Hypertonic Therapies: Addressing Chronic Inflammation Challenges
Hypertonic Therapy Background and Objectives
Hypertonic therapy has emerged as a promising approach in addressing chronic inflammation challenges, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of medical treatments. This innovative therapy leverages the principles of osmosis to create a hypertonic environment, which has shown potential in reducing inflammation and promoting healing in various chronic conditions.
The development of hypertonic therapies can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers first began exploring the effects of osmotic pressure on biological systems. However, it wasn't until recent decades that the potential applications in treating chronic inflammation gained substantial attention. The growing prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases, coupled with the limitations of conventional treatments, has driven the need for novel therapeutic approaches.
Chronic inflammation, characterized by persistent low-grade inflammation, is implicated in a wide range of disorders, including autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and neurodegenerative disorders. Traditional anti-inflammatory medications often come with significant side effects and may lose efficacy over time, creating a pressing need for alternative treatment modalities.
Hypertonic therapy aims to address these challenges by utilizing solutions with higher solute concentrations than physiological fluids. When applied to inflamed tissues, these solutions create an osmotic gradient that can help reduce edema, improve circulation, and modulate inflammatory responses. The underlying mechanism involves the movement of fluid from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher concentration, potentially alleviating tissue swelling and promoting the removal of inflammatory mediators.
The objectives of research in hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which hypertonic environments influence inflammatory processes at the cellular and molecular levels. This includes investigating the effects on immune cell function, cytokine production, and the resolution of inflammation.
Another key objective is to optimize the composition and delivery methods of hypertonic solutions for maximum therapeutic efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. This involves exploring various solutes, concentrations, and application techniques to tailor treatments for specific inflammatory conditions and patient populations.
Furthermore, researchers are focused on conducting rigorous clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of hypertonic therapies across different chronic inflammatory disorders. These studies aim to provide the necessary evidence base for potential regulatory approvals and widespread clinical adoption.
As the field progresses, there is also a growing emphasis on developing combination therapies that synergistically integrate hypertonic approaches with other anti-inflammatory strategies. This holistic approach seeks to enhance overall treatment outcomes and address the complex, multifaceted nature of chronic inflammation.
Market Analysis for Chronic Inflammation Treatments
The chronic inflammation treatment market has been experiencing significant growth due to the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the aging global population. This market segment encompasses a wide range of therapeutic approaches, including traditional pharmaceuticals, biologics, and emerging hypertonic therapies. The global market for chronic inflammation treatments was valued at approximately $93 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $130 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.8%.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising incidence of autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and metabolic syndromes. Additionally, the growing awareness of the long-term health impacts of chronic inflammation has led to increased demand for effective treatment options. The market is further bolstered by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at discovering novel therapeutic approaches, such as hypertonic therapies.
Geographically, North America dominates the chronic inflammation treatment market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the high prevalence of chronic diseases, well-established healthcare infrastructure, and significant investment in research and development. Europe follows closely, with a market share of around 30%, while the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years due to improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
The market is highly competitive, with major pharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer, AbbVie, and Novartis holding significant market shares. However, there is also a growing presence of smaller biotech firms and startups focusing on innovative approaches like hypertonic therapies. These emerging players are attracting substantial venture capital investment, indicating strong market potential for novel treatment modalities.
Hypertonic therapies, as a subset of the chronic inflammation treatment market, are gaining traction due to their potential to address inflammation through osmotic mechanisms. While still a relatively small portion of the overall market, hypertonic therapies are expected to see rapid growth as clinical evidence accumulates and regulatory pathways become clearer. The market for hypertonic therapies is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12% over the next five years, outpacing the overall chronic inflammation treatment market.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for non-invasive and natural treatment options, which could potentially benefit hypertonic therapies if they can demonstrate efficacy and safety. Additionally, the increasing focus on personalized medicine is likely to drive demand for targeted therapies that can address specific inflammatory pathways or patient subgroups.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Therapies
Hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in maintaining consistent osmotic gradients within target tissues over extended periods. The dynamic nature of biological systems often leads to rapid equilibration, reducing the therapeutic window and necessitating frequent administration.
Another challenge lies in the potential side effects associated with prolonged exposure to hypertonic environments. Cellular dehydration and osmotic stress can lead to unintended consequences, including tissue damage and altered cellular function. This is particularly problematic in sensitive organs and tissues, where the balance between therapeutic benefit and potential harm is delicate.
