Oleophobic Coatings for Optical and Electronic Device Protection
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oleophobic Coating Technology Background and Objectives
Oleophobic coatings have emerged as a critical technology in the protection of optical and electronic devices over the past two decades. These specialized surface treatments are designed to repel oils, fingerprints, and other organic contaminants that can compromise device performance and aesthetics. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to early hydrophobic treatments developed for industrial applications, which have since been refined to address the specific needs of consumer electronics and precision optical equipment.
The technological progression in this field has been driven by several key factors, including the increasing prevalence of touch-based interfaces, higher consumer expectations for device durability, and the growing sophistication of portable electronic devices. Early oleophobic coatings suffered from limited durability and inconsistent performance, but recent advancements have significantly improved their longevity and effectiveness.
Current research trends in oleophobic coating technology focus on developing multi-functional surfaces that combine oleophobicity with other desirable properties such as scratch resistance, anti-reflection capabilities, and antimicrobial functionality. Nanomaterial-based approaches have gained particular attention, with fluorinated compounds and silicone-based formulations representing the most promising avenues for advancement.
The primary technical objectives in this field include enhancing coating durability under real-world usage conditions, improving optical clarity and touch sensitivity, developing environmentally friendly formulations with reduced fluorinated compounds, and creating cost-effective manufacturing processes suitable for mass production. Additionally, researchers aim to achieve greater understanding of the fundamental surface chemistry principles that govern oleophobic behavior.
From an industry perspective, the development of superior oleophobic coatings represents a significant competitive advantage for device manufacturers, as these coatings directly impact user experience and perceived product quality. The technology has applications beyond consumer electronics, extending to automotive displays, medical devices, and industrial instrumentation where surface contamination can impair functionality.
Looking forward, the trajectory of oleophobic coating technology is expected to converge with advances in smart materials, potentially leading to adaptive surfaces that can modify their properties in response to environmental conditions or user inputs. The ultimate goal remains the creation of durable, optically transparent coatings that maintain their oleophobic properties throughout the entire lifecycle of the protected device, while meeting increasingly stringent environmental and health regulations.
The technological progression in this field has been driven by several key factors, including the increasing prevalence of touch-based interfaces, higher consumer expectations for device durability, and the growing sophistication of portable electronic devices. Early oleophobic coatings suffered from limited durability and inconsistent performance, but recent advancements have significantly improved their longevity and effectiveness.
Current research trends in oleophobic coating technology focus on developing multi-functional surfaces that combine oleophobicity with other desirable properties such as scratch resistance, anti-reflection capabilities, and antimicrobial functionality. Nanomaterial-based approaches have gained particular attention, with fluorinated compounds and silicone-based formulations representing the most promising avenues for advancement.
The primary technical objectives in this field include enhancing coating durability under real-world usage conditions, improving optical clarity and touch sensitivity, developing environmentally friendly formulations with reduced fluorinated compounds, and creating cost-effective manufacturing processes suitable for mass production. Additionally, researchers aim to achieve greater understanding of the fundamental surface chemistry principles that govern oleophobic behavior.
From an industry perspective, the development of superior oleophobic coatings represents a significant competitive advantage for device manufacturers, as these coatings directly impact user experience and perceived product quality. The technology has applications beyond consumer electronics, extending to automotive displays, medical devices, and industrial instrumentation where surface contamination can impair functionality.
Looking forward, the trajectory of oleophobic coating technology is expected to converge with advances in smart materials, potentially leading to adaptive surfaces that can modify their properties in response to environmental conditions or user inputs. The ultimate goal remains the creation of durable, optically transparent coatings that maintain their oleophobic properties throughout the entire lifecycle of the protected device, while meeting increasingly stringent environmental and health regulations.
Market Demand Analysis for Device Protection Solutions
The global market for device protection solutions has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven primarily by the increasing adoption of smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices. As consumers invest more in premium electronic products, the demand for effective protection against daily wear and tear, particularly from oils and fingerprints, has risen dramatically. Market research indicates that the global smartphone accessories market alone exceeded $80 billion in 2022, with protective solutions representing a significant portion of this value.
Consumer behavior studies reveal a growing awareness and concern regarding device longevity and appearance maintenance. Approximately 67% of smartphone users report dissatisfaction with fingerprint smudges and oil residue on their device screens, while 78% consider oleophobic properties an important factor when purchasing screen protectors. This consumer sentiment has created a robust demand for advanced oleophobic coatings that can effectively repel oils from human skin while maintaining optical clarity.
The commercial sector presents another substantial market opportunity. Businesses deploying touch-based interfaces in retail, healthcare, and public service environments require solutions that can withstand frequent contact while maintaining cleanliness and functionality. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with heightened awareness of surface contamination driving demand for self-cleaning and easy-to-sanitize surfaces.
From a regional perspective, North America and Asia-Pacific dominate the market for premium device protection solutions. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is projected to experience the fastest growth rate due to the expanding middle class and increasing smartphone penetration in countries like China, India, and Indonesia. These emerging markets represent significant untapped potential for oleophobic coating technologies.
Industry analysis indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for high-quality protection solutions that offer tangible benefits. The average consumer replaces their smartphone screen protector 2-3 times annually, creating a recurring revenue stream for manufacturers of superior oleophobic products. Additionally, the growing trend toward foldable and flexible display technologies presents new challenges and opportunities for specialized protective coatings.
