Hypochlorous Acid: Pathways to Efficiency in Regulatory Frameworks
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a significant player in various industries, particularly in disinfection and water treatment. Its history dates back to the early 19th century when it was first discovered as a component of chlorine water. Over time, the understanding of HOCl's properties and potential applications has evolved significantly, leading to its widespread use in modern times.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been driven by the increasing demand for safe, effective, and environmentally friendly disinfection solutions. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in HOCl due to its powerful antimicrobial properties and low toxicity profile. This has led to its adoption in healthcare settings, food processing industries, and water treatment facilities.
The primary objective of current HOCl research and development is to enhance its production efficiency, stability, and application methods. Researchers are focusing on optimizing the generation of HOCl through electrolysis of salt water, aiming to increase yield and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the shelf life of HOCl solutions, as they tend to degrade over time.
Another key goal is to expand the range of applications for HOCl. While its use in disinfection is well-established, there is ongoing exploration of its potential in wound healing, agriculture, and even as a treatment for certain respiratory conditions. These new applications require careful study of HOCl's interaction with different biological systems and materials.
The regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl is complex and varies across different regions and applications. A significant objective in the field is to establish clear, science-based regulatory frameworks that can keep pace with the rapidly evolving technology. This includes developing standardized testing methods for HOCl efficacy and safety, as well as guidelines for its production and use in various settings.
Environmental considerations are also at the forefront of HOCl technology development. As a chlorine-based compound, there are concerns about its potential environmental impact. Thus, a key objective is to ensure that HOCl production and use align with sustainability goals, minimizing any negative effects on ecosystems.
In the context of global health challenges, such as the recent pandemic, HOCl has gained renewed attention as a potential tool in infection control. This has spurred research into its viricidal properties and its potential role in large-scale disinfection strategies. The goal is to position HOCl as a versatile, safe, and effective solution in the arsenal against infectious diseases.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been driven by the increasing demand for safe, effective, and environmentally friendly disinfection solutions. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in HOCl due to its powerful antimicrobial properties and low toxicity profile. This has led to its adoption in healthcare settings, food processing industries, and water treatment facilities.
The primary objective of current HOCl research and development is to enhance its production efficiency, stability, and application methods. Researchers are focusing on optimizing the generation of HOCl through electrolysis of salt water, aiming to increase yield and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the shelf life of HOCl solutions, as they tend to degrade over time.
Another key goal is to expand the range of applications for HOCl. While its use in disinfection is well-established, there is ongoing exploration of its potential in wound healing, agriculture, and even as a treatment for certain respiratory conditions. These new applications require careful study of HOCl's interaction with different biological systems and materials.
The regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl is complex and varies across different regions and applications. A significant objective in the field is to establish clear, science-based regulatory frameworks that can keep pace with the rapidly evolving technology. This includes developing standardized testing methods for HOCl efficacy and safety, as well as guidelines for its production and use in various settings.
Environmental considerations are also at the forefront of HOCl technology development. As a chlorine-based compound, there are concerns about its potential environmental impact. Thus, a key objective is to ensure that HOCl production and use align with sustainability goals, minimizing any negative effects on ecosystems.
In the context of global health challenges, such as the recent pandemic, HOCl has gained renewed attention as a potential tool in infection control. This has spurred research into its viricidal properties and its potential role in large-scale disinfection strategies. The goal is to position HOCl as a versatile, safe, and effective solution in the arsenal against infectious diseases.
Market Analysis for HOCl Applications
The market for Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) applications has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its effectiveness as a disinfectant and sanitizer. The global HOCl market is projected to expand substantially, with key sectors including healthcare, agriculture, water treatment, and food processing leading the demand.
In the healthcare sector, HOCl has gained traction as a powerful yet safe disinfectant for medical facilities, surgical equipment, and wound care. Its ability to effectively eliminate a wide range of pathogens without harmful residues has positioned it as a preferred choice in hospitals and clinics worldwide. The ongoing focus on infection control and prevention, especially in light of recent global health challenges, is expected to further boost HOCl adoption in this sector.
