How to Implement Hypochlorous Acid in Newly Established Hygiene Protocols?
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising solution in the field of hygiene and disinfection, with its roots tracing back to the early 20th century. This naturally occurring molecule, produced by the human immune system to fight infections, has gained renewed interest in recent years due to its potent antimicrobial properties and environmental friendliness.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been marked by significant advancements in production methods and application techniques. Initially, HOCl was primarily generated through electrolysis of salt water, a process that has been refined over time to improve efficiency and stability. Recent innovations have led to the development of more sophisticated electrochemical cells and membrane technologies, enabling the production of higher concentrations of HOCl with extended shelf life.
In the context of newly established hygiene protocols, the implementation of HOCl represents a paradigm shift in disinfection strategies. The primary objective is to harness the broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy of HOCl while addressing the limitations of traditional chemical disinfectants, such as toxicity concerns and microbial resistance.
The technical goals for HOCl implementation encompass several key areas. Firstly, there is a focus on optimizing production methods to ensure consistent quality and concentration of HOCl solutions. This involves developing robust manufacturing processes and quality control measures to maintain the stability and efficacy of the product.
Secondly, research efforts are directed towards enhancing the delivery systems for HOCl. This includes the design of specialized sprayers, foggers, and other application devices that can effectively distribute HOCl in various environments, from healthcare facilities to public spaces.
Another critical objective is to establish standardized protocols for HOCl use in different settings. This involves determining optimal concentrations, contact times, and application frequencies for various surfaces and scenarios. The aim is to develop evidence-based guidelines that maximize the disinfection efficacy while ensuring safety and compatibility with different materials.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on integrating HOCl into comprehensive hygiene management systems. This includes developing smart dispensing systems, IoT-enabled monitoring devices, and data analytics platforms to track and optimize HOCl usage in real-time.
As the technology continues to evolve, future research directions are likely to focus on expanding the applications of HOCl beyond surface disinfection. Potential areas of exploration include air purification systems, water treatment technologies, and even medical applications such as wound care and respiratory therapies.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been marked by significant advancements in production methods and application techniques. Initially, HOCl was primarily generated through electrolysis of salt water, a process that has been refined over time to improve efficiency and stability. Recent innovations have led to the development of more sophisticated electrochemical cells and membrane technologies, enabling the production of higher concentrations of HOCl with extended shelf life.
In the context of newly established hygiene protocols, the implementation of HOCl represents a paradigm shift in disinfection strategies. The primary objective is to harness the broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy of HOCl while addressing the limitations of traditional chemical disinfectants, such as toxicity concerns and microbial resistance.
The technical goals for HOCl implementation encompass several key areas. Firstly, there is a focus on optimizing production methods to ensure consistent quality and concentration of HOCl solutions. This involves developing robust manufacturing processes and quality control measures to maintain the stability and efficacy of the product.
Secondly, research efforts are directed towards enhancing the delivery systems for HOCl. This includes the design of specialized sprayers, foggers, and other application devices that can effectively distribute HOCl in various environments, from healthcare facilities to public spaces.
Another critical objective is to establish standardized protocols for HOCl use in different settings. This involves determining optimal concentrations, contact times, and application frequencies for various surfaces and scenarios. The aim is to develop evidence-based guidelines that maximize the disinfection efficacy while ensuring safety and compatibility with different materials.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on integrating HOCl into comprehensive hygiene management systems. This includes developing smart dispensing systems, IoT-enabled monitoring devices, and data analytics platforms to track and optimize HOCl usage in real-time.
As the technology continues to evolve, future research directions are likely to focus on expanding the applications of HOCl beyond surface disinfection. Potential areas of exploration include air purification systems, water treatment technologies, and even medical applications such as wound care and respiratory therapies.
Market Analysis for HOCl-based Hygiene Solutions
The market for HOCl-based hygiene solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the importance of effective disinfection and the unique properties of hypochlorous acid. This market segment is positioned at the intersection of healthcare, consumer goods, and industrial applications, offering a wide range of potential uses and opportunities for expansion.
