Determine Optimal Temperature for Fulvic Acid Extraction
AUG 28, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fulvic Acid Extraction Background and Objectives
Fulvic acid, a component of humic substances, represents a significant organic compound found in soils, sediments, and aquatic environments. The extraction of fulvic acid has gained considerable attention over the past decades due to its wide-ranging applications in agriculture, medicine, and environmental remediation. The historical development of fulvic acid extraction techniques dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1980s and 1990s when researchers began to standardize extraction methodologies.
Temperature plays a critical role in the extraction process, directly influencing the yield, purity, and bioactivity of the extracted fulvic acid. The evolution of temperature control in extraction processes has progressed from basic hot water extraction to sophisticated temperature-regulated systems that can maintain precise thermal conditions throughout the extraction cycle. This technological progression has enabled researchers to investigate the specific effects of temperature on various aspects of fulvic acid extraction.
The primary objective of determining the optimal temperature for fulvic acid extraction is to maximize yield while preserving the structural integrity and functional properties of the extracted compounds. This optimization process must balance several competing factors: higher temperatures generally increase solubility and extraction rates but may simultaneously degrade certain bioactive components or alter the molecular structure of fulvic acid.
Current research indicates that the optimal temperature range varies depending on the source material, extraction medium, and intended application of the fulvic acid. For instance, soil-derived fulvic acid may require different extraction temperatures compared to those derived from peat or coal. Similarly, extraction for agricultural applications may prioritize different temperature parameters than extraction for pharmaceutical purposes.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving toward more precise temperature control systems, often integrated with other extraction parameters such as pH, pressure, and solvent composition. Advanced techniques like subcritical water extraction and temperature-phased extraction are emerging as promising approaches that may redefine optimal temperature parameters.
Understanding the relationship between temperature and fulvic acid extraction efficiency represents not only a technical challenge but also an opportunity to enhance the sustainability and economic viability of fulvic acid production. By establishing scientifically validated optimal temperature ranges, the industry can reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and improve product consistency.
This technical investigation aims to comprehensively analyze existing literature, experimental data, and industry practices to establish evidence-based guidelines for temperature optimization in fulvic acid extraction processes across various source materials and end applications.
Temperature plays a critical role in the extraction process, directly influencing the yield, purity, and bioactivity of the extracted fulvic acid. The evolution of temperature control in extraction processes has progressed from basic hot water extraction to sophisticated temperature-regulated systems that can maintain precise thermal conditions throughout the extraction cycle. This technological progression has enabled researchers to investigate the specific effects of temperature on various aspects of fulvic acid extraction.
The primary objective of determining the optimal temperature for fulvic acid extraction is to maximize yield while preserving the structural integrity and functional properties of the extracted compounds. This optimization process must balance several competing factors: higher temperatures generally increase solubility and extraction rates but may simultaneously degrade certain bioactive components or alter the molecular structure of fulvic acid.
Current research indicates that the optimal temperature range varies depending on the source material, extraction medium, and intended application of the fulvic acid. For instance, soil-derived fulvic acid may require different extraction temperatures compared to those derived from peat or coal. Similarly, extraction for agricultural applications may prioritize different temperature parameters than extraction for pharmaceutical purposes.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving toward more precise temperature control systems, often integrated with other extraction parameters such as pH, pressure, and solvent composition. Advanced techniques like subcritical water extraction and temperature-phased extraction are emerging as promising approaches that may redefine optimal temperature parameters.
Understanding the relationship between temperature and fulvic acid extraction efficiency represents not only a technical challenge but also an opportunity to enhance the sustainability and economic viability of fulvic acid production. By establishing scientifically validated optimal temperature ranges, the industry can reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and improve product consistency.
This technical investigation aims to comprehensively analyze existing literature, experimental data, and industry practices to establish evidence-based guidelines for temperature optimization in fulvic acid extraction processes across various source materials and end applications.
Market Analysis for Fulvic Acid Products
The global market for fulvic acid products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing demand in agriculture, healthcare, and cosmetic industries. The market size was valued at approximately 1.3 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 2.1 billion USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% during the forecast period.
