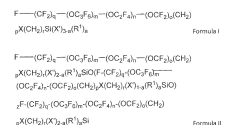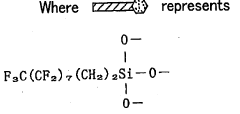Durability Testing and Adhesion of Oleophobic Coatings on Metals
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oleophobic Coating Technology Background and Objectives
Oleophobic coatings have emerged as a critical technology in various industrial applications, particularly in consumer electronics, automotive components, and precision instruments. These specialized coatings create surfaces that repel oils, fingerprints, and other organic contaminants, thereby maintaining aesthetic appeal and functional integrity of metal surfaces. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when hydrophobic coatings were first adapted to also exhibit oleophobic properties through the incorporation of fluorinated compounds.
The technological trajectory has been marked by significant advancements in chemical formulations, application methods, and performance characteristics. Initially, oleophobic coatings suffered from poor durability and adhesion to metal substrates, limiting their practical applications. However, continuous research efforts have led to the development of more robust solutions that can withstand mechanical abrasion, chemical exposure, and environmental stressors while maintaining their oil-repellent properties.
Current market demands are driving the development of oleophobic coatings that not only repel oils effectively but also adhere strongly to various metal substrates under diverse operating conditions. The primary technical objectives in this field include enhancing the durability of these coatings against mechanical wear, improving their resistance to chemical degradation, and ensuring long-term adhesion to metal surfaces without compromising the oleophobic functionality.
Recent technological trends indicate a shift towards environmentally friendly formulations that eliminate or reduce the use of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and other perfluorinated compounds, which have raised environmental and health concerns. This has spurred research into alternative chemistries based on silicones, modified polymers, and nano-structured materials that can deliver comparable or superior oleophobic performance.
The integration of nanotechnology has opened new avenues for creating hierarchical surface structures that enhance both oleophobicity and coating durability. These nano-engineered surfaces mimic natural oleophobic surfaces found in certain plant leaves and insect wings, offering a biomimetic approach to solving adhesion and durability challenges.
Looking forward, the technological goals include developing standardized testing protocols for evaluating the durability and adhesion of oleophobic coatings on various metal substrates, creating multi-functional coatings that combine oleophobicity with other desirable properties such as anti-corrosion or anti-microbial effects, and scaling up production processes to enable cost-effective application in mass-market products.
The technological trajectory has been marked by significant advancements in chemical formulations, application methods, and performance characteristics. Initially, oleophobic coatings suffered from poor durability and adhesion to metal substrates, limiting their practical applications. However, continuous research efforts have led to the development of more robust solutions that can withstand mechanical abrasion, chemical exposure, and environmental stressors while maintaining their oil-repellent properties.
Current market demands are driving the development of oleophobic coatings that not only repel oils effectively but also adhere strongly to various metal substrates under diverse operating conditions. The primary technical objectives in this field include enhancing the durability of these coatings against mechanical wear, improving their resistance to chemical degradation, and ensuring long-term adhesion to metal surfaces without compromising the oleophobic functionality.
Recent technological trends indicate a shift towards environmentally friendly formulations that eliminate or reduce the use of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and other perfluorinated compounds, which have raised environmental and health concerns. This has spurred research into alternative chemistries based on silicones, modified polymers, and nano-structured materials that can deliver comparable or superior oleophobic performance.
The integration of nanotechnology has opened new avenues for creating hierarchical surface structures that enhance both oleophobicity and coating durability. These nano-engineered surfaces mimic natural oleophobic surfaces found in certain plant leaves and insect wings, offering a biomimetic approach to solving adhesion and durability challenges.
Looking forward, the technological goals include developing standardized testing protocols for evaluating the durability and adhesion of oleophobic coatings on various metal substrates, creating multi-functional coatings that combine oleophobicity with other desirable properties such as anti-corrosion or anti-microbial effects, and scaling up production processes to enable cost-effective application in mass-market products.
Market Demand Analysis for Oleophobic Metal Surfaces
The global market for oleophobic coatings on metal surfaces has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing demand across multiple industries including consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. The hydrophobic and oleophobic properties of these coatings provide essential protection against fingerprints, oils, and other contaminants, making them particularly valuable for high-touch metal surfaces.
