Quantum Computing's Influence on Electronic Business Strategies
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Computing Evolution and Objectives
Quantum computing has emerged as a revolutionary technology with the potential to transform various industries, including electronic business. The evolution of quantum computing can be traced back to the early 1980s when physicist Richard Feynman proposed the idea of using quantum mechanical effects to perform computations. Since then, the field has progressed rapidly, driven by advancements in quantum physics, computer science, and engineering.
The development of quantum computing has been marked by several key milestones. In the 1990s, Peter Shor developed a quantum algorithm for factoring large numbers, demonstrating the potential of quantum computers to solve problems that are intractable for classical computers. This breakthrough sparked increased interest and investment in quantum computing research. The early 2000s saw the creation of the first rudimentary quantum processors, capable of manipulating a handful of qubits.
As the technology progressed, major tech companies and research institutions began to invest heavily in quantum computing. IBM, Google, and Microsoft, among others, have made significant strides in developing more powerful and stable quantum processors. In 2019, Google claimed to have achieved quantum supremacy, demonstrating that their quantum computer could perform a specific task faster than any classical computer.
The primary objective of quantum computing in the context of electronic business strategies is to leverage its unique capabilities to solve complex problems and optimize business processes. Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize areas such as cryptography, financial modeling, supply chain optimization, and machine learning. These applications could provide businesses with unprecedented computational power, enabling them to make more informed decisions, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the digital marketplace.
Looking ahead, the goals for quantum computing in electronic business include developing more robust and scalable quantum systems, creating practical quantum algorithms for business applications, and integrating quantum computing with existing IT infrastructure. Researchers and companies are working towards increasing the number of qubits while reducing error rates, aiming to create fault-tolerant quantum computers capable of solving real-world problems.
Another crucial objective is to bridge the gap between quantum computing theory and practical business applications. This involves developing user-friendly interfaces and tools that allow businesses to harness the power of quantum computing without requiring deep expertise in quantum mechanics. As the technology matures, the focus will shift towards creating industry-specific quantum solutions and fostering a quantum-ready workforce to support the integration of quantum computing into electronic business strategies.
The development of quantum computing has been marked by several key milestones. In the 1990s, Peter Shor developed a quantum algorithm for factoring large numbers, demonstrating the potential of quantum computers to solve problems that are intractable for classical computers. This breakthrough sparked increased interest and investment in quantum computing research. The early 2000s saw the creation of the first rudimentary quantum processors, capable of manipulating a handful of qubits.
As the technology progressed, major tech companies and research institutions began to invest heavily in quantum computing. IBM, Google, and Microsoft, among others, have made significant strides in developing more powerful and stable quantum processors. In 2019, Google claimed to have achieved quantum supremacy, demonstrating that their quantum computer could perform a specific task faster than any classical computer.
The primary objective of quantum computing in the context of electronic business strategies is to leverage its unique capabilities to solve complex problems and optimize business processes. Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize areas such as cryptography, financial modeling, supply chain optimization, and machine learning. These applications could provide businesses with unprecedented computational power, enabling them to make more informed decisions, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the digital marketplace.
Looking ahead, the goals for quantum computing in electronic business include developing more robust and scalable quantum systems, creating practical quantum algorithms for business applications, and integrating quantum computing with existing IT infrastructure. Researchers and companies are working towards increasing the number of qubits while reducing error rates, aiming to create fault-tolerant quantum computers capable of solving real-world problems.
Another crucial objective is to bridge the gap between quantum computing theory and practical business applications. This involves developing user-friendly interfaces and tools that allow businesses to harness the power of quantum computing without requiring deep expertise in quantum mechanics. As the technology matures, the focus will shift towards creating industry-specific quantum solutions and fostering a quantum-ready workforce to support the integration of quantum computing into electronic business strategies.
E-Business Market Demand for Quantum Solutions
The quantum computing market is experiencing a surge in demand from the e-business sector, driven by the potential of quantum technologies to revolutionize various aspects of electronic commerce. As traditional computing approaches their limits in handling complex business problems, quantum solutions offer unprecedented computational power and optimization capabilities that could transform e-business strategies.
One of the primary areas of interest for e-businesses is in quantum-enhanced machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies promise to significantly improve recommendation systems, personalization algorithms, and predictive analytics. E-commerce giants are particularly keen on leveraging quantum computing to analyze vast amounts of customer data more efficiently, potentially leading to more accurate product recommendations and targeted marketing strategies.