The agriculture industry has also recognized the potential of HOCl in crop protection and food safety. Farmers are increasingly using HOCl solutions for pre-harvest treatments, post-harvest sanitation, and irrigation water disinfection. This trend is driven by the growing demand for organic produce and the need to reduce chemical residues on crops. The market for HOCl in agriculture is anticipated to grow steadily as sustainable farming practices gain more prominence.
Water treatment represents another significant market for HOCl applications. Municipal water suppliers and industrial facilities are exploring HOCl as an alternative to traditional chlorine-based disinfection methods. The advantages of HOCl in terms of efficacy, safety, and environmental impact are driving its adoption in both developed and developing countries. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, the demand for efficient and eco-friendly water treatment solutions is expected to propel the HOCl market in this sector.
The food processing industry has emerged as a key growth area for HOCl applications. Food manufacturers are increasingly using HOCl for surface sanitation, equipment cleaning, and food preservation. The non-toxic nature of HOCl and its ability to extend shelf life without altering taste or quality make it an attractive option for food safety management. As consumers demand cleaner labels and safer food products, the adoption of HOCl in food processing is likely to accelerate.
Emerging applications in personal care and household cleaning products are opening new avenues for HOCl market expansion. The development of stable HOCl formulations suitable for consumer use has led to the introduction of HOCl-based hand sanitizers, skin care products, and all-purpose cleaners. This diversification is expected to contribute significantly to market growth in the coming years.
In the healthcare sector, HOCl has gained traction as a powerful yet safe disinfectant for medical facilities, surgical equipment, and wound care. Its ability to effectively eliminate a wide range of pathogens without harmful residues has positioned it as a preferred choice in hospitals and clinics worldwide. The ongoing focus on infection control and prevention, especially in light of recent global health challenges, is expected to further boost HOCl adoption in this sector.
The agriculture industry has also recognized the potential of HOCl in crop protection and food safety. Farmers are increasingly using HOCl solutions for pre-harvest treatments, post-harvest sanitation, and irrigation water disinfection. This trend is driven by the growing demand for organic produce and the need to reduce chemical residues on crops. The market for HOCl in agriculture is anticipated to grow steadily as sustainable farming practices gain more prominence.
Water treatment represents another significant market for HOCl applications. Municipal water suppliers and industrial facilities are exploring HOCl as an alternative to traditional chlorine-based disinfection methods. The advantages of HOCl in terms of efficacy, safety, and environmental impact are driving its adoption in both developed and developing countries. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, the demand for efficient and eco-friendly water treatment solutions is expected to propel the HOCl market in this sector.
The food processing industry has emerged as a key growth area for HOCl applications. Food manufacturers are increasingly using HOCl for surface sanitation, equipment cleaning, and food preservation. The non-toxic nature of HOCl and its ability to extend shelf life without altering taste or quality make it an attractive option for food safety management. As consumers demand cleaner labels and safer food products, the adoption of HOCl in food processing is likely to accelerate.
Emerging applications in personal care and household cleaning products are opening new avenues for HOCl market expansion. The development of stable HOCl formulations suitable for consumer use has led to the introduction of HOCl-based hand sanitizers, skin care products, and all-purpose cleaners. This diversification is expected to contribute significantly to market growth in the coming years.
HOCl Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory landscape for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) presents a complex set of challenges for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users. One of the primary hurdles is the lack of a unified regulatory framework across different regions and countries. This inconsistency creates significant obstacles for companies seeking to expand their HOCl-based products into new markets, as they must navigate a patchwork of varying requirements and standards.
In the United States, the regulatory status of HOCl is particularly nuanced. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HOCl as a pesticide under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) when used for antimicrobial purposes. However, when HOCl is used in other applications, such as wound care or food processing, it falls under the jurisdiction of different agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). This multi-agency oversight can lead to confusion and increased compliance costs for manufacturers.
The European Union presents its own set of regulatory challenges for HOCl. Under the EU's Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), HOCl is classified as an active substance, requiring extensive safety and efficacy data for approval. The process of obtaining authorization under the BPR can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially deterring smaller companies from entering the market. Additionally, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes further requirements on HOCl manufacturers and importers.