Consumer electronics represents the largest market segment, with smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices manufacturers seeking durable oleophobic coatings to enhance user experience and product longevity. Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay premium prices for devices with smudge-resistant surfaces, creating strong demand pull from manufacturers.
The automotive industry has emerged as a rapidly growing sector for oleophobic metal coatings, particularly for interior touch surfaces, displays, and exterior decorative elements. As vehicles incorporate more touch-based interfaces and premium metal finishes, the need for durable oleophobic treatments has intensified. Industry forecasts suggest this segment will grow at a compound annual rate exceeding the overall market average.
Medical device manufacturers represent another significant market, where oleophobic coatings on stainless steel and other metal instruments provide both functional benefits and infection control advantages. The ability to repel biological fluids while maintaining instrument integrity has become a critical requirement in this sector.
Geographically, North America and Asia-Pacific dominate the market demand, with China, Japan, South Korea, and the United States being the primary consumers. The concentration of electronics manufacturing in Asia drives significant regional demand, while North American demand is more diversified across multiple industries.
Market challenges primarily revolve around durability concerns. End-users across all industries report that current oleophobic coatings often degrade over time, particularly under heavy use conditions. This degradation results in reduced functionality and aesthetic appeal, creating substantial replacement and maintenance costs.
Price sensitivity varies significantly by application. While consumer electronics manufacturers demonstrate willingness to invest in premium solutions that enhance product differentiation, industrial applications tend to be more cost-conscious, creating distinct market segments with different value propositions.
The market shows clear signals that innovations improving the durability and adhesion of oleophobic coatings on metal surfaces would unlock substantial value. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers would accept price premiums of up to 30% for coatings demonstrating significantly improved durability metrics, particularly in high-wear applications.
Consumer electronics represents the largest market segment, with smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices manufacturers seeking durable oleophobic coatings to enhance user experience and product longevity. Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay premium prices for devices with smudge-resistant surfaces, creating strong demand pull from manufacturers.
The automotive industry has emerged as a rapidly growing sector for oleophobic metal coatings, particularly for interior touch surfaces, displays, and exterior decorative elements. As vehicles incorporate more touch-based interfaces and premium metal finishes, the need for durable oleophobic treatments has intensified. Industry forecasts suggest this segment will grow at a compound annual rate exceeding the overall market average.
Medical device manufacturers represent another significant market, where oleophobic coatings on stainless steel and other metal instruments provide both functional benefits and infection control advantages. The ability to repel biological fluids while maintaining instrument integrity has become a critical requirement in this sector.
Geographically, North America and Asia-Pacific dominate the market demand, with China, Japan, South Korea, and the United States being the primary consumers. The concentration of electronics manufacturing in Asia drives significant regional demand, while North American demand is more diversified across multiple industries.
Market challenges primarily revolve around durability concerns. End-users across all industries report that current oleophobic coatings often degrade over time, particularly under heavy use conditions. This degradation results in reduced functionality and aesthetic appeal, creating substantial replacement and maintenance costs.
Price sensitivity varies significantly by application. While consumer electronics manufacturers demonstrate willingness to invest in premium solutions that enhance product differentiation, industrial applications tend to be more cost-conscious, creating distinct market segments with different value propositions.
The market shows clear signals that innovations improving the durability and adhesion of oleophobic coatings on metal surfaces would unlock substantial value. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers would accept price premiums of up to 30% for coatings demonstrating significantly improved durability metrics, particularly in high-wear applications.
Current Challenges in Metal Surface Oleophobic Treatment
Despite significant advancements in oleophobic coating technologies for metal surfaces, several critical challenges persist that impede widespread industrial adoption and long-term performance reliability. The primary challenge remains the durability of these coatings under real-world conditions. Most current oleophobic treatments exhibit significant degradation after repeated mechanical abrasion, limiting their practical applications in high-touch or high-friction environments such as consumer electronics, automotive components, and industrial equipment.
Adhesion issues represent another fundamental challenge, particularly on non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper alloys. The inherent surface chemistry of these metals often results in weak interfacial bonding with oleophobic compounds, leading to premature delamination and coating failure. This problem is exacerbated when the metal substrates are exposed to temperature fluctuations, causing differential thermal expansion between the coating and substrate.
