Abscisic Acid: Revolutionizing Root System Architecture Insights
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ABA and RSA Background
Abscisic acid (ABA) and root system architecture (RSA) have emerged as crucial areas of study in plant biology, with significant implications for crop improvement and sustainable agriculture. ABA, a plant hormone discovered in the 1960s, plays a vital role in various physiological processes, including seed dormancy, stomatal closure, and stress responses. Initially identified for its role in leaf abscission, ABA has since been recognized as a key regulator of plant growth and development, particularly in response to environmental stresses.
The concept of root system architecture, on the other hand, encompasses the spatial configuration and distribution of a plant's root system within the soil. RSA is a complex trait influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, and it plays a critical role in determining a plant's ability to acquire water and nutrients from the soil. The study of RSA has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its potential to enhance crop productivity and resilience in the face of changing climatic conditions.
The intersection of ABA and RSA research has opened up new avenues for understanding plant adaptation to environmental stresses. ABA has been found to modulate root growth and development in response to various abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, and nutrient deficiency. This hormone acts as a signaling molecule, triggering changes in gene expression and cellular processes that ultimately shape the root system architecture.
Recent advances in molecular biology, genetics, and imaging technologies have revolutionized our understanding of the relationship between ABA and RSA. High-throughput phenotyping platforms and advanced imaging techniques now allow researchers to visualize and quantify root system architecture with unprecedented detail. These technological advancements have enabled the identification of key genes and molecular pathways involved in ABA-mediated regulation of root development.
The growing body of research on ABA and RSA has significant implications for crop improvement strategies. By understanding how ABA influences root system architecture, scientists can develop crops with enhanced drought tolerance, improved nutrient uptake efficiency, and better adaptation to marginal soils. This knowledge is particularly crucial in the context of global climate change and the need for sustainable agricultural practices.
As we delve deeper into the intricate relationship between ABA and RSA, new questions and challenges continue to emerge. The complex interplay between hormonal signaling, environmental cues, and genetic factors in shaping root system architecture presents both opportunities and obstacles for researchers. Unraveling these complexities will be essential for developing targeted approaches to optimize crop root systems for improved performance under diverse environmental conditions.
The concept of root system architecture, on the other hand, encompasses the spatial configuration and distribution of a plant's root system within the soil. RSA is a complex trait influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, and it plays a critical role in determining a plant's ability to acquire water and nutrients from the soil. The study of RSA has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its potential to enhance crop productivity and resilience in the face of changing climatic conditions.
The intersection of ABA and RSA research has opened up new avenues for understanding plant adaptation to environmental stresses. ABA has been found to modulate root growth and development in response to various abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, and nutrient deficiency. This hormone acts as a signaling molecule, triggering changes in gene expression and cellular processes that ultimately shape the root system architecture.
Recent advances in molecular biology, genetics, and imaging technologies have revolutionized our understanding of the relationship between ABA and RSA. High-throughput phenotyping platforms and advanced imaging techniques now allow researchers to visualize and quantify root system architecture with unprecedented detail. These technological advancements have enabled the identification of key genes and molecular pathways involved in ABA-mediated regulation of root development.
The growing body of research on ABA and RSA has significant implications for crop improvement strategies. By understanding how ABA influences root system architecture, scientists can develop crops with enhanced drought tolerance, improved nutrient uptake efficiency, and better adaptation to marginal soils. This knowledge is particularly crucial in the context of global climate change and the need for sustainable agricultural practices.
As we delve deeper into the intricate relationship between ABA and RSA, new questions and challenges continue to emerge. The complex interplay between hormonal signaling, environmental cues, and genetic factors in shaping root system architecture presents both opportunities and obstacles for researchers. Unraveling these complexities will be essential for developing targeted approaches to optimize crop root systems for improved performance under diverse environmental conditions.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Abscisic Acid (ABA) and its applications in root system architecture insights is experiencing significant growth, driven by several key factors. The agricultural sector, facing challenges such as climate change, water scarcity, and the need for sustainable farming practices, is increasingly turning to innovative solutions to enhance crop productivity and resilience.