In the healthcare sector, HOCl solutions have gained traction as a safe and effective alternative to traditional disinfectants. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities are adopting HOCl-based products for surface disinfection, wound care, and general hygiene purposes. The ongoing global focus on infection prevention and control has further accelerated the adoption of HOCl solutions in healthcare settings.
The consumer market for HOCl-based products has also seen substantial growth. With heightened public awareness of hygiene and sanitation, particularly in the wake of recent global health events, consumers are seeking effective yet gentle disinfection solutions for home use. This has led to an increase in HOCl-based products for household cleaning, personal care, and even pet care applications.
In the industrial and commercial sectors, HOCl solutions are finding applications in food processing, agriculture, and water treatment. The ability of HOCl to effectively eliminate pathogens without leaving harmful residues makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to maintain high hygiene standards while minimizing environmental impact.
The market demand for HOCl-based hygiene solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors contributing to this growth include the increasing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly disinfection methods, the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens necessitating new approaches to infection control, and the growing preference for non-toxic cleaning solutions in both professional and domestic settings.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for HOCl-based hygiene solutions, owing to stringent hygiene regulations and high consumer awareness. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific and Latin American markets, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of advanced hygiene practices.
The competitive landscape of the HOCl market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Key market players are focusing on product development, expanding their distribution networks, and engaging in strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The market also sees opportunities for differentiation through specialized formulations, innovative delivery systems, and targeted applications for specific industries or use cases.
In the healthcare sector, HOCl solutions have gained traction as a safe and effective alternative to traditional disinfectants. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities are adopting HOCl-based products for surface disinfection, wound care, and general hygiene purposes. The ongoing global focus on infection prevention and control has further accelerated the adoption of HOCl solutions in healthcare settings.
The consumer market for HOCl-based products has also seen substantial growth. With heightened public awareness of hygiene and sanitation, particularly in the wake of recent global health events, consumers are seeking effective yet gentle disinfection solutions for home use. This has led to an increase in HOCl-based products for household cleaning, personal care, and even pet care applications.
In the industrial and commercial sectors, HOCl solutions are finding applications in food processing, agriculture, and water treatment. The ability of HOCl to effectively eliminate pathogens without leaving harmful residues makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to maintain high hygiene standards while minimizing environmental impact.
The market demand for HOCl-based hygiene solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors contributing to this growth include the increasing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly disinfection methods, the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens necessitating new approaches to infection control, and the growing preference for non-toxic cleaning solutions in both professional and domestic settings.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for HOCl-based hygiene solutions, owing to stringent hygiene regulations and high consumer awareness. However, rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific and Latin American markets, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of advanced hygiene practices.
The competitive landscape of the HOCl market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Key market players are focusing on product development, expanding their distribution networks, and engaging in strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The market also sees opportunities for differentiation through specialized formulations, innovative delivery systems, and targeted applications for specific industries or use cases.
Current Challenges in HOCl Implementation
The implementation of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in newly established hygiene protocols faces several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of HOCl solutions. These solutions are known to degrade rapidly when exposed to light, heat, and organic matter, which can significantly reduce their effectiveness in real-world applications. This instability necessitates frequent preparation or specialized storage conditions, potentially increasing operational costs and complexity.
Another challenge lies in the standardization of HOCl production and application methods. The concentration and pH of HOCl solutions can vary widely depending on the production process, which affects their antimicrobial efficacy and safety profile. Establishing consistent protocols for production, testing, and application across different settings and industries remains a significant hurdle.
The lack of comprehensive regulatory guidelines specifically addressing HOCl use in various sectors poses additional difficulties. While HOCl is generally recognized as safe, the absence of clear regulatory frameworks can lead to uncertainty in its adoption, particularly in highly regulated industries such as healthcare and food processing.
