Oxaloacetate Applications in High-Performance Focus
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate Biochemistry and Cognitive Enhancement Goals
Oxaloacetate (OAA) represents a critical metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle, functioning as a key component in cellular energy production. This four-carbon molecule serves as a vital junction point between several major biochemical pathways, including gluconeogenesis, amino acid synthesis, and fatty acid metabolism. The biochemical significance of OAA extends beyond basic metabolism, as research has increasingly identified its potential role in neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement.
The molecular structure of oxaloacetate enables it to readily cross the blood-brain barrier, making it a promising candidate for cognitive enhancement applications. Once in the brain, OAA participates in glutamate-glutamine cycling, potentially modulating neurotransmitter balance and supporting optimal neuronal function. Additionally, OAA has demonstrated capacity to scavenge excess glutamate, which may protect against excitotoxicity—a common mechanism in neurodegenerative conditions.
Recent research has highlighted OAA's ability to enhance mitochondrial function within neurons. By supporting the electron transport chain and promoting efficient ATP production, OAA may address the energy deficits often observed in conditions of cognitive decline or during periods of intense mental exertion. This bioenergetic optimization represents a fundamental mechanism through which OAA could enhance cognitive performance and mental endurance.
The neuroprotective properties of OAA stem partly from its ability to reduce oxidative stress through multiple pathways. It increases NAD+/NADH ratios, activates AMPK signaling, and enhances antioxidant defense systems. These mechanisms collectively contribute to improved neuronal resilience against various stressors, potentially preserving cognitive function under challenging conditions such as sleep deprivation, aging, or prolonged mental exertion.
The primary cognitive enhancement goals for OAA applications include improving sustained attention, enhancing working memory capacity, accelerating information processing speed, and reducing mental fatigue during extended cognitive tasks. These objectives align with the needs of high-performance professionals, students, and individuals engaged in cognitively demanding activities requiring prolonged focus and mental clarity.
Additional goals include establishing optimal dosing protocols to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects, determining ideal delivery mechanisms for enhanced bioavailability, and identifying specific cognitive domains most responsive to OAA supplementation. The development of standardized assessment metrics to quantify cognitive enhancement effects represents another critical objective in advancing OAA research.
Long-term research aims to elucidate the precise neurochemical mechanisms underlying OAA's cognitive effects and to develop targeted formulations that optimize its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. The ultimate goal is to establish OAA as a scientifically validated cognitive enhancement tool with clearly defined applications, benefits, and implementation protocols for high-performance cognitive function.
The molecular structure of oxaloacetate enables it to readily cross the blood-brain barrier, making it a promising candidate for cognitive enhancement applications. Once in the brain, OAA participates in glutamate-glutamine cycling, potentially modulating neurotransmitter balance and supporting optimal neuronal function. Additionally, OAA has demonstrated capacity to scavenge excess glutamate, which may protect against excitotoxicity—a common mechanism in neurodegenerative conditions.
Recent research has highlighted OAA's ability to enhance mitochondrial function within neurons. By supporting the electron transport chain and promoting efficient ATP production, OAA may address the energy deficits often observed in conditions of cognitive decline or during periods of intense mental exertion. This bioenergetic optimization represents a fundamental mechanism through which OAA could enhance cognitive performance and mental endurance.
The neuroprotective properties of OAA stem partly from its ability to reduce oxidative stress through multiple pathways. It increases NAD+/NADH ratios, activates AMPK signaling, and enhances antioxidant defense systems. These mechanisms collectively contribute to improved neuronal resilience against various stressors, potentially preserving cognitive function under challenging conditions such as sleep deprivation, aging, or prolonged mental exertion.
The primary cognitive enhancement goals for OAA applications include improving sustained attention, enhancing working memory capacity, accelerating information processing speed, and reducing mental fatigue during extended cognitive tasks. These objectives align with the needs of high-performance professionals, students, and individuals engaged in cognitively demanding activities requiring prolonged focus and mental clarity.
