How to Benchmark Alkane Fluidity in Cold Climates
JAN 7, 20269 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkane Fluidity in Cold Climates: Background and Objectives
Alkane fluidity in cold climates represents a critical challenge across multiple industrial sectors, particularly in petroleum refining, fuel distribution, and chemical processing. The fundamental issue stems from the inherent molecular characteristics of alkanes, which exhibit significantly altered flow properties as temperatures decrease. Linear and branched alkanes undergo phase transitions and viscosity increases that can severely impair operational efficiency, leading to pipeline blockages, equipment failures, and compromised product quality in regions experiencing sub-zero temperatures.
The historical development of this technical domain traces back to early petroleum industry challenges in northern regions during the mid-20th century. Initial observations of fuel gelling and wax precipitation in Arctic operations prompted systematic investigations into hydrocarbon behavior under cold stress. Over subsequent decades, the field evolved from empirical observations to sophisticated molecular-level understanding, incorporating advances in rheology, thermodynamics, and materials science. The emergence of computational modeling in recent years has further accelerated progress, enabling predictive assessments of alkane performance across diverse temperature regimes.
Current technological objectives center on establishing standardized benchmarking methodologies that accurately predict and quantify alkane fluidity under cold climate conditions. This encompasses developing reliable measurement protocols, identifying critical performance indicators, and creating predictive models that correlate molecular structure with low-temperature flow characteristics. The goal extends beyond mere characterization to enabling rational design of alkane-based products optimized for cold weather applications.
The strategic importance of this research area continues to intensify due to expanding industrial activities in polar and sub-polar regions, driven by resource extraction, transportation infrastructure development, and climate change impacts on traditional operating environments. Effective benchmarking solutions promise substantial economic benefits through reduced operational disruptions, enhanced safety margins, and improved product formulations. Furthermore, environmental considerations demand better understanding of alkane behavior to prevent spills and contamination incidents in sensitive cold-climate ecosystems, adding urgency to developing robust assessment frameworks.
The historical development of this technical domain traces back to early petroleum industry challenges in northern regions during the mid-20th century. Initial observations of fuel gelling and wax precipitation in Arctic operations prompted systematic investigations into hydrocarbon behavior under cold stress. Over subsequent decades, the field evolved from empirical observations to sophisticated molecular-level understanding, incorporating advances in rheology, thermodynamics, and materials science. The emergence of computational modeling in recent years has further accelerated progress, enabling predictive assessments of alkane performance across diverse temperature regimes.
Current technological objectives center on establishing standardized benchmarking methodologies that accurately predict and quantify alkane fluidity under cold climate conditions. This encompasses developing reliable measurement protocols, identifying critical performance indicators, and creating predictive models that correlate molecular structure with low-temperature flow characteristics. The goal extends beyond mere characterization to enabling rational design of alkane-based products optimized for cold weather applications.
The strategic importance of this research area continues to intensify due to expanding industrial activities in polar and sub-polar regions, driven by resource extraction, transportation infrastructure development, and climate change impacts on traditional operating environments. Effective benchmarking solutions promise substantial economic benefits through reduced operational disruptions, enhanced safety margins, and improved product formulations. Furthermore, environmental considerations demand better understanding of alkane behavior to prevent spills and contamination incidents in sensitive cold-climate ecosystems, adding urgency to developing robust assessment frameworks.
Market Demand for Cold-Resistant Alkane Products
The demand for cold-resistant alkane products has experienced substantial growth across multiple industrial sectors, driven primarily by operational challenges in regions with extreme winter conditions. Industries operating in high-latitude areas face persistent difficulties with fuel gelling, lubricant viscosity increases, and equipment performance degradation when temperatures drop significantly below freezing. These challenges have created urgent market requirements for alkane-based products that maintain optimal fluidity and performance characteristics in cold climates.
The transportation and logistics sector represents a major demand driver, particularly in northern regions of North America, Scandinavia, Russia, and parts of Asia. Commercial trucking fleets, aviation fuel suppliers, and marine shipping operations require diesel fuels and jet fuels that resist wax crystal formation and maintain pumpability at temperatures reaching minus forty degrees Celsius or lower. Winter-grade diesel formulations with enhanced cold flow properties have become essential rather than optional in these markets, as equipment downtime directly translates to significant economic losses.
The energy sector constitutes another critical demand segment, especially for oil and gas extraction operations in Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. Hydraulic fluids, drilling muds, and pipeline transport systems all require specialized alkane formulations that prevent solidification and maintain viscosity within operational parameters during extreme cold exposure. The expansion of resource extraction activities into increasingly remote and cold environments has intensified requirements for reliable cold-weather performance testing and product certification.