Education and training present another substantial challenge. Many potential users, including healthcare professionals and facility managers, may be unfamiliar with HOCl's properties, benefits, and proper usage. This knowledge gap can lead to resistance in adopting new protocols or improper application, potentially compromising the effectiveness of HOCl-based hygiene measures.
The integration of HOCl into existing hygiene protocols also faces logistical and practical challenges. Many facilities have established routines and equipment designed for traditional disinfectants. Transitioning to HOCl may require modifications to cleaning procedures, storage facilities, and application equipment, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Furthermore, there are concerns about the potential long-term effects of widespread HOCl use. While HOCl is considered environmentally friendly, questions remain about its impact on surfaces, equipment, and human health with prolonged exposure. Addressing these concerns through long-term studies and risk assessments is crucial for widespread adoption.
Lastly, the economic feasibility of implementing HOCl-based protocols presents a challenge, particularly for smaller organizations. The initial investment in production equipment, training, and protocol development can be substantial, and the ongoing costs of maintaining HOCl solutions may be higher than those of traditional disinfectants. Demonstrating a clear return on investment and long-term cost-effectiveness is essential for overcoming this hurdle.
Another challenge lies in the standardization of HOCl production and application methods. The concentration and pH of HOCl solutions can vary widely depending on the production process, which affects their antimicrobial efficacy and safety profile. Establishing consistent protocols for production, testing, and application across different settings and industries remains a significant hurdle.
The lack of comprehensive regulatory guidelines specifically addressing HOCl use in various sectors poses additional difficulties. While HOCl is generally recognized as safe, the absence of clear regulatory frameworks can lead to uncertainty in its adoption, particularly in highly regulated industries such as healthcare and food processing.
Education and training present another substantial challenge. Many potential users, including healthcare professionals and facility managers, may be unfamiliar with HOCl's properties, benefits, and proper usage. This knowledge gap can lead to resistance in adopting new protocols or improper application, potentially compromising the effectiveness of HOCl-based hygiene measures.
The integration of HOCl into existing hygiene protocols also faces logistical and practical challenges. Many facilities have established routines and equipment designed for traditional disinfectants. Transitioning to HOCl may require modifications to cleaning procedures, storage facilities, and application equipment, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Furthermore, there are concerns about the potential long-term effects of widespread HOCl use. While HOCl is considered environmentally friendly, questions remain about its impact on surfaces, equipment, and human health with prolonged exposure. Addressing these concerns through long-term studies and risk assessments is crucial for widespread adoption.
Lastly, the economic feasibility of implementing HOCl-based protocols presents a challenge, particularly for smaller organizations. The initial investment in production equipment, training, and protocol development can be substantial, and the ongoing costs of maintaining HOCl solutions may be higher than those of traditional disinfectants. Demonstrating a clear return on investment and long-term cost-effectiveness is essential for overcoming this hurdle.
Existing HOCl Application Methods
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods for producing hypochlorous acid are described, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and novel techniques for generating stable hypochlorous acid solutions. These methods aim to improve the efficiency and purity of hypochlorous acid production for various applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: Stabilization of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining their efficacy over time. Various techniques are employed, such as pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging methods, to extend the shelf life and preserve the antimicrobial properties of hypochlorous acid products.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its natural occurrence in the human immune system and its ability to promote healing while combating infections make it a valuable component in various medical formulations.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental and industrial settings for purposes such as water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in breaking down pollutants make it a preferred choice for various cleaning and sanitization processes in industrial environments.
