Isotonic Vs Hypertonic Nasal Rinse
Nasal Rinse Evolution
Nasal irrigation has a rich history dating back to ancient Ayurvedic practices in India. The evolution of nasal rinse techniques and solutions has been driven by advancements in medical understanding and technological innovations. In the early stages, simple saline solutions were used for nasal cleansing, primarily as a traditional remedy for various respiratory ailments.
The 20th century saw significant developments in nasal rinse methodologies. The introduction of the neti pot in Western countries during the 1970s marked a pivotal moment, popularizing nasal irrigation as a home remedy. This traditional device, originating from India, provided a simple yet effective means of flushing the nasal passages with saline solution.
As medical research progressed, the composition of nasal rinse solutions became a subject of scientific inquiry. The distinction between isotonic and hypertonic solutions emerged as a key area of investigation. Isotonic solutions, with salt concentrations similar to body fluids, were initially favored for their gentleness and compatibility with nasal tissues.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a surge in clinical studies comparing the efficacy of isotonic and hypertonic nasal rinses. Researchers began to explore the potential benefits of hypertonic solutions, which have a higher salt concentration than body fluids. These studies aimed to determine whether hypertonic rinses could offer additional therapeutic effects, such as enhanced mucus thinning and improved symptom relief in conditions like chronic sinusitis.
Parallel to solution development, delivery methods also evolved. The introduction of squeeze bottles and pressurized spray devices in the 1990s and 2000s offered alternatives to the traditional neti pot. These new devices aimed to improve ease of use and ensure more consistent delivery of the rinse solution throughout the nasal passages.
Recent years have seen further refinements in nasal rinse formulations. The addition of ingredients like xylitol, a natural sugar alcohol with potential antimicrobial properties, represents an attempt to enhance the therapeutic effects of nasal irrigation. Additionally, the development of pre-mixed, sterile saline solutions has addressed concerns about contamination and improper mixing associated with homemade solutions.
The ongoing evolution of nasal rinse techniques and solutions reflects a growing recognition of the importance of nasal health in overall respiratory well-being. Current research continues to explore the optimal balance between solution tonicity, additives, and delivery methods to maximize the benefits of nasal irrigation while minimizing potential side effects.
Market Analysis
The market for nasal rinse solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of nasal hygiene and the rising prevalence of respiratory conditions. Both isotonic and hypertonic nasal rinses have carved out distinct niches within this expanding market, catering to different consumer needs and preferences.
Isotonic nasal rinses, which have a salt concentration similar to that of human cells, have traditionally dominated the market due to their gentle nature and suitability for daily use. These solutions are particularly popular among consumers seeking routine nasal care and those with sensitive nasal passages. The isotonic nasal rinse segment has shown steady growth, primarily fueled by its widespread acceptance among healthcare professionals as a safe and effective option for maintaining nasal health.
On the other hand, hypertonic nasal rinses, with their higher salt concentration, have gained traction in recent years. This growth is attributed to their perceived effectiveness in providing relief from congestion and allergies. The hypertonic segment has seen rapid expansion, particularly in regions with high allergy prevalence and among consumers seeking more potent solutions for specific nasal conditions.
Market research indicates that the global nasal rinse market is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors contributing to this growth include the increasing incidence of allergies and sinusitis, growing air pollution levels in urban areas, and a general trend towards preventive healthcare practices. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers have become more conscious of respiratory health and hygiene.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market, with the United States being the largest single market for nasal rinse products. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing promising growth potential, driven by rising disposable incomes and increasing healthcare awareness.
The market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and specialized nasal care brands. Recent years have seen a surge in product innovations, including the development of preservative-free formulations, convenient packaging designs, and the incorporation of natural ingredients. This trend towards product differentiation is expected to intensify as companies seek to capture market share in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Consumer preferences are evolving, with a growing demand for natural and organic nasal rinse solutions. This shift is particularly evident among younger consumers who are more inclined towards holistic health approaches. Additionally, there is an increasing interest in customized solutions that cater to specific nasal conditions or environmental factors.