The delivery of hypertonic solutions to specific sites of inflammation presents a substantial hurdle. Current methods often rely on systemic administration, which can result in dilution and reduced efficacy at the target site. Developing targeted delivery systems that can maintain hypertonicity at the point of inflammation while minimizing systemic effects remains a significant technical challenge.
Furthermore, the heterogeneity of chronic inflammatory conditions complicates the development of standardized hypertonic therapies. Different types of inflammation may respond variably to osmotic interventions, necessitating personalized approaches that are difficult to implement on a large scale.
The long-term effects of hypertonic therapies on tissue homeostasis and regeneration are not fully understood. There are concerns about potential disruptions to normal physiological processes, including cell signaling pathways and extracellular matrix composition, which could have implications for tissue repair and function.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape for hypertonic therapies is complex, with varying standards and requirements across different jurisdictions. This creates challenges in conducting large-scale clinical trials and obtaining regulatory approvals, slowing the progression from research to clinical application.
Lastly, there is a need for more sophisticated monitoring tools to assess the real-time effects of hypertonic therapies on inflammatory processes. Current diagnostic methods often lack the sensitivity and specificity required to optimize treatment protocols and evaluate long-term outcomes effectively.
Existing Hypertonic Solutions for Inflammation
01 Hypertonic solutions for treating chronic inflammation
Hypertonic solutions are used to treat chronic inflammation by reducing edema and promoting the removal of inflammatory mediators. These solutions can be administered through various routes, including inhalation for respiratory conditions or topical application for skin disorders. The high osmolarity of these solutions helps draw excess fluid from inflamed tissues, thereby alleviating symptoms and promoting healing.- Hypertonic solutions for treating chronic inflammation: Hypertonic solutions are used to treat chronic inflammation by reducing edema and modulating the inflammatory response. These solutions can be administered through various routes, including intravenous, topical, or inhalation methods, depending on the specific condition being treated.
- Biomarkers for assessing chronic inflammation and hypertonic therapy efficacy: Specific biomarkers are identified and measured to assess the severity of chronic inflammation and monitor the effectiveness of hypertonic therapies. These biomarkers can include inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress markers, and other molecular indicators associated with chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Hypertonic saline solutions for respiratory conditions: Hypertonic saline solutions are utilized in the treatment of chronic respiratory conditions, such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. These solutions help to improve mucociliary clearance, reduce airway inflammation, and enhance lung function in patients with chronic respiratory inflammation.
- Combination therapies with hypertonic solutions: Hypertonic therapies are combined with other treatment modalities to enhance their effectiveness in managing chronic inflammation. These combinations may include anti-inflammatory drugs, antioxidants, or other therapeutic agents that work synergistically with hypertonic solutions to address various aspects of chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Novel delivery systems for hypertonic therapies: Innovative delivery systems are developed to improve the efficacy and targeted application of hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation. These may include nanoparticle-based formulations, controlled-release mechanisms, or device-assisted delivery methods that enhance the penetration and sustained action of hypertonic solutions in affected tissues.
02 Biomarkers for assessing chronic inflammation and hypertonic therapy efficacy
Specific biomarkers are used to assess the severity of chronic inflammation and monitor the effectiveness of hypertonic therapies. These may include pro-inflammatory cytokines, acute phase proteins, or other molecular indicators. By measuring these biomarkers before and after treatment, healthcare providers can adjust therapy protocols and evaluate patient response to hypertonic interventions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination therapies involving hypertonic solutions and anti-inflammatory agents
Hypertonic therapies are often combined with anti-inflammatory agents to enhance their effectiveness in treating chronic inflammation. This approach may involve the use of hypertonic saline solutions alongside corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or other anti-inflammatory compounds. The synergistic effect of these combinations can lead to improved outcomes in managing various inflammatory conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel delivery systems for hypertonic therapies
Innovative delivery systems are being developed to improve the efficacy and patient compliance of hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation. These may include controlled-release formulations, nanoparticle-based delivery systems, or specialized devices for targeted administration. Such advancements aim to optimize the distribution of hypertonic solutions to affected tissues and maintain therapeutic concentrations over extended periods.Expand Specific Solutions05 Personalized hypertonic therapy approaches for chronic inflammation
Personalized medicine approaches are being applied to hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation. This involves tailoring treatment protocols based on individual patient characteristics, such as genetic markers, disease severity, and comorbidities. By customizing the concentration, frequency, and duration of hypertonic treatments, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes and minimize potential side effects for each patient.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Therapy Development
The research on hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for anti-inflammatory therapeutics is expanding, driven by the rising prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Pharmaceutica, and SetPoint Medical leading innovation. These firms are developing novel approaches, including targeted therapies and bioelectronic solutions. Academic institutions such as the University of Melbourne and The Feinstein Institutes are contributing significant research, while biotechnology companies like Guangzhou Enmai and MIRALOGX are exploring cutting-edge treatments. The involvement of diverse players indicates a competitive landscape with potential for breakthrough therapies.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
SetPoint Medical Corp.