02 Applications in disinfection and sterilization
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sterilizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications include water treatment, surface disinfection, and medical sterilization, with emphasis on its safety and eco-friendly nature compared to traditional chlorine-based disinfectants.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulations and stability enhancement
Research focuses on developing stable formulations of hypochlorous acid to extend its shelf life and maintain its effectiveness. This includes the use of specific additives, pH adjustments, and packaging innovations to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability for various applications in healthcare, agriculture, and industry.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic applications
Hypochlorous acid is explored for its potential in medical treatments and therapies. This includes wound healing, skin conditions, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Research focuses on its antimicrobial properties, ability to promote healing, and low toxicity to human cells when used in appropriate concentrations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial uses
Applications of hypochlorous acid in environmental remediation and industrial processes are investigated. This includes water and wastewater treatment, air purification, and use in food processing industries. The focus is on its effectiveness as a sanitizer and its potential to replace more harmful chemicals in various industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCl Industry
The implementation of hypochlorous acid in newly established hygiene protocols is gaining traction in a competitive landscape characterized by rapid technological advancements and growing market demand. The industry is in a growth phase, with an expanding market size driven by increased focus on sanitation and disinfection across various sectors. The technology's maturity is evolving, with companies like ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC. and Parasol Medical LLC leading in innovation. These firms, along with others such as Guangzhou Taidaoan Medical Technology Co., Ltd. and PCT Ltd., are developing advanced applications and delivery systems for hypochlorous acid, indicating a trend towards more sophisticated and efficient hygiene solutions. The competitive field includes both established players and emerging startups, suggesting a dynamic and innovative market environment.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS has developed a comprehensive approach to implementing hypochlorous acid in hygiene protocols, focusing on healthcare settings. Their system, known as the Annihilare™ Infection Control System, combines on-site HOCl generation with advanced application technologies[1]. The company's implementation strategy includes the use of electrostatic sprayers for efficient surface coverage, ensuring that HOCl reaches even hard-to-access areas[2]. They have also developed protocols for integrating HOCl into daily cleaning routines, with specific guidelines for high-touch surfaces and critical care areas. ANNIHILARE's system includes real-time monitoring and data logging capabilities, allowing facilities to track disinfection activities and ensure compliance with hygiene protocols[3].
Strengths: Tailored solutions for healthcare environments; advanced application technologies; comprehensive tracking and compliance features. Weaknesses: May require significant changes to existing protocols; potentially higher initial investment compared to traditional disinfection methods.
SANYO Electric Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: SANYO Electric Co., Ltd. has developed an innovative approach to implementing hypochlorous acid in hygiene protocols, leveraging their expertise in electronic and environmental technologies. Their strategy centers around the development of advanced HOCl generation systems that can be integrated into various environments, from households to large-scale facilities[1]. SANYO's implementation approach includes the design of compact, user-friendly HOCl generators that produce a stable form of hypochlorous acid on-demand[2]. These systems utilize electrolysis technology to convert salt and water into HOCl, ensuring a consistent supply of fresh disinfectant. SANYO has also developed smart dispensing systems that can be programmed to deliver precise amounts of HOCl for different applications, optimizing usage and reducing waste[3]. Their implementation strategy encompasses the integration of HOCl generation and dispensing systems into existing building management systems, allowing for automated and scheduled disinfection processes.
Strengths: Advanced technology integration; scalable solutions for various environments; energy-efficient and environmentally friendly approach. Weaknesses: May require significant infrastructure changes for full implementation; potential for higher initial costs compared to traditional disinfection methods.
Innovative HOCl Formulations
Medical antibacterial and disinfecting biodressing
PatentActiveZA202200034A
Innovation
- A composition combining acidic electrolytic water with polyvinyl pyrrolidone and modified chitosan, balanced at a pH range of 3.7-6.8, stabilizes hypochlorous acid for prolonged bio-surface disinfection, using polyvinyl pyrrolidone as a stabilizer and modified chitosan for bacteriostatic and absorption-promoting properties, and optionally adding corrosion inhibitors and thickeners like potassium phosphate and pentaerythritol.
