The Potential of 5G UC in Transforming the Insurance Industry
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC in Insurance: Background and Objectives
The evolution of 5G technology has ushered in a new era of connectivity, with 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) representing the pinnacle of this advancement. In the context of the insurance industry, 5G UC holds immense potential for transformative change. This technology builds upon the foundations laid by previous generations of mobile networks, offering unprecedented speed, reliability, and capacity.
The insurance sector, traditionally known for its conservative approach to technological adoption, now stands at the cusp of a digital revolution. The integration of 5G UC into insurance operations promises to address long-standing challenges and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation. From enhancing customer experiences to streamlining internal processes, the impact of this technology is expected to be far-reaching.
The primary objective of exploring 5G UC in insurance is to leverage its capabilities to create more efficient, responsive, and personalized insurance services. This includes real-time risk assessment, instant claim processing, and the development of new insurance products tailored to the digital age. By harnessing the power of 5G UC, insurers aim to improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Another crucial goal is to enhance data collection and analysis capabilities. The high-speed, low-latency nature of 5G UC enables the seamless integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors, allowing insurers to gather vast amounts of real-time data. This data can be used to refine risk models, detect fraud more effectively, and offer more accurate, usage-based insurance policies.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology aims to facilitate the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and augmented reality (AR) within the insurance sector. These technologies, when combined with the robust infrastructure of 5G UC, can revolutionize various aspects of insurance operations, from underwriting to claims management.
The implementation of 5G UC in insurance also aligns with the broader industry trend towards digital transformation. As customer expectations evolve, insurers are under pressure to provide more responsive, transparent, and personalized services. 5G UC is seen as a key enabler in meeting these expectations, allowing for seamless digital interactions, instant policy updates, and real-time customer support.
In summary, the background and objectives of 5G UC in insurance reflect a strategic move towards embracing cutting-edge technology to address industry challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. By setting clear goals for the implementation of 5G UC, the insurance sector aims to not only improve its current operations but also to position itself for future growth and innovation in an increasingly connected world.
The insurance sector, traditionally known for its conservative approach to technological adoption, now stands at the cusp of a digital revolution. The integration of 5G UC into insurance operations promises to address long-standing challenges and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation. From enhancing customer experiences to streamlining internal processes, the impact of this technology is expected to be far-reaching.
The primary objective of exploring 5G UC in insurance is to leverage its capabilities to create more efficient, responsive, and personalized insurance services. This includes real-time risk assessment, instant claim processing, and the development of new insurance products tailored to the digital age. By harnessing the power of 5G UC, insurers aim to improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Another crucial goal is to enhance data collection and analysis capabilities. The high-speed, low-latency nature of 5G UC enables the seamless integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors, allowing insurers to gather vast amounts of real-time data. This data can be used to refine risk models, detect fraud more effectively, and offer more accurate, usage-based insurance policies.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology aims to facilitate the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and augmented reality (AR) within the insurance sector. These technologies, when combined with the robust infrastructure of 5G UC, can revolutionize various aspects of insurance operations, from underwriting to claims management.
The implementation of 5G UC in insurance also aligns with the broader industry trend towards digital transformation. As customer expectations evolve, insurers are under pressure to provide more responsive, transparent, and personalized services. 5G UC is seen as a key enabler in meeting these expectations, allowing for seamless digital interactions, instant policy updates, and real-time customer support.
In summary, the background and objectives of 5G UC in insurance reflect a strategic move towards embracing cutting-edge technology to address industry challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. By setting clear goals for the implementation of 5G UC, the insurance sector aims to not only improve its current operations but also to position itself for future growth and innovation in an increasingly connected world.
Market Demand Analysis for 5G-Enabled Insurance Services
The insurance industry is experiencing a significant shift towards digitalization, and the advent of 5G technology is poised to accelerate this transformation. Market analysis reveals a growing demand for 5G-enabled insurance services, driven by the need for real-time data processing, enhanced customer experiences, and more efficient risk management.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the potential for real-time risk assessment and dynamic pricing. With 5G's high-speed, low-latency connectivity, insurers can collect and analyze vast amounts of data from IoT devices, wearables, and connected vehicles. This enables them to offer personalized, usage-based insurance products that more accurately reflect individual risk profiles, leading to fairer pricing and improved customer satisfaction.