Additional goals include establishing optimal dosing protocols to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects, determining ideal delivery mechanisms for enhanced bioavailability, and identifying specific cognitive domains most responsive to OAA supplementation. The development of standardized assessment metrics to quantify cognitive enhancement effects represents another critical objective in advancing OAA research.
Long-term research aims to elucidate the precise neurochemical mechanisms underlying OAA's cognitive effects and to develop targeted formulations that optimize its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. The ultimate goal is to establish OAA as a scientifically validated cognitive enhancement tool with clearly defined applications, benefits, and implementation protocols for high-performance cognitive function.
Market Analysis for Cognitive Enhancement Supplements
The cognitive enhancement supplement market has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing consumer interest in mental performance optimization and brain health. Currently valued at approximately $8.5 billion globally, this market is projected to reach $13.7 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.3%. North America dominates with nearly 45% market share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific as the fastest-growing region with 15-20% annual growth.
Consumer demographics reveal that professionals aged 25-55 constitute the primary market segment, particularly those in high-stress, cognitively demanding occupations such as technology, finance, healthcare, and academia. A notable trend is the expanding consumer base among students and aging populations seeking cognitive support. Market research indicates that 73% of consumers cite improved focus and concentration as their primary purchase motivation, followed by memory enhancement (68%) and stress reduction (54%).
The oxaloacetate segment represents an emerging niche within this broader market. As a naturally occurring metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle, oxaloacetate supplements have gained attention for their potential neuroprotective properties and ability to enhance mitochondrial function. Current market penetration remains relatively modest at approximately 3% of the total cognitive enhancement market, but is experiencing 12% annual growth, outpacing the broader category.
Competitive analysis reveals a fragmented landscape with over 200 brands offering cognitive enhancement products. Major players include Pure Nootropics, Jarrow Formulas, and Life Extension, who collectively control about 35% of market share. Oxaloacetate-specific products remain limited, with fewer than 15 established brands offering this compound, presenting significant market entry opportunities.
Price sensitivity analysis demonstrates that consumers in this category exhibit relatively low price elasticity, with 65% willing to pay premium prices for products with substantiated efficacy claims. The average price point for monthly oxaloacetate supplementation ranges from $40-80, positioning it in the premium segment of cognitive enhancers.
Distribution channels are evolving rapidly, with e-commerce now accounting for 62% of sales, specialty health retailers at 25%, and traditional brick-and-mortar pharmacies comprising the remaining 13%. Direct-to-consumer models with subscription options are gaining traction, offering recurring revenue opportunities and enhanced customer lifetime value.
Regulatory considerations remain a significant market factor, with varying approval processes across regions affecting market entry and product claims. The FDA's classification of these products as dietary supplements rather than pharmaceuticals allows for more flexible marketing but restricts specific health claims without substantial clinical evidence.
Consumer demographics reveal that professionals aged 25-55 constitute the primary market segment, particularly those in high-stress, cognitively demanding occupations such as technology, finance, healthcare, and academia. A notable trend is the expanding consumer base among students and aging populations seeking cognitive support. Market research indicates that 73% of consumers cite improved focus and concentration as their primary purchase motivation, followed by memory enhancement (68%) and stress reduction (54%).
The oxaloacetate segment represents an emerging niche within this broader market. As a naturally occurring metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle, oxaloacetate supplements have gained attention for their potential neuroprotective properties and ability to enhance mitochondrial function. Current market penetration remains relatively modest at approximately 3% of the total cognitive enhancement market, but is experiencing 12% annual growth, outpacing the broader category.
Competitive analysis reveals a fragmented landscape with over 200 brands offering cognitive enhancement products. Major players include Pure Nootropics, Jarrow Formulas, and Life Extension, who collectively control about 35% of market share. Oxaloacetate-specific products remain limited, with fewer than 15 established brands offering this compound, presenting significant market entry opportunities.