Innovative Hypertonic Therapy Mechanisms
- Administration of a hypochlorous acid solution with 20-5000 ppm available free chlorine, which is at least 90% hypochlorous acid relative to total concentration, to affected areas via various routes, providing anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory effects without the side effects of conventional agents.
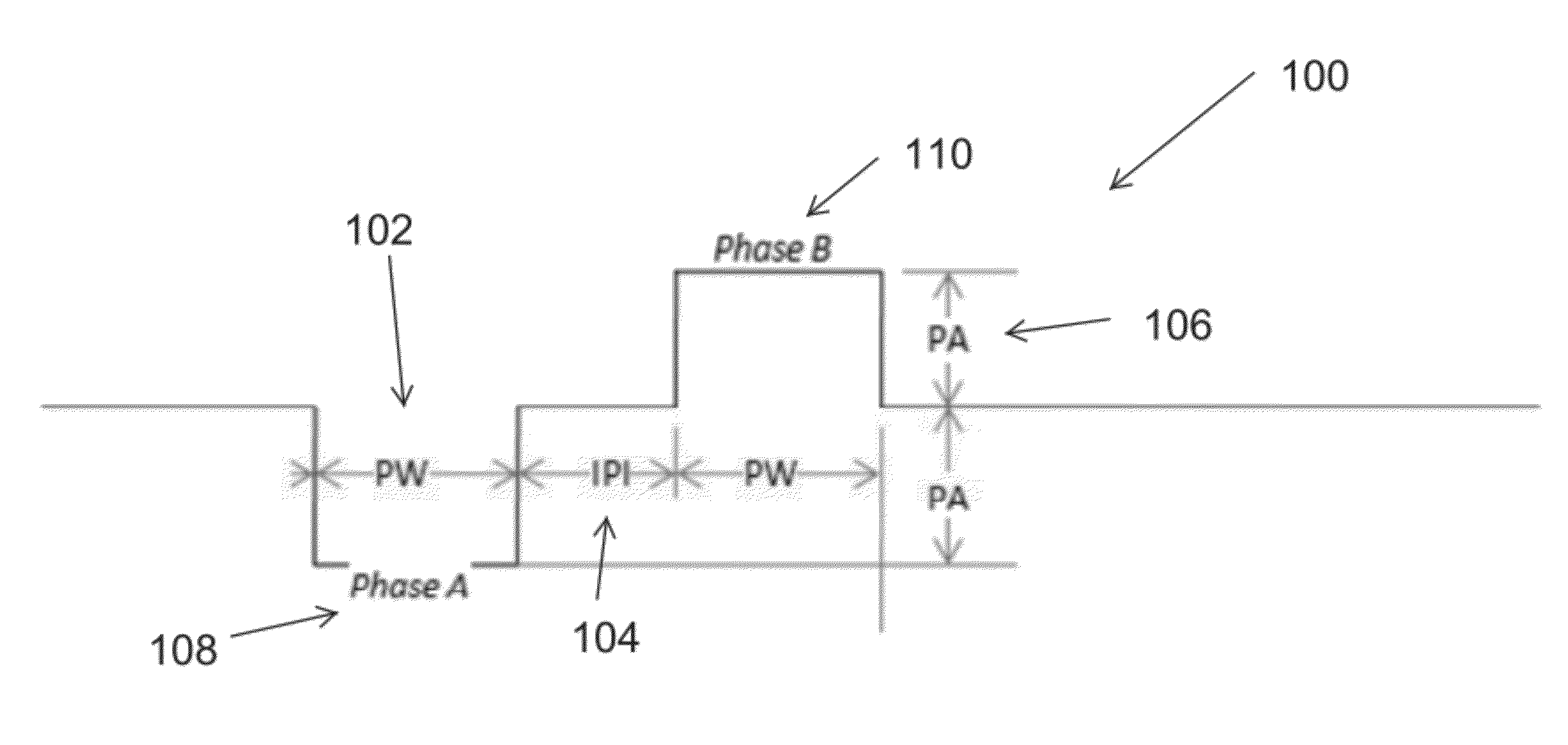
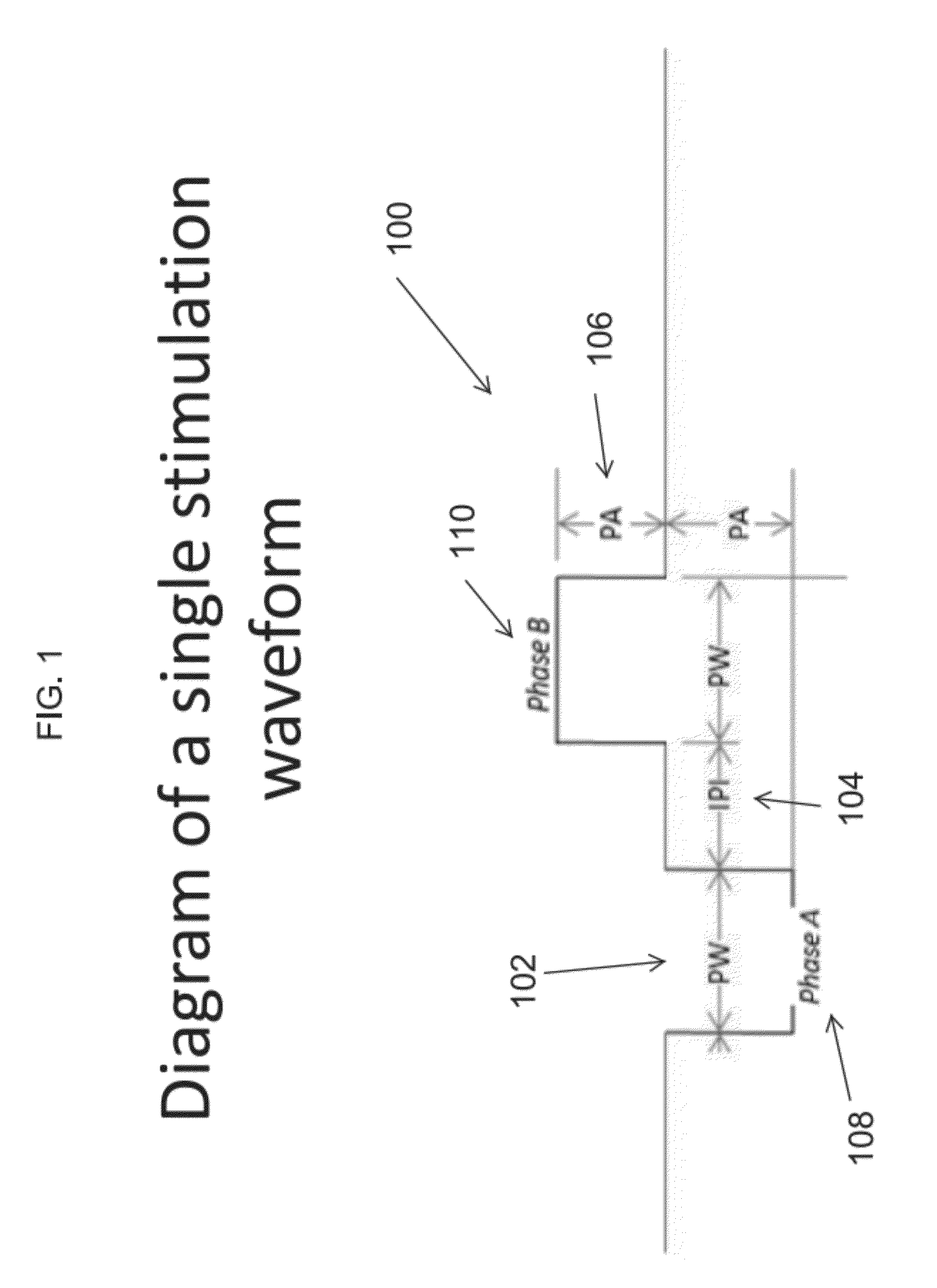