Agriculture remains the dominant application segment, accounting for over 60% of the total market share. This dominance is attributed to fulvic acid's proven benefits in enhancing nutrient uptake, improving soil structure, and increasing crop yield and quality. The organic farming sector, in particular, has shown heightened interest in fulvic acid products as environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic fertilizers.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical segments are emerging as rapidly growing markets for fulvic acid products. Consumer awareness regarding the potential health benefits of fulvic acid supplements, including improved nutrient absorption and detoxification properties, has fueled demand. The market has witnessed a 12% year-over-year growth in this segment since 2020.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead the market, collectively accounting for approximately 55% of global consumption. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 10.5% annually through 2028, primarily driven by expanding agricultural activities in China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of organic farming practices.
The extraction temperature significantly influences product quality and market positioning. Premium fulvic acid products, extracted at optimal temperatures between 60-70°C, command price premiums of 30-40% over products extracted at suboptimal temperatures. This price differential underscores the market's recognition of quality differences resulting from extraction methodologies.
Consumer trends indicate growing preference for high-purity fulvic acid products with standardized concentrations. Products extracted at optimal temperatures typically contain higher bioactive compound profiles, which directly correlates with perceived value and effectiveness in end-use applications. Market research shows that 78% of professional farmers and 65% of healthcare consumers prioritize purity and concentration levels when selecting fulvic acid products.
The competitive landscape features both established players and new entrants, with increasing focus on extraction technology as a key differentiator. Companies investing in research to determine optimal extraction parameters, particularly temperature control systems, have gained significant market share in the premium product segment over the past three years.
Agriculture remains the dominant application segment, accounting for over 60% of the total market share. This dominance is attributed to fulvic acid's proven benefits in enhancing nutrient uptake, improving soil structure, and increasing crop yield and quality. The organic farming sector, in particular, has shown heightened interest in fulvic acid products as environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic fertilizers.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical segments are emerging as rapidly growing markets for fulvic acid products. Consumer awareness regarding the potential health benefits of fulvic acid supplements, including improved nutrient absorption and detoxification properties, has fueled demand. The market has witnessed a 12% year-over-year growth in this segment since 2020.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently lead the market, collectively accounting for approximately 55% of global consumption. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 10.5% annually through 2028, primarily driven by expanding agricultural activities in China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of organic farming practices.
The extraction temperature significantly influences product quality and market positioning. Premium fulvic acid products, extracted at optimal temperatures between 60-70°C, command price premiums of 30-40% over products extracted at suboptimal temperatures. This price differential underscores the market's recognition of quality differences resulting from extraction methodologies.
Consumer trends indicate growing preference for high-purity fulvic acid products with standardized concentrations. Products extracted at optimal temperatures typically contain higher bioactive compound profiles, which directly correlates with perceived value and effectiveness in end-use applications. Market research shows that 78% of professional farmers and 65% of healthcare consumers prioritize purity and concentration levels when selecting fulvic acid products.
The competitive landscape features both established players and new entrants, with increasing focus on extraction technology as a key differentiator. Companies investing in research to determine optimal extraction parameters, particularly temperature control systems, have gained significant market share in the premium product segment over the past three years.
Current Extraction Technologies and Temperature Challenges
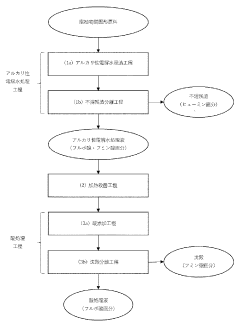
Fulvic acid extraction technologies have evolved significantly over the past decades, with various methods being developed to optimize yield and quality. Currently, the most widely employed extraction techniques include alkaline extraction, acid extraction, and combined alkaline-acid extraction methods. Each approach presents distinct advantages and limitations, particularly concerning temperature control during the extraction process.