System and method for effective cleaning and disinfecting protocol
PatentInactiveGB2594696A
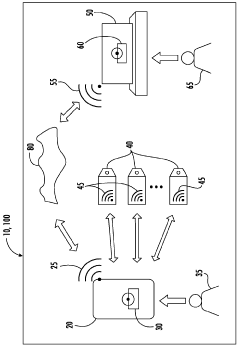
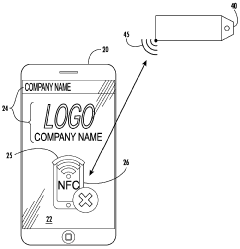
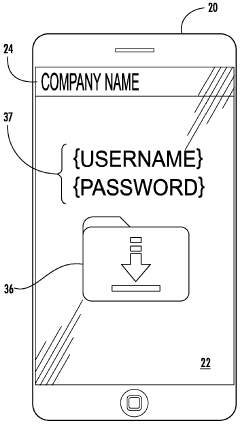
Innovation
- A system and method utilizing a portable computing device with RFID/NFC technology to track and verify adherence to cleaning protocols, ensuring the use of effective disinfectants within their lifecycle, including Hypochlorous acid, through authentication, data management, and reporting functionalities.
Regulatory Framework for HOCl Use
The regulatory framework for the use of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in hygiene protocols is complex and varies across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HOCl as a pesticide under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA has approved HOCl for use as a disinfectant and sanitizer in various settings, including healthcare facilities, food processing plants, and public spaces.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a role in regulating HOCl, particularly when it is used in food-contact applications or as an ingredient in medical devices. The FDA has granted Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status to HOCl for certain food-related uses, such as produce washing and food-contact surface sanitization.
In the European Union, HOCl falls under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which governs the use of biocidal active substances and products. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is responsible for implementing the BPR and has approved HOCl for various biocidal product types, including disinfectants and algaecides.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized HOCl as an effective disinfectant, particularly in the context of water treatment and healthcare settings. However, the WHO emphasizes the importance of proper concentration and application methods to ensure efficacy and safety.
When implementing HOCl in newly established hygiene protocols, organizations must consider occupational safety regulations. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines for the safe handling and use of disinfectants, including HOCl. These guidelines cover aspects such as personal protective equipment, proper storage, and handling procedures.
It is crucial for organizations to stay updated on regulatory changes and comply with local, national, and international standards when incorporating HOCl into their hygiene protocols. This may involve obtaining necessary certifications, conducting regular safety assessments, and maintaining detailed documentation of HOCl usage and application procedures.
Furthermore, organizations should be aware of specific regulations governing the marketing and labeling of HOCl products. Claims regarding efficacy, safety, and environmental impact must be substantiated and comply with relevant advertising standards and regulations.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a role in regulating HOCl, particularly when it is used in food-contact applications or as an ingredient in medical devices. The FDA has granted Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status to HOCl for certain food-related uses, such as produce washing and food-contact surface sanitization.
In the European Union, HOCl falls under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which governs the use of biocidal active substances and products. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is responsible for implementing the BPR and has approved HOCl for various biocidal product types, including disinfectants and algaecides.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized HOCl as an effective disinfectant, particularly in the context of water treatment and healthcare settings. However, the WHO emphasizes the importance of proper concentration and application methods to ensure efficacy and safety.
When implementing HOCl in newly established hygiene protocols, organizations must consider occupational safety regulations. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines for the safe handling and use of disinfectants, including HOCl. These guidelines cover aspects such as personal protective equipment, proper storage, and handling procedures.
It is crucial for organizations to stay updated on regulatory changes and comply with local, national, and international standards when incorporating HOCl into their hygiene protocols. This may involve obtaining necessary certifications, conducting regular safety assessments, and maintaining detailed documentation of HOCl usage and application procedures.
Furthermore, organizations should be aware of specific regulations governing the marketing and labeling of HOCl products. Claims regarding efficacy, safety, and environmental impact must be substantiated and comply with relevant advertising standards and regulations.