In many developing countries, the regulatory framework for HOCl is often less defined or still evolving. This can create uncertainty for companies looking to introduce HOCl-based products in these markets. The lack of clear guidelines may lead to inconsistent product quality and safety standards, potentially undermining consumer confidence and hindering market growth.
A significant challenge across all regions is the classification and labeling of HOCl products. Depending on the concentration, pH level, and intended use, HOCl may be classified differently, leading to varying safety requirements and marketing restrictions. This variability can complicate product development and marketing strategies for companies operating in multiple jurisdictions.
The rapidly evolving nature of HOCl applications, particularly in emerging fields such as advanced wound care and environmental disinfection, poses another regulatory challenge. Regulatory bodies often struggle to keep pace with technological advancements, leading to potential gaps in oversight or the application of outdated regulations to novel uses of HOCl.
Addressing these regulatory challenges requires a coordinated effort from industry stakeholders, regulatory agencies, and policymakers. Harmonization of standards across regions, clearer guidelines for emerging applications, and streamlined approval processes could significantly reduce the regulatory burden on HOCl manufacturers and distributors. Such improvements would not only foster innovation but also ensure consistent safety and efficacy standards for HOCl products globally.
In the United States, the regulatory status of HOCl is particularly nuanced. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HOCl as a pesticide under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) when used for antimicrobial purposes. However, when HOCl is used in other applications, such as wound care or food processing, it falls under the jurisdiction of different agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). This multi-agency oversight can lead to confusion and increased compliance costs for manufacturers.
The European Union presents its own set of regulatory challenges for HOCl. Under the EU's Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), HOCl is classified as an active substance, requiring extensive safety and efficacy data for approval. The process of obtaining authorization under the BPR can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially deterring smaller companies from entering the market. Additionally, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes further requirements on HOCl manufacturers and importers.
In many developing countries, the regulatory framework for HOCl is often less defined or still evolving. This can create uncertainty for companies looking to introduce HOCl-based products in these markets. The lack of clear guidelines may lead to inconsistent product quality and safety standards, potentially undermining consumer confidence and hindering market growth.
A significant challenge across all regions is the classification and labeling of HOCl products. Depending on the concentration, pH level, and intended use, HOCl may be classified differently, leading to varying safety requirements and marketing restrictions. This variability can complicate product development and marketing strategies for companies operating in multiple jurisdictions.
The rapidly evolving nature of HOCl applications, particularly in emerging fields such as advanced wound care and environmental disinfection, poses another regulatory challenge. Regulatory bodies often struggle to keep pace with technological advancements, leading to potential gaps in oversight or the application of outdated regulations to novel uses of HOCl.
Addressing these regulatory challenges requires a coordinated effort from industry stakeholders, regulatory agencies, and policymakers. Harmonization of standards across regions, clearer guidelines for emerging applications, and streamlined approval processes could significantly reduce the regulatory burden on HOCl manufacturers and distributors. Such improvements would not only foster innovation but also ensure consistent safety and efficacy standards for HOCl products globally.
Current HOCl Regulatory Compliance Strategies
01 Antimicrobial efficacy of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid demonstrates high efficiency as an antimicrobial agent. It effectively eliminates a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The compound's rapid action and broad-spectrum efficacy make it suitable for various disinfection applications in healthcare, food processing, and water treatment.- Antimicrobial efficacy of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid demonstrates high efficiency as an antimicrobial agent. It effectively eliminates a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The compound's rapid action and broad-spectrum activity make it suitable for various disinfection applications in healthcare, food processing, and water treatment.
- Stability and storage of hypochlorous acid solutions: Improving the stability and shelf life of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining its efficiency. Various methods and formulations have been developed to enhance the stability of hypochlorous acid, including pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging techniques. These advancements allow for longer storage periods without significant loss of antimicrobial activity.
- Production methods for hypochlorous acid: Efficient production methods for hypochlorous acid are essential for its widespread use. Electrolysis of salt solutions is a common technique, but innovations in electrode materials, cell design, and process control have led to improved yield and purity. Some methods focus on generating hypochlorous acid on-site to ensure maximum potency and reduce storage-related degradation.