Agricultural machinery operators in temperate zones with harsh winters also generate substantial demand for cold-resistant lubricants and fuels. Equipment must start reliably and operate efficiently during critical planting and harvesting windows, regardless of ambient temperatures. This seasonal but concentrated demand pattern has prompted manufacturers to develop and market specialized cold-weather product lines.
The military and defense sector maintains consistent demand for cold-resistant alkane products, as operational readiness in diverse climatic conditions remains a strategic priority. Military specifications often set stringent cold-flow performance standards that exceed civilian requirements, driving innovation in formulation chemistry and testing methodologies. This sector's willingness to invest in premium products has supported ongoing research and development efforts.
Consumer automotive markets in cold regions have increasingly demanded winter-grade fuels and synthetic lubricants that ensure vehicle reliability during cold starts and operation. Growing consumer awareness of cold-weather performance issues has expanded market opportunities for premium products with verified low-temperature capabilities, creating differentiation opportunities for suppliers who can demonstrate superior cold-climate performance through standardized benchmarking protocols.
The transportation and logistics sector represents a major demand driver, particularly in northern regions of North America, Scandinavia, Russia, and parts of Asia. Commercial trucking fleets, aviation fuel suppliers, and marine shipping operations require diesel fuels and jet fuels that resist wax crystal formation and maintain pumpability at temperatures reaching minus forty degrees Celsius or lower. Winter-grade diesel formulations with enhanced cold flow properties have become essential rather than optional in these markets, as equipment downtime directly translates to significant economic losses.
The energy sector constitutes another critical demand segment, especially for oil and gas extraction operations in Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. Hydraulic fluids, drilling muds, and pipeline transport systems all require specialized alkane formulations that prevent solidification and maintain viscosity within operational parameters during extreme cold exposure. The expansion of resource extraction activities into increasingly remote and cold environments has intensified requirements for reliable cold-weather performance testing and product certification.
Agricultural machinery operators in temperate zones with harsh winters also generate substantial demand for cold-resistant lubricants and fuels. Equipment must start reliably and operate efficiently during critical planting and harvesting windows, regardless of ambient temperatures. This seasonal but concentrated demand pattern has prompted manufacturers to develop and market specialized cold-weather product lines.
The military and defense sector maintains consistent demand for cold-resistant alkane products, as operational readiness in diverse climatic conditions remains a strategic priority. Military specifications often set stringent cold-flow performance standards that exceed civilian requirements, driving innovation in formulation chemistry and testing methodologies. This sector's willingness to invest in premium products has supported ongoing research and development efforts.
Consumer automotive markets in cold regions have increasingly demanded winter-grade fuels and synthetic lubricants that ensure vehicle reliability during cold starts and operation. Growing consumer awareness of cold-weather performance issues has expanded market opportunities for premium products with verified low-temperature capabilities, creating differentiation opportunities for suppliers who can demonstrate superior cold-climate performance through standardized benchmarking protocols.
Current Status and Challenges in Low-Temperature Alkane Fluidity
Alkane fluidity in cold climates represents a critical technical challenge across multiple industries, particularly in petroleum refining, fuel distribution, and chemical processing. The fundamental issue stems from the inherent molecular characteristics of alkanes, which undergo significant viscosity increases and phase transitions at reduced temperatures. Current research indicates that linear alkanes with carbon chains exceeding C18 begin experiencing flow restrictions below 0°C, while branched alkanes demonstrate marginally improved performance due to disrupted crystalline packing structures.
The primary technical obstacle involves accurately predicting and measuring pour point, cloud point, and cold filter plugging point under varying environmental conditions. Existing standardized testing methods, including ASTM D97 and ISO 3016, provide baseline measurements but often fail to replicate real-world operational scenarios where dynamic flow conditions, pressure variations, and compositional heterogeneity significantly influence fluidity behavior. This gap between laboratory assessments and field performance creates substantial uncertainty in cold climate applications.
Geographically, this challenge manifests most acutely in northern regions including Canada, Scandinavia, Russia, and Alaska, where ambient temperatures routinely drop below -30°C. These environments expose critical limitations in current additive technologies and blending strategies. Cold flow improvers, primarily polymeric dispersants and nucleation modifiers, demonstrate inconsistent effectiveness across different alkane compositions and temperature ranges. The performance variability stems from incomplete understanding of wax crystal morphology evolution and inter-molecular interactions at low temperatures.