Looking ahead, the market for nasal rinse solutions is poised for continued growth. The ongoing debate between isotonic and hypertonic solutions is likely to drive further research and product development, potentially leading to more specialized offerings. As consumer awareness grows and healthcare professionals increasingly recommend nasal irrigation, both segments are expected to expand, albeit potentially at different rates depending on emerging clinical evidence and consumer preferences.
Current Challenges
The current challenges in the research on isotonic vs hypertonic nasal rinse primarily revolve around the lack of standardized protocols and inconsistent findings across studies. One major obstacle is the variability in the concentration of saline solutions used in different studies, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the comparative efficacy of isotonic and hypertonic rinses.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the long-term effects of using hypertonic nasal rinses. While some studies suggest that hypertonic solutions may be more effective in reducing nasal congestion and improving mucociliary clearance, concerns persist about potential adverse effects on the nasal mucosa with prolonged use. This uncertainty has led to hesitation among healthcare providers in recommending hypertonic rinses for extended periods.
The lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials comparing isotonic and hypertonic nasal rinses poses a substantial hurdle in establishing clear clinical guidelines. Most existing studies have small sample sizes and short follow-up periods, limiting the generalizability of their findings. Additionally, there is a need for more research on specific patient populations, such as those with chronic rhinosinusitis or allergic rhinitis, to determine which type of nasal rinse is most beneficial for different conditions.
Another challenge lies in the measurement and quantification of nasal symptoms and quality of life improvements. The subjective nature of many nasal symptoms makes it difficult to objectively compare the effectiveness of different rinse concentrations. Developing more sensitive and standardized outcome measures is crucial for advancing research in this field.
The potential impact of environmental factors on the efficacy of nasal rinses also presents a challenge. Variations in climate, air quality, and allergen exposure may influence the effectiveness of isotonic vs hypertonic solutions, but these factors are often not adequately controlled for in existing studies. This variability makes it challenging to provide universal recommendations for nasal rinse use.
Lastly, there is a need for more research on the optimal delivery methods for nasal rinses. The effectiveness of different irrigation devices and techniques may vary between isotonic and hypertonic solutions, but this aspect has not been thoroughly investigated. Understanding these nuances is crucial for maximizing the therapeutic benefits of nasal irrigation and providing evidence-based recommendations to patients and healthcare providers.
Existing Solutions
01 Isotonic nasal rinse solutions
Isotonic nasal rinse solutions are formulated to match the tonicity of human nasal tissues, typically with a sodium chloride concentration of about 0.9%. These solutions help maintain the natural osmotic balance of nasal membranes, reducing irritation and promoting effective cleansing of the nasal passages.- Isotonic nasal rinse solutions: Isotonic nasal rinse solutions are formulated to match the tonicity of human nasal tissues, typically with a sodium chloride concentration of about 0.9%. These solutions help maintain the natural osmotic balance of nasal membranes, reducing irritation and promoting effective cleansing of the nasal passages.
- Hypertonic nasal rinse formulations: Hypertonic nasal rinse solutions contain a higher concentration of solutes than isotonic solutions, typically ranging from 2% to 3% sodium chloride. These formulations can help reduce nasal congestion by drawing excess fluid from swollen tissues through osmosis, potentially providing relief from sinus symptoms.
- Buffered nasal rinse solutions: Buffered nasal rinse solutions incorporate pH-balancing compounds to maintain a slightly acidic to neutral pH, typically between 6.2 and 7.6. This helps to mimic the natural pH of nasal secretions, reducing irritation and supporting the nasal mucosa's natural defense mechanisms against pathogens.
- Additives for enhanced therapeutic effects: Various additives can be incorporated into nasal rinse solutions to enhance their therapeutic effects. These may include xylitol for its antimicrobial properties, essential oils for their soothing effects, or specific minerals to support nasal health. The choice and concentration of additives are carefully balanced to maintain appropriate tonicity.