- Applications of hypochlorous acid in various industries: The high efficiency of hypochlorous acid has led to its adoption in diverse industries. It is used in medical settings for wound care and surface disinfection, in agriculture for crop protection and food safety, and in water treatment for purification. The compound's low toxicity to humans and environmental friendliness contribute to its versatility across different applications.
- Synergistic effects and formulations with hypochlorous acid: Research has shown that combining hypochlorous acid with other compounds can enhance its efficiency. Formulations incorporating surfactants, chelating agents, or other antimicrobial substances have demonstrated synergistic effects, leading to improved disinfection performance. These combinations often result in more effective and longer-lasting antimicrobial activity compared to hypochlorous acid alone.
02 Stability and storage of hypochlorous acid solutions
Improving the stability and shelf life of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining its efficiency. Various methods and formulations have been developed to enhance the stability of hypochlorous acid, including pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging techniques. These advancements allow for longer storage periods without significant loss of antimicrobial activity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Production methods for hypochlorous acid
Efficient production methods for hypochlorous acid are essential for its widespread use. Electrolysis of salt solutions is a common technique, but other methods such as chemical synthesis and on-site generation systems have been developed. These production methods aim to improve yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness of hypochlorous acid generation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of hypochlorous acid in various industries
Hypochlorous acid finds applications in diverse industries due to its efficiency. It is used in healthcare for wound care and surface disinfection, in agriculture for crop protection and food safety, in water treatment for purification, and in industrial cleaning processes. The compound's versatility and effectiveness make it a valuable solution across multiple sectors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental impact and safety of hypochlorous acid
The efficiency of hypochlorous acid is complemented by its favorable environmental profile and safety characteristics. It breaks down into harmless byproducts, reducing environmental impact. Additionally, when used at appropriate concentrations, it poses minimal risks to human health, making it a safe alternative to many traditional disinfectants and antimicrobial agents.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HOCl Industry Players
The hypochlorous acid market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective disinfection solutions across various industries. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB and Annihilare Medical Systems leading in on-site generation systems. Established players such as BASF Corp. and Industrie De Nora SpA are contributing to the maturation of production processes. Research institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Hunan University of Science & Technology are pushing the boundaries of efficiency and application. The regulatory landscape is evolving, with companies like Versitech Ltd. potentially playing a role in streamlining compliance processes for this emerging technology.
Industrie De Nora SpA
Technical Solution: Industrie De Nora SpA has developed advanced electrochemical technologies for the efficient production of hypochlorous acid. Their approach utilizes specialized electrode materials and optimized cell designs to enhance the electrolysis process, resulting in higher yields and purity of hypochlorous acid. The company has implemented a closed-loop system that recycles byproducts, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency[1]. Additionally, they have integrated smart monitoring systems to ensure precise control of pH levels and chlorine concentration, which is crucial for maintaining the stability and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid solutions[3].
Strengths: Advanced electrochemical expertise, efficient production processes, and integrated monitoring systems. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial investment costs and reliance on specialized equipment.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC. has pioneered a novel approach to hypochlorous acid production focusing on medical-grade applications. Their technology employs a proprietary membrane-based electrolysis system that ensures the production of ultra-pure hypochlorous acid with consistent pH and concentration levels[2]. The company has developed a portable, on-site generation system that allows for point-of-use production, reducing storage and transportation challenges associated with hypochlorous acid. Their process incorporates real-time quality control measures and automated adjustments to maintain optimal production parameters[4].
Strengths: High-purity production, on-site generation capabilities, and focus on medical applications. Weaknesses: Limited scalability for large-scale industrial applications and potential regulatory hurdles in diverse markets.
Innovative HOCl Regulatory Approaches
Improvements relating to hypochlorous acid
PatentWO2019106387A1
Innovation
- A method involving the addition of a substantially chloride-free acidifier to hypochlorite solutions over an extended period, in diluted form, and with dispersed addition and immediate mixing to counteract localized pH drops, thereby reducing chloride ion formation and enhancing stability of hypochlorous acid solutions.