The automotive insurance sector is particularly ripe for 5G-enabled innovations. Connected cars equipped with 5G technology can provide insurers with detailed driving behavior data, allowing for more accurate risk assessment and the development of pay-as-you-drive policies. This shift towards usage-based insurance is expected to gain significant traction, with market projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years.
In the health insurance domain, 5G technology enables remote patient monitoring and telemedicine services at an unprecedented scale. The demand for these services has surged, particularly in the wake of the global pandemic. Insurers are increasingly looking to incorporate 5G-enabled health monitoring devices into their offerings, allowing for proactive health management and potentially reducing claims through early intervention.
Property and casualty insurance is another area where 5G is driving market demand. Smart home devices and industrial IoT sensors connected via 5G networks can provide insurers with real-time data on property conditions, environmental factors, and potential risks. This enables the development of more sophisticated risk models and the ability to offer preventive services, such as early warning systems for natural disasters or equipment failures.
The commercial insurance sector is also showing strong interest in 5G-enabled services. Businesses are seeking more comprehensive risk management solutions that leverage real-time data analytics. 5G technology facilitates the deployment of advanced monitoring systems in industrial settings, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime-related losses.
As 5G networks continue to expand, the demand for insurance products that leverage this technology is expected to grow significantly. Industry analysts predict a substantial increase in the adoption of 5G-enabled insurance services over the next five years, with particularly strong growth in automotive, health, and commercial insurance segments.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the potential for real-time risk assessment and dynamic pricing. With 5G's high-speed, low-latency connectivity, insurers can collect and analyze vast amounts of data from IoT devices, wearables, and connected vehicles. This enables them to offer personalized, usage-based insurance products that more accurately reflect individual risk profiles, leading to fairer pricing and improved customer satisfaction.
The automotive insurance sector is particularly ripe for 5G-enabled innovations. Connected cars equipped with 5G technology can provide insurers with detailed driving behavior data, allowing for more accurate risk assessment and the development of pay-as-you-drive policies. This shift towards usage-based insurance is expected to gain significant traction, with market projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years.
In the health insurance domain, 5G technology enables remote patient monitoring and telemedicine services at an unprecedented scale. The demand for these services has surged, particularly in the wake of the global pandemic. Insurers are increasingly looking to incorporate 5G-enabled health monitoring devices into their offerings, allowing for proactive health management and potentially reducing claims through early intervention.
Property and casualty insurance is another area where 5G is driving market demand. Smart home devices and industrial IoT sensors connected via 5G networks can provide insurers with real-time data on property conditions, environmental factors, and potential risks. This enables the development of more sophisticated risk models and the ability to offer preventive services, such as early warning systems for natural disasters or equipment failures.
The commercial insurance sector is also showing strong interest in 5G-enabled services. Businesses are seeking more comprehensive risk management solutions that leverage real-time data analytics. 5G technology facilitates the deployment of advanced monitoring systems in industrial settings, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime-related losses.
As 5G networks continue to expand, the demand for insurance products that leverage this technology is expected to grow significantly. Industry analysts predict a substantial increase in the adoption of 5G-enabled insurance services over the next five years, with particularly strong growth in automotive, health, and commercial insurance segments.
Current State and Challenges of 5G UC in Insurance
The integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication) in the insurance industry is still in its early stages, with significant potential for transformation. Currently, the adoption of 5G UC in insurance is primarily focused on pilot projects and experimental implementations, as companies explore its capabilities and potential applications.
One of the main areas where 5G UC is being tested in insurance is in the realm of real-time risk assessment and claims processing. The ultra-low latency and high reliability of 5G UC enable insurers to collect and analyze data from various sources, including IoT devices, wearables, and connected vehicles, in near real-time. This capability allows for more accurate risk profiling and faster claims settlement.
However, the widespread implementation of 5G UC in insurance faces several challenges. Infrastructure limitations remain a significant hurdle, as 5G networks are not yet universally available, particularly in rural or less developed areas. This uneven coverage can create disparities in service quality and limit the full potential of 5G UC applications in insurance.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose substantial challenges. The increased connectivity and data transmission enabled by 5G UC raise questions about the protection of sensitive customer information and compliance with data protection regulations. Insurers must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against potential breaches and maintain customer trust.
