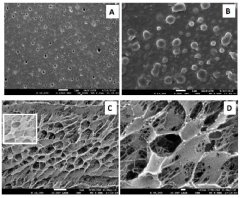
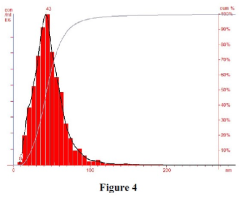
Sodium silicate as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Silicate Nanoparticle Synthesis Background
Sodium silicate, also known as water glass or liquid glass, has emerged as a promising green synthesis medium for nanoparticles in recent years. This environmentally friendly approach aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly production methods in nanotechnology. The use of sodium silicate as a synthesis medium represents a significant shift from traditional methods that often rely on toxic chemicals and energy-intensive processes.
The development of this technique can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative synthesis routes for nanoparticles. The motivation behind this exploration was driven by the need to address environmental concerns associated with conventional nanoparticle production methods. Sodium silicate, being non-toxic, abundant, and cost-effective, quickly gained attention as a potential candidate for green synthesis.
As research in this field progressed, scientists discovered that sodium silicate could serve multiple roles in the nanoparticle synthesis process. It acts as a stabilizing agent, preventing agglomeration of nanoparticles, and also functions as a reducing agent in some cases, eliminating the need for additional chemical reducers. Furthermore, its alkaline nature provides a suitable environment for the formation of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles.
The versatility of sodium silicate as a synthesis medium has been demonstrated across a wide range of nanoparticle types. It has been successfully employed in the production of silver, gold, copper, and various metal oxide nanoparticles, each with unique properties and potential applications. This adaptability has significantly contributed to the growing interest in sodium silicate-based synthesis methods within the scientific community.
One of the key advantages of using sodium silicate is its ability to facilitate the synthesis of nanoparticles at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This characteristic not only reduces energy consumption but also simplifies the production process, making it more accessible for large-scale manufacturing. Additionally, the use of sodium silicate often results in nanoparticles with well-controlled size distributions and morphologies, which are crucial factors in determining their properties and potential applications.
As the field of nanotechnology continues to evolve, the role of sodium silicate in green synthesis is expected to expand further. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing synthesis conditions, exploring new nanoparticle compositions, and investigating the scalability of these processes for industrial applications. The growing body of literature on this topic reflects the increasing recognition of sodium silicate's potential in advancing sustainable nanotechnology practices.
The development of this technique can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative synthesis routes for nanoparticles. The motivation behind this exploration was driven by the need to address environmental concerns associated with conventional nanoparticle production methods. Sodium silicate, being non-toxic, abundant, and cost-effective, quickly gained attention as a potential candidate for green synthesis.
As research in this field progressed, scientists discovered that sodium silicate could serve multiple roles in the nanoparticle synthesis process. It acts as a stabilizing agent, preventing agglomeration of nanoparticles, and also functions as a reducing agent in some cases, eliminating the need for additional chemical reducers. Furthermore, its alkaline nature provides a suitable environment for the formation of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles.
The versatility of sodium silicate as a synthesis medium has been demonstrated across a wide range of nanoparticle types. It has been successfully employed in the production of silver, gold, copper, and various metal oxide nanoparticles, each with unique properties and potential applications. This adaptability has significantly contributed to the growing interest in sodium silicate-based synthesis methods within the scientific community.
One of the key advantages of using sodium silicate is its ability to facilitate the synthesis of nanoparticles at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This characteristic not only reduces energy consumption but also simplifies the production process, making it more accessible for large-scale manufacturing. Additionally, the use of sodium silicate often results in nanoparticles with well-controlled size distributions and morphologies, which are crucial factors in determining their properties and potential applications.
As the field of nanotechnology continues to evolve, the role of sodium silicate in green synthesis is expected to expand further. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing synthesis conditions, exploring new nanoparticle compositions, and investigating the scalability of these processes for industrial applications. The growing body of literature on this topic reflects the increasing recognition of sodium silicate's potential in advancing sustainable nanotechnology practices.