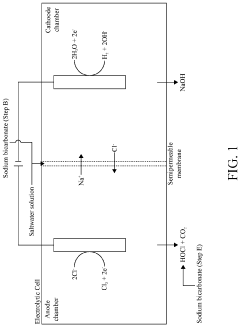
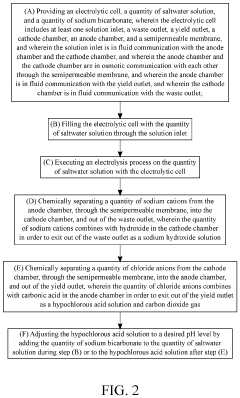
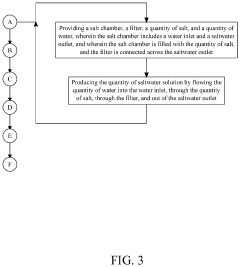
System and Method for Making Hypochlorous Acid Using Saltwater with Sodium Bicarbonate
PatentActiveUS20210395904A1
Innovation
- Incorporating sodium bicarbonate into the saltwater electrolysis process using a semipermeable membrane to separate the solutions, which forms purer hypochlorous acid by reacting chloride ions with carbonic acid, thereby maintaining a higher pH and eliminating strong hydrochloric acid.
Environmental Impact of HOCl
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has gained significant attention in recent years due to its effectiveness as a disinfectant and its potential for widespread use in various industries. However, the environmental impact of HOCl production and application must be carefully considered to ensure sustainable practices and regulatory compliance.
The production of HOCl typically involves electrolysis of salt water, which requires energy input and may contribute to carbon emissions depending on the energy source. However, compared to many traditional chemical disinfectants, HOCl production generally has a lower environmental footprint. The process does not generate harmful by-products, and the raw materials (salt and water) are abundant and renewable.
When released into the environment, HOCl quickly breaks down into its constituent elements: hydrogen, oxygen, and chlorine. This rapid decomposition means that HOCl does not persist in ecosystems, reducing the risk of long-term environmental contamination. The breakdown products are naturally occurring elements that do not pose significant ecological threats when present in typical concentrations resulting from HOCl use.
In aquatic environments, the impact of HOCl is generally minimal due to its rapid degradation. However, in cases of high-volume discharge or accidental spills, temporary increases in chlorine levels could potentially affect sensitive aquatic organisms. Proper dilution and controlled release are essential to mitigate such risks.
The use of HOCl as a disinfectant can have positive environmental implications by reducing the need for more harmful chemical alternatives. Many traditional disinfectants contain compounds that are toxic to aquatic life or contribute to the formation of disinfection by-products (DBPs) when they react with organic matter. HOCl, in contrast, produces fewer DBPs and is less likely to contaminate water sources.
In agricultural applications, HOCl can be used as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and fungicides. Its ability to control pathogens without leaving harmful residues on crops aligns with sustainable farming practices and reduces the environmental burden associated with persistent chemical treatments.
The regulatory framework surrounding HOCl must consider its unique properties and environmental behavior. While its safety profile is generally favorable, guidelines for proper use, storage, and disposal are crucial to prevent any potential negative impacts. Regulations should focus on ensuring appropriate concentration levels, application methods, and discharge protocols to maintain environmental integrity.
As research continues to explore new applications for HOCl, ongoing environmental monitoring and impact assessments will be essential. This will help refine regulatory approaches and ensure that the widespread adoption of HOCl technology aligns with broader environmental protection goals and sustainability initiatives.
The production of HOCl typically involves electrolysis of salt water, which requires energy input and may contribute to carbon emissions depending on the energy source. However, compared to many traditional chemical disinfectants, HOCl production generally has a lower environmental footprint. The process does not generate harmful by-products, and the raw materials (salt and water) are abundant and renewable.
When released into the environment, HOCl quickly breaks down into its constituent elements: hydrogen, oxygen, and chlorine. This rapid decomposition means that HOCl does not persist in ecosystems, reducing the risk of long-term environmental contamination. The breakdown products are naturally occurring elements that do not pose significant ecological threats when present in typical concentrations resulting from HOCl use.