Supply chain optimization is another critical area where quantum computing is generating substantial demand. E-businesses with complex logistics networks are exploring quantum algorithms to solve intricate routing and scheduling problems, potentially reducing costs and improving delivery times. This application is especially relevant for large-scale e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces that manage extensive distribution networks.
Financial services within the e-business ecosystem are also driving demand for quantum solutions. Quantum computing's ability to perform complex risk assessments and portfolio optimizations at speeds unattainable by classical computers is attracting significant interest from online banking and fintech companies. These organizations are looking to enhance fraud detection, improve credit scoring models, and optimize investment strategies using quantum algorithms.
Cybersecurity is a growing concern for e-businesses, and quantum computing offers both challenges and opportunities in this domain. While quantum computers pose a threat to current encryption methods, they also promise to enable quantum-resistant cryptography. E-businesses are increasingly investing in quantum-safe security solutions to protect sensitive customer data and financial transactions.
The demand for quantum solutions in e-business is not limited to large corporations. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the e-commerce space are also showing interest in quantum-as-a-service (QaaS) offerings. These cloud-based quantum computing services allow smaller players to access quantum resources without significant upfront investments, democratizing the technology and potentially leveling the playing field in the e-business sector.
As the quantum computing ecosystem matures, e-businesses are increasingly partnering with quantum technology providers and research institutions. These collaborations aim to develop industry-specific quantum applications and use cases, further driving demand for tailored quantum solutions in the e-business market.
One of the primary areas of interest for e-businesses is in quantum-enhanced machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies promise to significantly improve recommendation systems, personalization algorithms, and predictive analytics. E-commerce giants are particularly keen on leveraging quantum computing to analyze vast amounts of customer data more efficiently, potentially leading to more accurate product recommendations and targeted marketing strategies.
Supply chain optimization is another critical area where quantum computing is generating substantial demand. E-businesses with complex logistics networks are exploring quantum algorithms to solve intricate routing and scheduling problems, potentially reducing costs and improving delivery times. This application is especially relevant for large-scale e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces that manage extensive distribution networks.
Financial services within the e-business ecosystem are also driving demand for quantum solutions. Quantum computing's ability to perform complex risk assessments and portfolio optimizations at speeds unattainable by classical computers is attracting significant interest from online banking and fintech companies. These organizations are looking to enhance fraud detection, improve credit scoring models, and optimize investment strategies using quantum algorithms.
Cybersecurity is a growing concern for e-businesses, and quantum computing offers both challenges and opportunities in this domain. While quantum computers pose a threat to current encryption methods, they also promise to enable quantum-resistant cryptography. E-businesses are increasingly investing in quantum-safe security solutions to protect sensitive customer data and financial transactions.
The demand for quantum solutions in e-business is not limited to large corporations. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the e-commerce space are also showing interest in quantum-as-a-service (QaaS) offerings. These cloud-based quantum computing services allow smaller players to access quantum resources without significant upfront investments, democratizing the technology and potentially leveling the playing field in the e-business sector.
As the quantum computing ecosystem matures, e-businesses are increasingly partnering with quantum technology providers and research institutions. These collaborations aim to develop industry-specific quantum applications and use cases, further driving demand for tailored quantum solutions in the e-business market.
Quantum Computing Challenges in E-Business
Quantum computing presents significant challenges in the realm of electronic business, fundamentally altering the landscape of digital commerce and cybersecurity. The integration of quantum technologies into e-business infrastructures introduces a new paradigm of computational power, simultaneously offering unprecedented opportunities and posing complex obstacles.
One of the primary challenges lies in the potential disruption of current cryptographic systems. As quantum computers advance, they threaten to render many existing encryption methods obsolete. This vulnerability could compromise the security of sensitive financial transactions, customer data, and proprietary business information that form the backbone of e-commerce operations. E-businesses must grapple with the urgent need to develop and implement quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols to safeguard their digital assets and maintain customer trust.
The scalability and stability of quantum systems present another significant hurdle. While quantum computers promise exponential increases in processing power, their practical application in e-business environments remains limited due to issues such as qubit coherence and error rates. The challenge lies in developing quantum hardware and software that can reliably operate at scale, ensuring consistent performance for complex e-business applications such as real-time analytics, supply chain optimization, and personalized customer experiences.
Data management and integration pose additional challenges in the quantum era. E-businesses must adapt their data architectures to accommodate quantum algorithms and hybrid classical-quantum systems. This transition requires substantial investments in new infrastructure, skills development, and the reimagining of data processing pipelines to leverage quantum advantages while maintaining compatibility with existing systems.