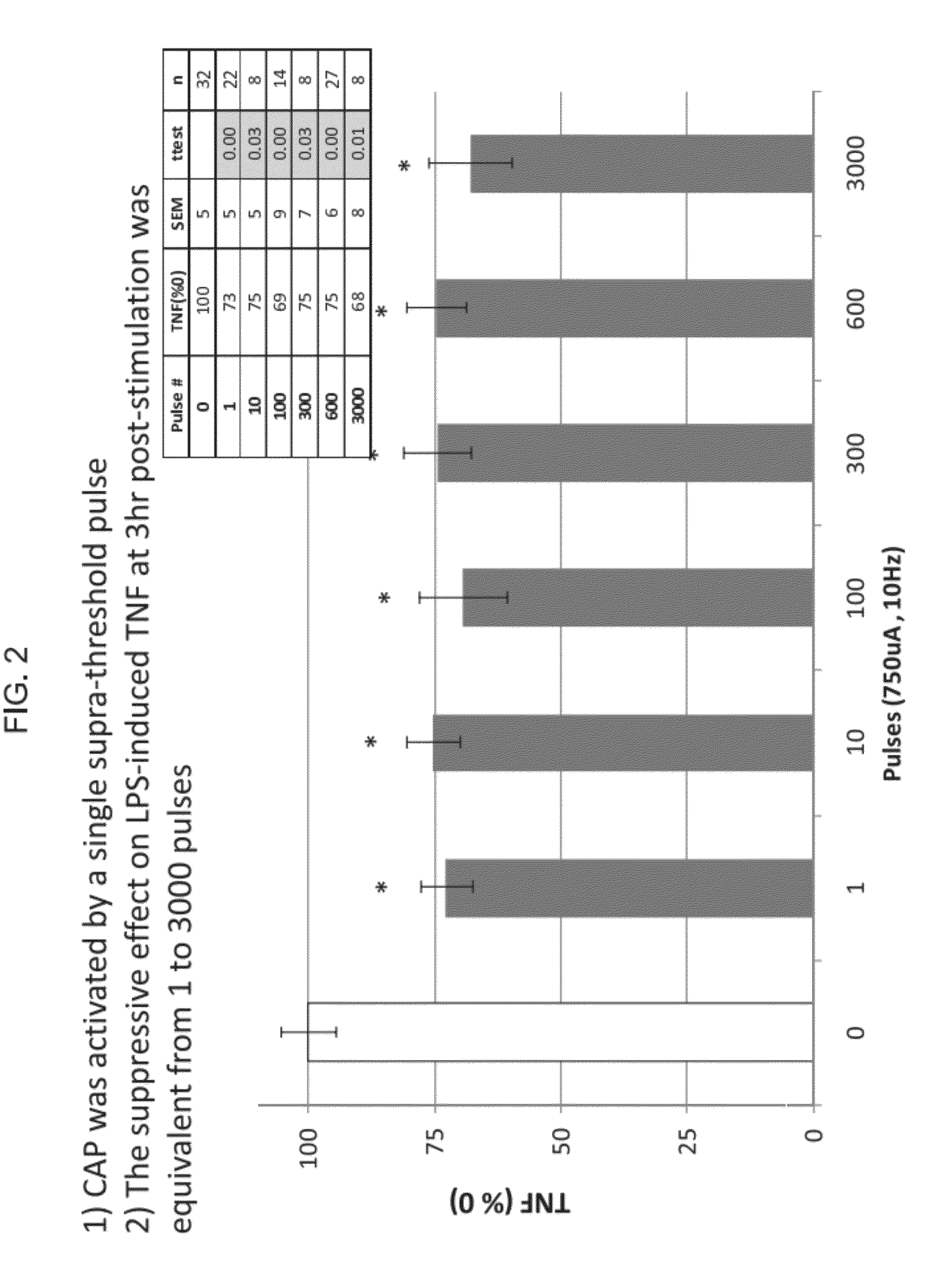
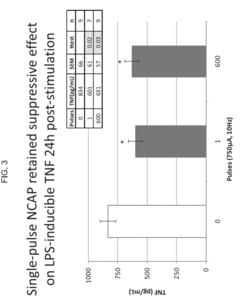
- The use of an extraordinarily low duty cycle stimulation of the vagus nerve, involving a single supra-threshold electrical pulse applied at extremely low power levels, with parameters such as one pulse every 4 to 48 hours and pulse amplitudes between 100 μA and 5000 μA, to modulate the inflammatory response through the nicotinic cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The safety and efficacy of hypertonic therapies for addressing chronic inflammation challenges are paramount considerations in the development and implementation of these treatments. Hypertonic solutions, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to physiological fluids, have shown promise in modulating inflammatory responses. However, their use necessitates careful evaluation of potential risks and benefits.
