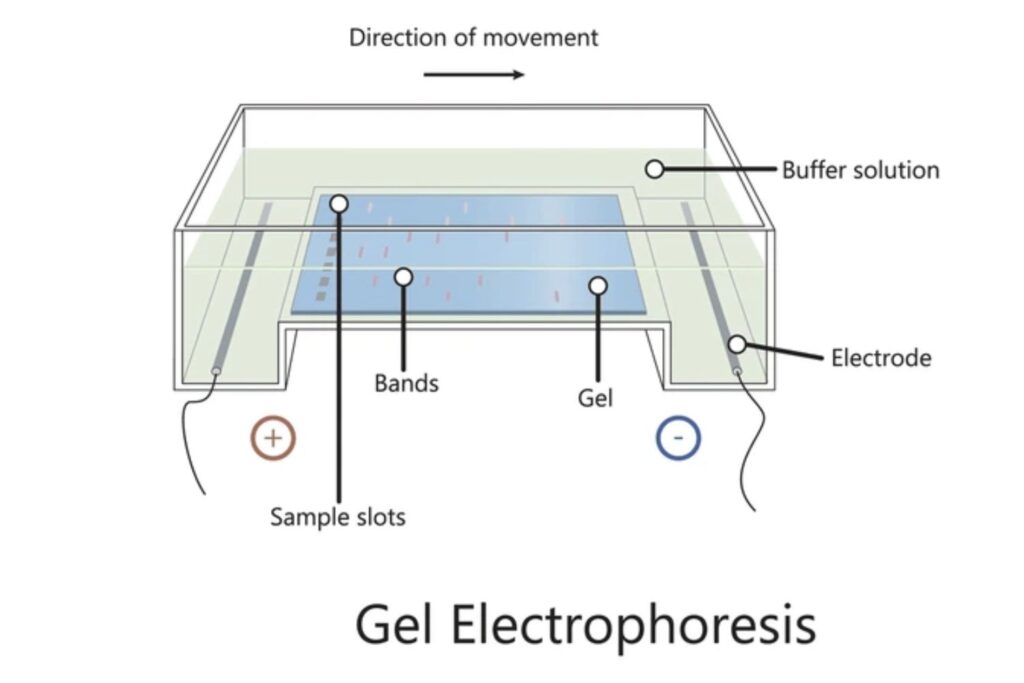
Gel electrophoresis is a cornerstone technique in molecular biology, enabling the separation and analysis of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. Its principle—molecule migration through a gel matrix under an electric field—has made it indispensable in genomic research, diagnostics, biotechnology, and forensic science.
As precision medicine, synthetic biology, and environmental genomics demand more accurate, high-throughput separation tools, gel electrophoresis continues to evolve. This article unpacks the science behind gel electrophoresis, explores its key applications, compares its strengths and limitations, highlights future trends, and integrates strategic insights via the PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.
Material Composition & Key Properties
- Gel electrophoresis typically utilizes agarose or polyacrylamide gels derived from seaweed polysaccharides or synthetic polymers.
- These gels are cast with wells and submerged in conductive buffer solutions that carry electric current.
- Molecules are driven through the gel based on their charge-to-mass ratio when voltage is applied.
- Key properties include:
- Excellent molecular sieving for size-based separation
- Compatibility with fluorescent and radioactive labeling
- Customizable pore sizes through gel concentration
- High reproducibility and affordability for routine lab use
Application Domains
1. Genomics & Molecular Biology
Gel electrophoresis is vital for DNA fragment analysis, plasmid screening, mutation identification, and CRISPR validation. Its simplicity and accuracy make it the gold standard in routine molecular biology workflows.
Research Frontlines: Integrating with real-time fluorescence imaging and AI-driven image quantification.
Related Reports:
- Gel Electrophoresis Techniques for DNA Analysis
- How Is Gel Electrophoresis Revolutionizing Molecular Biology?
- Enhancing Accuracy in Gel Electrophoresis: Tips & Tricks
- How to Optimize Gel Electrophoresis for DNA Separation?
- Advances in Gel Electrophoresis for RNA Analysis
- How to Improve Gel Electrophoresis Sensitivity?
- How to Prevent Band Smearing in Gel Electrophoresis?
2. Proteomics & Biochemistry
Gel electrophoresis enables protein sorting based on molecular weight or isoelectric point. It underpins Western blotting and 2D electrophoresis for biomarker discovery and disease profiling.
Research Frontlines: Innovations in native gel formats and combined gel–mass spectrometry pipelines.