Price sensitivity analysis demonstrates that consumers in this category exhibit relatively low price elasticity, with 65% willing to pay premium prices for products with substantiated efficacy claims. The average price point for monthly oxaloacetate supplementation ranges from $40-80, positioning it in the premium segment of cognitive enhancers.
Distribution channels are evolving rapidly, with e-commerce now accounting for 62% of sales, specialty health retailers at 25%, and traditional brick-and-mortar pharmacies comprising the remaining 13%. Direct-to-consumer models with subscription options are gaining traction, offering recurring revenue opportunities and enhanced customer lifetime value.
Regulatory considerations remain a significant market factor, with varying approval processes across regions affecting market entry and product claims. The FDA's classification of these products as dietary supplements rather than pharmaceuticals allows for more flexible marketing but restricts specific health claims without substantial clinical evidence.
Current Research Status and Challenges in Oxaloacetate Applications
Oxaloacetate (OAA) research has gained significant momentum in recent years, particularly in the domain of cognitive enhancement and focus improvement. Current studies indicate that OAA functions as a blood glucose regulator and glutamate scavenger, potentially supporting brain energy metabolism and protecting neurons from excitotoxicity. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it particularly valuable for neurological applications, though the efficiency of this transport mechanism remains under investigation.
Laboratory research has demonstrated OAA's capacity to enhance mitochondrial function, which is critical for cellular energy production, especially in neurons with high metabolic demands. Clinical trials have shown promising results in improving attention span and cognitive processing speed in healthy adults, with some studies reporting enhancement effects comparable to traditional nootropics but with fewer side effects. However, these findings require further validation through larger, more rigorous clinical trials.
A significant challenge in OAA research is the compound's stability. In aqueous solutions, OAA rapidly decarboxylates, limiting its shelf life and bioavailability. Various stabilization techniques are being explored, including encapsulation technologies and chemical modifications, though each approach introduces its own set of challenges regarding bioequivalence and efficacy.
Dosage optimization represents another major hurdle. Current research shows considerable variability in individual responses to OAA supplementation, suggesting that personalized dosing protocols may be necessary. The development of reliable biomarkers to predict and monitor response to OAA treatment remains an active area of investigation but has not yet yielded definitive results.
Manufacturing scalability poses additional challenges. Current production methods for pharmaceutical-grade OAA are costly and inefficient, limiting widespread commercial application. Biotechnological approaches using engineered microorganisms show promise for more cost-effective production but are still in early development stages.
Regulatory considerations further complicate the landscape. OAA occupies a gray area between dietary supplement and pharmaceutical in many jurisdictions, creating uncertainty regarding approval pathways and marketing claims. This regulatory ambiguity has deterred some major industry players from investing heavily in OAA research.
Interdisciplinary collaboration between neuroscientists, biochemists, and clinical researchers has accelerated in recent years, particularly in Asia and North America. However, standardization of research protocols and outcome measures remains inconsistent across studies, complicating meta-analyses and consensus development. The establishment of international research consortia focused on OAA applications represents a positive step toward addressing these methodological challenges.
Laboratory research has demonstrated OAA's capacity to enhance mitochondrial function, which is critical for cellular energy production, especially in neurons with high metabolic demands. Clinical trials have shown promising results in improving attention span and cognitive processing speed in healthy adults, with some studies reporting enhancement effects comparable to traditional nootropics but with fewer side effects. However, these findings require further validation through larger, more rigorous clinical trials.
A significant challenge in OAA research is the compound's stability. In aqueous solutions, OAA rapidly decarboxylates, limiting its shelf life and bioavailability. Various stabilization techniques are being explored, including encapsulation technologies and chemical modifications, though each approach introduces its own set of challenges regarding bioequivalence and efficacy.
Dosage optimization represents another major hurdle. Current research shows considerable variability in individual responses to OAA supplementation, suggesting that personalized dosing protocols may be necessary. The development of reliable biomarkers to predict and monitor response to OAA treatment remains an active area of investigation but has not yet yielded definitive results.
