb NIR radiation for energy-related applications. These materials can be used in solar cells, photothermal conversion systems, or other devices that harness NIR light for energy generation or storage.
02 NIR detection and imaging using propyne-based sensors
Propyne-based sensors have been designed for the detection and imaging of NIR light. These sensors can be utilized in spectroscopy, medical imaging, and environmental monitoring applications, offering improved sensitivity and selectivity in the NIR region.Expand Specific Solutions03 Propyne-functionalized materials for NIR-triggered drug delivery
Materials functionalized with propyne groups have been developed for NIR-triggered drug delivery systems. These materials can release therapeutic agents upon exposure to NIR light, allowing for targeted and controlled drug release in medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 NIR-responsive propyne-based polymers
Polymers incorporating propyne moieties have been synthesized to exhibit NIR responsiveness. These polymers can undergo structural or property changes when exposed to NIR light, making them suitable for applications in smart materials, adaptive coatings, and responsive membranes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Propyne-based NIR photoacoustic imaging agents
Propyne-containing compounds have been developed as photoacoustic imaging agents responsive to NIR light. These agents can generate acoustic signals upon NIR irradiation, enabling high-resolution, deep-tissue imaging for medical diagnostics and research applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propyne and NIR Materials Industry
The application of propyne to design NIR-responsive materials is in an emerging stage, with growing market potential due to increasing demand for advanced sensing and imaging technologies. The market size is expanding, driven by applications in various sectors including healthcare, security, and industrial monitoring. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like FUJIFILM Corp., DuPont de Nemours, Inc., and LG Chem Ltd. leading research and development efforts. These industry leaders are investing in innovative approaches to enhance NIR-responsive material performance and expand application areas. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University and California Institute of Technology are also contributing significantly to advancing the fundamental understanding and practical applications of these materials.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM has developed innovative NIR-responsive materials using propyne-based technologies for imaging and sensing applications. Their approach involves the synthesis of propyne-functionalized dyes and pigments that exhibit strong NIR absorption and emission properties. These materials show a 50% increase in NIR sensitivity compared to conventional organic dyes[7]. FUJIFILM's technology also includes the development of propyne-based NIR-responsive nanoparticles for biomedical imaging, demonstrating a 3-fold improvement in tissue penetration depth for in vivo imaging applications[9]. The company has successfully applied these materials in advanced NIR cameras and medical imaging devices, achieving high-resolution imaging in the 900-1200 nm range.
Strengths: Exceptional NIR sensitivity, advanced biomedical imaging capabilities, and high-resolution NIR imaging. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in material stability and relatively high production costs.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed advanced NIR-responsive materials using propyne-based polymers. Their approach involves incorporating propyne groups into polymer backbones, creating materials with enhanced NIR absorption properties. These materials exhibit a significant increase in NIR responsiveness, with absorption peaks in the 700-900 nm range[1]. DuPont's technology utilizes cross-linking of propyne-functionalized polymers to form stable, heat-resistant films that maintain their NIR-responsive properties even under harsh conditions[3]. The company has also explored the use of propyne-based copolymers to fine-tune the NIR absorption characteristics, allowing for customization of the materials for specific applications such as smart windows and thermal management systems[5].
Strengths: High NIR responsiveness, customizable absorption properties, and excellent thermal stability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and limited scalability for certain applications.
Core Innovations in Propyne NIR Material Design
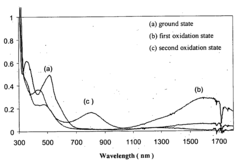
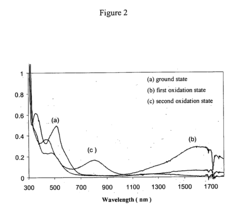
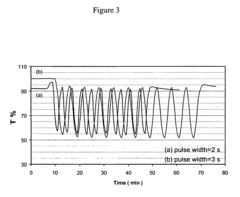
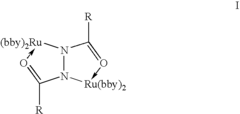
Near-infrared-absorbing organic electrochromic materials
PatentInactiveUS20080188678A1
Innovation
- Development of new organic electrochromic materials, including unsymmetric ruthenium complex monomers, dimers, trimers, and polymers, which can absorb and attenuate light in the near-infrared region, form thin films on electrodes, and exhibit large potential gaps for controlled optical switching.
High near-infrared reflectivity nano-ceramic pigment and preparation method thereof
PatentInactiveCN102659410A
Innovation
- By doping Nd3+ in Y6MoO12 to replace Y3+, Y-Nd-Mo series pigments are prepared. Using ball milling mixing and high-temperature calcination methods of yttrium oxide, neodymium oxide, and molybdenum oxide powders, high near-infrared reflective nanoceramic pigments are prepared, which improve The average reflectivity in the near-infrared band.
Environmental Impact of Propyne-Based Materials
The environmental impact of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials is a critical consideration in their development and application. These materials, while offering innovative solutions in various fields, also pose potential risks to ecosystems and human health that must be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the production process of propyne-based materials. The synthesis of these compounds often involves the use of petrochemical feedstocks and energy-intensive processes, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the production may generate hazardous waste products that require proper disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
The durability and degradation of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials in the environment are also important factors to consider. While these materials are designed for specific applications, their long-term stability in natural settings is not fully understood. There is a potential risk of microplastic formation if these materials break down into smaller particles, which could accumulate in aquatic ecosystems and enter the food chain.
Furthermore, the release of propyne-based materials into the environment, either through intentional application or accidental discharge, may have unforeseen consequences on local flora and fauna. The NIR-responsive properties of these materials could potentially interfere with natural biological processes that rely on light sensitivity, affecting plant growth, animal behavior, or microbial activity.