Another significant constraint involves the lack of standardized benchmarking protocols that account for compositional complexity in commercial alkane mixtures. Pure component studies provide theoretical insights but inadequately represent the synergistic effects observed in multi-component systems containing varying ratios of normal, iso, and cycloalkanes. This complexity is further compounded by the presence of trace aromatics and heteroatom-containing compounds that disproportionately influence crystallization kinetics.
Current analytical capabilities face limitations in real-time monitoring and predictive modeling. While differential scanning calorimetry and rheological measurements offer valuable data, they require extensive sample preparation and cannot provide continuous operational feedback. Advanced techniques such as cross-polarized microscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy remain largely confined to research settings due to cost and operational complexity. The absence of robust, field-deployable diagnostic tools hampers proactive management of fluidity issues in cold climate operations.
The primary technical obstacle involves accurately predicting and measuring pour point, cloud point, and cold filter plugging point under varying environmental conditions. Existing standardized testing methods, including ASTM D97 and ISO 3016, provide baseline measurements but often fail to replicate real-world operational scenarios where dynamic flow conditions, pressure variations, and compositional heterogeneity significantly influence fluidity behavior. This gap between laboratory assessments and field performance creates substantial uncertainty in cold climate applications.
Geographically, this challenge manifests most acutely in northern regions including Canada, Scandinavia, Russia, and Alaska, where ambient temperatures routinely drop below -30°C. These environments expose critical limitations in current additive technologies and blending strategies. Cold flow improvers, primarily polymeric dispersants and nucleation modifiers, demonstrate inconsistent effectiveness across different alkane compositions and temperature ranges. The performance variability stems from incomplete understanding of wax crystal morphology evolution and inter-molecular interactions at low temperatures.
Another significant constraint involves the lack of standardized benchmarking protocols that account for compositional complexity in commercial alkane mixtures. Pure component studies provide theoretical insights but inadequately represent the synergistic effects observed in multi-component systems containing varying ratios of normal, iso, and cycloalkanes. This complexity is further compounded by the presence of trace aromatics and heteroatom-containing compounds that disproportionately influence crystallization kinetics.
Current analytical capabilities face limitations in real-time monitoring and predictive modeling. While differential scanning calorimetry and rheological measurements offer valuable data, they require extensive sample preparation and cannot provide continuous operational feedback. Advanced techniques such as cross-polarized microscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy remain largely confined to research settings due to cost and operational complexity. The absence of robust, field-deployable diagnostic tools hampers proactive management of fluidity issues in cold climate operations.
Current Benchmarking Solutions for Alkane Fluidity
01 Use of pour point depressants and flow improvers
Chemical additives can be incorporated to modify the crystallization behavior of alkanes and improve their flow properties at low temperatures. These additives work by interfering with wax crystal formation and growth, preventing the formation of large crystal networks that impede flow. Various polymer-based and copolymer compounds have been developed to effectively reduce pour point and improve fluidity of alkane-containing compositions.- Use of pour point depressants and flow improvers: Chemical additives can be incorporated to modify the crystallization behavior of alkanes and improve their low-temperature flow properties. These additives work by interfering with wax crystal formation and growth, preventing the formation of interlocking crystal networks that impede flow. Such compounds are particularly effective in reducing the pour point and improving the pumpability of petroleum products and other alkane-containing fluids at low temperatures.
- Polymer-based viscosity modifiers: Polymeric compounds can be used to enhance the fluidity characteristics of alkane mixtures by modifying their rheological properties. These materials function by altering the viscosity-temperature relationship and preventing excessive viscosity increase at lower temperatures. The polymers can interact with alkane molecules to maintain better flow characteristics across a wider temperature range, making them valuable in applications requiring consistent fluid performance.
- Copolymer additives for wax crystal modification: Specialized copolymeric structures can be employed to control wax crystallization patterns in alkane systems. These copolymers act as crystal modifiers by adsorbing onto growing wax crystals and altering their morphology, resulting in smaller, more dispersed crystals that do not impede flow. This approach is effective in maintaining fluidity in waxy crude oils and other alkane-rich compositions under cold conditions.
- Alkylated aromatic compounds as fluidity enhancers: Aromatic compounds with alkyl substituents can serve as effective agents for improving alkane fluidity by disrupting the regular packing of linear alkane molecules. These compounds act as diluents and crystal growth inhibitors, preventing the formation of rigid wax structures. Their incorporation into alkane formulations helps maintain liquid state and flowability at temperatures where untreated materials would solidify or become highly viscous.
- Combination of dispersants and crystal nucleators: Synergistic formulations combining dispersing agents with nucleating compounds can effectively manage alkane fluidity by controlling both the formation and distribution of wax crystals. The nucleators promote the formation of numerous small crystal nuclei, while dispersants prevent their agglomeration, resulting in a fine dispersion that maintains flow properties. This dual-action approach provides superior performance compared to single-component systems in maintaining fluidity across varying temperature conditions.