Another challenge lies in the integration of 5G UC with existing legacy systems. Many insurance companies operate on older technological infrastructures, and the transition to 5G-enabled systems requires significant investment and technical expertise. This integration process can be complex and time-consuming, potentially slowing down the adoption of 5G UC across the industry.
The cost of implementing 5G UC technologies also presents a barrier for some insurers, particularly smaller companies. The expenses associated with upgrading infrastructure, developing new applications, and training staff can be substantial, leading to hesitation in fully embracing these new technologies.
Regulatory uncertainties surrounding the use of 5G UC in insurance add another layer of complexity. As the technology evolves, regulators are still working to develop appropriate frameworks to govern its use in financial services, including insurance. This regulatory landscape is still taking shape, which can create uncertainty for insurers looking to invest in 5G UC solutions.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 5G UC in transforming the insurance industry are significant. As the technology matures and these hurdles are addressed, it is expected that 5G UC will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of insurance services, enabling more personalized, efficient, and responsive insurance products and services.
One of the main areas where 5G UC is being tested in insurance is in the realm of real-time risk assessment and claims processing. The ultra-low latency and high reliability of 5G UC enable insurers to collect and analyze data from various sources, including IoT devices, wearables, and connected vehicles, in near real-time. This capability allows for more accurate risk profiling and faster claims settlement.
However, the widespread implementation of 5G UC in insurance faces several challenges. Infrastructure limitations remain a significant hurdle, as 5G networks are not yet universally available, particularly in rural or less developed areas. This uneven coverage can create disparities in service quality and limit the full potential of 5G UC applications in insurance.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose substantial challenges. The increased connectivity and data transmission enabled by 5G UC raise questions about the protection of sensitive customer information and compliance with data protection regulations. Insurers must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against potential breaches and maintain customer trust.
Another challenge lies in the integration of 5G UC with existing legacy systems. Many insurance companies operate on older technological infrastructures, and the transition to 5G-enabled systems requires significant investment and technical expertise. This integration process can be complex and time-consuming, potentially slowing down the adoption of 5G UC across the industry.
The cost of implementing 5G UC technologies also presents a barrier for some insurers, particularly smaller companies. The expenses associated with upgrading infrastructure, developing new applications, and training staff can be substantial, leading to hesitation in fully embracing these new technologies.
Regulatory uncertainties surrounding the use of 5G UC in insurance add another layer of complexity. As the technology evolves, regulators are still working to develop appropriate frameworks to govern its use in financial services, including insurance. This regulatory landscape is still taking shape, which can create uncertainty for insurers looking to invest in 5G UC solutions.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 5G UC in transforming the insurance industry are significant. As the technology matures and these hurdles are addressed, it is expected that 5G UC will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of insurance services, enabling more personalized, efficient, and responsive insurance products and services.
Existing 5G UC Solutions for Insurance Industry
01 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture
5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that provides enhanced capacity and performance in 5G networks. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to standard 5G implementations.- 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture: 5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that utilizes mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver enhanced capacity and performance. This architecture enables faster data speeds, lower latency, and improved network reliability compared to standard 5G networks. It incorporates advanced technologies such as massive MIMO, beamforming, and carrier aggregation to optimize spectrum usage and network efficiency.
- Resource Allocation and Management in 5G UC: Efficient resource allocation and management are crucial for 5G UC networks to maximize capacity and performance. This includes dynamic spectrum allocation, intelligent scheduling algorithms, and adaptive power control mechanisms. These techniques help optimize network resources based on user demand, traffic patterns, and network conditions, ensuring optimal utilization of the ultra-capacity capabilities.
- 5G UC Device Technologies: Devices supporting 5G UC require specialized hardware and software components to fully leverage the ultra-capacity capabilities. This includes advanced antenna designs, enhanced signal processing capabilities, and power-efficient chipsets. These technologies enable devices to efficiently communicate with 5G UC networks, support higher data rates, and maintain reliable connections across various network conditions.
- Integration of 5G UC with Edge Computing: The integration of 5G UC with edge computing technologies enhances the overall network performance and enables new use cases. By bringing computing resources closer to the network edge, latency is reduced, and data processing capabilities are improved. This integration supports applications requiring real-time processing, such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT.