Green Nanoparticle Market Analysis
The green nanoparticle market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable technologies. Sodium silicate, as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles, has emerged as a promising solution in this expanding market. The demand for eco-friendly nanoparticles spans across various industries, including healthcare, electronics, energy, and environmental remediation.
In the healthcare sector, green nanoparticles synthesized using sodium silicate have shown potential applications in drug delivery systems, biosensors, and antimicrobial coatings. The electronics industry is exploring these nanoparticles for use in conductive inks, flexible displays, and energy storage devices. The energy sector is particularly interested in their application in solar cells and catalysts for fuel cells, while environmental remediation efforts are focusing on their use in water purification and soil decontamination.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is leading the green nanoparticle market, with China and India being major contributors due to their rapidly growing industrial sectors and increasing environmental regulations. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by stringent environmental policies and substantial investments in research and development.
The market is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation, with numerous small and medium-sized enterprises competing alongside larger corporations. Key players in the market are focusing on strategic collaborations and partnerships to enhance their product portfolios and expand their market presence. Additionally, there is a growing trend of vertical integration, with companies aiming to control the entire value chain from raw material sourcing to end-product manufacturing.
Challenges in the green nanoparticle market include the high initial costs associated with research and development, as well as the need for standardization and regulatory approval processes. However, these challenges are offset by the potential for long-term cost savings and environmental benefits, which are driving continued investment and innovation in the field.
The market outlook for green nanoparticles synthesized using sodium silicate remains positive, with projections indicating sustained growth over the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing awareness of environmental issues, government initiatives promoting green technologies, and the expanding application scope of nanoparticles across various industries. As research continues to advance and new applications are discovered, the market is expected to diversify further, opening up new opportunities for both established players and innovative startups in the green technology sector.
In the healthcare sector, green nanoparticles synthesized using sodium silicate have shown potential applications in drug delivery systems, biosensors, and antimicrobial coatings. The electronics industry is exploring these nanoparticles for use in conductive inks, flexible displays, and energy storage devices. The energy sector is particularly interested in their application in solar cells and catalysts for fuel cells, while environmental remediation efforts are focusing on their use in water purification and soil decontamination.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is leading the green nanoparticle market, with China and India being major contributors due to their rapidly growing industrial sectors and increasing environmental regulations. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by stringent environmental policies and substantial investments in research and development.
The market is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation, with numerous small and medium-sized enterprises competing alongside larger corporations. Key players in the market are focusing on strategic collaborations and partnerships to enhance their product portfolios and expand their market presence. Additionally, there is a growing trend of vertical integration, with companies aiming to control the entire value chain from raw material sourcing to end-product manufacturing.
Challenges in the green nanoparticle market include the high initial costs associated with research and development, as well as the need for standardization and regulatory approval processes. However, these challenges are offset by the potential for long-term cost savings and environmental benefits, which are driving continued investment and innovation in the field.
The market outlook for green nanoparticles synthesized using sodium silicate remains positive, with projections indicating sustained growth over the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing awareness of environmental issues, government initiatives promoting green technologies, and the expanding application scope of nanoparticles across various industries. As research continues to advance and new applications are discovered, the market is expected to diversify further, opening up new opportunities for both established players and innovative startups in the green technology sector.
Current Challenges in Eco-Friendly Nanoparticle Synthesis
The synthesis of nanoparticles using eco-friendly methods has gained significant attention in recent years due to growing environmental concerns. However, several challenges persist in the development and implementation of green synthesis techniques, particularly when using sodium silicate as a medium.
One of the primary challenges is achieving precise control over nanoparticle size and morphology. The complex chemistry of sodium silicate solutions can lead to variations in reaction conditions, making it difficult to consistently produce nanoparticles with uniform characteristics. This lack of control can result in batch-to-batch inconsistencies, which is a significant hurdle for large-scale industrial applications.
Another major challenge is the limited understanding of the reaction mechanisms involved in sodium silicate-mediated nanoparticle synthesis. The interactions between sodium silicate, reducing agents, and metal precursors are not fully elucidated, making it challenging to optimize reaction parameters and predict outcomes. This knowledge gap hinders the development of more efficient and tailored synthesis protocols.