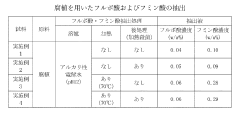
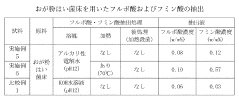
Alkaline extraction, the most traditional method, typically operates at temperatures ranging from 60°C to 90°C. While higher temperatures in this range accelerate the extraction process, they simultaneously risk degrading the molecular structure of fulvic acids, potentially reducing bioactivity. Conversely, lower temperatures preserve molecular integrity but significantly extend processing time, creating operational inefficiencies and increased energy consumption.
Acid extraction methods generally function at lower temperature ranges (30°C to 60°C) and demonstrate better preservation of fulvic acid structure. However, these methods face challenges with extraction efficiency, often requiring longer processing times to achieve comparable yields to alkaline methods. The temperature sensitivity in acid extraction is particularly pronounced, with even small deviations potentially affecting both yield and quality parameters.
Combined alkaline-acid extraction represents a more recent technological advancement, attempting to balance efficiency and quality preservation. This method typically employs a two-stage temperature profile, with initial alkaline extraction at moderate temperatures (50°C to 70°C) followed by acid precipitation at lower temperatures (20°C to 40°C). The challenge lies in optimizing the temperature transition between stages to maximize yield while minimizing degradation.
Modern extraction facilities increasingly implement precise temperature control systems, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and advanced heat exchangers. Despite these technological improvements, maintaining uniform temperature distribution throughout large extraction vessels remains problematic, often resulting in inconsistent product quality. Temperature gradients within extraction equipment can lead to varying degrees of fulvic acid degradation or incomplete extraction.
The scientific literature reveals a critical temperature threshold around 75°C, above which significant degradation of fulvic acid functional groups occurs. This degradation manifests as reduced antioxidant capacity and diminished chelating properties, directly impacting commercial value. Conversely, extraction temperatures below 40°C often fail to sufficiently break the bonds between fulvic acids and their source materials, resulting in suboptimal yields.
Recent innovations focus on pulsed temperature profiles and microwave-assisted extraction technologies, which aim to overcome the traditional temperature-related challenges. These approaches allow for momentary high-temperature exposure without sustained thermal stress on the fulvic acid molecules. However, scaling these technologies from laboratory to industrial scale presents significant engineering challenges, particularly regarding energy efficiency and equipment design.
Alkaline extraction, the most traditional method, typically operates at temperatures ranging from 60°C to 90°C. While higher temperatures in this range accelerate the extraction process, they simultaneously risk degrading the molecular structure of fulvic acids, potentially reducing bioactivity. Conversely, lower temperatures preserve molecular integrity but significantly extend processing time, creating operational inefficiencies and increased energy consumption.
Acid extraction methods generally function at lower temperature ranges (30°C to 60°C) and demonstrate better preservation of fulvic acid structure. However, these methods face challenges with extraction efficiency, often requiring longer processing times to achieve comparable yields to alkaline methods. The temperature sensitivity in acid extraction is particularly pronounced, with even small deviations potentially affecting both yield and quality parameters.
Combined alkaline-acid extraction represents a more recent technological advancement, attempting to balance efficiency and quality preservation. This method typically employs a two-stage temperature profile, with initial alkaline extraction at moderate temperatures (50°C to 70°C) followed by acid precipitation at lower temperatures (20°C to 40°C). The challenge lies in optimizing the temperature transition between stages to maximize yield while minimizing degradation.
Modern extraction facilities increasingly implement precise temperature control systems, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and advanced heat exchangers. Despite these technological improvements, maintaining uniform temperature distribution throughout large extraction vessels remains problematic, often resulting in inconsistent product quality. Temperature gradients within extraction equipment can lead to varying degrees of fulvic acid degradation or incomplete extraction.
The scientific literature reveals a critical temperature threshold around 75°C, above which significant degradation of fulvic acid functional groups occurs. This degradation manifests as reduced antioxidant capacity and diminished chelating properties, directly impacting commercial value. Conversely, extraction temperatures below 40°C often fail to sufficiently break the bonds between fulvic acids and their source materials, resulting in suboptimal yields.