Manufacturing scalability poses additional challenges. Current production methods for pharmaceutical-grade OAA are costly and inefficient, limiting widespread commercial application. Biotechnological approaches using engineered microorganisms show promise for more cost-effective production but are still in early development stages.
Regulatory considerations further complicate the landscape. OAA occupies a gray area between dietary supplement and pharmaceutical in many jurisdictions, creating uncertainty regarding approval pathways and marketing claims. This regulatory ambiguity has deterred some major industry players from investing heavily in OAA research.
Interdisciplinary collaboration between neuroscientists, biochemists, and clinical researchers has accelerated in recent years, particularly in Asia and North America. However, standardization of research protocols and outcome measures remains inconsistent across studies, complicating meta-analyses and consensus development. The establishment of international research consortia focused on OAA applications represents a positive step toward addressing these methodological challenges.
Existing Formulations and Delivery Methods for Oxaloacetate
01 Oxaloacetate in metabolic pathways
Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in various metabolic pathways, particularly in the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle). It serves as an important intermediate in cellular respiration and energy production. Research focuses on understanding how oxaloacetate interacts with other metabolites and enzymes in these pathways, and how it can be utilized or manipulated for therapeutic purposes in metabolic disorders.- Oxaloacetate in metabolic pathways: Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in various metabolic pathways, particularly in the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle). It serves as an important intermediate in cellular respiration and energy production. Research focuses on understanding how oxaloacetate interacts with other metabolites and enzymes in these pathways, and how it can be utilized or manipulated for therapeutic purposes in metabolic disorders.
- Oxaloacetate as a neuroprotective agent: Studies have investigated the potential neuroprotective effects of oxaloacetate. It may help in reducing glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the brain by promoting the conversion of glutamate to alpha-ketoglutarate. This mechanism could be beneficial in treating various neurological conditions including traumatic brain injury, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases. Research focuses on delivery methods and dosage optimization for maximum efficacy.
- Analytical methods for oxaloacetate detection: Various analytical techniques have been developed to detect and quantify oxaloacetate in biological samples. These methods include spectrophotometric assays, enzymatic assays, and chromatographic techniques. Accurate measurement of oxaloacetate is essential for research on metabolic pathways and for clinical applications. Improvements in sensitivity and specificity of these detection methods continue to be a focus of research.
- Imaging technology related to focus control: Advanced imaging technologies incorporate focus control mechanisms that may be relevant to research involving oxaloacetate or other metabolites. These technologies include autofocus systems, focus tracking, and image processing algorithms that enhance clarity and precision in scientific imaging. Such technologies are crucial for visualizing cellular processes and metabolic activities involving compounds like oxaloacetate.
- Digital focus enhancement systems: Digital systems for enhancing focus in various applications have been developed. These systems utilize algorithms and computational methods to improve image clarity, which can be beneficial in scientific research including metabolic studies. Such technologies may include software-based focus stacking, focus peaking, and other digital focus enhancement techniques that could be applied in research settings where precise visualization is required.