The stability of nanoparticles synthesized in sodium silicate medium is also a concern. While sodium silicate can act as a stabilizing agent, the long-term colloidal stability of the nanoparticles under various environmental conditions remains a challenge. This is particularly important for applications requiring prolonged shelf life or exposure to diverse pH and ionic strength conditions.
Scalability is another significant hurdle in eco-friendly nanoparticle synthesis using sodium silicate. While laboratory-scale syntheses have shown promising results, translating these processes to industrial scales while maintaining product quality and economic viability is challenging. Factors such as heat and mass transfer limitations, as well as the need for large volumes of environmentally benign reagents, pose significant engineering challenges.
The purification and separation of nanoparticles from the sodium silicate medium present additional difficulties. Traditional separation methods may not be suitable or efficient for these systems, necessitating the development of novel purification techniques that are both effective and environmentally friendly.
Furthermore, the characterization of nanoparticles synthesized in sodium silicate medium can be complex. The presence of silicate species can interfere with certain analytical techniques, making it challenging to accurately determine nanoparticle properties and composition. This complicates quality control processes and hinders the development of standardized protocols.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for green-synthesized nanoparticles is still evolving. The lack of established guidelines and standards for eco-friendly synthesis methods, including those using sodium silicate, creates uncertainty in product development and commercialization. This regulatory ambiguity can slow down innovation and market adoption of these environmentally friendly nanoparticles.
One of the primary challenges is achieving precise control over nanoparticle size and morphology. The complex chemistry of sodium silicate solutions can lead to variations in reaction conditions, making it difficult to consistently produce nanoparticles with uniform characteristics. This lack of control can result in batch-to-batch inconsistencies, which is a significant hurdle for large-scale industrial applications.
Another major challenge is the limited understanding of the reaction mechanisms involved in sodium silicate-mediated nanoparticle synthesis. The interactions between sodium silicate, reducing agents, and metal precursors are not fully elucidated, making it challenging to optimize reaction parameters and predict outcomes. This knowledge gap hinders the development of more efficient and tailored synthesis protocols.
The stability of nanoparticles synthesized in sodium silicate medium is also a concern. While sodium silicate can act as a stabilizing agent, the long-term colloidal stability of the nanoparticles under various environmental conditions remains a challenge. This is particularly important for applications requiring prolonged shelf life or exposure to diverse pH and ionic strength conditions.
Scalability is another significant hurdle in eco-friendly nanoparticle synthesis using sodium silicate. While laboratory-scale syntheses have shown promising results, translating these processes to industrial scales while maintaining product quality and economic viability is challenging. Factors such as heat and mass transfer limitations, as well as the need for large volumes of environmentally benign reagents, pose significant engineering challenges.
The purification and separation of nanoparticles from the sodium silicate medium present additional difficulties. Traditional separation methods may not be suitable or efficient for these systems, necessitating the development of novel purification techniques that are both effective and environmentally friendly.
Furthermore, the characterization of nanoparticles synthesized in sodium silicate medium can be complex. The presence of silicate species can interfere with certain analytical techniques, making it challenging to accurately determine nanoparticle properties and composition. This complicates quality control processes and hinders the development of standardized protocols.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for green-synthesized nanoparticles is still evolving. The lack of established guidelines and standards for eco-friendly synthesis methods, including those using sodium silicate, creates uncertainty in product development and commercialization. This regulatory ambiguity can slow down innovation and market adoption of these environmentally friendly nanoparticles.
Sodium Silicate-Based Synthesis Techniques
01 Synthesis of sodium silicate nanoparticles
Various methods are employed to synthesize sodium silicate nanoparticles, including sol-gel processes, hydrothermal synthesis, and precipitation techniques. These methods allow for control over particle size, morphology, and composition, resulting in nanoparticles with specific properties for diverse applications.- Synthesis of sodium silicate nanoparticles: Various methods are employed to synthesize sodium silicate nanoparticles, including sol-gel processes, hydrothermal synthesis, and precipitation techniques. These methods allow for control over particle size, morphology, and composition, resulting in nanoparticles with specific properties suitable for different applications.