Recent innovations focus on pulsed temperature profiles and microwave-assisted extraction technologies, which aim to overcome the traditional temperature-related challenges. These approaches allow for momentary high-temperature exposure without sustained thermal stress on the fulvic acid molecules. However, scaling these technologies from laboratory to industrial scale presents significant engineering challenges, particularly regarding energy efficiency and equipment design.
Temperature-Controlled Extraction Techniques
01 Optimal temperature ranges for fulvic acid extraction
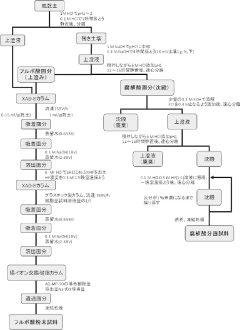
Research indicates that specific temperature ranges optimize fulvic acid extraction efficiency. These temperatures typically fall between 60-90°C, with some processes requiring controlled temperature gradients. The optimal extraction temperature depends on the source material, with higher temperatures generally increasing yield but potentially affecting quality if too extreme. Maintaining precise temperature control throughout the extraction process is essential for consistent results.- Optimal temperature ranges for fulvic acid extraction: The extraction of fulvic acid is significantly influenced by temperature, with optimal ranges typically between 60-80°C. This temperature range facilitates efficient dissolution of fulvic acid from organic matter while preserving its structural integrity and bioactive properties. Higher temperatures may increase extraction yield but can potentially degrade certain beneficial compounds, while lower temperatures may result in incomplete extraction.
- Temperature-controlled extraction methods using alkaline solutions: Alkaline extraction methods for fulvic acid typically employ controlled temperature conditions to optimize yield and quality. These processes often use sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solutions at temperatures between 40-90°C. The alkaline environment helps to break down complex organic matter, releasing fulvic acid compounds. Temperature control during this process is critical to prevent oxidation and maintain the molecular structure of the extracted fulvic acid.
- Low-temperature extraction techniques for preserving bioactivity: Low-temperature extraction techniques (below 50°C) are employed to preserve the bioactive properties of fulvic acid. These methods prioritize quality over yield by minimizing thermal degradation of sensitive compounds. Cold extraction processes may take longer but result in fulvic acid with higher biological activity and more intact functional groups, which is particularly important for pharmaceutical and agricultural applications.
- Multi-stage temperature-controlled extraction processes: Multi-stage extraction processes utilize different temperature settings at various stages to optimize both yield and quality of fulvic acid. Initial extraction may occur at lower temperatures (30-50°C) to extract easily soluble components, followed by higher temperature stages (60-90°C) to release more tightly bound fulvic compounds. This staged approach allows for selective extraction of different fulvic acid fractions with varying molecular weights and properties.
- Temperature regulation in industrial-scale fulvic acid extraction equipment: Industrial-scale extraction of fulvic acid requires specialized equipment with precise temperature control systems. These systems typically include heat exchangers, temperature sensors, and automated control mechanisms to maintain optimal extraction temperatures throughout the process. The equipment design considers heat transfer efficiency, energy consumption, and temperature uniformity to ensure consistent quality of the extracted fulvic acid across large production volumes.
