Profiling malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Malachite Processing Background and Objectives
Malachite, a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, has been a significant source of copper for centuries. Its processing in industrial solutions has evolved from rudimentary extraction methods to sophisticated hydrometallurgical techniques. The reactivity of malachite in these solutions plays a crucial role in copper recovery efficiency and overall process economics.
The primary objective of profiling malachite reactivity is to optimize copper extraction processes, reduce environmental impact, and enhance economic viability. By understanding the kinetics and mechanisms of malachite dissolution in various industrial solutions, researchers and engineers aim to develop more efficient and sustainable copper production methods.
Historically, malachite processing has been influenced by advancements in hydrometallurgy and the increasing demand for copper in the global market. Early techniques involved simple acid leaching, but modern approaches incorporate complex lixiviant systems and advanced recovery methods. The evolution of these processes has been driven by the need to process lower-grade ores and minimize waste generation.
Current research focuses on improving the selectivity and efficiency of malachite dissolution while reducing energy consumption and environmental footprint. Key areas of investigation include the development of novel lixiviants, optimization of leaching parameters, and the integration of in-situ recovery techniques.
The global shift towards renewable energy and electric vehicles has further intensified the demand for copper, making the efficient processing of malachite even more critical. This trend has spurred innovation in malachite reactivity profiling, with emphasis on developing processes that can handle complex ore compositions and varying mineralogical characteristics.
Understanding malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions is essential for addressing challenges such as acid consumption, impurity co-extraction, and precipitation of secondary phases. These factors significantly impact the overall efficiency and economics of copper production from malachite-bearing ores.
As the mining industry moves towards more sustainable practices, profiling malachite reactivity also aims to support the development of environmentally friendly extraction methods. This includes exploring bio-leaching options, investigating the potential for recycling process solutions, and minimizing the generation of hazardous waste streams.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of profiling malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions are rooted in the need for more efficient, economical, and environmentally responsible copper production methods. By advancing our understanding of malachite behavior in various leaching environments, we can pave the way for innovative technologies that will shape the future of copper extraction from this important mineral resource.
The primary objective of profiling malachite reactivity is to optimize copper extraction processes, reduce environmental impact, and enhance economic viability. By understanding the kinetics and mechanisms of malachite dissolution in various industrial solutions, researchers and engineers aim to develop more efficient and sustainable copper production methods.
Historically, malachite processing has been influenced by advancements in hydrometallurgy and the increasing demand for copper in the global market. Early techniques involved simple acid leaching, but modern approaches incorporate complex lixiviant systems and advanced recovery methods. The evolution of these processes has been driven by the need to process lower-grade ores and minimize waste generation.
Current research focuses on improving the selectivity and efficiency of malachite dissolution while reducing energy consumption and environmental footprint. Key areas of investigation include the development of novel lixiviants, optimization of leaching parameters, and the integration of in-situ recovery techniques.
The global shift towards renewable energy and electric vehicles has further intensified the demand for copper, making the efficient processing of malachite even more critical. This trend has spurred innovation in malachite reactivity profiling, with emphasis on developing processes that can handle complex ore compositions and varying mineralogical characteristics.
Understanding malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions is essential for addressing challenges such as acid consumption, impurity co-extraction, and precipitation of secondary phases. These factors significantly impact the overall efficiency and economics of copper production from malachite-bearing ores.
As the mining industry moves towards more sustainable practices, profiling malachite reactivity also aims to support the development of environmentally friendly extraction methods. This includes exploring bio-leaching options, investigating the potential for recycling process solutions, and minimizing the generation of hazardous waste streams.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of profiling malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions are rooted in the need for more efficient, economical, and environmentally responsible copper production methods. By advancing our understanding of malachite behavior in various leaching environments, we can pave the way for innovative technologies that will shape the future of copper extraction from this important mineral resource.
Industrial Demand for Malachite Processing
The industrial demand for malachite processing has been steadily increasing due to its diverse applications in various sectors. Malachite, a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, is primarily valued for its use in copper extraction and as an ornamental stone. In the mining and metallurgical industries, there is a growing need for efficient malachite processing techniques to meet the rising global demand for copper.
