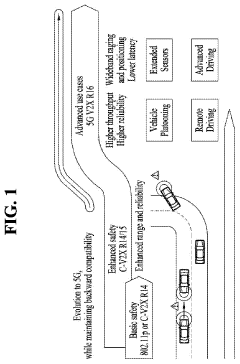
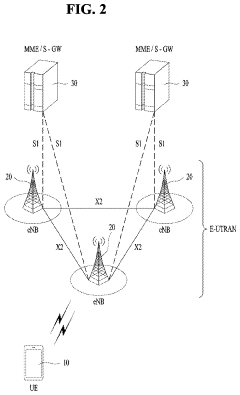
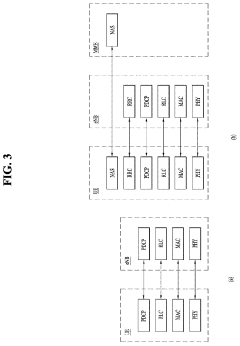
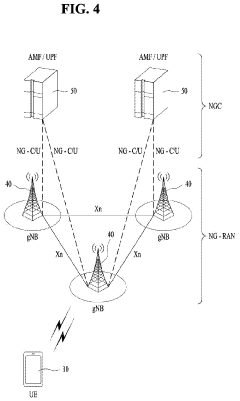
The Potential of 5G UC in Transforming the Real Estate Industry
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC in Real Estate: Background and Objectives
The evolution of 5G technology has ushered in a new era of connectivity, with 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) representing the pinnacle of this advancement. In the context of the real estate industry, 5G UC holds immense potential to revolutionize various aspects of property development, management, and user experience. This technological leap promises to address longstanding challenges and create new opportunities within the sector.
The real estate industry has traditionally been slow to adopt new technologies, often relying on conventional methods for property showcasing, management, and maintenance. However, the increasing demand for smart buildings, sustainable solutions, and enhanced user experiences has created a pressing need for technological innovation. 5G UC, with its ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and massive device connectivity, emerges as a key enabler for this transformation.
The primary objective of implementing 5G UC in real estate is to create intelligent, efficient, and user-centric environments. This technology aims to streamline property management processes, enhance security systems, and provide immersive experiences for potential buyers and tenants. Additionally, 5G UC seeks to facilitate the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling seamless communication between various building systems and occupants.
From a historical perspective, the real estate industry has witnessed gradual technological advancements, from basic property management software to the introduction of smart home devices. The advent of 5G UC marks a significant milestone in this progression, offering unprecedented capabilities that can address the sector's complex needs and future aspirations.
The implementation of 5G UC in real estate aligns with broader societal trends towards digitalization, sustainability, and enhanced quality of life. As urban populations continue to grow and environmental concerns become more pressing, the real estate industry faces increasing pressure to adopt innovative solutions. 5G UC technology presents an opportunity to meet these challenges head-on, by enabling more efficient resource management, reducing energy consumption, and creating adaptable living and working spaces.
Looking ahead, the integration of 5G UC in real estate is expected to drive the development of truly smart cities. This technology will serve as the backbone for interconnected urban ecosystems, where buildings communicate with each other and with city infrastructure to optimize resource allocation, improve traffic flow, and enhance overall urban living experiences. The long-term vision is to create sustainable, resilient, and technologically advanced urban environments that cater to the evolving needs of residents and businesses alike.
The real estate industry has traditionally been slow to adopt new technologies, often relying on conventional methods for property showcasing, management, and maintenance. However, the increasing demand for smart buildings, sustainable solutions, and enhanced user experiences has created a pressing need for technological innovation. 5G UC, with its ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and massive device connectivity, emerges as a key enabler for this transformation.
The primary objective of implementing 5G UC in real estate is to create intelligent, efficient, and user-centric environments. This technology aims to streamline property management processes, enhance security systems, and provide immersive experiences for potential buyers and tenants. Additionally, 5G UC seeks to facilitate the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling seamless communication between various building systems and occupants.