- Applications in energy storage and conversion: Sodium silicate nanoparticles find applications in energy storage and conversion technologies. They are used in the development of advanced battery materials, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. The nanoparticles can enhance the performance and efficiency of these energy devices due to their unique properties at the nanoscale.
- Use in coatings and surface treatments: Sodium silicate nanoparticles are utilized in various coating and surface treatment applications. They can improve the durability, corrosion resistance, and fire-retardant properties of materials. These nanoparticles are incorporated into paints, varnishes, and other protective coatings for metals, wood, and concrete surfaces.
- Environmental and water treatment applications: Sodium silicate nanoparticles play a role in environmental remediation and water treatment processes. They can be used for the removal of heavy metals and other contaminants from water and soil. The nanoparticles' high surface area and adsorption capacity make them effective in purification and filtration systems.
- Biomedical and pharmaceutical applications: Sodium silicate nanoparticles have potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields. They can be used as drug delivery vehicles, imaging agents, and in tissue engineering. The nanoparticles' biocompatibility and ability to be functionalized make them suitable for various medical applications.
02 Applications in energy storage and conversion
Sodium silicate nanoparticles find applications in energy storage and conversion technologies, such as batteries, fuel cells, and solar cells. Their unique properties, including high surface area and ion conductivity, make them suitable for enhancing the performance of these devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in coatings and surface treatments
Sodium silicate nanoparticles are utilized in various coating and surface treatment applications. They can improve the durability, corrosion resistance, and fire retardancy of materials. These nanoparticles are also used in self-cleaning and anti-fouling coatings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and catalytic applications
The nanoparticles have potential in environmental remediation and catalysis. They can be used for water treatment, air purification, and as supports for catalysts in various chemical processes. Their high surface area and reactivity make them effective in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Biomedical and pharmaceutical uses
Sodium silicate nanoparticles show promise in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. They can be used as drug delivery vehicles, imaging agents, and in tissue engineering. Their biocompatibility and ability to be functionalized make them versatile for these purposes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Nanomaterials
The field of sodium silicate as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles is in a growth phase, with increasing research and industrial applications. The market size is expanding due to the rising demand for eco-friendly nanoparticle synthesis methods across various sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with institutions like the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, Zhejiang University, and the University of Campinas leading research efforts. Companies such as Iharabras SA Indústrias Químicas and AVEKA, Inc. are exploring commercial applications. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing developments in process optimization and scalability. Collaboration between academic institutions and industry players is driving innovation and practical implementation of this green synthesis approach.
Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
Technical Solution: CSIR has developed an innovative green synthesis method using sodium silicate as a medium for nanoparticle production. Their approach involves the use of sodium silicate as both a reducing and stabilizing agent, eliminating the need for additional chemicals. The process typically involves mixing metal precursors with sodium silicate solution under controlled pH and temperature conditions. This results in the formation of stable nanoparticles with tunable sizes and shapes. CSIR has successfully synthesized various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles, including silver, gold, and iron oxide, using this method[1][3]. The process has shown high reproducibility and scalability, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Strengths: Environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and versatile for various nanoparticles. Weaknesses: May have limitations in controlling precise nanoparticle morphology for certain applications.
Zhejiang University
Technical Solution: Zhejiang University has pioneered a sodium silicate-based green synthesis approach for nanoparticles, focusing on enhancing the method's efficiency and applicability. Their technique involves a modified sol-gel process using sodium silicate as a precursor and structure-directing agent. By carefully controlling reaction parameters such as pH, temperature, and silicate concentration, they have achieved the synthesis of various nanostructured materials, including mesoporous silica nanoparticles and metal-doped silica nanocomposites[2][5]. The university's research has also explored the use of microwave-assisted synthesis in conjunction with sodium silicate, significantly reducing reaction times and energy consumption. Their method has shown particular promise in developing nanoparticles for environmental remediation and catalysis applications.