The electronics and electrical industries drive a significant portion of the demand for malachite processing. As these sectors continue to expand, particularly with the advent of 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT), the requirement for copper-based components has surged. This has led to increased interest in optimizing malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions to enhance copper yield and purity.
In the construction sector, malachite processing is gaining traction for its potential in developing eco-friendly building materials. Research into malachite-based cement additives and concrete formulations has shown promising results in improving durability and reducing carbon footprint. This emerging application has created a new market segment for malachite processing, attracting attention from both industry players and environmental advocates.
The renewable energy sector, particularly solar panel manufacturing, has also contributed to the growing demand for malachite processing. Copper extracted from malachite is a crucial component in photovoltaic systems, and as the global push for clean energy intensifies, the need for efficient malachite processing technologies is expected to rise correspondingly.
In the field of nanotechnology, malachite processing has found novel applications. Researchers are exploring the use of malachite-derived nanoparticles in catalysis, sensing, and biomedical applications. This cutting-edge research has opened up new avenues for malachite utilization, driving demand for advanced processing techniques that can produce high-purity, nano-scale malachite derivatives.
The chemical industry has shown increasing interest in malachite processing for the production of copper-based catalysts and pigments. These materials find applications in a wide range of products, from automotive coatings to specialty chemicals, further diversifying the demand for malachite processing solutions.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable and eco-friendly malachite processing methods. This has led to increased investment in research and development of green technologies that can efficiently extract copper from malachite while minimizing environmental impact. The demand for such environmentally responsible processing solutions is particularly strong in regions with strict environmental policies.
The electronics and electrical industries drive a significant portion of the demand for malachite processing. As these sectors continue to expand, particularly with the advent of 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT), the requirement for copper-based components has surged. This has led to increased interest in optimizing malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions to enhance copper yield and purity.
In the construction sector, malachite processing is gaining traction for its potential in developing eco-friendly building materials. Research into malachite-based cement additives and concrete formulations has shown promising results in improving durability and reducing carbon footprint. This emerging application has created a new market segment for malachite processing, attracting attention from both industry players and environmental advocates.
The renewable energy sector, particularly solar panel manufacturing, has also contributed to the growing demand for malachite processing. Copper extracted from malachite is a crucial component in photovoltaic systems, and as the global push for clean energy intensifies, the need for efficient malachite processing technologies is expected to rise correspondingly.
In the field of nanotechnology, malachite processing has found novel applications. Researchers are exploring the use of malachite-derived nanoparticles in catalysis, sensing, and biomedical applications. This cutting-edge research has opened up new avenues for malachite utilization, driving demand for advanced processing techniques that can produce high-purity, nano-scale malachite derivatives.
The chemical industry has shown increasing interest in malachite processing for the production of copper-based catalysts and pigments. These materials find applications in a wide range of products, from automotive coatings to specialty chemicals, further diversifying the demand for malachite processing solutions.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable and eco-friendly malachite processing methods. This has led to increased investment in research and development of green technologies that can efficiently extract copper from malachite while minimizing environmental impact. The demand for such environmentally responsible processing solutions is particularly strong in regions with strict environmental policies.
Current Challenges in Malachite Reactivity Profiling
Profiling malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals must address. One of the primary obstacles is the complex nature of malachite's chemical composition and structure. As a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, malachite's reactivity can vary significantly depending on its specific formation conditions and impurities present.
The heterogeneity of industrial processing solutions further complicates the profiling process. These solutions often contain a diverse array of chemical compounds, including acids, bases, and various metal ions, which can interact with malachite in unpredictable ways. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and accurately measure malachite's reactivity without interference from other solution components.
Another challenge lies in the development of standardized methodologies for profiling malachite reactivity. The lack of universally accepted protocols hinders the comparison of results across different studies and industrial applications. This inconsistency in measurement techniques and reporting standards makes it challenging to establish a comprehensive understanding of malachite's behavior in various processing environments.