From a historical perspective, the real estate industry has witnessed gradual technological advancements, from basic property management software to the introduction of smart home devices. The advent of 5G UC marks a significant milestone in this progression, offering unprecedented capabilities that can address the sector's complex needs and future aspirations.
The implementation of 5G UC in real estate aligns with broader societal trends towards digitalization, sustainability, and enhanced quality of life. As urban populations continue to grow and environmental concerns become more pressing, the real estate industry faces increasing pressure to adopt innovative solutions. 5G UC technology presents an opportunity to meet these challenges head-on, by enabling more efficient resource management, reducing energy consumption, and creating adaptable living and working spaces.
Looking ahead, the integration of 5G UC in real estate is expected to drive the development of truly smart cities. This technology will serve as the backbone for interconnected urban ecosystems, where buildings communicate with each other and with city infrastructure to optimize resource allocation, improve traffic flow, and enhance overall urban living experiences. The long-term vision is to create sustainable, resilient, and technologically advanced urban environments that cater to the evolving needs of residents and businesses alike.
Market Demand Analysis for 5G UC in Real Estate
The real estate industry is experiencing a significant shift in market demand due to the potential integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology. This advanced wireless network promises to revolutionize property management, enhance tenant experiences, and create new revenue streams for real estate developers and owners.
One of the primary drivers of market demand for 5G UC in real estate is the growing need for smart building solutions. Property managers and owners are increasingly seeking ways to optimize energy consumption, improve security, and streamline maintenance processes. 5G UC's high-speed, low-latency connectivity enables the deployment of a vast network of IoT sensors and devices throughout buildings, providing real-time data and control over various systems.
The demand for enhanced tenant experiences is another crucial factor driving the adoption of 5G UC in real estate. Commercial and residential tenants alike are expecting more from their living and working spaces. 5G UC can support advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR) for virtual property tours, seamless video conferencing capabilities, and personalized environmental controls, all of which contribute to higher tenant satisfaction and retention rates.
In the commercial real estate sector, there is a growing demand for flexible and technologically advanced workspaces. The rise of remote work and hybrid office models has created a need for buildings that can support high-bandwidth, low-latency communications. 5G UC can meet these requirements, enabling seamless connectivity for a distributed workforce and supporting advanced collaboration tools.
The residential real estate market is also showing increased interest in 5G UC technology. Homebuyers and renters are placing greater value on properties that offer smart home features and reliable, high-speed internet connectivity. This trend is particularly pronounced in urban areas and among younger demographics who prioritize tech-enabled living spaces.
From an investment perspective, real estate developers and property owners are recognizing the potential of 5G UC to increase property values and create new revenue streams. Buildings equipped with 5G infrastructure can command premium rents and attract high-value tenants, particularly in the commercial and industrial sectors.
The market demand for 5G UC in real estate is further fueled by the increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. The technology's ability to support advanced building management systems and optimize resource usage aligns with growing environmental concerns and regulatory requirements in many regions.
As cities worldwide pursue smart city initiatives, there is a growing synergy between urban development plans and the real estate sector's adoption of 5G UC. This alignment is creating opportunities for public-private partnerships and driving demand for 5G-enabled properties that can integrate seamlessly with smart city infrastructure.
One of the primary drivers of market demand for 5G UC in real estate is the growing need for smart building solutions. Property managers and owners are increasingly seeking ways to optimize energy consumption, improve security, and streamline maintenance processes. 5G UC's high-speed, low-latency connectivity enables the deployment of a vast network of IoT sensors and devices throughout buildings, providing real-time data and control over various systems.
The demand for enhanced tenant experiences is another crucial factor driving the adoption of 5G UC in real estate. Commercial and residential tenants alike are expecting more from their living and working spaces. 5G UC can support advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR) for virtual property tours, seamless video conferencing capabilities, and personalized environmental controls, all of which contribute to higher tenant satisfaction and retention rates.