02 Modification of alkane composition through blending
The fluidity of alkane mixtures can be enhanced by adjusting the composition through blending different hydrocarbon fractions or adding specific components. This approach involves selecting appropriate ratios of light and heavy fractions to optimize viscosity and flow characteristics. The blending strategy can also include incorporation of synthetic hydrocarbons or processed materials to achieve desired fluidity properties across various temperature ranges.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application of thermal treatment methods
Thermal processing techniques can be employed to improve alkane fluidity by modifying the physical and chemical properties of the hydrocarbon mixture. These methods may include controlled heating, cooling cycles, or specific temperature management protocols that affect the crystallization patterns and viscosity behavior. Such treatments can result in more stable flow properties and reduced tendency for solidification or gelation at lower temperatures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of dispersants and crystal modifiers
Specialized chemical agents can be added to alkane systems to disperse wax crystals and modify their morphology, thereby maintaining fluidity. These compounds act by altering the size, shape, and distribution of crystalline structures that form during cooling. The modification of crystal characteristics prevents agglomeration and network formation, allowing the material to maintain pumpability and flowability even under cold conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Incorporation of co-solvents and viscosity modifiers
The addition of compatible co-solvents or viscosity-modifying agents can significantly enhance alkane fluidity by reducing intermolecular interactions and lowering overall viscosity. These additives work by disrupting the packing efficiency of alkane molecules and reducing the activation energy required for flow. Various organic compounds and specially designed molecules have been identified as effective viscosity reducers that maintain stability and compatibility with the base alkane system.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Players in Cold Climate Lubricant Industry
The alkane fluidity benchmarking technology in cold climates operates within a mature yet evolving competitive landscape, primarily driven by established petroleum and chemical giants. The market is dominated by major integrated oil companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., PetroChina, and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, alongside specialized research institutes including Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing and Shanghai Petrochemical Research Institute. The industry has reached a consolidation phase with significant market scale, particularly in regions experiencing extreme cold conditions. Technology maturity varies across players, with Sinopec's multiple research divisions and PetroChina demonstrating advanced capabilities in low-temperature flow property testing and pour point depression technologies. International players like TotalEnergies OneTech and Schlumberger Technologies contribute specialized measurement and analytical solutions. Academic institutions such as Beihang University and Sichuan University provide fundamental research support, while industrial automation leaders like Siemens and General Electric enable sophisticated testing infrastructure, creating a comprehensive ecosystem spanning from basic research to commercial application.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: Sinopec has developed comprehensive cold flow property testing methodologies for alkane-based fuels and lubricants in low-temperature environments. Their approach integrates standardized ASTM D97 pour point testing with cloud point analysis (ASTM D2500) and cold filter plugging point (CFPP) measurements specifically designed for diesel and jet fuels containing various alkane compositions[1][4]. The company employs advanced rheological characterization using rotational viscometers at temperatures ranging from -40°C to +40°C to evaluate viscosity-temperature relationships of paraffinic hydrocarbons. Additionally, they utilize differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to identify crystallization onset temperatures and wax formation behavior in alkane mixtures. Their testing protocols include low-temperature operability assessments that simulate real-world cold climate conditions, incorporating both static and dynamic flow measurements through standardized pipelines and filters[6][8].
Strengths: Extensive experience in petroleum product testing with established infrastructure across multiple climate zones; comprehensive integration of multiple testing standards. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on fuel applications rather than pure alkane research; methodologies may be proprietary and less accessible to external researchers.
PetroChina Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: PetroChina has established specialized cold climate testing facilities in northern China and collaborated with research institutes to develop alkane fluidity benchmarking protocols tailored for extreme low-temperature conditions down to -50°C. Their methodology encompasses multi-parameter evaluation including kinematic viscosity measurements per ASTM D445 at various sub-zero temperatures, low-temperature flow test (LTFT) procedures, and wax appearance temperature (WAT) determination using cross-polarized microscopy[2][5]. The company has developed proprietary testing chambers that simulate diurnal temperature cycling to assess alkane behavior under realistic freeze-thaw conditions. They employ gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to correlate alkane carbon chain distribution with cold flow properties, enabling predictive modeling of fluidity based on compositional analysis. Their benchmarking framework includes pumpability tests using specialized low-shear viscometers and filterability assessments that measure pressure drop across standardized filter media at controlled low temperatures[7][9].