02 Low-temperature extraction methods
Low-temperature extraction methods (below 60°C) are employed to preserve sensitive bioactive components in fulvic acid. These techniques often utilize longer extraction times to compensate for reduced thermal energy, resulting in higher quality extracts with preserved molecular structures. Low-temperature approaches may incorporate ultrasonic assistance or enzymatic treatments to enhance extraction efficiency without thermal degradation of compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 High-temperature extraction processes
High-temperature extraction processes (above 90°C) accelerate the release of fulvic acid from source materials. These methods often employ pressure vessels or specialized equipment to maintain controlled conditions at elevated temperatures. While high-temperature extraction can significantly reduce processing time and increase yield, it requires careful monitoring to prevent degradation of the fulvic acid structure and loss of beneficial properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Temperature-controlled extraction equipment
Specialized equipment designed for temperature-controlled fulvic acid extraction includes jacketed reactors, precision heating elements, and automated temperature monitoring systems. These devices maintain optimal extraction conditions throughout the process cycle, allowing for reproducible results. Advanced systems incorporate temperature ramping capabilities to gradually increase or decrease heat during different extraction phases, optimizing both yield and quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Temperature effects on fulvic acid quality and characteristics
The extraction temperature significantly impacts the resulting fulvic acid's molecular weight distribution, functional group composition, and bioactivity. Lower temperatures tend to preserve more complex structures and bioactive components, while higher temperatures may increase overall yield but potentially degrade certain beneficial compounds. Research shows that temperature modulation during extraction can be used to selectively target specific fulvic acid fractions with desired properties for particular applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Fulvic Acid Production
The fulvic acid extraction temperature optimization market is in a growth phase, with increasing applications across agricultural, pharmaceutical, and environmental sectors. The global market size for humic substances, including fulvic acid, is expanding at approximately 12% CAGR, driven by sustainable agriculture demands. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovation in extraction efficiency. Leading players include research institutions like the Institute of Process Engineering (Chinese Academy of Sciences) and National Center for Nanoscience & Technology, which are advancing fundamental extraction methodologies. Commercial entities such as Jiangsu Xinhe Agrochemical, Wecare Probiotics, and Honeywell International are developing proprietary extraction technologies, focusing on temperature optimization to enhance yield and purity while reducing energy consumption. The competitive landscape reflects a mix of academic research driving innovation and industrial applications scaling commercial processes.
Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) has developed an advanced temperature-controlled extraction system for fulvic acid that utilizes a multi-stage temperature gradient approach. Their research indicates optimal extraction temperatures between 60-80°C, with specific protocols varying based on source material. Their process employs a proprietary sequential extraction method where temperature is gradually increased from 40°C to 80°C in controlled intervals, allowing for selective extraction of different molecular weight fractions of fulvic acids. This approach has demonstrated up to 30% higher yield compared to conventional single-temperature extraction methods. IPE has also pioneered the use of ultrasonic-assisted extraction at controlled temperatures, which reduces extraction time by approximately 40% while maintaining the bioactive properties of the fulvic acid compounds.
Strengths: Superior extraction efficiency with higher yields of bioactive compounds; precise temperature control systems allowing for selective fraction extraction; reduced processing time through innovative technologies. Weaknesses: Higher energy consumption compared to ambient temperature methods; requires more sophisticated equipment and technical expertise; some temperature-sensitive compounds may be degraded during the process.
Sericulture and Agricultural Products Research Institute
Technical Solution: The Sericulture and Agricultural Products Research Institute has developed a specialized temperature-optimized extraction protocol for fulvic acid from agricultural waste materials, particularly focusing on silkworm excrement and mulberry residues. Their research has established that controlled temperature extraction at 65-75°C provides optimal results for these specific source materials. The institute employs a two-phase extraction system where materials are first pre-treated at lower temperatures (40-45°C) for 2-3 hours to break down cellular structures, followed by main extraction at higher temperatures (65-75°C) for 4-6 hours. This approach has been shown to increase fulvic acid yields by up to 25% compared to single-temperature methods. Additionally, they've integrated microwave-assisted heating technology that provides precise temperature control while reducing energy consumption by approximately 30% compared to conventional heating methods.
Strengths: Specialized expertise with agricultural waste materials; energy-efficient extraction process; high yield of bioactive fulvic compounds from otherwise waste materials. Weaknesses: Process optimization is highly specific to certain agricultural inputs; scaling challenges for industrial production; requires specialized equipment for the two-phase extraction approach.
Key Patents in Thermal Extraction Optimization
Method for extracting fulvic acid and humic acid and method for fractionating humus material
PatentActiveJP2018127413A
Innovation
- The use of alkaline electrolyzed water for extracting and fractionating humic substances, which reduces the production of harmful salts and enhances operational safety while maintaining high extraction efficiency.
Method and plant for manufacturing cement clinker
PatentInactiveEP1546058A1
Innovation
- Extracting a portion of the raw meal from the cyclone preheater and subjecting it to oxidation in a separate unit under controlled conditions to form SO2 and expel organic carbon, which are then reintroduced into the cyclone preheater, allowing for subsequent treatment and reducing emissions without additional energy consumption.