In the commercial real estate sector, there is a growing demand for flexible and technologically advanced workspaces. The rise of remote work and hybrid office models has created a need for buildings that can support high-bandwidth, low-latency communications. 5G UC can meet these requirements, enabling seamless connectivity for a distributed workforce and supporting advanced collaboration tools.
The residential real estate market is also showing increased interest in 5G UC technology. Homebuyers and renters are placing greater value on properties that offer smart home features and reliable, high-speed internet connectivity. This trend is particularly pronounced in urban areas and among younger demographics who prioritize tech-enabled living spaces.
From an investment perspective, real estate developers and property owners are recognizing the potential of 5G UC to increase property values and create new revenue streams. Buildings equipped with 5G infrastructure can command premium rents and attract high-value tenants, particularly in the commercial and industrial sectors.
The market demand for 5G UC in real estate is further fueled by the increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. The technology's ability to support advanced building management systems and optimize resource usage aligns with growing environmental concerns and regulatory requirements in many regions.
As cities worldwide pursue smart city initiatives, there is a growing synergy between urban development plans and the real estate sector's adoption of 5G UC. This alignment is creating opportunities for public-private partnerships and driving demand for 5G-enabled properties that can integrate seamlessly with smart city infrastructure.
Current State and Challenges of 5G UC Implementation
The implementation of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) in the real estate industry is currently in its early stages, with significant potential for transformative applications. Many leading real estate companies and technology providers are actively exploring and testing 5G UC solutions, but widespread adoption is still limited.
One of the primary challenges in implementing 5G UC in real estate is the need for extensive infrastructure upgrades. The high-frequency signals used in 5G UC require a dense network of small cells and antennas, which can be costly and time-consuming to install, especially in existing buildings. This infrastructure challenge is particularly pronounced in urban areas with complex building structures and regulations.
Another significant hurdle is the lack of standardization across different 5G UC technologies and platforms. This fragmentation can lead to compatibility issues and increased complexity in integrating various smart building systems and IoT devices. As a result, many real estate developers and property managers are hesitant to invest heavily in 5G UC without clear industry standards.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose challenges to 5G UC implementation in real estate. The increased connectivity and data flow enabled by 5G UC raise questions about how to protect sensitive information and maintain user privacy, especially in residential and commercial properties where personal and business data are involved.
The current state of 5G UC in real estate is characterized by pilot projects and limited deployments, primarily in high-end commercial properties and newly constructed smart buildings. These early adopters are focusing on applications such as advanced building management systems, immersive virtual property tours, and enhanced tenant experiences through augmented reality.
However, the full potential of 5G UC in transforming real estate operations and services is yet to be realized. Many promising use cases, such as real-time energy optimization, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration of autonomous systems, are still in the conceptual or early testing phases.
The geographic distribution of 5G UC implementation in real estate is uneven, with major urban centers and technology hubs leading the way. This disparity is due to factors such as infrastructure readiness, regulatory support, and the concentration of early adopters and tech-savvy tenants in these areas.
As the technology matures and costs decrease, it is expected that 5G UC adoption in real estate will accelerate. However, overcoming the current challenges will require collaborative efforts between real estate developers, technology providers, and regulatory bodies to create a more conducive environment for widespread implementation.
One of the primary challenges in implementing 5G UC in real estate is the need for extensive infrastructure upgrades. The high-frequency signals used in 5G UC require a dense network of small cells and antennas, which can be costly and time-consuming to install, especially in existing buildings. This infrastructure challenge is particularly pronounced in urban areas with complex building structures and regulations.
Another significant hurdle is the lack of standardization across different 5G UC technologies and platforms. This fragmentation can lead to compatibility issues and increased complexity in integrating various smart building systems and IoT devices. As a result, many real estate developers and property managers are hesitant to invest heavily in 5G UC without clear industry standards.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose challenges to 5G UC implementation in real estate. The increased connectivity and data flow enabled by 5G UC raise questions about how to protect sensitive information and maintain user privacy, especially in residential and commercial properties where personal and business data are involved.