Chemical stability presents ongoing difficulties, especially in aggressive environments. Many oleophobic coatings demonstrate poor resistance to acidic or alkaline conditions, UV radiation, and oxidizing agents. Industrial applications often require simultaneous resistance to multiple chemical stressors, creating a complex materials engineering challenge that current solutions inadequately address.
The thickness-performance paradox further complicates development efforts. Thicker coatings generally offer improved durability but frequently compromise the oleophobic properties and optical clarity. Conversely, ultra-thin coatings with excellent oleophobic performance typically suffer from reduced mechanical robustness and shorter service life.
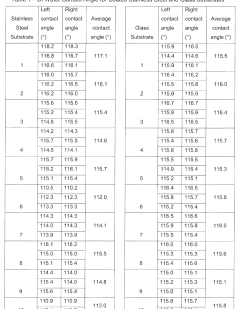
Standardization of testing protocols represents a significant industry-wide challenge. Current durability assessment methods vary considerably across research institutions and manufacturers, making direct comparisons between different oleophobic solutions difficult. The lack of universally accepted accelerated aging tests that accurately predict real-world performance creates uncertainty in product development and commercialization timelines.
Cost-effectiveness remains a substantial barrier to widespread implementation. Many high-performance oleophobic treatments require expensive precursor materials, specialized application equipment, or energy-intensive curing processes. This economic constraint limits adoption in price-sensitive market segments and mass-production scenarios where cost optimization is critical.
Environmental and regulatory concerns have emerged as increasingly important challenges. Traditional fluorinated compounds used in many oleophobic formulations face growing scrutiny due to their environmental persistence and potential health impacts. Developing equally effective non-fluorinated alternatives that meet stringent performance requirements while addressing sustainability concerns represents perhaps the most pressing challenge facing the industry today.
Adhesion issues represent another fundamental challenge, particularly on non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper alloys. The inherent surface chemistry of these metals often results in weak interfacial bonding with oleophobic compounds, leading to premature delamination and coating failure. This problem is exacerbated when the metal substrates are exposed to temperature fluctuations, causing differential thermal expansion between the coating and substrate.
Chemical stability presents ongoing difficulties, especially in aggressive environments. Many oleophobic coatings demonstrate poor resistance to acidic or alkaline conditions, UV radiation, and oxidizing agents. Industrial applications often require simultaneous resistance to multiple chemical stressors, creating a complex materials engineering challenge that current solutions inadequately address.
The thickness-performance paradox further complicates development efforts. Thicker coatings generally offer improved durability but frequently compromise the oleophobic properties and optical clarity. Conversely, ultra-thin coatings with excellent oleophobic performance typically suffer from reduced mechanical robustness and shorter service life.
Standardization of testing protocols represents a significant industry-wide challenge. Current durability assessment methods vary considerably across research institutions and manufacturers, making direct comparisons between different oleophobic solutions difficult. The lack of universally accepted accelerated aging tests that accurately predict real-world performance creates uncertainty in product development and commercialization timelines.
Cost-effectiveness remains a substantial barrier to widespread implementation. Many high-performance oleophobic treatments require expensive precursor materials, specialized application equipment, or energy-intensive curing processes. This economic constraint limits adoption in price-sensitive market segments and mass-production scenarios where cost optimization is critical.
Environmental and regulatory concerns have emerged as increasingly important challenges. Traditional fluorinated compounds used in many oleophobic formulations face growing scrutiny due to their environmental persistence and potential health impacts. Developing equally effective non-fluorinated alternatives that meet stringent performance requirements while addressing sustainability concerns represents perhaps the most pressing challenge facing the industry today.
Current Adhesion Solutions for Metal Substrates
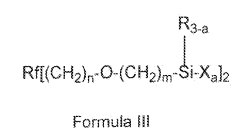
01 Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings
Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic properties on metal surfaces due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically contain fluorinated compounds such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), fluorosilanes, or perfluoropolyethers. The fluorine-containing molecules create a surface that repels oils and other hydrocarbons effectively. To enhance durability and adhesion to metal substrates, these coatings often incorporate adhesion promoters or undergo surface pretreatment processes. The resulting coatings demonstrate superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and environmental factors while maintaining strong adhesion to the metal substrate.- Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings: Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic properties on metal surfaces due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically contain fluorinated compounds such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), fluorosilanes, or perfluoropolyethers. The fluorine-containing molecules create a surface that repels oils and other hydrocarbons effectively. To enhance durability and adhesion to metal substrates, these coatings often incorporate adhesion promoters or undergo surface preparation techniques such as plasma treatment or chemical etching.