Strengths: Access to natural cold climate testing environments in northern regions; strong integration of compositional analysis with performance testing; extensive field validation capabilities. Weaknesses: Testing protocols may be optimized primarily for crude oil and refined products rather than pure alkane standards; limited published data on methodology specifics.
Key Technologies in Low-Temperature Flow Testing
Method for determining the characteristics of crude oils and mixtures of chain molecules by diffusion, relaxation and density measurements
PatentInactiveUS8206993B2
Innovation
- The method employs scaling laws based on chain length to determine diffusion coefficients and relaxation times, using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques to characterize the composition of oil mixtures by correlating diffusion distributions with chain lengths and mean chain lengths, accounting for temperature and pressure dependencies.
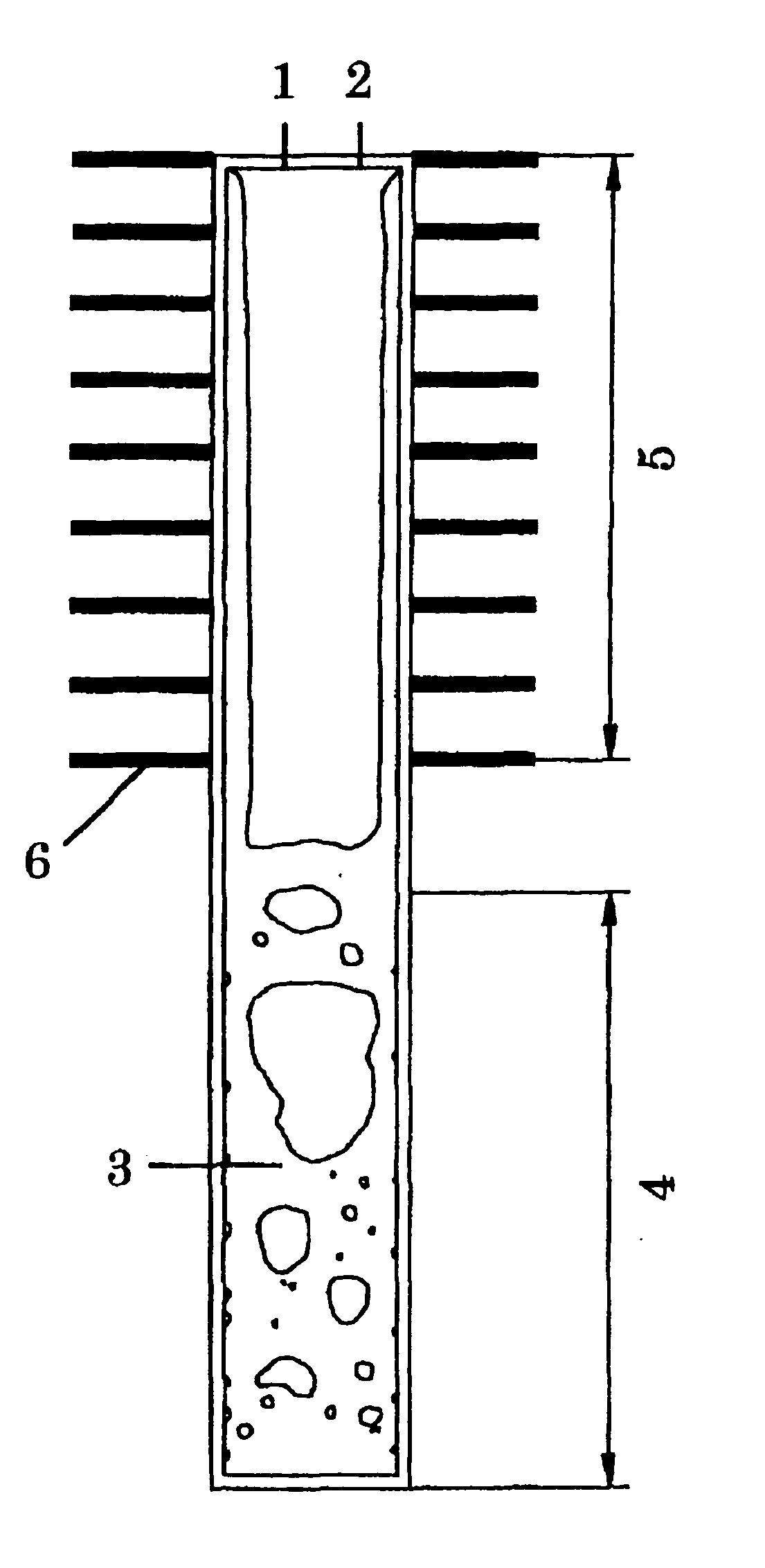
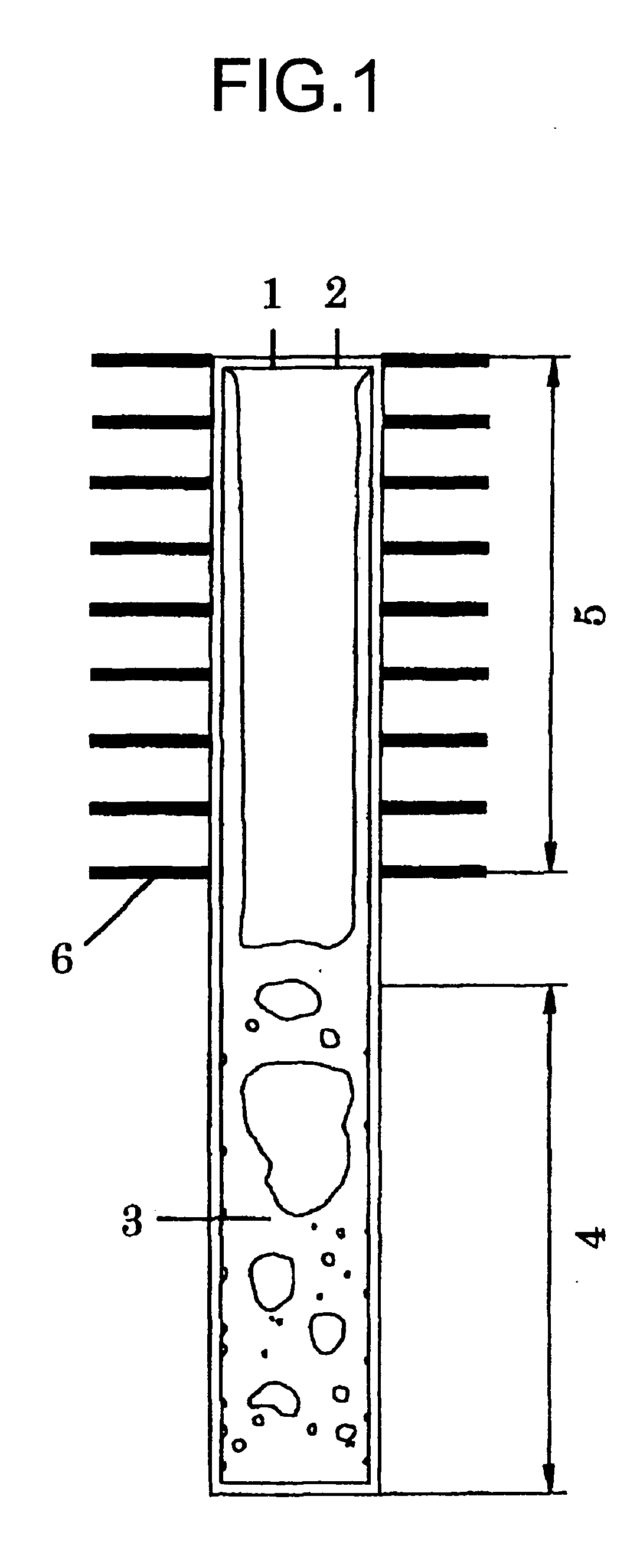
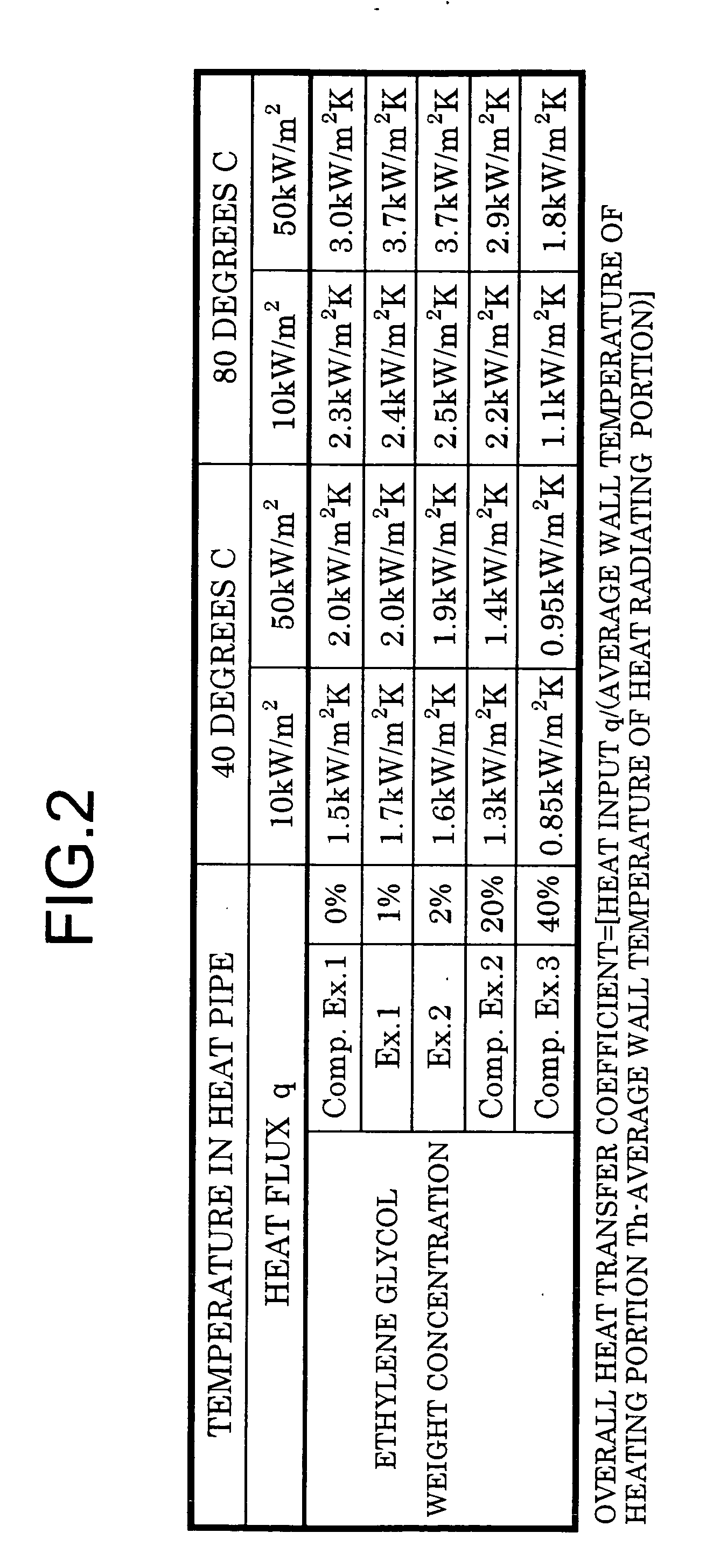
Heat pipe
PatentInactiveUS20060060329A1
Innovation
- A heat pipe using an aqueous solution with 0.5 to 10 wt% glycols, preferably ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, as the working fluid, which freezes into sherbet-like ice, preventing pipe bursting and maintaining high heat conductivity.