The current state of 5G UC in real estate is characterized by pilot projects and limited deployments, primarily in high-end commercial properties and newly constructed smart buildings. These early adopters are focusing on applications such as advanced building management systems, immersive virtual property tours, and enhanced tenant experiences through augmented reality.
However, the full potential of 5G UC in transforming real estate operations and services is yet to be realized. Many promising use cases, such as real-time energy optimization, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration of autonomous systems, are still in the conceptual or early testing phases.
The geographic distribution of 5G UC implementation in real estate is uneven, with major urban centers and technology hubs leading the way. This disparity is due to factors such as infrastructure readiness, regulatory support, and the concentration of early adopters and tech-savvy tenants in these areas.
As the technology matures and costs decrease, it is expected that 5G UC adoption in real estate will accelerate. However, overcoming the current challenges will require collaborative efforts between real estate developers, technology providers, and regulatory bodies to create a more conducive environment for widespread implementation.
Existing 5G UC Solutions for Real Estate
01 Network architecture for 5G Ultra-Capacity
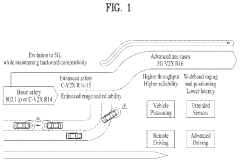
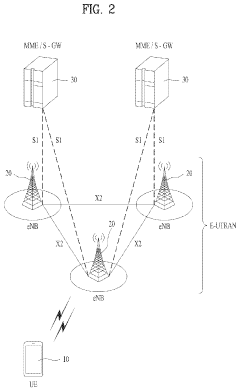
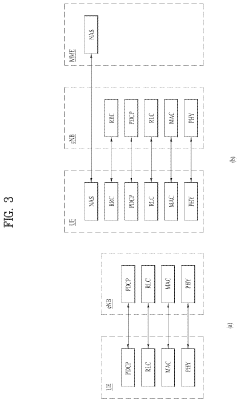
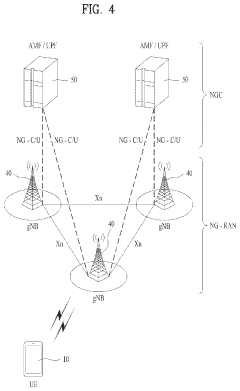
5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) networks employ advanced architectures to deliver high-speed, low-latency connectivity. These architectures may include massive MIMO, beamforming, and network slicing technologies to optimize spectrum usage and enhance network performance. The design focuses on increasing capacity and coverage while maintaining reliability for various use cases.- 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture: 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) refers to an advanced network architecture that enables high-speed, low-latency communication. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to provide enhanced capacity and coverage. This architecture supports massive device connectivity and enables advanced applications such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
- Spectrum Management in 5G UC: Efficient spectrum management is crucial for 5G UC networks. This involves dynamic allocation of frequency bands, carrier aggregation techniques, and advanced spectrum sharing methods. These techniques optimize the use of available spectrum resources, ensuring maximum throughput and coverage for ultra-capacity networks.
- Beamforming and MIMO Technologies: 5G UC networks heavily rely on advanced beamforming and Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) technologies. These techniques enhance signal quality, increase data rates, and improve overall network capacity. Massive MIMO systems with hundreds of antennas are employed to support ultra-high capacity and multi-user scenarios in dense urban environments.
- Network Slicing and Virtualization: Network slicing and virtualization are key enablers for 5G UC networks. These technologies allow the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, each tailored to specific service requirements. This flexibility enables efficient resource allocation and supports diverse use cases with varying performance needs.
- Edge Computing Integration: 5G UC networks integrate edge computing capabilities to reduce latency and improve service quality. By bringing computing resources closer to the end-users, edge computing enables real-time processing of data-intensive applications. This integration is crucial for supporting ultra-low latency services and enhancing the overall performance of the 5G UC network.