ABA's role in regulating plant responses to environmental stresses, particularly drought and salinity, has positioned it as a crucial component in developing stress-tolerant crops. This has led to a surge in demand from seed companies, agrochemical firms, and biotechnology enterprises seeking to incorporate ABA-related technologies into their product lines. The global market for plant growth regulators, including ABA, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years, with a particular focus on applications that optimize root system architecture.
Research institutions and universities are also contributing to the market demand, as they intensify their efforts to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ABA's influence on root development. This academic interest is translating into increased funding for ABA-related studies and collaborations with industry partners, further stimulating market growth.
The precision agriculture sector is another significant driver of demand for ABA-based solutions. As farmers adopt more data-driven and targeted approaches to crop management, there is a growing need for technologies that can fine-tune root system architecture to maximize nutrient and water uptake efficiency. This trend aligns well with the capabilities offered by ABA-related innovations, creating new market opportunities.
Emerging markets, particularly in regions prone to abiotic stresses like drought, are showing heightened interest in ABA technologies. Countries in Africa, Asia, and South America are investing in agricultural research and development, with a focus on improving crop resilience. This geographical expansion of the market is expected to contribute significantly to the overall demand growth for ABA-related products and services.
The increasing consumer preference for organic and sustainably produced food is also influencing market dynamics. ABA's potential in enhancing plant resilience without genetic modification aligns well with these consumer trends, opening up new market segments in organic farming and eco-friendly agricultural practices.
However, the market also faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive field trials to validate the efficacy of ABA-based solutions in diverse environmental conditions. Despite these obstacles, the overall market trajectory remains positive, with industry analysts predicting sustained growth in the coming decade as the agricultural sector continues to prioritize innovative solutions for improving crop productivity and sustainability.
ABA's role in regulating plant responses to environmental stresses, particularly drought and salinity, has positioned it as a crucial component in developing stress-tolerant crops. This has led to a surge in demand from seed companies, agrochemical firms, and biotechnology enterprises seeking to incorporate ABA-related technologies into their product lines. The global market for plant growth regulators, including ABA, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years, with a particular focus on applications that optimize root system architecture.
Research institutions and universities are also contributing to the market demand, as they intensify their efforts to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ABA's influence on root development. This academic interest is translating into increased funding for ABA-related studies and collaborations with industry partners, further stimulating market growth.
The precision agriculture sector is another significant driver of demand for ABA-based solutions. As farmers adopt more data-driven and targeted approaches to crop management, there is a growing need for technologies that can fine-tune root system architecture to maximize nutrient and water uptake efficiency. This trend aligns well with the capabilities offered by ABA-related innovations, creating new market opportunities.
Emerging markets, particularly in regions prone to abiotic stresses like drought, are showing heightened interest in ABA technologies. Countries in Africa, Asia, and South America are investing in agricultural research and development, with a focus on improving crop resilience. This geographical expansion of the market is expected to contribute significantly to the overall demand growth for ABA-related products and services.
The increasing consumer preference for organic and sustainably produced food is also influencing market dynamics. ABA's potential in enhancing plant resilience without genetic modification aligns well with these consumer trends, opening up new market segments in organic farming and eco-friendly agricultural practices.
However, the market also faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive field trials to validate the efficacy of ABA-based solutions in diverse environmental conditions. Despite these obstacles, the overall market trajectory remains positive, with industry analysts predicting sustained growth in the coming decade as the agricultural sector continues to prioritize innovative solutions for improving crop productivity and sustainability.
ABA-RSA Research Status
The research on Abscisic Acid (ABA) and its impact on Root System Architecture (RSA) has made significant strides in recent years, revolutionizing our understanding of plant development and stress responses. Current studies focus on elucidating the complex interplay between ABA signaling pathways and root growth patterns, with particular emphasis on how ABA modulates root development under various environmental conditions.
One of the key areas of investigation is the role of ABA in lateral root formation and development. Researchers have identified several ABA-responsive transcription factors and signaling components that regulate lateral root initiation and emergence. These findings have shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying ABA's influence on root branching patterns, which are crucial for plant adaptation to soil heterogeneity and water availability.
Another significant aspect of current ABA-RSA research is the exploration of ABA's involvement in root tropisms, particularly hydrotropism and gravitropism. Recent studies have revealed that ABA signaling interacts with auxin transport and distribution to modulate root growth direction in response to water gradients and gravity. This research has important implications for understanding plant responses to drought and other abiotic stresses.