- Security and Privacy in 5G UC Networks: Ensuring robust security and privacy measures is critical for 5G UC networks due to the increased network capacity and diverse use cases. This includes advanced encryption techniques, secure authentication mechanisms, and privacy-preserving protocols. These measures protect user data, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain the integrity of the ultra-capacity network infrastructure.
02 Spectrum Utilization in 5G UC
5G UC leverages a wide range of spectrum bands, including mid-band (2.5 GHz to 6 GHz) and millimeter-wave frequencies (24 GHz and above). This multi-band approach allows for improved coverage, capacity, and data speeds in urban and high-density areas.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced Antenna Technologies for 5G UC
5G UC implementations often incorporate advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and beamforming. These technologies enable more efficient use of spectrum, improved signal quality, and increased network capacity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Network Slicing and Virtualization in 5G UC
5G UC networks utilize network slicing and virtualization techniques to create multiple virtual networks tailored for specific use cases or applications. This allows for optimized resource allocation and improved quality of service for different types of traffic.Expand Specific Solutions05 Edge Computing Integration with 5G UC
5G UC networks often integrate edge computing capabilities to reduce latency and improve overall network performance. This involves deploying computing resources closer to the network edge, enabling faster processing and reduced backhaul traffic for latency-sensitive applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC and InsurTech
The 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) market in the insurance industry is in its early growth stage, with significant potential for transformation. The market size is expanding rapidly as insurers recognize the value of 5G UC in enhancing operational efficiency and customer experience. While the technology is still evolving, major players like Ericsson, Huawei, and NTT Docomo are driving innovation and deployment. Companies such as LG Electronics and Apple are developing compatible devices, while AT&T and Verizon are rolling out 5G networks. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with telecom providers, technology giants, and specialized 5G solution providers vying for market share in this emerging field.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson is leveraging 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) to revolutionize the insurance industry through its advanced network solutions. Their approach includes implementing edge computing and network slicing technologies to enable real-time data processing and analysis for insurers[1]. This allows for more accurate risk assessment and personalized policy offerings. Ericsson's 5G UC solutions also support the deployment of IoT devices for enhanced telematics in auto insurance, enabling usage-based insurance models[2]. Additionally, they are developing AI-powered fraud detection systems that can process vast amounts of data in real-time, significantly reducing false claims and improving overall operational efficiency for insurance companies[3].
Strengths: Strong network infrastructure expertise, global presence, and partnerships with major telecom operators. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in adapting to specific insurance industry needs and competition from specialized InsurTech firms.
AT&T Intellectual Property I LP
Technical Solution: AT&T is harnessing the power of 5G UC to transform the insurance sector through its comprehensive network solutions and partnerships. Their approach focuses on enabling high-speed, low-latency connectivity for insurers, facilitating real-time data collection and analysis[1]. AT&T's 5G UC network supports advanced IoT implementations, allowing for more accurate risk assessment in areas such as property and casualty insurance[2]. They are also developing solutions for enhanced mobile experiences, enabling insurers to provide seamless customer service and claims processing through high-quality video consultations and augmented reality-assisted damage assessments[3]. Furthermore, AT&T is collaborating with insurance companies to implement blockchain technology for secure and transparent policy management and claims processing[4].
Strengths: Extensive network coverage, strong partnerships with technology providers, and experience in enterprise solutions. Weaknesses: May face challenges in developing insurance-specific applications and competing with specialized InsurTech startups.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Insurance Applications
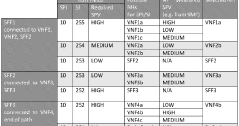
Determining and communicating security posture attributes
PatentWO2018075930A1
Innovation
- A framework is developed to derive and measure a Security Posture Value (SPV) based on a 360° security assessment, considering physical and cyber security attributes, and stakeholder policies, to ensure secure delivery of 5G services by evaluating the trustworthiness of network slices and individual network functions.