Safety considerations for hypertonic therapies primarily focus on osmotic effects and electrolyte imbalances. The introduction of hypertonic solutions into the body can lead to rapid fluid shifts, potentially causing dehydration of cells and tissues. This osmotic stress may result in cellular damage or dysfunction if not carefully managed. Additionally, the high solute concentration, often involving sodium chloride or other electrolytes, can disrupt the body's delicate electrolyte balance, potentially leading to hypernatremia or other electrolyte disturbances.
Cardiovascular effects are another critical safety concern. Rapid infusion of hypertonic solutions can cause sudden increases in blood volume and pressure, potentially straining the cardiovascular system. This is particularly relevant for patients with pre-existing heart conditions or compromised circulatory function. Renal function must also be closely monitored, as the kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte homeostasis in response to hypertonic therapies.
Efficacy considerations for hypertonic therapies in chronic inflammation are multifaceted. These therapies have demonstrated potential in reducing tissue edema, improving microcirculation, and modulating inflammatory mediators. The hyperosmolar environment created by hypertonic solutions can draw fluid from inflamed tissues, potentially reducing swelling and improving local blood flow. This mechanism may enhance the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to affected areas while facilitating the removal of inflammatory byproducts.
Furthermore, hypertonic therapies have shown immunomodulatory effects, potentially altering the function of immune cells involved in chronic inflammation. Studies have suggested that hypertonic environments can influence neutrophil activity, cytokine production, and the expression of adhesion molecules. These effects may contribute to the resolution of chronic inflammatory states by modulating the immune response.
However, the efficacy of hypertonic therapies can vary depending on the specific inflammatory condition, the concentration and composition of the hypertonic solution, and the method of administration. Factors such as the duration of treatment, frequency of application, and individual patient characteristics can significantly influence treatment outcomes. Therefore, optimizing these parameters through rigorous clinical research is essential to maximize the therapeutic potential of hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation.
Regulatory Landscape for Hypertonic Therapies
The regulatory landscape for hypertonic therapies addressing chronic inflammation challenges is complex and evolving. Regulatory bodies worldwide are closely monitoring the development and application of these therapies due to their potential impact on patient health and safety. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the approval process for hypertonic therapies. The FDA categorizes these treatments based on their intended use, mechanism of action, and potential risks.
For hypertonic therapies targeting chronic inflammation, the regulatory pathway often involves rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) typically oversees the approval process for pharmaceutical-based hypertonic therapies, while medical devices utilizing hypertonic solutions may fall under the purview of the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH).
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for evaluating and monitoring hypertonic therapies. The EMA's regulatory framework emphasizes a risk-based approach, requiring manufacturers to provide comprehensive data on the therapy's quality, safety, and efficacy. The EU's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) may also apply to certain hypertonic therapy delivery systems, imposing additional requirements on manufacturers.
Regulatory bodies in other regions, such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), have their own specific requirements for hypertonic therapies. These agencies often consider international guidelines and standards while adapting them to their local healthcare contexts.
A key regulatory consideration for hypertonic therapies is the potential for off-label use. Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing the promotion and use of these therapies beyond their approved indications, particularly in the context of chronic inflammation management. Manufacturers and healthcare providers must navigate strict guidelines regarding marketing and patient education to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Post-market surveillance is another critical aspect of the regulatory landscape for hypertonic therapies. Regulatory bodies require ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events, as well as long-term safety and efficacy data. This continuous evaluation helps identify potential risks and informs updates to product labeling and usage guidelines.
As research in hypertonic therapies for chronic inflammation advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging technologies, such as personalized medicine approaches and novel delivery systems, may necessitate the development of new regulatory pathways or the adaptation of existing ones. Regulatory agencies are increasingly collaborating internationally to harmonize standards and streamline approval processes, potentially facilitating global access to innovative hypertonic therapies while maintaining rigorous safety and efficacy standards.