The dynamic nature of industrial processing conditions poses additional difficulties. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and pH can fluctuate during processing, affecting malachite's reactivity in real-time. Capturing these variations and their impact on reactivity profiles requires sophisticated monitoring systems and data analysis techniques that are not always readily available or easily implemented in industrial settings.
Furthermore, the scale-up from laboratory experiments to industrial-scale processes introduces new variables that can affect malachite reactivity. What works in a controlled laboratory environment may not translate directly to large-scale industrial applications, necessitating extensive testing and optimization at each stage of scale-up.
The environmental and health considerations associated with malachite processing also present challenges in reactivity profiling. Ensuring that profiling methods are safe, environmentally friendly, and compliant with regulations adds another layer of complexity to the research and development process.
Lastly, the economic feasibility of implementing advanced profiling techniques in industrial settings remains a significant hurdle. Many cutting-edge analytical methods require expensive equipment and specialized expertise, which may not be justifiable for all industrial applications. Striking a balance between accuracy, practicality, and cost-effectiveness in malachite reactivity profiling continues to be a major challenge for the industry.
The heterogeneity of industrial processing solutions further complicates the profiling process. These solutions often contain a diverse array of chemical compounds, including acids, bases, and various metal ions, which can interact with malachite in unpredictable ways. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and accurately measure malachite's reactivity without interference from other solution components.
Another challenge lies in the development of standardized methodologies for profiling malachite reactivity. The lack of universally accepted protocols hinders the comparison of results across different studies and industrial applications. This inconsistency in measurement techniques and reporting standards makes it challenging to establish a comprehensive understanding of malachite's behavior in various processing environments.
The dynamic nature of industrial processing conditions poses additional difficulties. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and pH can fluctuate during processing, affecting malachite's reactivity in real-time. Capturing these variations and their impact on reactivity profiles requires sophisticated monitoring systems and data analysis techniques that are not always readily available or easily implemented in industrial settings.
Furthermore, the scale-up from laboratory experiments to industrial-scale processes introduces new variables that can affect malachite reactivity. What works in a controlled laboratory environment may not translate directly to large-scale industrial applications, necessitating extensive testing and optimization at each stage of scale-up.
The environmental and health considerations associated with malachite processing also present challenges in reactivity profiling. Ensuring that profiling methods are safe, environmentally friendly, and compliant with regulations adds another layer of complexity to the research and development process.
Lastly, the economic feasibility of implementing advanced profiling techniques in industrial settings remains a significant hurdle. Many cutting-edge analytical methods require expensive equipment and specialized expertise, which may not be justifiable for all industrial applications. Striking a balance between accuracy, practicality, and cost-effectiveness in malachite reactivity profiling continues to be a major challenge for the industry.
Existing Malachite Reactivity Profiling Methods
01 Chemical reactivity of malachite
Malachite, a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, exhibits various chemical reactions. It can be used in chemical processes involving copper compounds, including oxidation-reduction reactions and acid-base interactions. The reactivity of malachite is often exploited in industrial applications and scientific research.- Malachite as a catalyst in chemical reactions: Malachite, a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, exhibits catalytic properties in various chemical reactions. Its reactivity is utilized in organic synthesis, oxidation processes, and environmental applications. The unique structure and composition of malachite contribute to its effectiveness as a heterogeneous catalyst.
- Malachite in electrochemical applications: The reactivity of malachite is exploited in electrochemical systems, including sensors, electrodes, and energy storage devices. Its ability to undergo redox reactions and its conductive properties make it suitable for various electrochemical applications, enhancing the performance and sensitivity of these systems.
- Malachite in environmental remediation: Malachite demonstrates reactivity towards various pollutants, making it useful in environmental remediation processes. Its ability to adsorb heavy metals, organic compounds, and other contaminants from water and soil has been studied and applied in pollution control and water treatment technologies.
- Synthesis and modification of malachite nanostructures: Research focuses on synthesizing and modifying malachite nanostructures to enhance their reactivity and specific properties. Various methods are employed to control the size, shape, and composition of malachite nanoparticles, leading to improved performance in catalysis, sensing, and other applications.