Environmental Impact of HOCl
The implementation of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in newly established hygiene protocols presents a significant opportunity for enhancing environmental sustainability in cleaning and disinfection practices. HOCl is a naturally occurring compound that is both highly effective against a wide range of pathogens and environmentally friendly. Unlike many traditional chemical disinfectants, HOCl breaks down into simple salt and water, leaving no harmful residues or by-products.
The environmental impact of HOCl is notably positive when compared to conventional cleaning agents. Its production process requires only salt, water, and electricity, reducing the need for complex chemical manufacturing and transportation. This simplicity in production translates to a lower carbon footprint and reduced energy consumption throughout the supply chain. Furthermore, the on-site generation of HOCl can significantly decrease packaging waste and the environmental costs associated with shipping and storing large quantities of pre-made disinfectants.
In aquatic ecosystems, HOCl demonstrates minimal toxicity to non-target organisms. When released into water bodies, it rapidly dissipates without accumulating or causing long-term ecological damage. This characteristic is particularly crucial in settings where runoff from cleaning activities may enter natural water systems. The biodegradability of HOCl ensures that it does not contribute to the persistent chemical pollution that plagues many waterways and marine environments.
Air quality is another area where HOCl implementation shows promise. Unlike chlorine-based disinfectants or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in many cleaning products, HOCl does not release harmful fumes or contribute to indoor air pollution. This aspect is especially beneficial in enclosed spaces where air quality is a significant concern, such as healthcare facilities, schools, and office buildings.
The adoption of HOCl in hygiene protocols also aligns with the growing trend towards green chemistry and sustainable practices in industrial and institutional settings. By reducing the reliance on harsh chemicals, organizations can minimize their environmental liability and improve their sustainability profiles. This shift not only benefits the environment but also enhances worker safety by reducing exposure to potentially harmful substances.
However, it is important to consider the energy requirements for on-site HOCl generation. While the overall environmental impact is generally positive, the electricity used in the electrolysis process should ideally come from renewable sources to maximize the sustainability benefits. Additionally, proper training and equipment maintenance are essential to ensure optimal HOCl production and application, thereby preventing waste and maintaining its environmental advantages.
The environmental impact of HOCl is notably positive when compared to conventional cleaning agents. Its production process requires only salt, water, and electricity, reducing the need for complex chemical manufacturing and transportation. This simplicity in production translates to a lower carbon footprint and reduced energy consumption throughout the supply chain. Furthermore, the on-site generation of HOCl can significantly decrease packaging waste and the environmental costs associated with shipping and storing large quantities of pre-made disinfectants.
In aquatic ecosystems, HOCl demonstrates minimal toxicity to non-target organisms. When released into water bodies, it rapidly dissipates without accumulating or causing long-term ecological damage. This characteristic is particularly crucial in settings where runoff from cleaning activities may enter natural water systems. The biodegradability of HOCl ensures that it does not contribute to the persistent chemical pollution that plagues many waterways and marine environments.
Air quality is another area where HOCl implementation shows promise. Unlike chlorine-based disinfectants or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in many cleaning products, HOCl does not release harmful fumes or contribute to indoor air pollution. This aspect is especially beneficial in enclosed spaces where air quality is a significant concern, such as healthcare facilities, schools, and office buildings.
The adoption of HOCl in hygiene protocols also aligns with the growing trend towards green chemistry and sustainable practices in industrial and institutional settings. By reducing the reliance on harsh chemicals, organizations can minimize their environmental liability and improve their sustainability profiles. This shift not only benefits the environment but also enhances worker safety by reducing exposure to potentially harmful substances.
However, it is important to consider the energy requirements for on-site HOCl generation. While the overall environmental impact is generally positive, the electricity used in the electrolysis process should ideally come from renewable sources to maximize the sustainability benefits. Additionally, proper training and equipment maintenance are essential to ensure optimal HOCl production and application, thereby preventing waste and maintaining its environmental advantages.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!