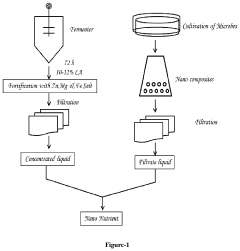
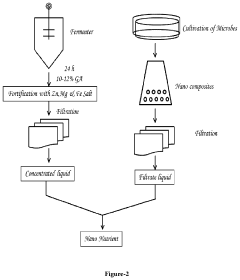
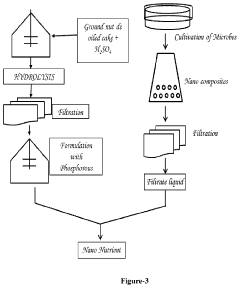
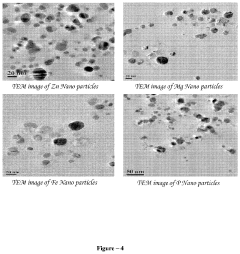
Hypertonic Fertilizers: Revolutionizing Plant Nutrition
Hypertonic Fertilizers: Background and Objectives
Hypertonic fertilizers represent a groundbreaking innovation in agricultural technology, poised to revolutionize plant nutrition and crop management. This novel approach to fertilization leverages the principles of osmosis to enhance nutrient uptake and utilization by plants. The concept of hypertonic fertilizers has emerged from the intersection of plant physiology, soil science, and advanced material engineering.
The development of hypertonic fertilizers can be traced back to the early 21st century, as researchers sought more efficient and sustainable methods of nutrient delivery to crops. Traditional fertilization techniques often suffer from low efficiency, with a significant portion of applied nutrients lost to the environment through leaching, volatilization, or runoff. This not only represents an economic loss for farmers but also contributes to environmental pollution and degradation.
Hypertonic fertilizers aim to address these challenges by creating a concentrated nutrient solution that draws water and dissolved nutrients into plant roots through osmotic pressure. This mechanism ensures a more targeted and efficient delivery of essential elements to plants, potentially reducing the overall amount of fertilizer required and minimizing environmental impact.
The primary objective of research in hypertonic fertilizers is to optimize nutrient formulations and delivery systems that can significantly enhance crop yields while promoting sustainable agricultural practices. This involves exploring various aspects such as the ideal concentration of nutrients, the most effective chemical compounds to use, and the development of controlled-release mechanisms to maintain optimal nutrient levels over time.
Another critical goal is to understand and mitigate potential risks associated with hypertonic fertilizers, such as soil salinization or alterations in soil microbial communities. Researchers are investigating ways to balance the benefits of enhanced nutrient uptake with long-term soil health and ecosystem sustainability.
As global food demand continues to rise and arable land becomes increasingly scarce, the development of hypertonic fertilizers aligns with the broader trend towards precision agriculture and sustainable intensification. By improving nutrient use efficiency, these advanced fertilizers have the potential to significantly boost crop productivity on existing agricultural lands, reducing the pressure to expand farming into natural ecosystems.
The evolution of hypertonic fertilizer technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing food security challenges, particularly in regions with poor soil quality or limited water resources. As such, research in this field is not only advancing agricultural science but also contributing to global efforts in sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Market Analysis for Advanced Fertilizer Solutions
The global market for advanced fertilizer solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices and the need to enhance crop yields. Hypertonic fertilizers, a cutting-edge development in plant nutrition, are poised to revolutionize the industry by offering more efficient nutrient delivery systems.
The current market size for advanced fertilizers is substantial, with projections indicating continued expansion over the next decade. This growth is fueled by several factors, including the rising global population, shrinking arable land, and the imperative to improve food security. Farmers and agricultural enterprises are increasingly seeking innovative solutions to maximize crop productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Hypertonic fertilizers represent a promising segment within the advanced fertilizer market. These products leverage osmotic principles to enhance nutrient uptake by plants, potentially leading to improved crop yields and reduced fertilizer runoff. The market for hypertonic fertilizers is still in its early stages but shows strong potential for rapid growth as awareness of their benefits spreads among agricultural stakeholders.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption rates for advanced fertilizer solutions. Developed countries in North America and Europe are at the forefront of implementing these technologies, driven by stringent environmental regulations and a focus on sustainable farming practices. Emerging economies in Asia and South America are also showing increased interest, particularly as they seek to modernize their agricultural sectors and boost food production.