- Malachite in biomedical applications: The reactivity of malachite is explored in biomedical fields, including drug delivery, biosensing, and antimicrobial applications. Its unique properties and biocompatibility make it a promising material for developing novel therapeutic and diagnostic tools in medicine.
02 Malachite in catalytic processes
Malachite-based materials have shown potential as catalysts in various chemical reactions. The unique structure and composition of malachite allow it to facilitate certain reactions, particularly in organic synthesis and environmental applications. Research has focused on optimizing malachite-derived catalysts for improved efficiency and selectivity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Malachite in environmental remediation
The reactivity of malachite has been studied for its potential in environmental remediation processes. Its ability to adsorb and react with certain pollutants makes it a candidate for water and soil treatment applications. Research has explored the use of malachite in removing heavy metals and organic contaminants from various environmental matrices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Malachite in material science applications
The reactive properties of malachite have been investigated for use in material science applications. This includes the development of novel composites, coatings, and functional materials. The incorporation of malachite into various matrices can impart unique properties such as antimicrobial activity or enhanced mechanical characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Malachite in biomedical applications
Research has explored the potential of malachite's reactivity in biomedical applications. This includes its use in biosensors, drug delivery systems, and antimicrobial agents. The controlled reactivity of malachite-based materials in biological environments offers promising avenues for medical and pharmaceutical developments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Malachite Processing
The profiling of malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions is currently in an early development stage, with a growing market driven by increasing demand for copper and other minerals. The global market size for this technology is expanding, though still relatively niche. Technical maturity is progressing, with key players like Vale SA, Shanghai ChemPartner, and Sumitomo Metal Mining leading research efforts. Universities such as Columbia and Sydney are contributing to fundamental understanding, while companies like BHP Billiton and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp are exploring practical applications. The competitive landscape is diverse, with mining giants, research institutions, and specialized chemical companies all vying for advancements in this field.
Vale SA
Technical Solution: Vale SA has developed advanced profiling techniques for malachite reactivity in industrial processing solutions. Their approach combines in-situ spectroscopic analysis with machine learning algorithms to predict and optimize malachite dissolution rates in various leaching environments[1]. The company utilizes a proprietary multi-parameter model that accounts for solution pH, temperature, and impurity levels to accurately profile malachite behavior during copper extraction processes[3]. Vale's system employs real-time monitoring sensors integrated into their processing circuits, allowing for dynamic adjustments to maximize copper recovery while minimizing reagent consumption[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive real-time monitoring and predictive capabilities. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment for implementation in existing operations.
Sumitomo Metal Mining Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Metal Mining has pioneered a novel approach to profiling malachite reactivity using advanced X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) techniques. Their method combines synchrotron-based XAS with a custom-designed flow-through reaction cell to study malachite dissolution kinetics under industrially relevant conditions[2]. This allows for in-situ observation of changes in copper speciation during leaching processes. The company has also developed a complementary computational model that integrates thermodynamic data with experimental results to predict malachite behavior across a wide range of processing conditions[4].
Strengths: High-resolution, atomic-level insights into malachite reactivity. Weaknesses: Requires access to specialized synchrotron facilities for some analyses.
Core Innovations in Malachite Characterization
Process for the heterogeneous catalyzed preparation of n-alkyl substituted aminoalkines
PatentInactiveEP0827949A1
Innovation
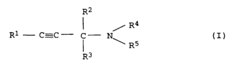
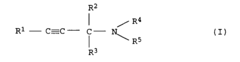
- A heterogeneously catalyzed process using an unsupported copper catalyst derived from malachite, preferably in an activated form like copper acetylide, which allows for reactions with alkynes and amines in a neutral to alkaline pH range without the need for high pressures, enabling high yields and selectivity.
Treatment of non-sulfidic nikeliferous resources and recovery of metal values therefrom
PatentActiveUS20190024211A1
Innovation
- A two-step leaching process using oxalic acid-based and ammoniacal leaching under atmospheric pressure to extract high-grade nickel from non-sulfidic nickeliferous materials, reducing particle size and employing organic acids to selectively dissolve iron, followed by ammoniacal leaching to produce a nickel-rich solution and subsequent thermal decomposition to achieve a high-grade nickel product.