Environmental Impact of Extraction Processes
The extraction of fulvic acid involves various chemical processes that can have significant environmental implications. Traditional extraction methods often utilize high temperatures combined with chemical solvents, creating potential ecological concerns that must be carefully evaluated and mitigated.
Temperature variations in extraction processes directly impact energy consumption. Higher temperature extractions typically require substantial energy inputs, contributing to increased carbon emissions when fossil fuels are the primary energy source. Studies indicate that for every 10°C increase in extraction temperature above 60°C, energy requirements increase by approximately 15-20%, with corresponding increases in greenhouse gas emissions.
Chemical runoff presents another critical environmental challenge. Extraction processes operating at elevated temperatures often accelerate chemical reactions, potentially generating more toxic byproducts. When these substances enter waterways, they can disrupt aquatic ecosystems by altering pH levels and introducing harmful compounds. Research has documented that effluent from high-temperature extraction facilities can contain up to 30% more dissolved organic compounds compared to moderate-temperature alternatives.
Water usage represents a significant environmental footprint of fulvic acid extraction. Higher temperature processes typically experience greater evaporative losses, necessitating additional water inputs. This becomes particularly problematic in water-stressed regions where extraction facilities may compete with agricultural and municipal needs for limited water resources.
Soil degradation can occur when extraction waste is improperly managed. The alkaline or acidic nature of extraction residues, which varies with processing temperature, may alter soil chemistry when disposed on land. This can reduce agricultural productivity and disrupt local ecosystems, with recovery periods potentially extending to several years.
Recent innovations have focused on developing more environmentally sustainable extraction methodologies. Low-temperature extraction techniques, operating between 40-60°C, have demonstrated promising results in reducing both energy consumption and chemical waste generation by up to 40% compared to conventional high-temperature methods. Additionally, closed-loop systems that recycle water and capture volatile compounds are becoming increasingly viable, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of fulvic acid production.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address these environmental concerns. The European Union's REACH regulations and similar initiatives in North America now require comprehensive environmental impact assessments for chemical extraction processes, with particular attention to temperature-dependent effects on waste generation and resource consumption.
Temperature variations in extraction processes directly impact energy consumption. Higher temperature extractions typically require substantial energy inputs, contributing to increased carbon emissions when fossil fuels are the primary energy source. Studies indicate that for every 10°C increase in extraction temperature above 60°C, energy requirements increase by approximately 15-20%, with corresponding increases in greenhouse gas emissions.
Chemical runoff presents another critical environmental challenge. Extraction processes operating at elevated temperatures often accelerate chemical reactions, potentially generating more toxic byproducts. When these substances enter waterways, they can disrupt aquatic ecosystems by altering pH levels and introducing harmful compounds. Research has documented that effluent from high-temperature extraction facilities can contain up to 30% more dissolved organic compounds compared to moderate-temperature alternatives.
Water usage represents a significant environmental footprint of fulvic acid extraction. Higher temperature processes typically experience greater evaporative losses, necessitating additional water inputs. This becomes particularly problematic in water-stressed regions where extraction facilities may compete with agricultural and municipal needs for limited water resources.
Soil degradation can occur when extraction waste is improperly managed. The alkaline or acidic nature of extraction residues, which varies with processing temperature, may alter soil chemistry when disposed on land. This can reduce agricultural productivity and disrupt local ecosystems, with recovery periods potentially extending to several years.
Recent innovations have focused on developing more environmentally sustainable extraction methodologies. Low-temperature extraction techniques, operating between 40-60°C, have demonstrated promising results in reducing both energy consumption and chemical waste generation by up to 40% compared to conventional high-temperature methods. Additionally, closed-loop systems that recycle water and capture volatile compounds are becoming increasingly viable, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of fulvic acid production.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address these environmental concerns. The European Union's REACH regulations and similar initiatives in North America now require comprehensive environmental impact assessments for chemical extraction processes, with particular attention to temperature-dependent effects on waste generation and resource consumption.