- Silane-based coupling agents for improved adhesion: Silane coupling agents play a crucial role in improving the adhesion of oleophobic coatings to metal surfaces. These compounds contain functional groups that can bond with both the metal substrate and the coating material, creating a strong chemical bridge between them. Common silanes used include aminosilanes, epoxysilanes, and mercaptosilanes. The metal surface is typically pretreated with these coupling agents before applying the main oleophobic coating, resulting in significantly enhanced durability and resistance to delamination under mechanical stress or chemical exposure.
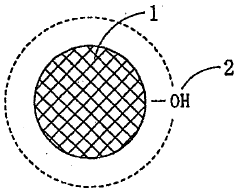
- Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings: Incorporating nanoparticles into oleophobic coating formulations significantly improves their durability and adhesion to metal surfaces. Nanoparticles such as silica, alumina, or titanium dioxide create a hierarchical surface structure that enhances both oleophobicity and mechanical strength. These particles can be surface-modified with oleophobic agents to maintain or enhance the oil-repellent properties. The nanostructured surface increases the coating's resistance to abrasion and weathering while maintaining strong adhesion to the metal substrate through increased surface area and mechanical interlocking mechanisms.
- Surface preparation techniques for metal substrates: Proper surface preparation of metal substrates is essential for ensuring strong adhesion and durability of oleophobic coatings. Techniques include mechanical abrasion, chemical etching, plasma treatment, and solvent cleaning to remove contaminants and create an optimal surface profile. Some methods involve creating micro-roughness on the metal surface to increase the effective surface area for coating adhesion. Acid etching and alkaline cleaning processes are commonly used to remove oxides and create reactive sites on the metal surface, significantly improving the bonding strength between the oleophobic coating and the substrate.
- Cross-linking mechanisms for enhanced durability: Cross-linking mechanisms significantly enhance the durability and adhesion of oleophobic coatings on metal surfaces. These mechanisms involve the formation of covalent bonds within the coating matrix, creating a three-dimensional network that resists mechanical abrasion, chemical attack, and thermal degradation. Common cross-linking approaches include thermal curing, UV radiation, and chemical cross-linkers such as isocyanates or epoxides. Some advanced formulations incorporate self-healing properties through reversible cross-links that can reform after damage, extending the coating's effective lifespan and maintaining oleophobic properties over prolonged periods of use.
02 Surface pretreatment methods for improved adhesion
Various pretreatment methods can significantly enhance the adhesion of oleophobic coatings to metal surfaces. These include chemical etching, plasma treatment, corona discharge, and application of primer layers. Such pretreatments modify the surface energy of the metal substrate, remove contaminants, and create anchor points for the coating. Techniques like phosphating, chromating, or application of silane coupling agents create chemical bonds between the metal surface and the oleophobic coating. These pretreatment processes are crucial for ensuring long-term durability and preventing delamination of the coating under mechanical stress or environmental exposure.Expand Specific Solutions03 Silane-based oleophobic coatings
Silane-based compounds are widely used to create durable oleophobic coatings on metal surfaces. These coatings typically utilize alkylsilanes, fluorosilanes, or organosilicon compounds that form strong covalent bonds with the metal substrate. The silane molecules create a cross-linked network structure that provides excellent adhesion while the hydrophobic or fluorinated end groups deliver the oleophobic properties. These coatings can be applied through various methods including dip-coating, spray coating, or vapor deposition. The resulting thin films offer good thermal stability, chemical resistance, and long-lasting oleophobic performance while maintaining strong adhesion to the metal substrate.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings
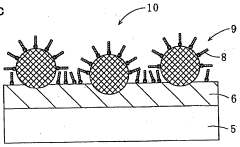
Incorporating nanoparticles into oleophobic coating formulations can significantly enhance their durability and adhesion properties. Nanoparticles such as silica, titanium dioxide, or zinc oxide create a hierarchical surface structure that improves both the oleophobic performance and mechanical durability of the coating. These particles can be surface-modified with fluorinated or silane compounds to maintain oleophobicity while providing reinforcement to the coating matrix. The nanostructured surface increases the contact angle with oils and reduces sliding angles. Additionally, the nanoparticles can improve scratch resistance, abrasion resistance, and overall coating lifespan when applied to metal substrates.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-layer coating systems for enhanced durability