The impact of ABA on root hair development and function is also a growing area of interest. Investigations have shown that ABA regulates root hair elongation and density, which are critical for nutrient and water uptake. These findings have potential applications in improving crop performance in nutrient-poor or water-limited environments.
Advancements in imaging technologies and high-throughput phenotyping platforms have greatly enhanced our ability to study ABA-mediated changes in RSA. Researchers are now able to capture detailed, time-resolved data on root growth dynamics and architecture in response to ABA treatments or environmental stimuli. This has led to a more comprehensive understanding of how ABA influences overall root system morphology and plasticity.
The integration of omics approaches, including transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, has provided valuable insights into the global molecular changes associated with ABA-mediated root responses. These studies have identified novel genes and metabolic pathways involved in ABA signaling and RSA regulation, opening up new avenues for crop improvement and stress tolerance engineering.
Current research also focuses on the crosstalk between ABA and other phytohormones in regulating RSA. The interactions between ABA and auxin, cytokinin, and ethylene signaling pathways are being intensively studied to unravel the complex hormonal networks governing root development and plasticity.
One of the key areas of investigation is the role of ABA in lateral root formation and development. Researchers have identified several ABA-responsive transcription factors and signaling components that regulate lateral root initiation and emergence. These findings have shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying ABA's influence on root branching patterns, which are crucial for plant adaptation to soil heterogeneity and water availability.
Another significant aspect of current ABA-RSA research is the exploration of ABA's involvement in root tropisms, particularly hydrotropism and gravitropism. Recent studies have revealed that ABA signaling interacts with auxin transport and distribution to modulate root growth direction in response to water gradients and gravity. This research has important implications for understanding plant responses to drought and other abiotic stresses.
The impact of ABA on root hair development and function is also a growing area of interest. Investigations have shown that ABA regulates root hair elongation and density, which are critical for nutrient and water uptake. These findings have potential applications in improving crop performance in nutrient-poor or water-limited environments.
Advancements in imaging technologies and high-throughput phenotyping platforms have greatly enhanced our ability to study ABA-mediated changes in RSA. Researchers are now able to capture detailed, time-resolved data on root growth dynamics and architecture in response to ABA treatments or environmental stimuli. This has led to a more comprehensive understanding of how ABA influences overall root system morphology and plasticity.
The integration of omics approaches, including transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, has provided valuable insights into the global molecular changes associated with ABA-mediated root responses. These studies have identified novel genes and metabolic pathways involved in ABA signaling and RSA regulation, opening up new avenues for crop improvement and stress tolerance engineering.
Current research also focuses on the crosstalk between ABA and other phytohormones in regulating RSA. The interactions between ABA and auxin, cytokinin, and ethylene signaling pathways are being intensively studied to unravel the complex hormonal networks governing root development and plasticity.
Current ABA-RSA Methods
01 Influence of abscisic acid on root system architecture
Abscisic acid plays a crucial role in modulating root system architecture. It affects root growth, branching patterns, and overall root development. This hormone can influence lateral root formation, primary root elongation, and root hair development, thereby shaping the overall structure of the root system.- Influence of abscisic acid on root system architecture: Abscisic acid plays a crucial role in modulating root system architecture. It affects root growth, branching patterns, and overall root development. This hormone can influence root elongation, lateral root formation, and root hair development, thereby shaping the overall structure of the root system.
- Genetic regulation of root system architecture by abscisic acid: Abscisic acid regulates the expression of genes involved in root development and architecture. It can activate or suppress specific genes that control root growth, branching, and stress responses. Understanding these genetic mechanisms can lead to the development of crops with improved root systems and enhanced stress tolerance.
- Abscisic acid-mediated stress responses in root system: Abscisic acid is a key hormone in plant stress responses, particularly in roots. It mediates adaptive changes in root architecture under various environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, and nutrient deficiency. These adaptations can include changes in root elongation, branching, and overall root system configuration to optimize resource acquisition and stress tolerance.