- Delivery systems for controlled tonicity: Specialized delivery systems and devices are designed to ensure accurate mixing and administration of nasal rinse solutions with controlled tonicity. These may include pre-measured packets, dual-chamber containers, or electronic mixing devices that help users prepare solutions with consistent and appropriate tonicity for safe and effective nasal rinsing.
02 Hypertonic nasal rinse formulations
Hypertonic nasal rinse solutions contain a higher concentration of solutes than isotonic solutions, typically ranging from 2% to 3% sodium chloride. These formulations can help reduce nasal congestion by drawing excess fluid from swollen tissues through osmosis, potentially providing relief from sinus symptoms.Expand Specific Solutions03 Buffered nasal rinse solutions
Buffered nasal rinse solutions incorporate pH-balancing compounds to maintain a slightly alkaline environment, typically between pH 6.2 and 8.0. These formulations help stabilize the solution and may enhance its effectiveness in cleansing and soothing nasal passages while minimizing potential irritation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nasal rinse devices with tonicity control
Specialized nasal rinse devices are designed to allow users to adjust the tonicity of the rinse solution. These devices may incorporate mechanisms for mixing concentrated saline solutions with water or provide separate compartments for different tonicity levels, enabling customization based on individual needs or medical recommendations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Additives for modifying nasal rinse tonicity
Various additives can be incorporated into nasal rinse solutions to modify their tonicity or enhance their therapeutic effects. These may include electrolytes, minerals, or natural compounds that can influence osmolarity while potentially providing additional benefits such as moisturizing or anti-inflammatory properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The research on isotonic vs hypertonic nasal rinse is in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to rising awareness of nasal health. The technology is relatively mature, with established players like Water Pik, Inc. and RhinoSystems, Inc. leading the market. However, there's ongoing innovation, as evidenced by research institutions like Mayo Foundation and University of Sheffield participating. The competitive landscape is diverse, including pharmaceutical companies like Glenmark Specialty SA and Johnson & Johnson, alongside specialized medical device manufacturers. This diversity suggests a dynamic market with potential for further technological advancements and market expansion.
RhinoSystems, Inc.
Laboratoire de la Mer SAS
Core Innovations
- A hypertonic seawater composition with a 70% volume fraction of filtered and sterilized seawater, 24 g/l sodium chloride, pH 8.2, and specific mineral concentrations (1.04 g/l magnesium, 0.39 g/l calcium, 0.25 g/l potassium, 0.09 mg/l zinc, and 0.04 mg/l copper) is developed, administered as nebulized microparticles to optimize osmotic drainage without irritating the nasal mucosa.
- A hand-held nasal irrigation device with a source of saline solution, an effluent receptacle, a nasal interface, fluid passageways, and a switch and valve assembly that utilizes gravity, pressure, and powered suction to deliver saline solution effectively while collecting effluent for easy disposal, accommodating various nasal dimensions.
Clinical Efficacy
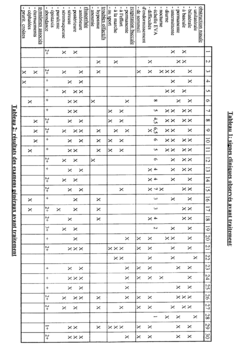
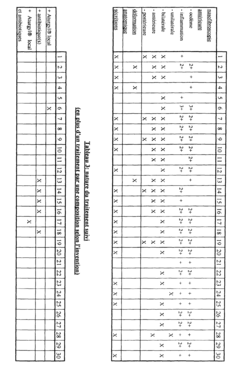
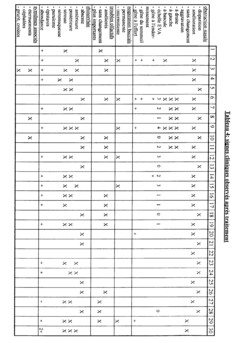
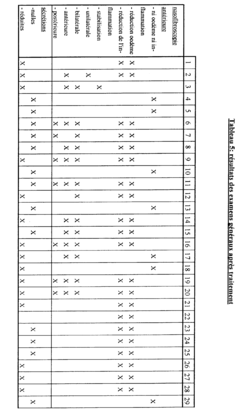
The clinical efficacy of isotonic versus hypertonic nasal rinses has been a subject of extensive research in recent years. Studies have shown that both types of nasal rinses can be effective in managing various nasal conditions, but their efficacy may differ depending on the specific condition being treated and individual patient factors.