Environmental Impact of Malachite Processing
The environmental impact of malachite processing is a critical consideration in industrial operations. Malachite, a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, is commonly used in various industries, including metallurgy and pigment production. However, its processing can lead to significant environmental concerns that require careful management and mitigation strategies.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with malachite processing is the release of copper into ecosystems. Copper, while an essential micronutrient, can become toxic to aquatic life and plants at elevated concentrations. Industrial effluents containing dissolved copper from malachite processing can contaminate water bodies, leading to adverse effects on fish populations, algae growth, and overall aquatic ecosystem health. Soil contamination is another concern, as copper accumulation in soils can inhibit plant growth and disrupt soil microbial communities.
Air pollution is also a potential consequence of malachite processing, particularly during high-temperature operations. The release of fine particulate matter containing copper and other trace elements can contribute to air quality degradation in surrounding areas. This may pose health risks to both workers and nearby communities, potentially leading to respiratory issues and other health complications.
The generation of acidic waste streams is another significant environmental challenge. Malachite processing often involves acid leaching, which can result in the production of acidic solutions. If not properly managed, these acidic effluents can cause soil and water acidification, further exacerbating environmental damage and potentially mobilizing other toxic metals present in the surrounding geology.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of malachite processing. The disposal of solid residues and tailings from processing operations can lead to long-term environmental liabilities if not handled correctly. These wastes may contain residual copper and other potentially harmful substances, posing risks of leaching and contamination of groundwater and surface water resources.
Energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions are additional environmental considerations. Malachite processing often requires significant energy inputs, particularly in high-temperature operations or electrochemical processes. The carbon footprint of these activities contributes to broader climate change concerns and necessitates the exploration of more energy-efficient processing technologies.
To address these environmental challenges, industries involved in malachite processing are increasingly adopting cleaner production techniques and implementing robust environmental management systems. These may include closed-loop water recycling systems, advanced effluent treatment technologies, and improved air pollution control measures. Additionally, research into more environmentally friendly processing methods, such as bioleaching and low-temperature extraction techniques, is ongoing to reduce the overall environmental footprint of malachite utilization in industrial applications.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with malachite processing is the release of copper into ecosystems. Copper, while an essential micronutrient, can become toxic to aquatic life and plants at elevated concentrations. Industrial effluents containing dissolved copper from malachite processing can contaminate water bodies, leading to adverse effects on fish populations, algae growth, and overall aquatic ecosystem health. Soil contamination is another concern, as copper accumulation in soils can inhibit plant growth and disrupt soil microbial communities.
Air pollution is also a potential consequence of malachite processing, particularly during high-temperature operations. The release of fine particulate matter containing copper and other trace elements can contribute to air quality degradation in surrounding areas. This may pose health risks to both workers and nearby communities, potentially leading to respiratory issues and other health complications.
The generation of acidic waste streams is another significant environmental challenge. Malachite processing often involves acid leaching, which can result in the production of acidic solutions. If not properly managed, these acidic effluents can cause soil and water acidification, further exacerbating environmental damage and potentially mobilizing other toxic metals present in the surrounding geology.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of malachite processing. The disposal of solid residues and tailings from processing operations can lead to long-term environmental liabilities if not handled correctly. These wastes may contain residual copper and other potentially harmful substances, posing risks of leaching and contamination of groundwater and surface water resources.
Energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions are additional environmental considerations. Malachite processing often requires significant energy inputs, particularly in high-temperature operations or electrochemical processes. The carbon footprint of these activities contributes to broader climate change concerns and necessitates the exploration of more energy-efficient processing technologies.
To address these environmental challenges, industries involved in malachite processing are increasingly adopting cleaner production techniques and implementing robust environmental management systems. These may include closed-loop water recycling systems, advanced effluent treatment technologies, and improved air pollution control measures. Additionally, research into more environmentally friendly processing methods, such as bioleaching and low-temperature extraction techniques, is ongoing to reduce the overall environmental footprint of malachite utilization in industrial applications.