02 Spectrum utilization in 5G UC
5G UC leverages a combination of low-band, mid-band, and high-band (mmWave) spectrum to provide ultra-fast speeds and increased capacity. Efficient spectrum utilization techniques, such as carrier aggregation and dynamic spectrum sharing, are implemented to maximize the use of available frequency bands and improve overall network performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Device-to-network communication protocols
5G UC implements advanced communication protocols to facilitate seamless interaction between devices and the network. These protocols enable features like ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC). They also support efficient handovers and load balancing across different network layers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy efficiency in 5G UC networks
5G UC networks incorporate energy-efficient technologies and algorithms to optimize power consumption while maintaining high performance. This includes adaptive power control mechanisms, sleep modes for base stations, and intelligent resource allocation strategies. These techniques help reduce operational costs and environmental impact without compromising network capacity and coverage.Expand Specific Solutions05 Security and privacy in 5G UC
5G UC networks implement robust security measures to protect user data and network infrastructure. This includes advanced encryption algorithms, secure authentication protocols, and network slicing for isolation of sensitive traffic. Privacy-enhancing technologies are also integrated to ensure user anonymity and prevent unauthorized access to personal information in high-capacity networks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC and Real Estate Tech
The 5G UC technology in the real estate industry is in its early growth stage, with significant potential for market expansion. The global market size for 5G in real estate is projected to grow rapidly, driven by increasing demand for smart buildings and IoT integration. Technologically, 5G UC is still evolving, with companies like LG Electronics and AT&T Intellectual Property I LP leading in innovation. LG Electronics is leveraging its expertise in electronics and IoT to develop 5G-enabled smart home solutions, while AT&T is focusing on network infrastructure and connectivity. Shanghai Peiyuan Electronics Co., Ltd. is emerging as a key player in integrated circuit design for 5G applications, potentially influencing the hardware aspect of 5G UC implementation in real estate.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG Electronics is leveraging 5G UC technology to transform the real estate industry through innovative smart home and building solutions. The company's ThinQ AI platform, integrated with 5G UC, enables seamless connectivity and control of smart appliances and systems within properties. LG's 5G-enabled smart home devices can process data up to 100 times faster than 4G networks[3], allowing for real-time adjustments to heating, lighting, and security systems. In the real estate context, LG is developing 5G UC-powered digital signage and information kiosks that provide interactive property information and virtual tours to potential buyers or tenants. The company is also working on 5G-enabled building management systems that can monitor and optimize energy consumption, air quality, and occupancy levels in real-time, potentially reducing operational costs by up to 30%[4].
Strengths: Strong presence in consumer electronics and smart home technology, established brand recognition. Weaknesses: Limited direct experience in real estate-specific applications, potential interoperability issues with other systems.
AT&T Intellectual Property I LP
Technical Solution: AT&T's 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology is poised to revolutionize the real estate industry through its ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and massive device connectivity. In the real estate sector, AT&T is leveraging 5G UC to enable immersive virtual property tours, smart building management systems, and enhanced IoT integration. The company's 5G UC network supports speeds up to 1 Gbps[1], allowing for seamless 4K video streaming and AR/VR experiences during property showcases. AT&T is also developing edge computing solutions that work in tandem with 5G UC to process data from smart building sensors in real-time, optimizing energy usage and maintenance schedules[2]. Additionally, their network slicing capabilities ensure dedicated bandwidth for critical real estate applications, such as security systems and automated property management tools.
Strengths: Extensive network infrastructure, strong partnerships with real estate tech companies, and advanced edge computing capabilities. Weaknesses: High implementation costs and potential coverage limitations in some areas.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Property Management
Relay UE selection method on basis of QOS in wireless communication system
PatentPendingUS20240196301A1
Innovation
- A method for relay UE selection based on quality of service (QoS) and Uu link threshold-related information, where the remote UE receives signals from candidate relay UEs, performs measurements, and selects the relay UE with the highest received signal strength and Uu link threshold values suitable for the specific service requirements.
Method for terminal to transmit and receive signal in wireless communication system
PatentActiveUS20220248176A1
Innovation
- A method and system that simplifies the structure of RSUs by using a dedicated auxiliary device for installing and managing construction site guidance devices, allowing them to share location information and provide real-time construction site area information through I2I communication, reducing the need for GPS devices in RSUs and lowering installation costs.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC in Real Estate
The regulatory framework for 5G UC in real estate is a critical aspect that will shape the implementation and adoption of this transformative technology. As 5G UC promises to revolutionize the real estate industry, governments and regulatory bodies are working to establish guidelines that ensure its safe and effective deployment.