Key market drivers for hypertonic fertilizers include the growing emphasis on precision agriculture, the need for water-efficient farming methods, and the push for environmentally friendly agricultural inputs. Additionally, the rising costs of traditional fertilizers and concerns over their environmental impact are prompting farmers to explore alternative solutions.
Market challenges for hypertonic fertilizers include the need for extensive education and demonstration to convince farmers of their efficacy, potential higher upfront costs compared to conventional fertilizers, and the need for specialized application equipment. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for widespread market adoption.
The competitive landscape for advanced fertilizer solutions is diverse, with both established agrochemical companies and innovative startups vying for market share. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to create proprietary hypertonic fertilizer formulations, while smaller companies are focusing on niche applications and specialized crop solutions.
Looking ahead, the market for hypertonic fertilizers is expected to see robust growth as agricultural practices continue to evolve towards more sustainable and efficient models. The integration of hypertonic fertilizers with precision agriculture technologies, such as smart irrigation systems and soil sensors, presents significant opportunities for market expansion and product differentiation.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Fertilizer Technology
Hypertonic fertilizers, while promising significant advancements in plant nutrition, face several challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary obstacles is the potential for soil salinization. The high salt concentration in these fertilizers can lead to an accumulation of salts in the soil over time, particularly in areas with low rainfall or inadequate irrigation. This salt buildup can negatively impact soil structure, reduce water infiltration, and ultimately decrease crop yields.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise application of hypertonic fertilizers. Due to their concentrated nature, even slight miscalculations in dosage or distribution can result in nutrient imbalances or plant stress. This necessitates advanced application technologies and sophisticated monitoring systems, which may be cost-prohibitive for many farmers, especially in developing regions.
The environmental impact of hypertonic fertilizers also presents a considerable concern. Excess nutrients that are not absorbed by plants can leach into groundwater or run off into surface water bodies, contributing to eutrophication and water pollution. Developing formulations that maximize nutrient uptake efficiency while minimizing environmental runoff remains a critical challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Furthermore, the interaction between hypertonic fertilizers and soil microbiota is not fully understood. These concentrated solutions may disrupt the delicate balance of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, potentially affecting long-term soil health and fertility. Research into microbial-friendly formulations and application methods is ongoing but faces significant hurdles.
The economic viability of hypertonic fertilizers poses another challenge. While they offer the potential for increased crop yields and reduced application frequency, the initial costs associated with their production, specialized equipment, and farmer training can be substantial. Bridging this economic gap and demonstrating long-term cost-effectiveness is crucial for wider adoption.
Lastly, regulatory frameworks and standards for hypertonic fertilizers are still evolving. The lack of comprehensive guidelines for their use, safety assessments, and environmental impact studies creates uncertainty for both manufacturers and end-users. Establishing clear, science-based regulations that ensure product safety and environmental protection while fostering innovation remains a complex challenge for policymakers and industry stakeholders.
Existing Hypertonic Fertilizer Formulations
01 Composition of hypertonic fertilizers
Hypertonic fertilizers are formulated with high concentrations of nutrients to create a solution with higher osmotic pressure than plant cells. These fertilizers typically contain a balanced mix of macronutrients and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements. The hypertonic nature of these fertilizers enhances nutrient uptake by creating a concentration gradient that facilitates the movement of nutrients into plant tissues.- Composition of hypertonic fertilizers: Hypertonic fertilizers are formulated with high concentrations of soluble nutrients to create a solution with higher osmotic pressure than plant cells. These fertilizers typically contain a balanced mixture of essential macro and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements. The hypertonic nature of these fertilizers enhances nutrient uptake by creating a concentration gradient that facilitates the movement of nutrients into plant tissues.
- Application methods for hypertonic fertilizers: Various application methods are employed for hypertonic fertilizers to maximize their effectiveness in plant nutrition. These include foliar spraying, fertigation through irrigation systems, and soil drenching. The choice of application method depends on factors such as crop type, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Proper application techniques ensure optimal nutrient absorption and minimize the risk of plant stress or damage due to the high osmotic pressure of the fertilizer solution.