Strengths: High degree of control over nanoparticle properties, energy-efficient when combined with microwave synthesis. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal results, potentially limiting widespread adoption.
Innovations in Sodium Silicate Nanoparticle Production
Green process for synthesizing metal nanoparticles within polymeric matrices
PatentActiveIN202121046488A
Innovation
- A green synthetic process using bio-reducing agents like Aloe vera or Asparagus racemosus extracts under sunlight exposure to rapidly form silver nanoparticles in situ within polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) or polypropylene glycol (PPG) polymer matrices, achieving uniform spherical particles of 10-50 nm diameter within 4-10 minutes.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of sodium silicate as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of environmental impact. This assessment examines the ecological implications of this innovative approach to nanoparticle production.
Sodium silicate, also known as water glass, is a non-toxic and environmentally friendly compound. Its use as a synthesis medium aligns with green chemistry principles, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of nanoparticle production. The aqueous nature of sodium silicate eliminates the need for organic solvents, which are often associated with harmful emissions and waste generation in traditional synthesis methods.
The process of nanoparticle synthesis using sodium silicate typically requires lower energy inputs compared to conventional methods. This energy efficiency translates to reduced carbon emissions and overall environmental impact. Additionally, the synthesis can often be conducted at room temperature or with minimal heating, further minimizing energy consumption.
Waste reduction is another significant environmental benefit of this approach. The reaction byproducts are primarily silica-based materials, which are generally inert and can be easily recycled or repurposed. This characteristic contributes to a more circular economy model in nanoparticle production, reducing the burden on landfills and waste treatment facilities.
However, the environmental impact assessment must also consider potential drawbacks. The increased demand for sodium silicate could lead to intensified mining and processing of raw materials, particularly sand and soda ash. This may result in localized environmental disturbances, including habitat disruption and increased water consumption in production areas.
The release of nanoparticles into the environment during production or application remains a concern. While sodium silicate itself is environmentally benign, the nanoparticles synthesized within it may have unknown long-term effects on ecosystems. Careful containment and disposal practices are essential to mitigate potential risks to aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Water usage in the synthesis process, although generally lower than in traditional methods, still requires consideration. Proper water management and recycling systems should be implemented to minimize the overall water footprint of nanoparticle production using sodium silicate.
In conclusion, the use of sodium silicate as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles offers significant environmental advantages over conventional methods. However, a comprehensive life cycle assessment and ongoing monitoring of ecosystem impacts are crucial to ensure that this approach truly delivers on its promise of environmental sustainability in nanoparticle production.
Sodium silicate, also known as water glass, is a non-toxic and environmentally friendly compound. Its use as a synthesis medium aligns with green chemistry principles, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of nanoparticle production. The aqueous nature of sodium silicate eliminates the need for organic solvents, which are often associated with harmful emissions and waste generation in traditional synthesis methods.
The process of nanoparticle synthesis using sodium silicate typically requires lower energy inputs compared to conventional methods. This energy efficiency translates to reduced carbon emissions and overall environmental impact. Additionally, the synthesis can often be conducted at room temperature or with minimal heating, further minimizing energy consumption.
Waste reduction is another significant environmental benefit of this approach. The reaction byproducts are primarily silica-based materials, which are generally inert and can be easily recycled or repurposed. This characteristic contributes to a more circular economy model in nanoparticle production, reducing the burden on landfills and waste treatment facilities.
However, the environmental impact assessment must also consider potential drawbacks. The increased demand for sodium silicate could lead to intensified mining and processing of raw materials, particularly sand and soda ash. This may result in localized environmental disturbances, including habitat disruption and increased water consumption in production areas.
The release of nanoparticles into the environment during production or application remains a concern. While sodium silicate itself is environmentally benign, the nanoparticles synthesized within it may have unknown long-term effects on ecosystems. Careful containment and disposal practices are essential to mitigate potential risks to aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Water usage in the synthesis process, although generally lower than in traditional methods, still requires consideration. Proper water management and recycling systems should be implemented to minimize the overall water footprint of nanoparticle production using sodium silicate.