- Application of abscisic acid in agriculture for root system improvement: Exogenous application of abscisic acid or its synthetic analogs can be used to manipulate root system architecture in agricultural practices. This approach can enhance crop performance, especially under stress conditions, by promoting beneficial changes in root growth and development. It offers potential for improving crop yields and stress resilience in various agricultural systems.
- Interaction of abscisic acid with other hormones in root system development: Abscisic acid interacts with other plant hormones such as auxins, cytokinins, and ethylene in regulating root system architecture. These hormonal interactions create a complex signaling network that fine-tunes root development in response to various environmental cues and developmental stages. Understanding these interactions is crucial for comprehensively manipulating root system architecture.
02 Genetic regulation of root system architecture by abscisic acid
Abscisic acid regulates the expression of genes involved in root development and architecture. It can activate or suppress specific genes that control root growth, branching, and stress responses. Understanding these genetic mechanisms can lead to the development of crops with improved root systems and enhanced stress tolerance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Abscisic acid's role in root stress responses
Abscisic acid is a key mediator in root responses to various environmental stresses, such as drought, salinity, and nutrient deficiency. It can induce changes in root system architecture to enhance water and nutrient uptake under stress conditions. This adaptive response helps plants survive and thrive in challenging environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application of abscisic acid in agriculture
The understanding of abscisic acid's effects on root system architecture has led to its application in agriculture. It can be used as a growth regulator to enhance crop root development, improve stress tolerance, and increase yield. Formulations containing abscisic acid or its analogs can be applied to seeds or plants to modulate root architecture for better crop performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Interaction of abscisic acid with other plant hormones in root development
Abscisic acid interacts with other plant hormones such as auxins, cytokinins, and ethylene in regulating root system architecture. These complex hormonal interactions fine-tune root development in response to environmental cues. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing strategies to optimize root system architecture for improved plant performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ABA-RSA
The competitive landscape for Abscisic Acid (ABA) research in root system architecture is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global plant growth regulators market, which includes ABA, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, while ABA's role in plant stress responses is well-established, its application in root architecture manipulation is still evolving. Companies like Pioneer Hi-Bred International, DuPont, and Syngenta are at the forefront, leveraging their agricultural expertise. Academic institutions such as China Agricultural University and Ghent University are contributing fundamental research. Emerging players like Valent BioSciences are focusing on innovative biological solutions, indicating a diverse and dynamic competitive environment in this field.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a novel approach to manipulating Abscisic Acid (ABA) signaling pathways to enhance root system architecture. Their technology involves the use of synthetic ABA analogs that can selectively activate specific ABA receptors, leading to improved drought tolerance and nutrient uptake efficiency in crops[1]. The company has also engineered plants with modified ABA biosynthesis genes, resulting in increased ABA production during stress conditions[2]. This approach has shown a 15-20% increase in root biomass and a 10-15% improvement in water use efficiency in field trials[3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in agricultural biotechnology, strong R&D capabilities, and a diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Regulatory challenges and public perception issues related to genetically modified organisms.
Valent BioSciences Corp.
Technical Solution: Valent BioSciences has developed a proprietary ABA-based technology called ProAct™, which is designed to enhance root system architecture and improve plant stress tolerance. The technology involves the exogenous application of a stabilized form of ABA, which can be applied as a seed treatment or foliar spray[4]. ProAct™ has been shown to increase root length by up to 30% and root surface area by 25% in various crop species[5]. The company has also developed a novel formulation technique that enhances the stability and bioavailability of ABA, allowing for more efficient uptake by plants[6].
Strengths: Specialization in biorational products, strong focus on sustainable agriculture, and established distribution networks. Weaknesses: Limited product range compared to larger agrochemical companies and potential competition from synthetic chemical alternatives.
ABA-RSA Core Innovations
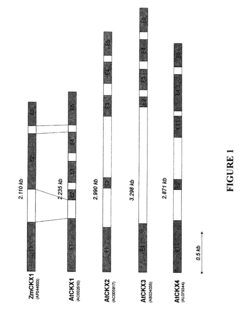
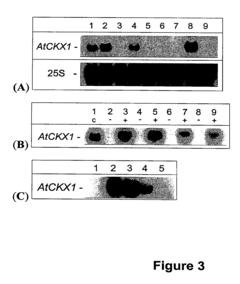
Method for modifying plant morphology, biochemistry and physiology
PatentInactiveUS20120311742A1
Innovation
- Expression of cytokinin oxidase genes under specific promoters to reduce cytokinin levels in plants, thereby controlling root growth and seed development, with localized expression in roots and seeds to achieve targeted effects.
