Technological Progress in Hypertonic Compound Formulation
Hypertonic Compound Evolution and Objectives
Hypertonic compound formulation has undergone significant evolution over the past decades, driven by advancements in pharmaceutical sciences and the growing demand for more effective drug delivery systems. The journey of hypertonic compounds began with simple salt solutions and has progressed to complex, multi-component formulations designed to enhance therapeutic efficacy and patient compliance.
The primary objective of hypertonic compound formulation is to create solutions with higher solute concentrations than physiological fluids, thereby inducing osmotic effects for various medical applications. These formulations have found widespread use in areas such as wound care, respiratory therapy, and ophthalmic treatments. The evolution of hypertonic compounds has been marked by a continuous effort to improve their stability, biocompatibility, and targeted delivery capabilities.
In the early stages, hypertonic solutions were primarily composed of inorganic salts like sodium chloride. However, as research progressed, the focus shifted towards incorporating organic compounds and polymers to enhance the formulations' properties. This transition has led to the development of more sophisticated hypertonic compounds with improved osmotic potential and reduced side effects.
One of the key milestones in this field was the introduction of sugar-based hypertonic solutions, which offered better tolerability and reduced irritation compared to their salt-based counterparts. Subsequently, the integration of biocompatible polymers and hydrogels into hypertonic formulations opened up new possibilities for controlled release and prolonged therapeutic effects.
The current technological landscape of hypertonic compound formulation is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining principles from physical chemistry, materials science, and pharmacology. Researchers are now exploring advanced techniques such as nanotechnology and smart materials to create responsive hypertonic systems that can adapt to physiological conditions.
Looking ahead, the objectives for future developments in hypertonic compound formulation are multifaceted. There is a growing emphasis on developing personalized hypertonic solutions tailored to individual patient needs. Additionally, researchers are striving to create formulations with enhanced tissue penetration and cellular uptake, potentially revolutionizing treatments for conditions like cystic fibrosis and chronic wounds.
Another important goal is the development of environmentally friendly and sustainable hypertonic compounds, addressing concerns about the ecological impact of pharmaceutical products. This includes exploring bio-based materials and green chemistry approaches in formulation design.
Market Analysis for Hypertonic Formulations
The market for hypertonic formulations has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand in various medical applications and the expanding pharmaceutical industry. Hypertonic solutions, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to physiological fluids, have found widespread use in treating conditions such as edema, intracranial pressure, and dehydration.
The global hypertonic formulations market is primarily segmented into intravenous solutions, oral rehydration therapies, and topical applications. Among these, intravenous hypertonic saline solutions hold the largest market share due to their critical role in emergency medicine and intensive care settings. The oral rehydration segment is expected to witness the fastest growth, propelled by the rising incidence of diarrheal diseases and the need for effective rehydration therapies in developing countries.
Geographically, North America dominates the hypertonic formulations market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant portion of the market share, attributed to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are projected to exhibit the highest growth rates in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising awareness about the benefits of hypertonic therapies.
Key factors contributing to market growth include the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, growing geriatric population, and advancements in drug delivery technologies. The rising incidence of traumatic brain injuries and the subsequent need for intracranial pressure management have also boosted the demand for hypertonic solutions in neurocritical care.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the potential side effects associated with hypertonic formulations and the availability of alternative treatment options. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials for new formulations also pose obstacles to market expansion.
The competitive landscape of the hypertonic formulations market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging players. Major market participants are focusing on product innovation, strategic collaborations, and geographical expansion to gain a competitive edge. The development of novel hypertonic compound formulations with improved efficacy and reduced side effects is a key area of focus for many companies in this space.
Looking ahead, the market for hypertonic formulations is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with opportunities arising from the development of personalized medicine approaches and the exploration of new therapeutic applications. The integration of advanced technologies, such as nanotechnology and controlled-release systems, in hypertonic formulations is likely to open up new avenues for market expansion and product differentiation.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Compound Development
The development of hypertonic compound formulations faces several significant challenges that hinder progress in this field. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining the stability of these compounds over extended periods. Hypertonic solutions are inherently prone to precipitation and crystallization, which can compromise their efficacy and safety. Researchers are grappling with finding optimal stabilizing agents and formulation techniques to ensure long-term stability without affecting the therapeutic properties of the compounds.
Another major challenge lies in the bioavailability of hypertonic compounds. Due to their high osmolarity, these formulations can cause local irritation and discomfort upon administration, leading to poor patient compliance. Additionally, the rapid absorption of water from surrounding tissues can create a barrier to drug penetration, reducing overall bioavailability. Developing delivery systems that can overcome these physiological barriers while maintaining the hypertonic nature of the compound is a complex task that requires innovative approaches.
The scalability of production processes for hypertonic compounds presents another significant hurdle. Maintaining consistent quality and homogeneity in large-scale manufacturing is challenging due to the precise control required over osmolarity and solute concentration. This issue is particularly pronounced when dealing with complex multi-component hypertonic formulations, where even slight variations in composition can lead to significant changes in osmotic pressure and therapeutic efficacy.