The ethical implications of quantum computing in e-business cannot be overlooked. The potential for quantum algorithms to process vast amounts of personal data raises concerns about privacy and data sovereignty. E-businesses must navigate the complex landscape of evolving regulations and ethical standards to ensure responsible use of quantum technologies while maintaining competitive advantages.
Talent acquisition and workforce development emerge as critical challenges as quantum computing intersects with e-business. The scarcity of professionals with expertise in both quantum technologies and e-commerce creates a significant skills gap. Organizations must invest in training programs and partnerships with academic institutions to cultivate a workforce capable of implementing and managing quantum solutions in e-business contexts.
Lastly, the economic challenges of adopting quantum technologies in e-business are substantial. The high costs associated with quantum hardware, software development, and ongoing maintenance may present barriers to entry for smaller e-commerce players, potentially exacerbating market concentration and limiting innovation in the sector.
One of the primary challenges lies in the potential disruption of current cryptographic systems. As quantum computers advance, they threaten to render many existing encryption methods obsolete. This vulnerability could compromise the security of sensitive financial transactions, customer data, and proprietary business information that form the backbone of e-commerce operations. E-businesses must grapple with the urgent need to develop and implement quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols to safeguard their digital assets and maintain customer trust.
The scalability and stability of quantum systems present another significant hurdle. While quantum computers promise exponential increases in processing power, their practical application in e-business environments remains limited due to issues such as qubit coherence and error rates. The challenge lies in developing quantum hardware and software that can reliably operate at scale, ensuring consistent performance for complex e-business applications such as real-time analytics, supply chain optimization, and personalized customer experiences.
Data management and integration pose additional challenges in the quantum era. E-businesses must adapt their data architectures to accommodate quantum algorithms and hybrid classical-quantum systems. This transition requires substantial investments in new infrastructure, skills development, and the reimagining of data processing pipelines to leverage quantum advantages while maintaining compatibility with existing systems.
The ethical implications of quantum computing in e-business cannot be overlooked. The potential for quantum algorithms to process vast amounts of personal data raises concerns about privacy and data sovereignty. E-businesses must navigate the complex landscape of evolving regulations and ethical standards to ensure responsible use of quantum technologies while maintaining competitive advantages.
Talent acquisition and workforce development emerge as critical challenges as quantum computing intersects with e-business. The scarcity of professionals with expertise in both quantum technologies and e-commerce creates a significant skills gap. Organizations must invest in training programs and partnerships with academic institutions to cultivate a workforce capable of implementing and managing quantum solutions in e-business contexts.
Lastly, the economic challenges of adopting quantum technologies in e-business are substantial. The high costs associated with quantum hardware, software development, and ongoing maintenance may present barriers to entry for smaller e-commerce players, potentially exacerbating market concentration and limiting innovation in the sector.
Current Quantum Strategies in E-Commerce
01 Quantum computing architectures
This category focuses on the design and implementation of quantum computing systems. It includes innovations in qubit arrangements, quantum circuit layouts, and scalable quantum processor architectures. These advancements aim to improve the stability, coherence, and overall performance of quantum computers.- Quantum Circuit Design and Optimization: This area focuses on developing and optimizing quantum circuits for various applications. It involves creating efficient quantum gate sequences, reducing circuit depth, and improving qubit connectivity. Techniques include circuit decomposition, gate synthesis, and noise mitigation strategies to enhance the performance of quantum algorithms on real quantum hardware.
- Error Correction and Fault Tolerance: Error correction and fault tolerance are crucial for building reliable quantum computers. This field involves developing quantum error correction codes, implementing fault-tolerant quantum gates, and designing architectures that can withstand noise and decoherence. Techniques include surface codes, topological quantum computing, and magic state distillation.
- Quantum-Classical Hybrid Algorithms: Hybrid algorithms combine quantum and classical computing to solve complex problems. This approach leverages the strengths of both paradigms, using quantum processors for specific subroutines while classical computers handle other parts of the algorithm. Examples include variational quantum eigensolvers (VQE) and quantum approximate optimization algorithms (QAOA).
- Quantum Machine Learning: Quantum machine learning explores the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning. It involves developing quantum algorithms for tasks such as classification, clustering, and data fitting. This field aims to achieve quantum speedups for machine learning tasks and create new quantum-inspired classical algorithms.