One of the primary concerns addressed by regulatory frameworks is the allocation of spectrum for 5G UC networks. Regulatory bodies are tasked with managing the limited radio frequency spectrum to accommodate the high-bandwidth requirements of 5G UC while avoiding interference with existing wireless services. This often involves reallocating spectrum from other uses or opening up new frequency bands specifically for 5G UC applications in real estate.
Privacy and data protection regulations play a crucial role in the 5G UC ecosystem for real estate. As smart buildings and IoT devices become more prevalent, the amount of data collected and transmitted increases exponentially. Regulatory frameworks must address the collection, storage, and use of personal and sensitive information to protect tenants, property owners, and other stakeholders.
Security regulations are another key component of the 5G UC regulatory framework for real estate. With the increased connectivity and reliance on digital systems, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Regulations often mandate specific security protocols, encryption standards, and regular security audits to safeguard against potential breaches and cyber attacks on smart real estate infrastructure.
Environmental and health considerations are also addressed in regulatory frameworks. Concerns about the potential health effects of increased electromagnetic radiation from 5G UC networks have led to regulations governing the placement and power output of 5G antennas and base stations in and around real estate properties.
Building codes and standards are being updated to accommodate the integration of 5G UC technology in real estate. This includes regulations on the installation of small cells, distributed antenna systems, and other 5G UC infrastructure within buildings. These codes ensure that 5G UC deployments meet safety standards and do not interfere with other building systems.
Cross-border regulations are becoming increasingly important as 5G UC enables more seamless global connectivity in the real estate sector. Regulatory bodies are working to harmonize standards across different countries to facilitate international real estate transactions and operations enabled by 5G UC technology.
Lastly, regulatory frameworks are addressing the competitive landscape to promote innovation and prevent monopolistic practices in the 5G UC real estate market. This includes regulations on network sharing, open access requirements, and measures to ensure a level playing field for both established players and new entrants in the 5G UC-enabled real estate technology space.
One of the primary concerns addressed by regulatory frameworks is the allocation of spectrum for 5G UC networks. Regulatory bodies are tasked with managing the limited radio frequency spectrum to accommodate the high-bandwidth requirements of 5G UC while avoiding interference with existing wireless services. This often involves reallocating spectrum from other uses or opening up new frequency bands specifically for 5G UC applications in real estate.
Privacy and data protection regulations play a crucial role in the 5G UC ecosystem for real estate. As smart buildings and IoT devices become more prevalent, the amount of data collected and transmitted increases exponentially. Regulatory frameworks must address the collection, storage, and use of personal and sensitive information to protect tenants, property owners, and other stakeholders.
Security regulations are another key component of the 5G UC regulatory framework for real estate. With the increased connectivity and reliance on digital systems, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Regulations often mandate specific security protocols, encryption standards, and regular security audits to safeguard against potential breaches and cyber attacks on smart real estate infrastructure.
Environmental and health considerations are also addressed in regulatory frameworks. Concerns about the potential health effects of increased electromagnetic radiation from 5G UC networks have led to regulations governing the placement and power output of 5G antennas and base stations in and around real estate properties.
Building codes and standards are being updated to accommodate the integration of 5G UC technology in real estate. This includes regulations on the installation of small cells, distributed antenna systems, and other 5G UC infrastructure within buildings. These codes ensure that 5G UC deployments meet safety standards and do not interfere with other building systems.
Cross-border regulations are becoming increasingly important as 5G UC enables more seamless global connectivity in the real estate sector. Regulatory bodies are working to harmonize standards across different countries to facilitate international real estate transactions and operations enabled by 5G UC technology.
Lastly, regulatory frameworks are addressing the competitive landscape to promote innovation and prevent monopolistic practices in the 5G UC real estate market. This includes regulations on network sharing, open access requirements, and measures to ensure a level playing field for both established players and new entrants in the 5G UC-enabled real estate technology space.