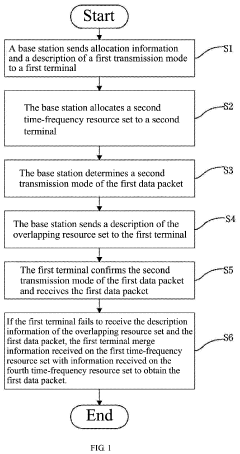
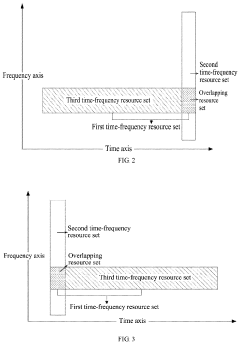
Robust data transmission method in internet of things
PatentActiveUS20200366443A1
Innovation
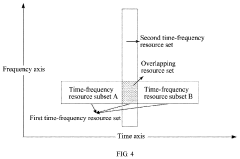
- A robust data transmission method is implemented where a base station allocates and manages time-frequency resources dynamically, using multiple transmission modes and resource sets to ensure reliable data packet transmission, including the use of overlapping resource sets, and merging information from different resource sets when necessary, to enhance demodulation performance and spectral efficiency.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC in Insurance
The regulatory framework for 5G UC in the insurance industry is evolving rapidly to keep pace with technological advancements. Regulatory bodies worldwide are working to establish guidelines that balance innovation with consumer protection and data security. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has been at the forefront of 5G regulation, allocating spectrum and setting standards for network deployment. However, when it comes to insurance-specific applications, state-level insurance commissioners play a crucial role in overseeing the implementation of 5G UC technologies.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) has been proactive in addressing the challenges posed by emerging technologies. They have established working groups to develop model laws and regulations that can be adopted by individual states. These regulations focus on key areas such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and fair pricing practices in the context of 5G-enabled insurance products and services.
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provides a comprehensive framework for data protection that applies to 5G UC applications in insurance. The European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA) has also issued guidelines on the use of big data analytics in insurance, which are relevant to 5G UC implementations. These guidelines emphasize the importance of transparency, fairness, and non-discrimination in algorithmic decision-making processes.
Asian countries, particularly China and South Korea, have been at the forefront of 5G deployment and are now developing regulatory frameworks for its application in various industries, including insurance. The China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) has issued guidelines on the use of big data and artificial intelligence in insurance, which indirectly affect 5G UC applications.
One of the key challenges for regulators is striking a balance between fostering innovation and protecting consumer interests. This includes ensuring that 5G UC-enabled insurance products do not lead to unfair discrimination or exclusion of certain customer segments. Regulators are also grappling with issues related to data ownership, portability, and the right to be forgotten in the context of highly connected insurance ecosystems.
Cybersecurity is another critical area of regulatory focus. As 5G UC enables more devices and sensors to be connected to insurance networks, the attack surface for potential cyber threats expands significantly. Regulators are working on establishing minimum security standards and protocols for 5G-enabled insurance systems to mitigate these risks.
Looking ahead, the regulatory landscape for 5G UC in insurance is likely to continue evolving. Regulators will need to stay agile and responsive to technological advancements while ensuring that fundamental principles of consumer protection and fair competition are upheld. Collaboration between telecommunications regulators, insurance supervisors, and data protection authorities will be crucial in developing a coherent and effective regulatory framework for this transformative technology.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) has been proactive in addressing the challenges posed by emerging technologies. They have established working groups to develop model laws and regulations that can be adopted by individual states. These regulations focus on key areas such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and fair pricing practices in the context of 5G-enabled insurance products and services.
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provides a comprehensive framework for data protection that applies to 5G UC applications in insurance. The European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA) has also issued guidelines on the use of big data analytics in insurance, which are relevant to 5G UC implementations. These guidelines emphasize the importance of transparency, fairness, and non-discrimination in algorithmic decision-making processes.
Asian countries, particularly China and South Korea, have been at the forefront of 5G deployment and are now developing regulatory frameworks for its application in various industries, including insurance. The China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) has issued guidelines on the use of big data and artificial intelligence in insurance, which indirectly affect 5G UC applications.
One of the key challenges for regulators is striking a balance between fostering innovation and protecting consumer interests. This includes ensuring that 5G UC-enabled insurance products do not lead to unfair discrimination or exclusion of certain customer segments. Regulators are also grappling with issues related to data ownership, portability, and the right to be forgotten in the context of highly connected insurance ecosystems.
Cybersecurity is another critical area of regulatory focus. As 5G UC enables more devices and sensors to be connected to insurance networks, the attack surface for potential cyber threats expands significantly. Regulators are working on establishing minimum security standards and protocols for 5G-enabled insurance systems to mitigate these risks.