- Quantum Simulation and Chemistry: Quantum computers show promise in simulating quantum systems and solving complex chemistry problems. This area focuses on developing algorithms for simulating molecular dynamics, electronic structure calculations, and quantum many-body systems. Applications include drug discovery, materials science, and understanding chemical reactions at the quantum level.
02 Error correction and fault tolerance
This area addresses the challenges of maintaining quantum information integrity in the presence of noise and decoherence. It encompasses techniques for quantum error correction, fault-tolerant quantum gates, and methods to mitigate the effects of environmental disturbances on quantum systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum algorithms and applications
This category covers the development of quantum algorithms for various computational problems and their practical applications. It includes quantum algorithms for optimization, simulation, machine learning, and cryptography, as well as methods for implementing these algorithms on quantum hardware.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum-classical hybrid systems
This area focuses on integrating quantum and classical computing resources to leverage the strengths of both paradigms. It includes techniques for quantum-classical algorithm design, interfacing quantum processors with classical hardware, and optimizing the distribution of computational tasks between quantum and classical components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum communication and networking
This category encompasses technologies for transmitting quantum information over long distances and creating quantum networks. It includes advancements in quantum key distribution, entanglement distribution, and the development of quantum repeaters and routers for building scalable quantum communication infrastructures.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Quantum E-Business Solutions
The quantum computing landscape is evolving rapidly, with significant implications for electronic business strategies. The industry is in its early growth stage, characterized by intense research and development efforts from both established tech giants and specialized startups. Market size projections vary, but estimates suggest a multi-billion dollar market by 2030. Technological maturity is advancing, with companies like IBM, Google, and Zapata Computing leading in quantum hardware and software development. However, practical business applications are still emerging, with financial services firms like Wells Fargo and Bank of America exploring potential use cases. As the technology progresses, it is expected to revolutionize areas such as cryptography, optimization, and machine learning, potentially disrupting traditional electronic business models and creating new opportunities for innovation.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google's quantum computing strategy focuses on developing its own quantum hardware, the Sycamore processor, which achieved quantum supremacy in 2019[1]. They are also working on quantum algorithms and error correction techniques. For electronic business, Google is exploring quantum machine learning applications to enhance recommendation systems and optimize supply chain logistics. Their quantum neural network models show potential for more accurate predictions in e-commerce[2]. Google's Quantum AI lab collaborates with businesses to identify use cases in finance, cybersecurity, and drug discovery that could revolutionize electronic business operations[3].
Strengths: Strong research team, advanced hardware, and integration with existing cloud services. Weaknesses: Still in early stages of commercialization, and quantum advantage for many business applications remains theoretical.
Zapata Computing, Inc.
Technical Solution: Zapata Computing specializes in quantum software and algorithms, focusing on near-term quantum applications for businesses. Their Orquestra platform enables the development and deployment of quantum-ready applications that can run on various quantum hardware[4]. For electronic business, Zapata is developing quantum-enhanced optimization algorithms for supply chain management, financial portfolio optimization, and fraud detection in e-commerce transactions. They have demonstrated a 100x speedup in certain optimization problems compared to classical methods[5]. Zapata also offers quantum-inspired algorithms that can provide immediate benefits to businesses using classical hardware while preparing for the quantum future[6].
Strengths: Focused on practical, near-term quantum solutions for businesses; hardware-agnostic approach. Weaknesses: Reliant on the progress of quantum hardware manufacturers; limited by current quantum computing capabilities.
Breakthrough Quantum Algorithms for E-Business
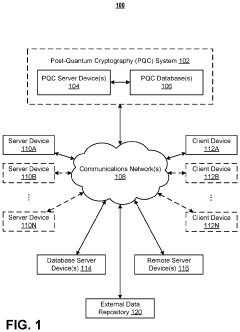
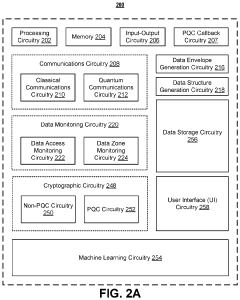
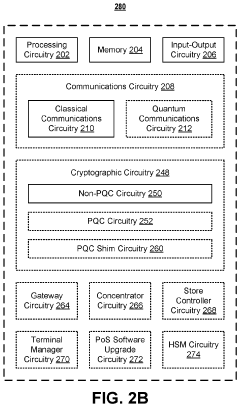
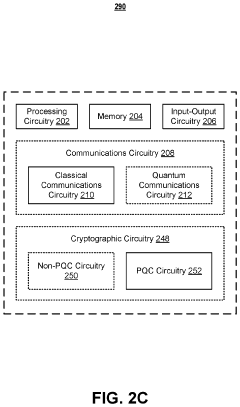
Self-contained encrypted data and decryption application for third party data storage and data dissemination
PatentActiveUS11995194B1
Innovation
- Implementing post-quantum cryptography (PQC) techniques such as hash-based, lattice-based, isogeny-based, code-based, and zero-knowledge proof methods to secure data storage against quantum computer attacks, by using encryption bundles that include decryption applications and credentials to ensure secure access and storage.
