Intelligent Control Strategies For Autonomous Systems - Eureka
JUN 17, 20253 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Intelligent Control Strategies Overview and Goals
The primary objective is to develop intelligent control strategies that enable autonomous systems to operate safely, efficiently, and reliably in complex and dynamic environments. This involves integrating advanced techniques from various fields, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, control theory, and robotics. Key challenges include handling uncertainties, adapting to changing conditions, and ensuring robust decision-making capabilities.
Potential research directions may explore areas such as reinforcement learning for optimal control policies, multi-agent coordination strategies, and the integration of perception, planning, and control modules. Additionally, addressing safety and ethical considerations in autonomous decision-making is crucial for real-world deployment.
Potential research directions may explore areas such as reinforcement learning for optimal control policies, multi-agent coordination strategies, and the integration of perception, planning, and control modules. Additionally, addressing safety and ethical considerations in autonomous decision-making is crucial for real-world deployment.
Market Demand for Autonomous Systems
- Growing Demand for Automation
The market for autonomous systems is rapidly expanding due to the increasing need for automation across various industries, such as manufacturing, transportation, and logistics. - Cost Optimization
Autonomous systems offer the potential for significant cost savings by reducing labor expenses and improving operational efficiency. - Safety and Reliability
Autonomous systems can operate in hazardous environments and perform tasks with higher precision and consistency, leading to improved safety and reliability. - Emerging Applications
New applications for autonomous systems are emerging, such as self-driving vehicles, autonomous drones, and robotic assistants, driving market growth. - Regulatory Landscape
The development of regulations and standards for autonomous systems is shaping the market, with varying levels of adoption across different regions and industries.
Current State and Challenges in Autonomous Control
- Technological Limitations
Current autonomous systems face challenges in handling complex and dynamic environments, requiring more robust perception, decision-making, and control algorithms. - Computational Constraints
Real-time processing of sensor data and decision-making for autonomous systems demand significant computational resources, which can be a bottleneck. - Safety and Reliability Concerns
Ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous systems in unpredictable situations is a critical challenge, particularly in safety-critical applications. - Scalability and Generalization
Developing control strategies that can scale and generalize to diverse environments and scenarios remains a significant hurdle. - Integration and Interoperability
Seamless integration of various components, such as sensors, actuators, and communication systems, is essential for effective autonomous control.
Existing Solutions for Intelligent Control in Autonomous Systems
01 Autonomous vehicle control systems
These systems enable autonomous operation and control of various vehicles, including cars, aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They involve perception, decision-making, and motion control for autonomous navigation.- Autonomous vehicle control systems: These systems enable autonomous operation and control of various vehicles, including cars, aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They involve technologies like perception, decision-making, and motion control for autonomous navigation and operation.
- Intelligent autonomous control systems: Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning, these systems enable intelligent and adaptive control of autonomous systems like robots, spacecraft, and other agents. They optimize decision-making and performance in complex, dynamic environments.
- Human intervention in autonomous vehicles: These systems allow for autonomous vehicle operation while providing mechanisms for human intervention or control retaking. They enable smooth transitions between autonomous and manual modes, ensuring safety and flexibility.
- Infrastructure protection systems: Designed for autonomous operation and control of systems or vehicles, these systems protect infrastructure by monitoring and securing critical facilities or assets.
- Hybrid and distributed autonomous control: Combining multiple control strategies or distributing control across components, these systems enable robust and efficient autonomous vehicle operation through hierarchical architectures or ensemble-based decision-making.
02 Intelligent autonomous control systems
Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning, these systems enable intelligent and adaptive control of autonomous systems like robots and spacecraft, optimizing decision-making and performance in complex environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safe autonomous vehicle control
Focusing on safe and reliable operation, these systems incorporate features like control retaking, mode switching, and infrastructure protection to enhance the safety and robustness of autonomous vehicle control.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hierarchical and distributed control
Employing hierarchical or distributed architectures, these systems handle different aspects of control, such as decision-making, task allocation, and motion control, aiming to improve scalability, modularity, and robustness.Expand Specific Solutions05 Domain-specific autonomous control
Designed for specific applications like thermal control, convoy control, manipulator control, or earth-moving vehicle operations, these systems incorporate domain-specific knowledge and techniques for optimized performance and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Autonomous Systems Industry
The intelligent control strategies for autonomous systems market is rapidly growing, with significant investments driving advancements. Key players include established giants like GM, Robert Bosch, TuSimple, Amazon, and Google, as well as innovative startups like SafeAI and Brain Corp.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Robert Bosch GmbH develops advanced intelligent control strategies, focusing on sensor fusion, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing for automotive and industrial applications.
Strength: High reliability and integration capabilities. Weakness: High cost and complexity.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google LLC's Waymo division leverages deep learning, extensive real-world testing, and high-definition mapping for safe and efficient autonomous driving.
Strength: Extensive real-world testing and data. Weakness: High dependency on mapping data.
Core Innovations in Autonomous Control Strategies
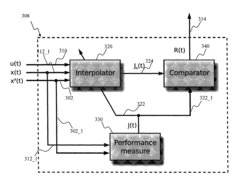
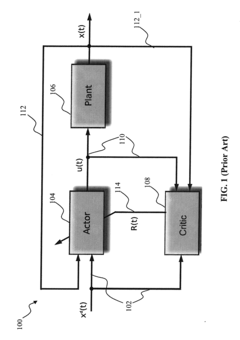
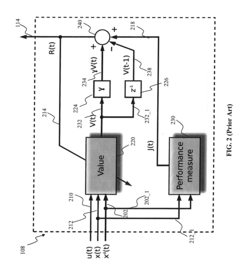
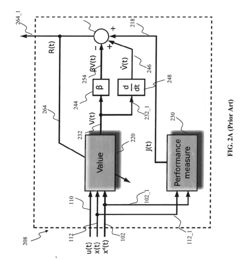
Adaptive critic apparatus and methods
PatentActiveUS20130073080A1
Innovation
- The use of adaptive critic designs, which are algorithms for learning in noisy, nonlinear, and non-stationary dynamic systems. these algorithms enable the critic module to estimate the effect of the control law on the control performance, allowing for continuous improvement of the control rules.
- The scheme incorporates sensing or state estimation apparatus to provide a real-time estimate of the plant state, providing a foundation for adaptive control.
Regulatory Landscape for Autonomous Systems
Intelligent control strategies for autonomous systems aim to enable systems to operate independently and adapt to dynamic environments. The key objectives are to develop algorithms that can perceive the surroundings, make decisions, and execute actions without human intervention. This technology has applications in robotics, self-driving vehicles, and industrial automation. The market demand is driven by the need for increased efficiency, safety, and cost reduction across various industries. Current challenges include sensor integration, decision-making under uncertainty, and ensuring system reliability and robustness. Potential innovation directions involve advanced machine learning techniques, multi-agent coordination, and the integration of artificial intelligence for more sophisticated decision-making capabilities.
Ethical and Safety Considerations in Autonomous Control
Intelligent control strategies for autonomous systems aim to enable systems to operate independently and adapt to dynamic environments. The key objectives are to develop algorithms that can perceive the environment, make decisions, and execute actions without human intervention. This technology has applications in robotics, self-driving vehicles, and industrial automation. The market demand is driven by the need for increased efficiency, safety, and cost reduction across various industries. Current challenges include sensor integration, decision-making under uncertainty, and ensuring system reliability and security. Potential innovation directions involve advancements in machine learning, multi-agent coordination, and the integration of emerging technologies like edge computing and 5G communication.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!