- Controlled release mechanisms in hypertonic fertilizers: Advanced formulations of hypertonic fertilizers incorporate controlled release mechanisms to regulate nutrient availability over time. These mechanisms may include polymer coatings, encapsulation technologies, or chemical modifications that gradually release nutrients in response to environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, or soil pH. Controlled release hypertonic fertilizers provide sustained nutrition to plants, reducing the frequency of applications and minimizing nutrient losses through leaching or volatilization.
- Customized hypertonic fertilizer blends for specific crops: Hypertonic fertilizers are tailored to meet the specific nutritional requirements of different crops and growth stages. These customized blends consider factors such as crop type, soil conditions, and target yield. By optimizing the nutrient ratios and concentrations in the fertilizer solution, these specialized formulations enhance crop performance, improve quality, and address specific deficiencies or imbalances in plant nutrition.
- Environmental impact and sustainability of hypertonic fertilizers: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental sustainability of hypertonic fertilizers. This includes developing eco-friendly formulations with reduced environmental impact, optimizing nutrient use efficiency to minimize runoff and leaching, and incorporating organic or bio-based components. Sustainable hypertonic fertilizers aim to balance high crop yields with environmental protection and long-term soil health.
02 Application methods for hypertonic fertilizers
Various application methods are used for hypertonic fertilizers to maximize their effectiveness in plant nutrition. These include foliar spraying, fertigation through irrigation systems, and soil drenching. The choice of application method depends on factors such as crop type, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Proper application techniques ensure optimal nutrient absorption and minimize the risk of plant stress or damage due to the high osmotic pressure of the fertilizer solution.Expand Specific Solutions03 Controlled release mechanisms in hypertonic fertilizers
Controlled release mechanisms are incorporated into hypertonic fertilizers to regulate nutrient availability over time. These mechanisms may include coating technologies, chemical modifications, or the use of specific compounds that gradually release nutrients. By controlling the release of nutrients, these fertilizers can provide a steady supply of essential elements to plants, reducing the risk of nutrient loss and improving overall plant nutrition efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Customization of hypertonic fertilizers for specific crops
Hypertonic fertilizers are often customized to meet the specific nutritional requirements of different crops. This involves adjusting the nutrient ratios, concentrations, and formulations to match the needs of particular plant species or growth stages. Customized hypertonic fertilizers can address specific deficiencies, enhance crop quality, and improve yield by providing targeted nutrition that aligns with the physiological demands of the plants.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental considerations in hypertonic fertilizer use
The use of hypertonic fertilizers requires careful consideration of environmental factors to minimize potential negative impacts. This includes strategies to prevent soil salinization, reduce nutrient runoff, and protect water resources. Advanced formulations may incorporate slow-release technologies, organic components, or biostimulants to enhance nutrient use efficiency and promote sustainable agricultural practices while maintaining the benefits of hypertonic fertilization for plant nutrition.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Fertilizer Industry
The research on hypertonic fertilizers is in an emerging stage, with growing market potential as agriculture seeks more efficient nutrient delivery systems. The global market for specialty fertilizers, including hypertonic solutions, is expanding rapidly, driven by the need for sustainable and high-yield farming practices. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Evogene Ltd., Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc., and Coromandel International Ltd. leading innovation. These firms are developing advanced formulations and application methods, leveraging biotechnology and precision agriculture techniques. Universities such as Cornell and the University of California are contributing significant research, while startups like Kiverdi, Inc. are exploring novel approaches, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape with diverse players from academia and industry.
Shandong Agricultural University Fertilizer Sci. & Tech. Co.
Huai'an Chaimihe Agriculture Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
Innovative Approaches in Hypertonic Fertilizer Research
- The development of Natural Organic Nano-Fertilizers using chelated nano-nutrients synthesized through Lactate/Gluconate/Proteinate technology, which involves cultivating microorganisms to produce bioactive components that form nanoparticles below 20 nm for enhanced nutrient absorption and soil health improvement.
- A fertilizer absorption enhancer composition combining a surfactant and heptonic acid or its salt, applied as an aqueous solution to plant roots and leaves, enhances the absorption of fertilizer components like calcium, preventing phytotoxicity and improving nutrient distribution within the plant.