Systems and methods for quantum based optimization of a personalized portfolio
PatentActiveUS20210374585A1
Innovation
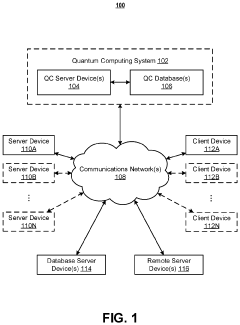
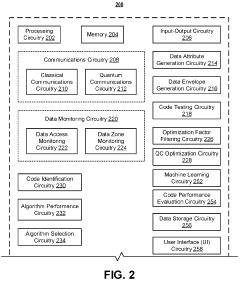
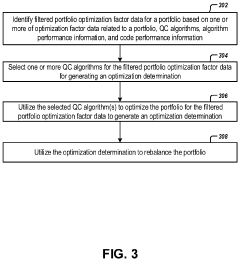
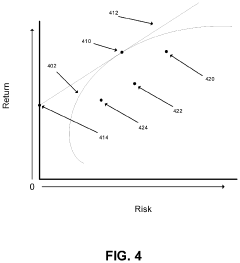
- A quantum computing-based system that utilizes QC optimization factor filtering circuitry to identify and optimize personalized portfolio data, selects appropriate QC algorithms, and rebalances portfolios based on owner feedback and constraints, while also providing post-quantum cryptography solutions to mitigate vulnerabilities in traditional cryptographic systems.
Quantum Security Implications for E-Business
Quantum computing's potential impact on electronic business security is profound and multifaceted. As quantum technologies advance, they pose both significant threats and opportunities for e-business security strategies. One of the primary concerns is the potential for quantum computers to break current encryption methods, particularly those based on factoring large numbers or solving discrete logarithm problems. This vulnerability could compromise the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive business data, financial transactions, and customer information.
To address these challenges, businesses must consider implementing quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, also known as post-quantum cryptography. These algorithms are designed to withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is currently in the process of standardizing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, which will be crucial for e-businesses to adopt in the coming years.
However, quantum technologies also offer enhanced security measures. Quantum key distribution (QKD) provides a method for secure key exchange that is theoretically unbreakable, even by quantum computers. This technology could revolutionize secure communication for e-businesses, particularly in sectors dealing with highly sensitive information such as finance and healthcare.
The integration of quantum-safe security measures into existing e-business infrastructure presents significant challenges. Legacy systems may require extensive upgrades or replacements to accommodate new quantum-resistant protocols. This transition period could be particularly vulnerable, as businesses balance the need for continued operations with the imperative to update security measures.
E-businesses must also consider the implications of quantum computing on data retention policies. Information that is securely encrypted today may become vulnerable in the future when sufficiently powerful quantum computers become available. This "harvest now, decrypt later" threat necessitates a reevaluation of long-term data storage and protection strategies.
Furthermore, the advent of quantum sensing and quantum networking could introduce new paradigms in secure communication and data transfer for e-businesses. These technologies may enable ultra-secure transactions and communications, potentially reshaping the landscape of online business operations and customer interactions.
As quantum technologies mature, e-businesses will need to invest in quantum literacy and expertise. This includes training personnel, partnering with quantum security specialists, and potentially developing in-house quantum capabilities. The competitive advantage in the future e-business landscape may well depend on an organization's ability to harness quantum technologies for security and operational efficiency.
To address these challenges, businesses must consider implementing quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, also known as post-quantum cryptography. These algorithms are designed to withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is currently in the process of standardizing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, which will be crucial for e-businesses to adopt in the coming years.
However, quantum technologies also offer enhanced security measures. Quantum key distribution (QKD) provides a method for secure key exchange that is theoretically unbreakable, even by quantum computers. This technology could revolutionize secure communication for e-businesses, particularly in sectors dealing with highly sensitive information such as finance and healthcare.