Multi-layer coating systems offer superior durability and adhesion for oleophobic applications on metal surfaces. These systems typically consist of a primer layer that bonds strongly to the metal substrate, intermediate layers that provide corrosion protection and mechanical strength, and a top oleophobic layer that repels oils and other contaminants. The layered approach allows optimization of each coating layer for specific functions while maintaining overall system performance. Some systems incorporate gradient compositions that transition from adhesion-promoting chemistry near the substrate to oleophobic chemistry at the surface. This approach results in coatings with excellent durability under mechanical stress, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The oleophobic coating market for metals is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing demand for durable, adhesive solutions across consumer electronics, automotive, and optical industries. The global market size is expanding due to rising applications in smartphones, eyewear, and industrial equipment. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels with established players like Apple and 3M leading innovation alongside specialized coating experts. EssilorLuxottica dominates in optical applications, while Apple and Sony have advanced consumer electronics implementations. Saint-Gobain and Henkel demonstrate strong industrial applications, with 3M Innovative Properties holding significant intellectual property. Academic-industry partnerships, particularly with Cornell University and Stevens Institute of Technology, are accelerating development of more durable oleophobic solutions that maintain long-term adhesion on metal surfaces.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has developed advanced oleophobic coating technology primarily for touchscreen devices that repels oils from fingertips while maintaining optical clarity. Their approach involves applying fluoropolymer-based nano-coatings to metal and glass surfaces through vapor deposition processes. The company has patented methods for improving durability through multi-layer structures where a base layer provides strong adhesion to the substrate while the top layer delivers oleophobic properties. Apple's testing protocols include accelerated wear testing using standardized abrasion methods (linear and rotational), chemical resistance tests, and environmental aging simulations. Their coatings are engineered to withstand thousands of swipe cycles while maintaining hydrophobic properties with contact angles exceeding 90 degrees. Recent innovations include self-healing oleophobic coatings that can recover from minor surface damage through thermal or UV-activated mechanisms.
Strengths: Superior integration with consumer electronics manufacturing processes; excellent optical properties maintaining touchscreen sensitivity; proven durability in real-world consumer applications. Weaknesses: Relatively high manufacturing costs; potential environmental concerns with fluorinated compounds; performance degradation over extended device lifetime requiring periodic reapplication.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has pioneered comprehensive oleophobic coating solutions for metal surfaces using fluorochemical-based technologies. Their approach involves applying perfluoropolyether (PFPE) derivatives that create ultra-thin (5-20 nm) protective layers with exceptional oil and water repellency. 3M's durability testing methodology is particularly robust, employing standardized ASTM protocols including Taber abrasion testing, cross-hatch adhesion testing, and accelerated weathering chambers that simulate years of environmental exposure. Their proprietary adhesion promotion system uses silane coupling agents that form covalent bonds between the metal substrate and the fluoropolymer coating, significantly enhancing long-term durability. 3M has developed specialized formulations for different metal substrates including aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium alloys, each optimized for the specific surface chemistry. Their coatings maintain oleophobic properties (contact angles >110°) even after 10,000+ abrasion cycles and exposure to industrial chemicals and solvents.
Strengths: Extensive experience with industrial applications across diverse environments; comprehensive testing infrastructure; excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability; scalable manufacturing processes suitable for large metal components. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to conventional protective coatings; some formulations contain PFAS compounds facing increasing regulatory scrutiny; requires specialized application equipment for optimal performance.
Key Patents and Innovations in Oleophobic Durability
Process for forming an Anti-fouling coating system
PatentWO2012148537A1
Innovation
- A process involving surface modification of substrates followed by application and curing of alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether adducts in multiple layers to form a durable, hydrophobic, and oleophobic coating system, ensuring adherence and resistance to stains.