In conclusion, the use of sodium silicate as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles offers significant environmental advantages over conventional methods. However, a comprehensive life cycle assessment and ongoing monitoring of ecosystem impacts are crucial to ensure that this approach truly delivers on its promise of environmental sustainability in nanoparticle production.
Scalability and Industrial Applications
The scalability and industrial applications of sodium silicate as a green synthesis medium for nanoparticles present significant opportunities and challenges. The process of using sodium silicate for nanoparticle synthesis has shown promising results in laboratory settings, but scaling up to industrial levels requires careful consideration of several factors.
One of the primary advantages of sodium silicate-based synthesis is its potential for large-scale production. The raw materials are readily available and relatively inexpensive, making it an attractive option for industrial applications. Additionally, the process is generally less energy-intensive compared to traditional methods, which can lead to reduced production costs and improved sustainability.
However, scaling up the synthesis process presents several technical challenges. Maintaining consistent nanoparticle size and morphology across large batches can be difficult, as slight variations in reaction conditions can significantly impact the final product. Developing robust quality control measures and standardized production protocols is crucial for ensuring consistent results at an industrial scale.
The industrial applications of nanoparticles synthesized using sodium silicate are diverse and span multiple sectors. In the field of catalysis, these nanoparticles show promise for enhancing chemical reactions in various industrial processes. The automotive industry may benefit from incorporating these nanoparticles into coatings for improved durability and corrosion resistance. In the electronics sector, they could be used in the development of advanced sensors and electronic components.
Environmental remediation is another area where sodium silicate-synthesized nanoparticles show potential. Their high surface area and reactivity make them suitable for applications such as water treatment and soil decontamination. The construction industry may also benefit from incorporating these nanoparticles into building materials to enhance strength and durability.
To fully realize the industrial potential of this synthesis method, further research and development are needed. This includes optimizing reaction conditions for large-scale production, developing efficient separation and purification techniques, and exploring new applications across various industries. Collaboration between academic institutions and industrial partners will be crucial in addressing these challenges and advancing the technology towards commercial viability.
As the demand for sustainable and cost-effective nanoparticle synthesis methods continues to grow, sodium silicate-based processes are likely to gain increased attention. With continued research and development, this green synthesis medium has the potential to revolutionize nanoparticle production across multiple industries, offering both economic and environmental benefits.
One of the primary advantages of sodium silicate-based synthesis is its potential for large-scale production. The raw materials are readily available and relatively inexpensive, making it an attractive option for industrial applications. Additionally, the process is generally less energy-intensive compared to traditional methods, which can lead to reduced production costs and improved sustainability.
However, scaling up the synthesis process presents several technical challenges. Maintaining consistent nanoparticle size and morphology across large batches can be difficult, as slight variations in reaction conditions can significantly impact the final product. Developing robust quality control measures and standardized production protocols is crucial for ensuring consistent results at an industrial scale.
The industrial applications of nanoparticles synthesized using sodium silicate are diverse and span multiple sectors. In the field of catalysis, these nanoparticles show promise for enhancing chemical reactions in various industrial processes. The automotive industry may benefit from incorporating these nanoparticles into coatings for improved durability and corrosion resistance. In the electronics sector, they could be used in the development of advanced sensors and electronic components.
Environmental remediation is another area where sodium silicate-synthesized nanoparticles show potential. Their high surface area and reactivity make them suitable for applications such as water treatment and soil decontamination. The construction industry may also benefit from incorporating these nanoparticles into building materials to enhance strength and durability.
To fully realize the industrial potential of this synthesis method, further research and development are needed. This includes optimizing reaction conditions for large-scale production, developing efficient separation and purification techniques, and exploring new applications across various industries. Collaboration between academic institutions and industrial partners will be crucial in addressing these challenges and advancing the technology towards commercial viability.
As the demand for sustainable and cost-effective nanoparticle synthesis methods continues to grow, sodium silicate-based processes are likely to gain increased attention. With continued research and development, this green synthesis medium has the potential to revolutionize nanoparticle production across multiple industries, offering both economic and environmental benefits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!