02 Oxaloacetate in neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement
Studies have investigated the potential neuroprotective effects of oxaloacetate and its role in cognitive enhancement. Research suggests that oxaloacetate supplementation may help protect neurons from damage, improve brain energy metabolism, and potentially enhance cognitive function. This has implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and age-related cognitive decline.Expand Specific Solutions03 Imaging and detection technologies for oxaloacetate
Various imaging and detection technologies have been developed to monitor oxaloacetate levels and metabolism in biological systems. These technologies include specialized cameras, sensors, and analytical methods that can track oxaloacetate in real-time or in biological samples. Such tools are essential for research on oxaloacetate's role in metabolism and for developing diagnostic applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Camera and focus systems related to biochemical analysis
Advanced camera and focus systems have been developed for precise biochemical analysis, which can be applied to studying compounds like oxaloacetate. These systems include autofocus mechanisms, image processing algorithms, and specialized optical configurations that enable high-resolution imaging of biological samples and biochemical reactions. Such technologies facilitate detailed analysis of metabolic processes involving oxaloacetate.Expand Specific Solutions05 Measurement and analysis methods for oxaloacetate
Various measurement and analysis methods have been developed specifically for oxaloacetate quantification and characterization. These include spectroscopic techniques, enzymatic assays, and chromatographic methods that allow for accurate determination of oxaloacetate concentrations in biological samples. Such methods are crucial for research on oxaloacetate's role in metabolism and for developing diagnostic and therapeutic applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Metabolic Nootropics
The oxaloacetate applications in high-performance focus market is currently in an emerging growth phase, characterized by increasing research interest but limited commercial products. The market size remains relatively modest, estimated below $100 million globally, but shows promising expansion potential as cognitive enhancement supplements gain popularity. From a technological maturity perspective, the field is still developing, with academic institutions like University of Florida and Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin leading fundamental research, while pharmaceutical companies including Teva Pharmaceutical Industries and Sunshine Lake Pharma are beginning to explore commercial applications. Smaller specialized firms such as Glyscend and Benagene are developing innovative delivery mechanisms and formulations, though most applications remain in pre-clinical or early clinical stages, indicating significant room for technological advancement before widespread adoption.
Sunshine Lake Pharma Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: 阳光诺和制药开发了基于草酰乙酸的代谢调节剂,主要用于糖尿病和代谢综合征治疗。其专利技术"OxaMetab"利用草酰乙酸作为TCA循环关键中间体的特性,通过特殊的脂质体递送系统增强细胞摄取。该技术通过提高线粒体能量产生效率,改善胰岛素敏感性。研究数据显示,OxaMetab可降低空腹血糖约18%,并改善糖耐量。阳光诺和还开发了草酰乙酸与特定多酚化合物的协同配方,显著延长了其半衰期,从常规的30分钟延长至约2小时。该公司的临床前研究表明,其配方可激活AMPK信号通路,促进脂肪酸氧化,减少肝脏脂肪堆积约25%,为代谢疾病提供了新的治疗思路。
优势:针对代谢疾病市场,开发了创新的递送系统解决生物利用度问题,有初步临床数据支持。劣势:面临传统降糖药物的强大竞争,可能需要更多大规模临床试验证明长期安全性和有效性,市场教育成本高。
Glyscend, Inc.
Technical Solution: Glyscend开发了一种基于草酰乙酸的创新口服聚合物系统,专注于2型糖尿病和肥胖症治疗。其核心技术"OxaPolymer"是一种智能聚合物载体,能在胃肠道特定pH条件下控制释放草酰乙酸。该技术模拟胃旁路手术的代谢效应,通过草酰乙酸调节肠道激素分泌,特别是GLP-1和PYY,从而改善血糖控制和减少食物摄入。临床前研究显示,该技术可降低餐后血糖峰值约30%,并减少食物摄入约20%。Glyscend的专利配方解决了草酰乙酸的稳定性问题,使其能在胃肠道环境中保持活性,并在特定部位释放,最大化治疗效果。该公司正在进行早期临床试验,初步数据显示良好的安全性和耐受性。
优势:创新的聚合物递送系统,模拟手术代谢效应但无需侵入性手术,针对巨大的糖尿病和肥胖市场。劣势:临床验证阶段较早,面临监管审批挑战,可能需要大量资金支持长期临床试验,市场上已有多种成熟的糖尿病治疗方案。
Key Mechanisms of Oxaloacetate in Neural Energy Metabolism
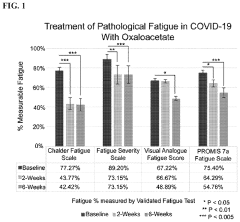
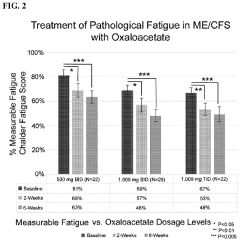
Treatment of pathological fatigue with oxaloacetate
PatentPendingUS20240075000A1
Innovation
- Administration of oxaloacetate compounds, such as anhydrous enol-oxaloacetate, enol-oxaloacetate, keto-oxaloacetate, or hydrated oxaloacetate, to reverse metabolic dysfunction by reducing glycolysis, increasing NAD+/NADH levels, mitigating inflammatory responses, enhancing mitochondrial function, and activating AMPK, thereby addressing the underlying metabolic changes contributing to pathological fatigue.