Regulatory challenges also pose a considerable obstacle in the development of hypertonic compound formulations. The unique properties of these formulations often require specialized testing methods and safety assessments that may not be fully addressed by current regulatory guidelines. This can lead to prolonged approval processes and increased development costs, potentially deterring investment in this area.
Furthermore, the development of hypertonic compounds for specific therapeutic applications faces challenges in achieving targeted delivery. While the hypertonic nature can be beneficial for certain indications, such as reducing edema, it can be detrimental in other contexts. Researchers are working on developing smart delivery systems that can modulate the hypertonic effect based on the specific physiological environment, but this remains a complex and evolving area of research.
Lastly, there is a growing need to address the environmental impact of hypertonic compound formulations. The high salt content in these formulations can have ecological consequences if not properly managed in waste streams. Developing eco-friendly formulations and sustainable production processes that minimize environmental impact is becoming an increasingly important consideration in the field.
Existing Hypertonic Formulation Strategies
01 Formulation of hypertonic solutions for medical applications
Hypertonic solutions are developed for various medical applications, including wound healing, osmotic therapy, and treatment of edema. These formulations typically contain high concentrations of solutes, such as salts or sugars, to create an osmotic gradient. The hypertonic nature of these compounds helps in drawing excess fluid from tissues or promoting cellular dehydration for therapeutic purposes.- Hypertonic solutions for medical applications: Hypertonic compound formulations are used in various medical applications, including wound healing, reducing edema, and treating certain respiratory conditions. These solutions have a higher solute concentration than body fluids, creating an osmotic gradient that can draw fluid out of tissues or airways.
- Osmotic agents in hypertonic formulations: Various osmotic agents are used in hypertonic compound formulations to create the desired osmotic effect. These may include sugars, salts, and other solutes that can be safely administered to patients. The choice of osmotic agent depends on the specific application and desired therapeutic effect.
- Delivery methods for hypertonic compounds: Hypertonic compound formulations can be administered through various routes, including inhalation, topical application, and intravenous infusion. The delivery method is chosen based on the target tissue or organ and the desired therapeutic outcome. Specialized devices or formulations may be developed to enhance the effectiveness of delivery.
- Stabilization and preservation of hypertonic formulations: Techniques for stabilizing and preserving hypertonic compound formulations are crucial to maintain their efficacy and shelf life. This may involve the use of specific excipients, pH adjustments, or packaging methods to prevent degradation or contamination of the active ingredients.
- Combination therapies with hypertonic compounds: Hypertonic compound formulations are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance their effectiveness or provide synergistic effects. This may include combining hypertonic solutions with antimicrobial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, or other active ingredients to address multiple aspects of a medical condition.
02 Hypertonic compound formulations for ophthalmic use
Specialized hypertonic formulations are designed for ophthalmic applications, such as treating dry eye syndrome or reducing intraocular pressure. These formulations often include osmotically active agents like glycerin or sodium chloride, along with other components to enhance ocular comfort and efficacy. The hypertonic nature of these compounds helps in drawing out excess fluid from the cornea or conjunctiva.Expand Specific Solutions03 Development of hypertonic solutions for respiratory therapy
Hypertonic solutions are formulated for use in respiratory therapy, particularly for conditions like cystic fibrosis or bronchiolitis. These formulations typically contain high concentrations of salt, such as hypertonic saline, which can help improve mucociliary clearance and reduce airway inflammation. The hypertonic nature of these compounds aids in drawing water into the airway surface liquid, improving hydration and facilitating mucus clearance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypertonic formulations for parenteral nutrition
Hypertonic solutions are developed for parenteral nutrition, providing concentrated sources of nutrients for patients unable to receive adequate nutrition orally or enterally. These formulations typically contain high concentrations of glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes. The hypertonic nature of these compounds allows for the delivery of a large amount of nutrients in a small volume, which is particularly useful in fluid-restricted patients.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hypertonic compound formulations for topical applications
Hypertonic formulations are designed for topical use in various dermatological and wound care applications. These formulations often include osmotically active agents like glycerin or urea, which can help in drawing out excess fluid from the skin or wound bed. The hypertonic nature of these compounds aids in reducing edema, promoting wound healing, and improving skin hydration in certain conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Compound Industry
The technological progress in hypertonic compound formulation is in a mature development stage, with a significant market size driven by pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. The market is characterized by intense competition among established players and emerging biotech firms. Companies like Novartis AG, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. are at the forefront, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global presence. The technology's maturity is evident in the diverse applications across various therapeutic areas, with ongoing innovations from research institutions such as The Scripps Research Institute and University of Florida. Smaller, specialized firms like Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. are also making notable contributions, focusing on niche areas within the hypertonic compound space.
Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Novartis AG
Innovative Approaches in Hypertonic Compound Design
- A non-invasive poly-herbal formulation, WICS, is developed, combining nine herbal ingredients with documented antimicrobial and antifungal properties, utilizing a synergistic approach to create a potent antifungal agent effective against Candida albicans, incorporating Quercetin, tryptophan, and other phytochemicals like phenolic compounds, tannins, and phytosterols.
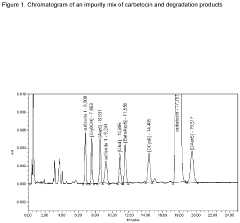
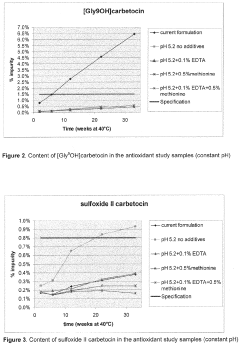
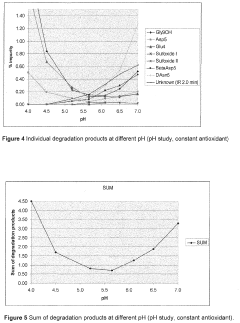
- A liquid pharmaceutical composition of carbetocin with a pH range of 5.0 to 6.0, stabilized with succinic acid as a buffering agent, providing room temperature stability for up to two years and long-term stability at high temperatures, allowing for unrefrigerated storage and use in tropical regions.
Regulatory Framework for Hypertonic Compounds
The regulatory framework for hypertonic compounds plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of these formulations. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of hypertonic compounds, particularly those used in medical applications. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating new drug applications, including those for hypertonic formulations.
Regulatory requirements for hypertonic compounds typically include extensive preclinical and clinical testing to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality. The FDA also requires comprehensive documentation of the formulation process, stability studies, and analytical methods used for quality control.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for the development and marketing of hypertonic compounds. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) is responsible for evaluating marketing authorization applications. Similar to the FDA, the EMA requires rigorous clinical trials and quality control measures.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established specific guidelines for hypertonic solutions used in various medical applications. For instance, the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide standards for the composition and quality of hypertonic saline solutions used in healthcare settings.
The regulatory landscape for hypertonic compounds is continually evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. Recent trends include the development of more targeted regulations for novel formulations, such as those incorporating nanoparticles or advanced delivery systems. Regulatory agencies are also focusing on harmonizing international standards to facilitate global development and marketing of hypertonic compounds.
Manufacturers of hypertonic compounds must navigate complex regulatory pathways, which often involve multiple stages of review and approval. This process typically includes submitting an Investigational New Drug (IND) application, conducting clinical trials, and filing a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA) for final approval.
As the field of hypertonic compound formulation continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging challenges. These include the regulation of personalized medicine approaches, combination products, and innovative delivery systems. Regulatory agencies are also placing increased emphasis on post-market surveillance to monitor long-term safety and efficacy of hypertonic compounds in real-world settings.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The safety and efficacy of hypertonic compound formulations are paramount considerations in their development and application. These formulations, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to physiological fluids, have shown promising results in various therapeutic areas. However, their use necessitates careful evaluation of potential risks and benefits.
Safety considerations for hypertonic compounds primarily focus on osmotic effects and electrolyte imbalances. The high solute concentration can lead to rapid fluid shifts, potentially causing dehydration or electrolyte disturbances in surrounding tissues. This is particularly crucial in sensitive areas such as the central nervous system or when used in patients with compromised renal function. Researchers have been developing strategies to mitigate these risks, including controlled release mechanisms and targeted delivery systems.
Efficacy of hypertonic formulations is often linked to their ability to create osmotic gradients, which can be beneficial in certain therapeutic contexts. For instance, in the treatment of cerebral edema, hypertonic solutions can effectively reduce intracranial pressure. However, the duration of this effect and potential rebound phenomena require careful consideration. Recent advancements have focused on optimizing the composition of these formulations to prolong their therapeutic effects while minimizing adverse reactions.
Another critical aspect is the potential for tissue irritation or damage at the site of administration. Hypertonic solutions may cause local inflammation or pain, especially when administered parenterally. Innovations in excipient selection and formulation techniques aim to reduce these local effects while maintaining the desired osmotic properties. This includes the development of novel buffer systems and the incorporation of protective agents to enhance tissue compatibility.
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of hypertonic compounds present unique challenges. Their rapid distribution and potential for systemic effects require precise dosing and administration protocols. Ongoing research is exploring the use of advanced drug delivery systems, such as nanocarriers or hydrogels, to modulate the release kinetics and enhance the targeted delivery of hypertonic agents.
Regulatory considerations for hypertonic formulations have evolved to address their specific safety and efficacy profiles. Regulatory bodies now require comprehensive preclinical and clinical data demonstrating not only the immediate effects but also long-term safety and efficacy outcomes. This has led to more rigorous testing protocols and post-market surveillance strategies for hypertonic products.