Climate and Environmental Standards for Cold Regions
Benchmarking alkane fluidity in cold climates necessitates adherence to rigorous climate and environmental standards specifically designed for cold regions. These standards provide the foundational framework for ensuring that testing methodologies accurately reflect real-world operational conditions while maintaining environmental responsibility. International organizations such as ISO, ASTM, and regional bodies like the Arctic Council have established comprehensive guidelines that define acceptable temperature ranges, humidity levels, and atmospheric pressure conditions for cold climate testing. These standards typically specify testing environments ranging from -40°C to -60°C, representing extreme Arctic and sub-Arctic conditions where alkane behavior becomes critically important for industrial applications.
Environmental standards for cold regions extend beyond temperature specifications to encompass ecological protection measures. Testing protocols must account for the unique vulnerability of cold climate ecosystems, requiring containment procedures that prevent alkane contamination of permafrost, ice formations, and cold-water bodies. Standards such as ISO 15156 and ASTM D5133 provide specific guidance on material compatibility and environmental safety in low-temperature environments, ensuring that benchmark testing does not compromise fragile Arctic ecosystems.
Regulatory frameworks in cold regions also mandate consideration of seasonal variations and microclimate effects. Standards require testing across multiple temperature cycles to simulate diurnal and seasonal fluctuations characteristic of polar and high-altitude environments. This includes protocols for freeze-thaw cycling, ice crystal formation assessment, and long-term stability evaluation under sustained cold exposure. Compliance with these standards ensures that fluidity benchmarks reflect not just instantaneous performance but sustained operational reliability.
Furthermore, cold region standards incorporate specific requirements for instrumentation calibration and data validation under extreme conditions. Measurement equipment must meet enhanced accuracy specifications when operating at low temperatures, as sensor performance can degrade significantly below standard operating ranges. Standards such as ASTM D7346 address these challenges by defining calibration procedures and uncertainty quantification methods specific to cold climate testing, ensuring that benchmark data maintains scientific validity and industrial applicability across diverse geographical locations where alkane fluidity assessment is critical.