In aquatic environments, the impact of HOCl is generally minimal due to its rapid degradation. However, in cases of high-volume discharge or accidental spills, temporary increases in chlorine levels could potentially affect sensitive aquatic organisms. Proper dilution and controlled release are essential to mitigate such risks.
The use of HOCl as a disinfectant can have positive environmental implications by reducing the need for more harmful chemical alternatives. Many traditional disinfectants contain compounds that are toxic to aquatic life or contribute to the formation of disinfection by-products (DBPs) when they react with organic matter. HOCl, in contrast, produces fewer DBPs and is less likely to contaminate water sources.
In agricultural applications, HOCl can be used as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and fungicides. Its ability to control pathogens without leaving harmful residues on crops aligns with sustainable farming practices and reduces the environmental burden associated with persistent chemical treatments.
The regulatory framework surrounding HOCl must consider its unique properties and environmental behavior. While its safety profile is generally favorable, guidelines for proper use, storage, and disposal are crucial to prevent any potential negative impacts. Regulations should focus on ensuring appropriate concentration levels, application methods, and discharge protocols to maintain environmental integrity.
As research continues to explore new applications for HOCl, ongoing environmental monitoring and impact assessments will be essential. This will help refine regulatory approaches and ensure that the widespread adoption of HOCl technology aligns with broader environmental protection goals and sustainability initiatives.
International HOCl Regulations
The regulatory landscape for Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting diverse approaches to its classification, production, and application. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HOCl under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), classifying it as a pesticide when used for antimicrobial purposes. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also oversees HOCl in certain applications, such as food contact surfaces and medical devices.
In the European Union, HOCl falls under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which governs the use of biocidal active substances and products. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) plays a crucial role in assessing the safety and efficacy of HOCl for various applications. The EU's regulatory framework emphasizes the importance of risk assessment and requires extensive documentation for product registration.
Japan's approach to HOCl regulation is notably different, with the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare recognizing it as a food additive when used in specific concentrations. This classification allows for broader applications in food processing and sanitation compared to some other countries. Similarly, Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has approved certain HOCl-based products for use as disinfectants and sanitizers.
In Canada, HOCl is regulated by Health Canada under the Pest Control Products Act when used as a disinfectant. The agency has established specific guidelines for the concentration and application of HOCl in various settings, including healthcare facilities and food processing plants.
Developing countries often face challenges in establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks for HOCl. Many rely on guidelines from international organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) or adopt regulations from more established regulatory bodies like the EPA or ECHA.
The global regulatory landscape for HOCl is continually evolving, with increasing recognition of its potential benefits in various sectors. However, the lack of harmonization in international regulations can create barriers to trade and innovation. Efforts are underway to establish more consistent global standards for HOCl production, testing, and application, which could streamline regulatory processes and facilitate broader adoption of HOCl-based technologies.
In the European Union, HOCl falls under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which governs the use of biocidal active substances and products. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) plays a crucial role in assessing the safety and efficacy of HOCl for various applications. The EU's regulatory framework emphasizes the importance of risk assessment and requires extensive documentation for product registration.
Japan's approach to HOCl regulation is notably different, with the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare recognizing it as a food additive when used in specific concentrations. This classification allows for broader applications in food processing and sanitation compared to some other countries. Similarly, Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has approved certain HOCl-based products for use as disinfectants and sanitizers.
In Canada, HOCl is regulated by Health Canada under the Pest Control Products Act when used as a disinfectant. The agency has established specific guidelines for the concentration and application of HOCl in various settings, including healthcare facilities and food processing plants.
Developing countries often face challenges in establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks for HOCl. Many rely on guidelines from international organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) or adopt regulations from more established regulatory bodies like the EPA or ECHA.
The global regulatory landscape for HOCl is continually evolving, with increasing recognition of its potential benefits in various sectors. However, the lack of harmonization in international regulations can create barriers to trade and innovation. Efforts are underway to establish more consistent global standards for HOCl production, testing, and application, which could streamline regulatory processes and facilitate broader adoption of HOCl-based technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!