Related Reports:
- Gel Electrophoresis Methods for Protein Sorting
- Gel Electrophoresis for Proteomics: Latest Developments
- Gel Electrophoresis: Techniques for Enhancing Precision
- How to Improve Protein Purification with Gel Electrophoresis?
- How to Improve Quantitative Analysis in Gel Electrophoresis?
- Gel Electrophoresis for Enzyme Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis in Structural Genomics: New Pathways
3. Biomedical Diagnostics & Personalized Medicine
As a diagnostic tool, gel electrophoresis helps detect genetic mutations, abnormal protein profiles, and microbial pathogens. It plays a growing role in patient-specific treatment strategies.
Research Frontlines: Microfluidic electrophoresis and lab-on-a-chip integrations.
Related Reports:
- Gel Electrophoresis in Diagnostics: Cutting-Edge Applications
- How Does Gel Electrophoresis Support Personalized Medicine?
- Gel Electrophoresis in Prenatal Testing: Future Directions
- Gel Electrophoresis for Biomarker Discovery: Latest Insights
- Gel Electrophoresis in Clinical Trials: Impact Analysis
- Gel Electrophoresis and Its Impact on Antibody Research
- Gel Electrophoresis in Veterinary Diagnostics: Top Uses
4. Forensics & Environmental Science
Gel electrophoresis assists in DNA fingerprinting, biodiversity tracking, and pollutant biomarker identification. Its reliability is crucial for legal, ecological, and public health applications.
Research Frontlines: Field-portable systems and eco-friendly gel formulations.
Related Reports:
- Gel Electrophoresis in Forensic Science: Key Innovations
- Gel Electrophoresis in Environmental Science: New Horizons
- How Does Gel Electrophoresis Enhance Biodiversity Studies?
- Gel Electrophoresis Applications in Environmental Bioremediation
- Gel Electrophoresis in Zoonotic Disease Studies: Advances
- Gel Electrophoresis in Civic Health Studies: Emerging Roles
- Gel Electrophoresis in Phytopathology: Recent Breakthroughs
5. Biotechnology & Synthetic Biology
From gene assembly monitoring to synthetic construct validation, gel electrophoresis is indispensable in synthetic biology workflows. It also supports advances in gene editing and synthetic genomes.
Research Frontlines: Coupling electrophoresis with real-time DNA assembly visualization and machine learning.
Related Reports:
- Gel Electrophoresis and CRISPR: Synergistic Advances
- Gel Electrophoresis and Its Role in Synthetic Biology
- Gel Electrophoresis in Biotechnology: Key Innovations
- How to Utilize Gel Electrophoresis for Mutation Screening?
- Gel Electrophoresis in Synthetic Genomics: Key Applications
- Gel Electrophoresis in Cell Genomics: Revolutionary Insights
- Gel Electrophoresis Techniques in Biomedical Engineering
Comparative Advantages & Limitations
Advantages:
● High precision for separating nucleic acids and proteins
● Low-cost and easy-to-implement in most lab settings
● Supports a wide range of applications from diagnostics to research
● Adaptable for fluorescent and colorimetric detection
Limitations:
● Limited throughput and automation in traditional setups
● Sample size constraints for certain gel formats
● Susceptibility to artifacts like smearing or diffusion
● Environmental impact from gel disposal and buffer waste
● Lower resolution compared to next-gen capillary electrophoresis in some use cases
Future Outlook & Research Frontiers
Over the next decade, gel electrophoresis is set to evolve into a smart, automated platform embedded within advanced analytical workflows. Expect developments in:
- AI-integrated imaging systems
- 3D gel electrophoresis and microfluidic formats
- Multiplexing and parallel analysis systems
- Ultra-sensitive detection for trace biomolecules
- Eco-sustainable gel and buffer alternatives
These trends will make gel electrophoresis more versatile, scalable, and sustainable for emerging fields such as precision agriculture, neurogenetics, and functional lipidomics.
Conclusion & Strategic Takeaways
Gel electrophoresis remains a foundational tool in the molecular sciences. Its simplicity, adaptability, and effectiveness across research, clinical, and industrial settings make it a vital instrument in advancing life science innovation. As precision, speed, and sustainability become priorities, gel electrophoresis is well-positioned to power the next generation of genomic and proteomic technologies.
Accelerate Innovation with PatSnap Eureka AI Agent
The research ecosystem around gel electrophoresis is becoming increasingly data-intensive and fragmented. With PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, you can:
- Discover emerging application clusters across thousands of global patents
- Benchmark top innovators and institutional R&D investments
- Identify untapped white spaces and cross-domain opportunities
👉 Ready to stay ahead of the molecular research curve through PatSnap Eureka AI Agent?