Isotonic saline nasal rinses, which have a salt concentration similar to that of body fluids, have demonstrated significant benefits in improving nasal symptoms and quality of life for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. These rinses help to cleanse the nasal passages, remove allergens and irritants, and improve mucociliary clearance. Research has shown that regular use of isotonic nasal rinses can reduce the need for antibiotics and corticosteroids in patients with chronic sinusitis.
Hypertonic saline nasal rinses, containing a higher salt concentration than isotonic solutions, have shown promising results in certain clinical scenarios. Studies have indicated that hypertonic rinses may be more effective in reducing nasal congestion and improving mucociliary clearance compared to isotonic rinses. This is attributed to their ability to create an osmotic gradient, drawing fluid from the nasal tissues and potentially reducing mucosal edema.
In the treatment of acute upper respiratory tract infections, both isotonic and hypertonic nasal rinses have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating symptoms and potentially shortening the duration of illness. However, some studies suggest that hypertonic solutions may provide slightly better symptom relief, particularly in reducing nasal congestion and rhinorrhea.
For patients with allergic rhinitis, both types of nasal rinses have shown benefits in reducing nasal symptoms and improving quality of life. Some research indicates that hypertonic rinses may be more effective in reducing nasal eosinophilia and inflammatory markers associated with allergic reactions.
It is important to note that while hypertonic solutions may offer some advantages in certain conditions, they can also cause more nasal irritation and discomfort compared to isotonic rinses. This may affect patient compliance and long-term adherence to treatment regimens.
In pediatric populations, both isotonic and hypertonic nasal rinses have demonstrated safety and efficacy in managing various nasal conditions. However, isotonic rinses are often preferred due to their better tolerability and lower risk of irritation in children.
Overall, the clinical efficacy of isotonic versus hypertonic nasal rinses appears to be condition-specific and may vary among individual patients. While both types of rinses offer benefits, the choice between them should be based on the specific condition being treated, patient tolerance, and individual response to treatment.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for nasal rinse products, including both isotonic and hypertonic solutions, is primarily governed by health authorities and regulatory bodies in different countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies most nasal rinse products as medical devices, specifically under the category of Class I devices. This classification means they are subject to general controls but are exempt from premarket notification requirements.
The FDA has established specific guidelines for the manufacturing, labeling, and marketing of nasal irrigation devices. These guidelines ensure that the products are safe for consumer use and that their claims are substantiated. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and maintain proper documentation of their production processes.
In the European Union, nasal rinse products fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR, which came into full effect in May 2021, has introduced more stringent requirements for medical devices, including nasal rinse products. Manufacturers must now provide more comprehensive clinical data and post-market surveillance reports to maintain their products' certification.
The regulatory landscape also extends to the ingredients used in nasal rinse solutions. Both isotonic and hypertonic solutions typically contain sodium chloride as the primary ingredient. However, the concentration of salt differs between the two types. Regulatory bodies require that the salt concentration be clearly stated on the product label and that any additional ingredients, such as preservatives or buffering agents, be listed and approved for use in nasal applications.
In terms of marketing claims, regulatory agencies closely scrutinize the language used to describe the benefits of nasal rinse products. Claims related to the treatment or prevention of specific medical conditions are generally not permitted without substantial clinical evidence. Instead, manufacturers typically focus on general statements about nasal cleansing and symptom relief.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses quality control measures. Manufacturers must implement robust quality management systems to ensure consistency in product formulation and packaging. This includes regular testing of both raw materials and finished products to verify their safety and efficacy.
As research continues to explore the differences between isotonic and hypertonic nasal rinses, regulatory bodies may update their guidelines to reflect new findings. This could potentially lead to more specific regulations regarding the use of different salt concentrations for various indications or patient populations.