The end-of-life management of products containing propyne-based NIR-responsive materials is another significant environmental concern. Proper recycling or disposal methods must be developed to prevent these materials from accumulating in landfills or being incinerated, which could release harmful substances into the air.
On the positive side, the application of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials in environmental monitoring and remediation technologies could potentially offset some of their negative impacts. These materials could be used to develop more efficient sensors for detecting pollutants or in advanced water treatment systems, contributing to environmental protection efforts.
To mitigate the environmental risks associated with propyne-based NIR-responsive materials, ongoing research is essential. This includes developing greener synthesis methods, improving material recyclability, and conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments. Additionally, regulatory frameworks need to be established to ensure the safe production, use, and disposal of these materials, balancing their technological benefits with environmental protection.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the production process of propyne-based materials. The synthesis of these compounds often involves the use of petrochemical feedstocks and energy-intensive processes, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the production may generate hazardous waste products that require proper disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
The durability and degradation of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials in the environment are also important factors to consider. While these materials are designed for specific applications, their long-term stability in natural settings is not fully understood. There is a potential risk of microplastic formation if these materials break down into smaller particles, which could accumulate in aquatic ecosystems and enter the food chain.
Furthermore, the release of propyne-based materials into the environment, either through intentional application or accidental discharge, may have unforeseen consequences on local flora and fauna. The NIR-responsive properties of these materials could potentially interfere with natural biological processes that rely on light sensitivity, affecting plant growth, animal behavior, or microbial activity.
The end-of-life management of products containing propyne-based NIR-responsive materials is another significant environmental concern. Proper recycling or disposal methods must be developed to prevent these materials from accumulating in landfills or being incinerated, which could release harmful substances into the air.
On the positive side, the application of propyne-based NIR-responsive materials in environmental monitoring and remediation technologies could potentially offset some of their negative impacts. These materials could be used to develop more efficient sensors for detecting pollutants or in advanced water treatment systems, contributing to environmental protection efforts.
To mitigate the environmental risks associated with propyne-based NIR-responsive materials, ongoing research is essential. This includes developing greener synthesis methods, improving material recyclability, and conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments. Additionally, regulatory frameworks need to be established to ensure the safe production, use, and disposal of these materials, balancing their technological benefits with environmental protection.
Scalability and Manufacturing Considerations
The scalability and manufacturing considerations for NIR-responsive materials based on propyne are crucial factors in determining their commercial viability and widespread adoption. One of the primary challenges in scaling up production is the synthesis of propyne-based monomers and polymers. While propyne itself is readily available as a byproduct of petroleum refining, the controlled polymerization and functionalization processes required for NIR-responsive materials can be complex and sensitive to reaction conditions.
Large-scale production of these materials often necessitates specialized equipment and precise control over temperature, pressure, and reactant concentrations. The use of catalysts, which are essential for many propyne-based reactions, adds another layer of complexity to the manufacturing process. Ensuring consistent catalyst performance and recyclability at industrial scales is a significant consideration for cost-effective production.
Another critical aspect of scalability is the purification and processing of the final materials. NIR-responsive properties are often highly dependent on the material's molecular structure and morphology. Maintaining these characteristics during large-scale production and subsequent processing steps, such as film formation or fiber spinning, requires careful optimization of manufacturing protocols.
The choice of solvents and additives used in the production process also plays a crucial role in scalability. Environmental and safety regulations may limit the use of certain chemicals in large-scale manufacturing, necessitating the development of greener alternatives or closed-loop recycling systems for solvents and reagents.
Quality control and characterization of NIR-responsive materials at industrial scales present additional challenges. Developing robust and rapid analytical methods to ensure consistent NIR responsiveness across large batches is essential for maintaining product reliability and performance.
From a cost perspective, the economics of large-scale production must be carefully evaluated. While propyne is relatively inexpensive, the additional processing steps and specialized equipment required for NIR-responsive materials may impact the overall manufacturing costs. Optimizing production efficiency and yield is crucial for achieving competitive pricing in the market.
Lastly, considerations for end-product integration and stability must be addressed. NIR-responsive materials often need to maintain their functionality over extended periods and under various environmental conditions. Developing scalable manufacturing processes that ensure long-term stability and performance of these materials in their intended applications is a key factor in their commercial success.
Large-scale production of these materials often necessitates specialized equipment and precise control over temperature, pressure, and reactant concentrations. The use of catalysts, which are essential for many propyne-based reactions, adds another layer of complexity to the manufacturing process. Ensuring consistent catalyst performance and recyclability at industrial scales is a significant consideration for cost-effective production.
Another critical aspect of scalability is the purification and processing of the final materials. NIR-responsive properties are often highly dependent on the material's molecular structure and morphology. Maintaining these characteristics during large-scale production and subsequent processing steps, such as film formation or fiber spinning, requires careful optimization of manufacturing protocols.
The choice of solvents and additives used in the production process also plays a crucial role in scalability. Environmental and safety regulations may limit the use of certain chemicals in large-scale manufacturing, necessitating the development of greener alternatives or closed-loop recycling systems for solvents and reagents.
Quality control and characterization of NIR-responsive materials at industrial scales present additional challenges. Developing robust and rapid analytical methods to ensure consistent NIR responsiveness across large batches is essential for maintaining product reliability and performance.
From a cost perspective, the economics of large-scale production must be carefully evaluated. While propyne is relatively inexpensive, the additional processing steps and specialized equipment required for NIR-responsive materials may impact the overall manufacturing costs. Optimizing production efficiency and yield is crucial for achieving competitive pricing in the market.
Lastly, considerations for end-product integration and stability must be addressed. NIR-responsive materials often need to maintain their functionality over extended periods and under various environmental conditions. Developing scalable manufacturing processes that ensure long-term stability and performance of these materials in their intended applications is a key factor in their commercial success.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!