The integration of quantum-safe security measures into existing e-business infrastructure presents significant challenges. Legacy systems may require extensive upgrades or replacements to accommodate new quantum-resistant protocols. This transition period could be particularly vulnerable, as businesses balance the need for continued operations with the imperative to update security measures.
E-businesses must also consider the implications of quantum computing on data retention policies. Information that is securely encrypted today may become vulnerable in the future when sufficiently powerful quantum computers become available. This "harvest now, decrypt later" threat necessitates a reevaluation of long-term data storage and protection strategies.
Furthermore, the advent of quantum sensing and quantum networking could introduce new paradigms in secure communication and data transfer for e-businesses. These technologies may enable ultra-secure transactions and communications, potentially reshaping the landscape of online business operations and customer interactions.
As quantum technologies mature, e-businesses will need to invest in quantum literacy and expertise. This includes training personnel, partnering with quantum security specialists, and potentially developing in-house quantum capabilities. The competitive advantage in the future e-business landscape may well depend on an organization's ability to harness quantum technologies for security and operational efficiency.
Quantum-Ready E-Business Infrastructure
As quantum computing continues to advance, businesses must prepare their e-commerce infrastructure to harness its potential. A quantum-ready e-business infrastructure requires significant adaptations to existing systems and the development of new capabilities.
One key aspect is the enhancement of data processing and storage capabilities. Quantum computers can process vast amounts of data exponentially faster than classical computers, necessitating upgrades to data centers and network infrastructure. This includes implementing quantum-resistant encryption protocols to protect sensitive information from potential quantum attacks.
Another critical component is the integration of quantum algorithms into e-business applications. These algorithms can optimize supply chain management, improve recommendation systems, and enhance fraud detection. Businesses need to develop or acquire quantum software development kits (SDKs) and application programming interfaces (APIs) to facilitate the creation of quantum-enhanced applications.
Quantum-ready infrastructure also demands a shift in cloud computing strategies. Hybrid quantum-classical cloud services are emerging, allowing businesses to leverage quantum computing power without significant on-premises investments. E-commerce platforms must be adapted to seamlessly integrate with these hybrid cloud environments.
The workforce must also be prepared for the quantum era. Training programs and recruitment strategies should focus on building a team with quantum computing expertise. This includes data scientists, software engineers, and cybersecurity specialists with knowledge of quantum technologies.
Additionally, businesses need to establish partnerships with quantum hardware providers and research institutions. These collaborations can provide access to cutting-edge quantum technologies and expertise, enabling e-commerce companies to stay at the forefront of quantum advancements.
Lastly, a quantum-ready e-business infrastructure requires a robust testing and validation framework. As quantum technologies are still evolving, businesses must continuously assess the performance and reliability of quantum-enhanced systems in real-world e-commerce scenarios.
By investing in these areas, e-commerce businesses can position themselves to leverage the transformative power of quantum computing, gaining a significant competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving digital marketplace.
One key aspect is the enhancement of data processing and storage capabilities. Quantum computers can process vast amounts of data exponentially faster than classical computers, necessitating upgrades to data centers and network infrastructure. This includes implementing quantum-resistant encryption protocols to protect sensitive information from potential quantum attacks.
Another critical component is the integration of quantum algorithms into e-business applications. These algorithms can optimize supply chain management, improve recommendation systems, and enhance fraud detection. Businesses need to develop or acquire quantum software development kits (SDKs) and application programming interfaces (APIs) to facilitate the creation of quantum-enhanced applications.
Quantum-ready infrastructure also demands a shift in cloud computing strategies. Hybrid quantum-classical cloud services are emerging, allowing businesses to leverage quantum computing power without significant on-premises investments. E-commerce platforms must be adapted to seamlessly integrate with these hybrid cloud environments.
The workforce must also be prepared for the quantum era. Training programs and recruitment strategies should focus on building a team with quantum computing expertise. This includes data scientists, software engineers, and cybersecurity specialists with knowledge of quantum technologies.
Additionally, businesses need to establish partnerships with quantum hardware providers and research institutions. These collaborations can provide access to cutting-edge quantum technologies and expertise, enabling e-commerce companies to stay at the forefront of quantum advancements.
Lastly, a quantum-ready e-business infrastructure requires a robust testing and validation framework. As quantum technologies are still evolving, businesses must continuously assess the performance and reliability of quantum-enhanced systems in real-world e-commerce scenarios.
By investing in these areas, e-commerce businesses can position themselves to leverage the transformative power of quantum computing, gaining a significant competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving digital marketplace.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!