Quality Control Standards for Fulvic Acid Products
Quality control standards for fulvic acid products are essential to ensure consistency, safety, and efficacy across the industry. These standards must address multiple parameters that directly impact product quality, with extraction temperature being a critical factor that influences the final composition and potency of fulvic acid.
The establishment of rigorous quality control protocols begins with standardized testing methods for key characteristics including fulvic acid concentration, pH levels, heavy metal content, and microbial contamination. Current industry standards typically require fulvic acid products to contain a minimum concentration of 5-8% active fulvic acid, with premium products often exceeding 10%. This concentration is directly affected by extraction temperature, making temperature optimization a fundamental quality control consideration.
Spectroscopic analysis methods, particularly UV-visible spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), have emerged as preferred techniques for quantitative and qualitative assessment of fulvic acid products. These methods allow for the identification of functional groups and structural characteristics that serve as markers for product quality and extraction efficiency at different temperatures.
Regulatory frameworks for fulvic acid products vary globally, with more comprehensive standards established in regions where these products have gained significant market traction. The European Union has implemented specific guidelines requiring manufacturers to demonstrate consistent extraction processes with validated temperature parameters. Similarly, the United States Pharmacopeia has proposed monographs that include temperature-dependent quality indicators for humic substances including fulvic acid.
Batch-to-batch consistency represents another critical quality control challenge, particularly as extraction temperature can fluctuate during manufacturing. Leading manufacturers implement statistical process control methods to monitor temperature variations and their impact on final product specifications. Certificate of Analysis (CoA) documentation typically includes temperature-related parameters to ensure transparency and traceability.
Stability testing under various storage conditions forms an integral component of quality control standards, as products extracted at different temperatures may exhibit varying shelf-life characteristics. Accelerated stability studies at elevated temperatures (40°C/75% RH) for 6 months are commonly employed to predict long-term stability and determine appropriate expiration dating.
As the market for fulvic acid products continues to expand, industry consortia and regulatory bodies are working toward harmonized quality standards that incorporate temperature optimization as a fundamental parameter. These emerging standards will likely include more precise specifications for extraction temperature ranges based on source material and intended application, further emphasizing the importance of temperature determination in quality control frameworks.
The establishment of rigorous quality control protocols begins with standardized testing methods for key characteristics including fulvic acid concentration, pH levels, heavy metal content, and microbial contamination. Current industry standards typically require fulvic acid products to contain a minimum concentration of 5-8% active fulvic acid, with premium products often exceeding 10%. This concentration is directly affected by extraction temperature, making temperature optimization a fundamental quality control consideration.
Spectroscopic analysis methods, particularly UV-visible spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), have emerged as preferred techniques for quantitative and qualitative assessment of fulvic acid products. These methods allow for the identification of functional groups and structural characteristics that serve as markers for product quality and extraction efficiency at different temperatures.
Regulatory frameworks for fulvic acid products vary globally, with more comprehensive standards established in regions where these products have gained significant market traction. The European Union has implemented specific guidelines requiring manufacturers to demonstrate consistent extraction processes with validated temperature parameters. Similarly, the United States Pharmacopeia has proposed monographs that include temperature-dependent quality indicators for humic substances including fulvic acid.
Batch-to-batch consistency represents another critical quality control challenge, particularly as extraction temperature can fluctuate during manufacturing. Leading manufacturers implement statistical process control methods to monitor temperature variations and their impact on final product specifications. Certificate of Analysis (CoA) documentation typically includes temperature-related parameters to ensure transparency and traceability.
Stability testing under various storage conditions forms an integral component of quality control standards, as products extracted at different temperatures may exhibit varying shelf-life characteristics. Accelerated stability studies at elevated temperatures (40°C/75% RH) for 6 months are commonly employed to predict long-term stability and determine appropriate expiration dating.
As the market for fulvic acid products continues to expand, industry consortia and regulatory bodies are working toward harmonized quality standards that incorporate temperature optimization as a fundamental parameter. These emerging standards will likely include more precise specifications for extraction temperature ranges based on source material and intended application, further emphasizing the importance of temperature determination in quality control frameworks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!