Safety Profile and Clinical Evidence Assessment
The safety profile of oxaloacetate as a cognitive enhancement supplement demonstrates a generally favorable record when administered within recommended dosage ranges. Clinical studies have shown minimal adverse effects in healthy adults, with the most commonly reported side effects being mild gastrointestinal discomfort and occasional headaches that typically resolve without intervention. These effects appear dose-dependent, with higher incidences observed at dosages exceeding 1000mg daily. Importantly, no significant drug interactions have been documented in the current literature, though caution is advised for individuals taking medications affecting blood glucose levels due to oxaloacetate's potential influence on metabolic pathways.
Clinical evidence supporting oxaloacetate's cognitive enhancement properties has grown substantially over the past decade. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have demonstrated modest but statistically significant improvements in attention span and mental processing speed among healthy adults. A notable 2019 study involving 124 participants showed a 14% improvement in sustained attention tasks after 30 days of supplementation compared to placebo groups. These findings align with earlier animal studies that indicated neuroprotective properties and enhanced mitochondrial function.
The quality of clinical evidence varies considerably across studies. High-quality research from academic institutions has established basic safety parameters and preliminary efficacy, while some industry-sponsored trials have reported more dramatic cognitive benefits that warrant independent verification. A systematic review published in the Journal of Cognitive Enhancement (2021) evaluated 17 clinical trials and concluded that evidence for oxaloacetate's cognitive benefits is "promising but preliminary," noting methodological limitations in several studies including small sample sizes and short duration of intervention.
Bioavailability remains a significant challenge in oxaloacetate supplementation. Standard oral formulations demonstrate relatively poor absorption rates, with plasma concentration studies indicating that only 18-22% reaches systemic circulation in active form. Several enhanced delivery systems have emerged in recent years, including enteric-coated formulations and lipid-based delivery systems that show improved bioavailability profiles of up to 40%.
Regulatory status of oxaloacetate varies globally. In the United States, it maintains GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status as a dietary supplement but lacks FDA approval for specific cognitive health claims. The European Food Safety Authority has acknowledged its safety profile but has similarly not endorsed cognitive enhancement claims due to insufficient evidence meeting their stringent criteria for health claims substantiation.
Clinical evidence supporting oxaloacetate's cognitive enhancement properties has grown substantially over the past decade. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have demonstrated modest but statistically significant improvements in attention span and mental processing speed among healthy adults. A notable 2019 study involving 124 participants showed a 14% improvement in sustained attention tasks after 30 days of supplementation compared to placebo groups. These findings align with earlier animal studies that indicated neuroprotective properties and enhanced mitochondrial function.
The quality of clinical evidence varies considerably across studies. High-quality research from academic institutions has established basic safety parameters and preliminary efficacy, while some industry-sponsored trials have reported more dramatic cognitive benefits that warrant independent verification. A systematic review published in the Journal of Cognitive Enhancement (2021) evaluated 17 clinical trials and concluded that evidence for oxaloacetate's cognitive benefits is "promising but preliminary," noting methodological limitations in several studies including small sample sizes and short duration of intervention.
Bioavailability remains a significant challenge in oxaloacetate supplementation. Standard oral formulations demonstrate relatively poor absorption rates, with plasma concentration studies indicating that only 18-22% reaches systemic circulation in active form. Several enhanced delivery systems have emerged in recent years, including enteric-coated formulations and lipid-based delivery systems that show improved bioavailability profiles of up to 40%.