Economic Impact of 5G UC on Real Estate Sector
The integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in the real estate sector is poised to have a significant economic impact, revolutionizing various aspects of the industry. This advanced connectivity solution offers unprecedented speed, reliability, and capacity, enabling a wide range of applications that can transform property management, construction, and real estate transactions.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in real estate is the potential for increased property values. Smart buildings equipped with 5G-enabled IoT devices and sensors can offer enhanced energy efficiency, security, and comfort, making them more attractive to potential buyers and tenants. This technological upgrade can justify higher rental rates and sale prices, ultimately boosting the overall value of real estate portfolios.
The construction industry, a crucial component of the real estate sector, stands to gain substantial economic advantages from 5G UC implementation. Real-time data transmission and analysis can optimize project management, reducing delays and cost overruns. Advanced technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), powered by 5G, can streamline design processes and improve collaboration among stakeholders, leading to faster project completion and reduced labor costs.
In the realm of property management, 5G UC can drive significant cost savings through predictive maintenance and automated systems. By leveraging real-time data from IoT sensors, property managers can identify and address issues before they escalate, minimizing repair costs and extending the lifespan of building systems. This proactive approach can result in substantial long-term savings for property owners and investors.
The real estate transaction process is also set to benefit economically from 5G UC technology. Virtual property tours and remote property inspections, enabled by high-quality video streaming and AR applications, can reduce the time and resources required for in-person visits. This efficiency can lead to faster sales cycles and reduced transaction costs, benefiting both buyers and sellers in the market.
Furthermore, 5G UC can facilitate the development of new revenue streams within the real estate sector. For instance, property owners can monetize their buildings' digital infrastructure by offering advanced connectivity services to tenants or hosting edge computing facilities. This diversification of income sources can enhance the overall economic resilience of real estate investments.
The economic impact of 5G UC extends beyond individual properties to entire urban ecosystems. Smart city initiatives, powered by 5G networks, can improve urban planning, traffic management, and public services. These enhancements can increase the attractiveness and livability of certain areas, potentially driving up property values and stimulating economic growth in the surrounding real estate markets.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in real estate is the potential for increased property values. Smart buildings equipped with 5G-enabled IoT devices and sensors can offer enhanced energy efficiency, security, and comfort, making them more attractive to potential buyers and tenants. This technological upgrade can justify higher rental rates and sale prices, ultimately boosting the overall value of real estate portfolios.
The construction industry, a crucial component of the real estate sector, stands to gain substantial economic advantages from 5G UC implementation. Real-time data transmission and analysis can optimize project management, reducing delays and cost overruns. Advanced technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), powered by 5G, can streamline design processes and improve collaboration among stakeholders, leading to faster project completion and reduced labor costs.
In the realm of property management, 5G UC can drive significant cost savings through predictive maintenance and automated systems. By leveraging real-time data from IoT sensors, property managers can identify and address issues before they escalate, minimizing repair costs and extending the lifespan of building systems. This proactive approach can result in substantial long-term savings for property owners and investors.
The real estate transaction process is also set to benefit economically from 5G UC technology. Virtual property tours and remote property inspections, enabled by high-quality video streaming and AR applications, can reduce the time and resources required for in-person visits. This efficiency can lead to faster sales cycles and reduced transaction costs, benefiting both buyers and sellers in the market.
Furthermore, 5G UC can facilitate the development of new revenue streams within the real estate sector. For instance, property owners can monetize their buildings' digital infrastructure by offering advanced connectivity services to tenants or hosting edge computing facilities. This diversification of income sources can enhance the overall economic resilience of real estate investments.
The economic impact of 5G UC extends beyond individual properties to entire urban ecosystems. Smart city initiatives, powered by 5G networks, can improve urban planning, traffic management, and public services. These enhancements can increase the attractiveness and livability of certain areas, potentially driving up property values and stimulating economic growth in the surrounding real estate markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!