Environmental standards for cold regions extend beyond temperature specifications to encompass ecological protection measures. Testing protocols must account for the unique vulnerability of cold climate ecosystems, requiring containment procedures that prevent alkane contamination of permafrost, ice formations, and cold-water bodies. Standards such as ISO 15156 and ASTM D5133 provide specific guidance on material compatibility and environmental safety in low-temperature environments, ensuring that benchmark testing does not compromise fragile Arctic ecosystems.
Regulatory frameworks in cold regions also mandate consideration of seasonal variations and microclimate effects. Standards require testing across multiple temperature cycles to simulate diurnal and seasonal fluctuations characteristic of polar and high-altitude environments. This includes protocols for freeze-thaw cycling, ice crystal formation assessment, and long-term stability evaluation under sustained cold exposure. Compliance with these standards ensures that fluidity benchmarks reflect not just instantaneous performance but sustained operational reliability.
Furthermore, cold region standards incorporate specific requirements for instrumentation calibration and data validation under extreme conditions. Measurement equipment must meet enhanced accuracy specifications when operating at low temperatures, as sensor performance can degrade significantly below standard operating ranges. Standards such as ASTM D7346 address these challenges by defining calibration procedures and uncertainty quantification methods specific to cold climate testing, ensuring that benchmark data maintains scientific validity and industrial applicability across diverse geographical locations where alkane fluidity assessment is critical.
Standardization Framework for Fluidity Benchmarking
Establishing a robust standardization framework for fluidity benchmarking of alkanes in cold climates requires the integration of multiple measurement protocols, environmental parameters, and quality assurance mechanisms. The framework must address the inherent variability in testing conditions while ensuring reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and geographical locations. This necessitates the development of unified testing procedures that account for temperature ranges, pressure conditions, and sample preparation methods specific to cold climate applications.
The foundation of this framework rests on defining precise measurement standards for key fluidity indicators, including pour point, cloud point, cold filter plugging point, and viscosity at low temperatures. Each parameter requires specific instrumentation calibration protocols and reference materials that maintain stability under extreme cold conditions. The framework should incorporate international standards such as ASTM D97, ASTM D2500, and ISO 3016, while introducing supplementary guidelines tailored to arctic and subarctic environments where conventional methods may prove inadequate.
Quality control mechanisms form a critical component, encompassing sample handling procedures from collection through analysis. The framework must specify container materials, storage temperatures, and maximum holding times to prevent compositional changes that could affect fluidity measurements. Inter-laboratory proficiency testing programs should be established to validate measurement consistency and identify systematic deviations in testing procedures.
Data reporting standardization ensures meaningful comparison of results across different studies and applications. The framework should mandate comprehensive documentation of testing conditions, including ambient temperature, sample history, and equipment specifications. Digital data formats and metadata requirements facilitate the creation of centralized databases that support long-term trend analysis and predictive modeling.
Implementation guidelines must address the practical challenges of conducting fluidity tests in remote cold climate locations, including portable equipment specifications, field calibration procedures, and environmental compensation factors. The framework should also establish certification requirements for testing personnel and periodic equipment validation protocols to maintain measurement integrity throughout the operational lifecycle.
The foundation of this framework rests on defining precise measurement standards for key fluidity indicators, including pour point, cloud point, cold filter plugging point, and viscosity at low temperatures. Each parameter requires specific instrumentation calibration protocols and reference materials that maintain stability under extreme cold conditions. The framework should incorporate international standards such as ASTM D97, ASTM D2500, and ISO 3016, while introducing supplementary guidelines tailored to arctic and subarctic environments where conventional methods may prove inadequate.
Quality control mechanisms form a critical component, encompassing sample handling procedures from collection through analysis. The framework must specify container materials, storage temperatures, and maximum holding times to prevent compositional changes that could affect fluidity measurements. Inter-laboratory proficiency testing programs should be established to validate measurement consistency and identify systematic deviations in testing procedures.
Data reporting standardization ensures meaningful comparison of results across different studies and applications. The framework should mandate comprehensive documentation of testing conditions, including ambient temperature, sample history, and equipment specifications. Digital data formats and metadata requirements facilitate the creation of centralized databases that support long-term trend analysis and predictive modeling.
Implementation guidelines must address the practical challenges of conducting fluidity tests in remote cold climate locations, including portable equipment specifications, field calibration procedures, and environmental compensation factors. The framework should also establish certification requirements for testing personnel and periodic equipment validation protocols to maintain measurement integrity throughout the operational lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!