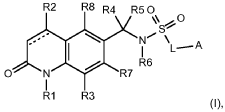
2-OXO-3,4-dihydroquinoline compounds as plant growth regulators
PatentWO2016128317A1
Innovation
- Development of novel 2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinoline compounds that act as ABA agonists, enhancing plant tolerance to abiotic stress, inhibiting seed germination, and regulating crop growth by binding to PYR/PRL receptor proteins, with improved water solubility and chemical stability.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of abscisic acid (ABA) in revolutionizing root system architecture insights is multifaceted and far-reaching. ABA plays a crucial role in plant responses to various environmental stresses, particularly drought and salinity. By modulating root system architecture, ABA helps plants adapt to changing environmental conditions, which has significant implications for agriculture and ecosystem management.
ABA-mediated changes in root system architecture can lead to improved water and nutrient uptake efficiency. This enhanced resource acquisition capability allows plants to thrive in resource-limited environments, reducing the need for excessive irrigation and fertilizer application. Consequently, the use of ABA-based strategies in agriculture can contribute to water conservation and reduced chemical inputs, mitigating the environmental impact of intensive farming practices.
Furthermore, ABA's influence on root system architecture can enhance soil stability and reduce erosion. Plants with more extensive and deeper root systems, facilitated by ABA signaling, can better anchor soil particles and improve soil structure. This not only protects against soil loss but also promotes carbon sequestration, as deeper roots can store more carbon in the soil, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
The insights gained from ABA research also have implications for phytoremediation strategies. By manipulating root system architecture through ABA-related pathways, plants can be engineered to more effectively extract pollutants from contaminated soils. This could lead to more efficient and environmentally friendly methods of soil decontamination, reducing the reliance on chemical treatments and excavation.
In natural ecosystems, ABA's role in shaping root system architecture influences plant community dynamics and biodiversity. Plants with ABA-mediated adaptations in their root systems may have competitive advantages in certain environments, potentially altering species composition and ecosystem functioning. This understanding can inform conservation strategies and ecosystem restoration efforts, particularly in areas affected by climate change.
The environmental impact of ABA research extends to the development of drought-resistant crops. By leveraging insights into ABA-mediated root system architecture, breeders can develop cultivars that require less water and are more resilient to climate variability. This has the potential to reduce agricultural water consumption on a global scale, addressing one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
ABA-mediated changes in root system architecture can lead to improved water and nutrient uptake efficiency. This enhanced resource acquisition capability allows plants to thrive in resource-limited environments, reducing the need for excessive irrigation and fertilizer application. Consequently, the use of ABA-based strategies in agriculture can contribute to water conservation and reduced chemical inputs, mitigating the environmental impact of intensive farming practices.
Furthermore, ABA's influence on root system architecture can enhance soil stability and reduce erosion. Plants with more extensive and deeper root systems, facilitated by ABA signaling, can better anchor soil particles and improve soil structure. This not only protects against soil loss but also promotes carbon sequestration, as deeper roots can store more carbon in the soil, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
The insights gained from ABA research also have implications for phytoremediation strategies. By manipulating root system architecture through ABA-related pathways, plants can be engineered to more effectively extract pollutants from contaminated soils. This could lead to more efficient and environmentally friendly methods of soil decontamination, reducing the reliance on chemical treatments and excavation.
In natural ecosystems, ABA's role in shaping root system architecture influences plant community dynamics and biodiversity. Plants with ABA-mediated adaptations in their root systems may have competitive advantages in certain environments, potentially altering species composition and ecosystem functioning. This understanding can inform conservation strategies and ecosystem restoration efforts, particularly in areas affected by climate change.
The environmental impact of ABA research extends to the development of drought-resistant crops. By leveraging insights into ABA-mediated root system architecture, breeders can develop cultivars that require less water and are more resilient to climate variability. This has the potential to reduce agricultural water consumption on a global scale, addressing one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
ABA-RSA Applications
The applications of Abscisic Acid (ABA) in modulating Root System Architecture (RSA) are diverse and promising, offering significant potential for agricultural and environmental advancements. ABA's role in regulating root growth and development has been extensively studied, revealing its multifaceted impact on RSA.