Water-repellent, oil-repellent, soil-resistant glass plate, method of manufacturing the same, and transport equipment, construction and optical equipment using the same
PatentWO2009078109A1
Innovation
- A water-repellent, oil-repellent, and soil-resistant glass plate is created by coating transparent particles with a water-repellent, oil-repellent, and soil-resistant coating, which are then fixed to the glass surface via a transparent metal oxide film, such as a silica-based glass film, using a method involving metal alkoxide and heat treatment to enhance bonding and durability.
Material Compatibility and Surface Preparation Techniques
The compatibility between oleophobic coatings and metal substrates represents a critical factor in determining coating performance and longevity. Different metal alloys exhibit varying surface energies, chemical reactivities, and microstructural characteristics that significantly influence coating adhesion. Aluminum alloys typically demonstrate excellent compatibility with fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings due to their natural oxide layer, while stainless steel variants require more specialized formulations to achieve optimal adhesion. Copper and its alloys present unique challenges due to their susceptibility to oxidation, often necessitating specialized primer systems.
Surface preparation techniques play a decisive role in enhancing coating-substrate interactions and ultimately determining coating durability. Mechanical preparation methods such as abrasive blasting, sanding, and polishing create increased surface area through controlled roughness profiles, providing mechanical interlocking opportunities for the coating. Research indicates that surface roughness values between 0.8-2.5 μm often yield optimal adhesion for oleophobic coatings on metals, balancing mechanical anchoring with coating uniformity requirements.
Chemical pretreatments represent another critical approach to surface preparation. Acid etching using phosphoric or chromic acid solutions creates microscopic pitting that enhances mechanical adhesion while removing surface contaminants. Alkaline cleaning processes effectively remove organic residues and oils that would otherwise impair coating adhesion. Advanced techniques such as plasma treatment have demonstrated particular efficacy for oleophobic coating applications, as they simultaneously clean surfaces and modify surface energy characteristics without dimensional alterations.
Conversion coatings serve as intermediate layers that significantly enhance oleophobic coating adhesion to metal substrates. Phosphate conversion coatings create crystalline structures that provide excellent mechanical anchoring points, while chromate conversion layers offer superior corrosion resistance beneath the oleophobic coating. Sol-gel derived conversion layers have emerged as environmentally preferable alternatives that create nanoscale surface features conducive to strong coating adhesion.
Environmental factors during surface preparation critically impact coating performance. Temperature and humidity control during preparation processes significantly influences coating adhesion, with research indicating that relative humidity below 60% during application optimizes bonding for most oleophobic formulations. The time interval between surface preparation and coating application represents another crucial parameter, with extended delays frequently resulting in surface recontamination and oxidation that compromise adhesion.
Recent advances in surface preparation technologies include atmospheric plasma treatments, laser surface texturing, and nanostructured primer systems specifically engineered for oleophobic coating applications on metals. These emerging techniques demonstrate promising results in enhancing both initial adhesion strength and long-term durability under challenging environmental conditions and mechanical stresses.
Surface preparation techniques play a decisive role in enhancing coating-substrate interactions and ultimately determining coating durability. Mechanical preparation methods such as abrasive blasting, sanding, and polishing create increased surface area through controlled roughness profiles, providing mechanical interlocking opportunities for the coating. Research indicates that surface roughness values between 0.8-2.5 μm often yield optimal adhesion for oleophobic coatings on metals, balancing mechanical anchoring with coating uniformity requirements.
Chemical pretreatments represent another critical approach to surface preparation. Acid etching using phosphoric or chromic acid solutions creates microscopic pitting that enhances mechanical adhesion while removing surface contaminants. Alkaline cleaning processes effectively remove organic residues and oils that would otherwise impair coating adhesion. Advanced techniques such as plasma treatment have demonstrated particular efficacy for oleophobic coating applications, as they simultaneously clean surfaces and modify surface energy characteristics without dimensional alterations.
Conversion coatings serve as intermediate layers that significantly enhance oleophobic coating adhesion to metal substrates. Phosphate conversion coatings create crystalline structures that provide excellent mechanical anchoring points, while chromate conversion layers offer superior corrosion resistance beneath the oleophobic coating. Sol-gel derived conversion layers have emerged as environmentally preferable alternatives that create nanoscale surface features conducive to strong coating adhesion.