Safety Protocols in Malachite Handling
Malachite, a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, requires careful handling in industrial processing due to its potential health and environmental risks. Establishing comprehensive safety protocols is crucial for protecting workers, equipment, and the environment. These protocols should encompass proper personal protective equipment (PPE), handling procedures, storage guidelines, and emergency response measures.
Workers involved in malachite processing must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection. The type of respiratory protection depends on the specific processing activities and potential exposure levels. In dusty environments, N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) may be necessary. Protective clothing, such as chemical-resistant suits or aprons, should also be worn to prevent skin contact with malachite particles or solutions.
Proper handling procedures are essential to minimize exposure risks. These include using enclosed systems for crushing, grinding, and mixing operations to reduce dust generation. When transferring malachite solutions, closed-loop systems or splash guards should be employed to prevent spills and splashes. Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and work areas are crucial to prevent the accumulation of malachite dust or residues.
Storage guidelines for malachite should address both raw materials and processed solutions. Raw malachite should be stored in sealed containers in well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials such as strong acids. Processed malachite solutions should be stored in appropriate chemical-resistant containers with proper labeling. Secondary containment measures should be implemented to prevent environmental contamination in case of leaks or spills.
Emergency response measures must be in place to address potential incidents involving malachite. This includes having readily available spill kits, eye wash stations, and safety showers. Workers should be trained in proper spill containment and cleanup procedures, as well as first aid measures for potential exposures. A clear communication plan should be established to ensure rapid response in case of emergencies.
Regular monitoring of air quality and worker exposure levels is essential to ensure the effectiveness of safety protocols. This may involve periodic air sampling and personal exposure monitoring for workers handling malachite. Results should be used to adjust safety measures as needed and to ensure compliance with occupational exposure limits.
Training programs should be implemented to educate workers on the hazards associated with malachite, proper use of PPE, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher training and safety drills should be conducted to maintain awareness and preparedness among workers.
By implementing these comprehensive safety protocols, industrial facilities can significantly reduce the risks associated with malachite handling and processing, ensuring a safer work environment and minimizing potential environmental impacts.
Workers involved in malachite processing must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection. The type of respiratory protection depends on the specific processing activities and potential exposure levels. In dusty environments, N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) may be necessary. Protective clothing, such as chemical-resistant suits or aprons, should also be worn to prevent skin contact with malachite particles or solutions.
Proper handling procedures are essential to minimize exposure risks. These include using enclosed systems for crushing, grinding, and mixing operations to reduce dust generation. When transferring malachite solutions, closed-loop systems or splash guards should be employed to prevent spills and splashes. Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and work areas are crucial to prevent the accumulation of malachite dust or residues.
Storage guidelines for malachite should address both raw materials and processed solutions. Raw malachite should be stored in sealed containers in well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials such as strong acids. Processed malachite solutions should be stored in appropriate chemical-resistant containers with proper labeling. Secondary containment measures should be implemented to prevent environmental contamination in case of leaks or spills.
Emergency response measures must be in place to address potential incidents involving malachite. This includes having readily available spill kits, eye wash stations, and safety showers. Workers should be trained in proper spill containment and cleanup procedures, as well as first aid measures for potential exposures. A clear communication plan should be established to ensure rapid response in case of emergencies.
Regular monitoring of air quality and worker exposure levels is essential to ensure the effectiveness of safety protocols. This may involve periodic air sampling and personal exposure monitoring for workers handling malachite. Results should be used to adjust safety measures as needed and to ensure compliance with occupational exposure limits.
Training programs should be implemented to educate workers on the hazards associated with malachite, proper use of PPE, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher training and safety drills should be conducted to maintain awareness and preparedness among workers.
By implementing these comprehensive safety protocols, industrial facilities can significantly reduce the risks associated with malachite handling and processing, ensuring a safer work environment and minimizing potential environmental impacts.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!