Regulatory status of oxaloacetate varies globally. In the United States, it maintains GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status as a dietary supplement but lacks FDA approval for specific cognitive health claims. The European Food Safety Authority has acknowledged its safety profile but has similarly not endorsed cognitive enhancement claims due to insufficient evidence meeting their stringent criteria for health claims substantiation.
Regulatory Framework for Metabolic Cognitive Enhancers
The regulatory landscape for metabolic cognitive enhancers like oxaloacetate remains complex and evolving across global markets. In the United States, the FDA classifies oxaloacetate as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical, placing it under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This classification allows manufacturers to market oxaloacetate without the rigorous pre-market approval process required for drugs, provided they avoid making specific disease treatment claims.
European regulations present a more stringent framework through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which requires substantial scientific evidence for cognitive enhancement claims. Currently, oxaloacetate lacks EFSA-approved health claims for cognitive function, limiting marketing possibilities compared to the US market. The Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 may also apply if oxaloacetate is considered a novel ingredient without significant consumption history in Europe.
Asian markets demonstrate considerable regulatory diversity. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system potentially allows cognitive enhancement claims with sufficient evidence, while China's regulatory framework under the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) remains particularly stringent for metabolic enhancers marketed for cognitive benefits.
Clinical research requirements vary significantly across jurisdictions. The FDA requires that supplement manufacturers ensure product safety before marketing but doesn't mandate clinical trials. However, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and many Asian regulatory bodies increasingly demand human clinical data demonstrating both safety and efficacy for cognitive enhancement claims.
Quality control standards represent another critical regulatory consideration. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) compliance is mandatory in most developed markets, with increasing focus on stability testing, bioavailability verification, and consistent metabolic activity across production batches.
Labeling regulations present particular challenges for oxaloacetate marketers. The FDA prohibits disease treatment claims for supplements, requiring careful wording around "supporting cognitive function" rather than "improving focus" or "treating cognitive decline." Similar restrictions exist in most regulated markets, though specific permissible language varies considerably.
Future regulatory trends suggest increasing scrutiny of cognitive enhancers globally. The emergence of specialized regulatory frameworks for "nootropics" or "cognitive enhancers" appears likely as these categories gain mainstream attention. Manufacturers should anticipate stricter evidence requirements and potentially new classification systems that bridge the current gap between supplements and pharmaceuticals.
European regulations present a more stringent framework through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which requires substantial scientific evidence for cognitive enhancement claims. Currently, oxaloacetate lacks EFSA-approved health claims for cognitive function, limiting marketing possibilities compared to the US market. The Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 may also apply if oxaloacetate is considered a novel ingredient without significant consumption history in Europe.
Asian markets demonstrate considerable regulatory diversity. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system potentially allows cognitive enhancement claims with sufficient evidence, while China's regulatory framework under the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) remains particularly stringent for metabolic enhancers marketed for cognitive benefits.
Clinical research requirements vary significantly across jurisdictions. The FDA requires that supplement manufacturers ensure product safety before marketing but doesn't mandate clinical trials. However, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and many Asian regulatory bodies increasingly demand human clinical data demonstrating both safety and efficacy for cognitive enhancement claims.
Quality control standards represent another critical regulatory consideration. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) compliance is mandatory in most developed markets, with increasing focus on stability testing, bioavailability verification, and consistent metabolic activity across production batches.
Labeling regulations present particular challenges for oxaloacetate marketers. The FDA prohibits disease treatment claims for supplements, requiring careful wording around "supporting cognitive function" rather than "improving focus" or "treating cognitive decline." Similar restrictions exist in most regulated markets, though specific permissible language varies considerably.
Future regulatory trends suggest increasing scrutiny of cognitive enhancers globally. The emergence of specialized regulatory frameworks for "nootropics" or "cognitive enhancers" appears likely as these categories gain mainstream attention. Manufacturers should anticipate stricter evidence requirements and potentially new classification systems that bridge the current gap between supplements and pharmaceuticals.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!