Environmental Impact of Hypertonic Fertilizers
The environmental impact of hypertonic fertilizers is a critical consideration in their development and application. These fertilizers, designed to deliver high concentrations of nutrients to plants, have the potential to significantly alter soil chemistry and ecosystem dynamics.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for soil salinization. Hypertonic fertilizers, by their nature, introduce high levels of salts into the soil. Over time, this can lead to an accumulation of salts in the upper soil layers, particularly in areas with low rainfall or poor drainage. Increased soil salinity can negatively affect plant growth, reduce soil fertility, and alter soil structure, potentially leading to long-term degradation of agricultural lands.
Water quality is another area of environmental concern. Runoff from fields treated with hypertonic fertilizers can lead to nutrient pollution in nearby water bodies. This excess of nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, can cause eutrophication, leading to algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems. The impact on water resources extends beyond surface water to groundwater, as these highly soluble fertilizers can leach into aquifers, potentially contaminating drinking water sources.
The use of hypertonic fertilizers may also influence soil microbial communities. The high salt concentrations can be detrimental to certain beneficial soil microorganisms, potentially disrupting important soil processes such as nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition. This alteration of soil biology could have cascading effects on overall soil health and ecosystem functioning.
Furthermore, the production and transportation of hypertonic fertilizers contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy-intensive manufacturing processes and the need for specialized handling and application equipment add to the carbon footprint of agricultural operations using these fertilizers.
However, it's important to note that hypertonic fertilizers also offer potential environmental benefits. Their high nutrient concentration means that smaller quantities are required compared to traditional fertilizers, potentially reducing overall fertilizer use and associated environmental impacts. Additionally, their precise application can lead to more efficient nutrient uptake by plants, reducing the amount of excess nutrients left in the soil or lost to the environment.
To mitigate the environmental risks associated with hypertonic fertilizers, research is focusing on developing formulations that minimize salt accumulation and improve nutrient use efficiency. Precision agriculture techniques, such as targeted application and real-time monitoring of soil conditions, are being explored to optimize the use of these fertilizers while minimizing environmental impact.
Regulatory Framework for Novel Fertilizer Technologies
The regulatory framework for novel fertilizer technologies, including hypertonic fertilizers, plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and effective implementation of these innovative solutions in agriculture. As hypertonic fertilizers represent a significant advancement in plant nutrition, it is essential to establish comprehensive guidelines and standards to govern their development, production, and application.
At the international level, organizations such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide overarching principles for fertilizer regulation. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national and regional regulatory bodies to develop more specific frameworks. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, a joint FAO/WHO program, has established standards for contaminants and toxins in food and feed, which indirectly influence fertilizer regulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Department of Agriculture (USDA) are the primary regulatory bodies overseeing fertilizer technologies. The EPA regulates fertilizers under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) and the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). These acts ensure that new fertilizer technologies, including hypertonic fertilizers, do not pose unreasonable risks to human health or the environment.
The European Union has implemented the Fertilizing Products Regulation (EU) 2019/1009, which came into effect in July 2022. This regulation establishes a harmonized regulatory framework for fertilizers, including novel technologies, across all EU member states. It sets strict criteria for product safety, quality, and labeling, promoting innovation while safeguarding environmental and human health.
Developing countries are also recognizing the importance of regulating novel fertilizer technologies. For instance, India has introduced the Fertilizer Control Order (FCO) under the Essential Commodities Act, which provides a framework for registering and regulating new fertilizer products, including hypertonic formulations.
As the field of hypertonic fertilizers continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are faced with the challenge of keeping pace with technological advancements. This necessitates the development of adaptive regulatory frameworks that can accommodate emerging technologies while maintaining rigorous safety and efficacy standards. Collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and regulatory agencies are essential to establish science-based regulations that foster innovation without compromising environmental and public health.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for novel fertilizer technologies, particularly hypertonic fertilizers, is complex and dynamic. As these technologies continue to revolutionize plant nutrition, it is imperative that regulatory frameworks evolve to ensure their safe and effective implementation while promoting sustainable agricultural practices.