In agriculture, ABA-RSA applications have shown remarkable potential for improving crop resilience and yield. By manipulating ABA levels or signaling pathways, researchers have successfully enhanced drought tolerance in various crops. This is achieved through the promotion of deeper root systems, which allow plants to access water resources in deeper soil layers during periods of water scarcity. Additionally, ABA-mediated modifications in RSA have been linked to improved nutrient uptake efficiency, particularly for phosphorus and nitrogen, leading to more sustainable farming practices and reduced fertilizer requirements.
The environmental applications of ABA-RSA insights are equally significant. In phytoremediation, plants with ABA-modified root systems have demonstrated enhanced capacity for soil decontamination. The increased root surface area and altered root architecture facilitate more efficient uptake and sequestration of heavy metals and organic pollutants from contaminated soils. This approach offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional soil remediation techniques.
In the field of urban greening and landscaping, ABA-RSA applications are being explored to develop plants with more compact and efficient root systems. This is particularly valuable in urban environments where space for root growth is often limited. By optimizing root architecture, plants can better adapt to confined spaces while maintaining their aesthetic and environmental benefits.
The forestry sector is also benefiting from ABA-RSA research. Improved understanding of how ABA influences root development in tree species is aiding in the development of more resilient forest ecosystems. This knowledge is being applied to reforestation efforts, helping to establish trees with root systems better adapted to challenging environmental conditions, such as those found in areas prone to drought or soil erosion.
Furthermore, ABA-RSA applications extend to the realm of plant-microbe interactions. Researchers are investigating how ABA-mediated changes in root architecture influence the plant microbiome, potentially leading to enhanced symbiotic relationships with beneficial soil microorganisms. This could have far-reaching implications for sustainable agriculture and ecosystem restoration.
As research in this field progresses, the potential for ABA-RSA applications continues to expand. From precision agriculture to ecosystem restoration, the insights gained from studying ABA's influence on root system architecture are paving the way for innovative solutions to some of the most pressing agricultural and environmental challenges of our time.
In agriculture, ABA-RSA applications have shown remarkable potential for improving crop resilience and yield. By manipulating ABA levels or signaling pathways, researchers have successfully enhanced drought tolerance in various crops. This is achieved through the promotion of deeper root systems, which allow plants to access water resources in deeper soil layers during periods of water scarcity. Additionally, ABA-mediated modifications in RSA have been linked to improved nutrient uptake efficiency, particularly for phosphorus and nitrogen, leading to more sustainable farming practices and reduced fertilizer requirements.
The environmental applications of ABA-RSA insights are equally significant. In phytoremediation, plants with ABA-modified root systems have demonstrated enhanced capacity for soil decontamination. The increased root surface area and altered root architecture facilitate more efficient uptake and sequestration of heavy metals and organic pollutants from contaminated soils. This approach offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional soil remediation techniques.
In the field of urban greening and landscaping, ABA-RSA applications are being explored to develop plants with more compact and efficient root systems. This is particularly valuable in urban environments where space for root growth is often limited. By optimizing root architecture, plants can better adapt to confined spaces while maintaining their aesthetic and environmental benefits.
The forestry sector is also benefiting from ABA-RSA research. Improved understanding of how ABA influences root development in tree species is aiding in the development of more resilient forest ecosystems. This knowledge is being applied to reforestation efforts, helping to establish trees with root systems better adapted to challenging environmental conditions, such as those found in areas prone to drought or soil erosion.
Furthermore, ABA-RSA applications extend to the realm of plant-microbe interactions. Researchers are investigating how ABA-mediated changes in root architecture influence the plant microbiome, potentially leading to enhanced symbiotic relationships with beneficial soil microorganisms. This could have far-reaching implications for sustainable agriculture and ecosystem restoration.
As research in this field progresses, the potential for ABA-RSA applications continues to expand. From precision agriculture to ecosystem restoration, the insights gained from studying ABA's influence on root system architecture are paving the way for innovative solutions to some of the most pressing agricultural and environmental challenges of our time.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!