Environmental factors during surface preparation critically impact coating performance. Temperature and humidity control during preparation processes significantly influences coating adhesion, with research indicating that relative humidity below 60% during application optimizes bonding for most oleophobic formulations. The time interval between surface preparation and coating application represents another crucial parameter, with extended delays frequently resulting in surface recontamination and oxidation that compromise adhesion.
Recent advances in surface preparation technologies include atmospheric plasma treatments, laser surface texturing, and nanostructured primer systems specifically engineered for oleophobic coating applications on metals. These emerging techniques demonstrate promising results in enhancing both initial adhesion strength and long-term durability under challenging environmental conditions and mechanical stresses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of oleophobic coating technologies on metals represents a critical consideration in their industrial application. Traditional oleophobic coatings often contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), which have been identified as persistent organic pollutants with significant bioaccumulation potential. These substances remain in the environment for extended periods and can travel long distances through air and water, posing risks to ecosystems and human health.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including the Stockholm Convention and various regional restrictions, have accelerated the transition toward more environmentally benign alternatives. This shift has prompted research into bio-based oleophobic coatings derived from renewable resources such as plant waxes, modified cellulose, and silicone-based compounds that maintain performance while reducing environmental footprint.
The manufacturing processes for oleophobic coatings also present sustainability challenges. Conventional application methods often involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as carriers, contributing to air pollution and potential health hazards for workers. Energy-intensive curing processes further increase the carbon footprint of these coatings. Emerging technologies such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and supercritical CO2 processes offer more environmentally friendly alternatives with reduced waste generation and energy consumption.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental impact of oleophobic coatings extends beyond production to include durability considerations. More durable coatings, while potentially requiring more resource-intensive manufacturing, may offer net environmental benefits through extended service life and reduced replacement frequency. This highlights the importance of balancing immediate manufacturing impacts against long-term performance benefits.
End-of-life management presents another significant environmental challenge. The removal of oleophobic coatings from metal substrates often requires aggressive chemical treatments or mechanical processes that generate hazardous waste. Developing coatings designed for easier removal or recycling represents an important frontier in sustainable coating technology. Some promising approaches include thermally degradable linkages and pH-responsive coating systems that facilitate controlled delamination.
Water consumption in coating processes also warrants attention, particularly in regions facing water scarcity. Advanced application technologies such as powder coating and electrostatic spray methods can significantly reduce water usage compared to traditional wet application processes. Additionally, closed-loop water recycling systems in manufacturing facilities can minimize wastewater discharge and associated environmental impacts.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including the Stockholm Convention and various regional restrictions, have accelerated the transition toward more environmentally benign alternatives. This shift has prompted research into bio-based oleophobic coatings derived from renewable resources such as plant waxes, modified cellulose, and silicone-based compounds that maintain performance while reducing environmental footprint.
The manufacturing processes for oleophobic coatings also present sustainability challenges. Conventional application methods often involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as carriers, contributing to air pollution and potential health hazards for workers. Energy-intensive curing processes further increase the carbon footprint of these coatings. Emerging technologies such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and supercritical CO2 processes offer more environmentally friendly alternatives with reduced waste generation and energy consumption.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental impact of oleophobic coatings extends beyond production to include durability considerations. More durable coatings, while potentially requiring more resource-intensive manufacturing, may offer net environmental benefits through extended service life and reduced replacement frequency. This highlights the importance of balancing immediate manufacturing impacts against long-term performance benefits.
End-of-life management presents another significant environmental challenge. The removal of oleophobic coatings from metal substrates often requires aggressive chemical treatments or mechanical processes that generate hazardous waste. Developing coatings designed for easier removal or recycling represents an important frontier in sustainable coating technology. Some promising approaches include thermally degradable linkages and pH-responsive coating systems that facilitate controlled delamination.
Water consumption in coating processes also warrants attention, particularly in regions facing water scarcity. Advanced application technologies such as powder coating and electrostatic spray methods can significantly reduce water usage compared to traditional wet application processes. Additionally, closed-loop water recycling systems in manufacturing facilities can minimize wastewater discharge and associated environmental impacts.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!