Looking ahead, the regulatory landscape for 5G UC in insurance is likely to continue evolving. Regulators will need to stay agile and responsive to technological advancements while ensuring that fundamental principles of consumer protection and fair competition are upheld. Collaboration between telecommunications regulators, insurance supervisors, and data protection authorities will be crucial in developing a coherent and effective regulatory framework for this transformative technology.
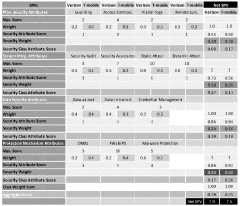
Data Security and Privacy Considerations in 5G-Enabled Insurance
The integration of 5G UC technology in the insurance industry brings significant advancements in data processing and connectivity, but it also introduces new challenges in data security and privacy. As insurers increasingly rely on real-time data collection and analysis, the protection of sensitive customer information becomes paramount.
One of the primary concerns is the increased attack surface that 5G networks present. With more devices connected and greater data transmission speeds, potential vulnerabilities multiply. Insurers must implement robust encryption protocols and secure communication channels to safeguard data in transit and at rest. This includes end-to-end encryption for all customer interactions and transactions conducted over 5G networks.
Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, pose additional challenges for insurers leveraging 5G technology. The ability to collect and process vast amounts of personal data in real-time requires stringent compliance measures. Insurers must establish clear data governance policies, including data minimization practices and explicit consent mechanisms for data collection and usage.
The use of edge computing in 5G networks introduces new considerations for data localization and sovereignty. Insurers need to carefully manage where customer data is processed and stored, ensuring compliance with regional data protection laws. This may require implementing distributed data processing architectures that can adapt to varying regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions.
Identity management and authentication become more critical in a 5G-enabled insurance ecosystem. With the potential for numerous IoT devices and sensors contributing to risk assessment and policy management, insurers must implement strong identity verification mechanisms. This includes multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and secure device attestation to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
The increased reliance on AI and machine learning algorithms for real-time risk assessment and claims processing in 5G-enabled insurance systems raises concerns about algorithmic transparency and fairness. Insurers must ensure that their data processing algorithms are explainable, unbiased, and compliant with anti-discrimination laws. Regular audits and impact assessments should be conducted to identify and mitigate potential biases in automated decision-making processes.
Lastly, the interconnected nature of 5G networks necessitates a collaborative approach to cybersecurity. Insurers should engage in information sharing and threat intelligence partnerships with other industry players, telecom providers, and cybersecurity firms. This collective effort can help identify and respond to emerging threats more effectively, ensuring the overall resilience of the 5G-enabled insurance ecosystem.
One of the primary concerns is the increased attack surface that 5G networks present. With more devices connected and greater data transmission speeds, potential vulnerabilities multiply. Insurers must implement robust encryption protocols and secure communication channels to safeguard data in transit and at rest. This includes end-to-end encryption for all customer interactions and transactions conducted over 5G networks.
Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, pose additional challenges for insurers leveraging 5G technology. The ability to collect and process vast amounts of personal data in real-time requires stringent compliance measures. Insurers must establish clear data governance policies, including data minimization practices and explicit consent mechanisms for data collection and usage.
The use of edge computing in 5G networks introduces new considerations for data localization and sovereignty. Insurers need to carefully manage where customer data is processed and stored, ensuring compliance with regional data protection laws. This may require implementing distributed data processing architectures that can adapt to varying regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions.
Identity management and authentication become more critical in a 5G-enabled insurance ecosystem. With the potential for numerous IoT devices and sensors contributing to risk assessment and policy management, insurers must implement strong identity verification mechanisms. This includes multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and secure device attestation to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
The increased reliance on AI and machine learning algorithms for real-time risk assessment and claims processing in 5G-enabled insurance systems raises concerns about algorithmic transparency and fairness. Insurers must ensure that their data processing algorithms are explainable, unbiased, and compliant with anti-discrimination laws. Regular audits and impact assessments should be conducted to identify and mitigate potential biases in automated decision-making processes.
Lastly, the interconnected nature of 5G networks necessitates a collaborative approach to cybersecurity. Insurers should engage in information sharing and threat intelligence partnerships with other industry players, telecom providers, and cybersecurity firms. This collective effort can help identify and respond to emerging threats more effectively, ensuring the overall resilience of the 5G-enabled insurance ecosystem.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!