Environmental considerations are also shaping market demands, with increasing consumer preference for sustainable and non-toxic protection solutions. Regulations limiting the use of certain fluorinated compounds traditionally used in oleophobic coatings have spurred research into environmentally friendly alternatives, creating a distinct market segment for "green" protection technologies that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Consumer behavior studies reveal a growing awareness and concern regarding device longevity and appearance maintenance. Approximately 67% of smartphone users report dissatisfaction with fingerprint smudges and oil residue on their device screens, while 78% consider oleophobic properties an important factor when purchasing screen protectors. This consumer sentiment has created a robust demand for advanced oleophobic coatings that can effectively repel oils from human skin while maintaining optical clarity.
The commercial sector presents another substantial market opportunity. Businesses deploying touch-based interfaces in retail, healthcare, and public service environments require solutions that can withstand frequent contact while maintaining cleanliness and functionality. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with heightened awareness of surface contamination driving demand for self-cleaning and easy-to-sanitize surfaces.
From a regional perspective, North America and Asia-Pacific dominate the market for premium device protection solutions. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is projected to experience the fastest growth rate due to the expanding middle class and increasing smartphone penetration in countries like China, India, and Indonesia. These emerging markets represent significant untapped potential for oleophobic coating technologies.
Industry analysis indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for high-quality protection solutions that offer tangible benefits. The average consumer replaces their smartphone screen protector 2-3 times annually, creating a recurring revenue stream for manufacturers of superior oleophobic products. Additionally, the growing trend toward foldable and flexible display technologies presents new challenges and opportunities for specialized protective coatings.
Environmental considerations are also shaping market demands, with increasing consumer preference for sustainable and non-toxic protection solutions. Regulations limiting the use of certain fluorinated compounds traditionally used in oleophobic coatings have spurred research into environmentally friendly alternatives, creating a distinct market segment for "green" protection technologies that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Current State and Challenges in Oleophobic Coating Development
Oleophobic coatings have seen significant advancements globally, with research centers in North America, Europe, and East Asia leading development efforts. Current state-of-the-art coatings utilize fluorinated compounds, particularly perfluorinated silanes and fluoropolymers, which demonstrate excellent water and oil repellency. These materials create low surface energy interfaces that prevent liquid adhesion through the formation of micro and nano-structured surfaces. Commercial implementations have achieved contact angles exceeding 110° for oils and 150° for water, representing substantial progress in the field.
Despite these achievements, several critical challenges persist in oleophobic coating development. Durability remains a primary concern, as most current coatings deteriorate under mechanical abrasion, repeated touching, and environmental exposure. Field tests indicate significant performance degradation after 3-6 months of regular device usage, with contact angles often decreasing by 30-40% and compromising protective capabilities. This limitation severely restricts application in high-touch consumer electronics.
Another significant challenge involves the environmental and health implications of fluorinated compounds. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), historically used in these applications, face increasing regulatory restrictions worldwide due to their persistence, bioaccumulation potential, and toxicity concerns. The industry is under pressure to develop fluorine-free alternatives that maintain comparable performance metrics.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional obstacles. Current high-performance oleophobic coatings often require specialized deposition techniques such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition or complex multi-step processes that are difficult to implement in mass production environments. These processes typically demand precise control of environmental parameters and extended curing times, increasing production costs and limiting widespread adoption.
Optical clarity trade-offs constitute another technical hurdle. As coating thickness increases to improve durability, light transmission typically decreases while haze increases. Current solutions struggle to balance the competing requirements of oleophobicity, scratch resistance, and optical transparency, particularly for high-resolution display applications where even minor visual impairments are unacceptable.
Adhesion to diverse substrate materials represents a persistent challenge, especially for devices incorporating multiple surface types. Current coating technologies often require different formulations or surface treatments for glass, polymers, and metals, complicating manufacturing processes for complex devices that integrate multiple materials. This limitation has restricted the comprehensive protection of entire device surfaces with consistent performance characteristics.
Despite these achievements, several critical challenges persist in oleophobic coating development. Durability remains a primary concern, as most current coatings deteriorate under mechanical abrasion, repeated touching, and environmental exposure. Field tests indicate significant performance degradation after 3-6 months of regular device usage, with contact angles often decreasing by 30-40% and compromising protective capabilities. This limitation severely restricts application in high-touch consumer electronics.
Another significant challenge involves the environmental and health implications of fluorinated compounds. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), historically used in these applications, face increasing regulatory restrictions worldwide due to their persistence, bioaccumulation potential, and toxicity concerns. The industry is under pressure to develop fluorine-free alternatives that maintain comparable performance metrics.
Manufacturing scalability presents additional obstacles. Current high-performance oleophobic coatings often require specialized deposition techniques such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition or complex multi-step processes that are difficult to implement in mass production environments. These processes typically demand precise control of environmental parameters and extended curing times, increasing production costs and limiting widespread adoption.
Optical clarity trade-offs constitute another technical hurdle. As coating thickness increases to improve durability, light transmission typically decreases while haze increases. Current solutions struggle to balance the competing requirements of oleophobicity, scratch resistance, and optical transparency, particularly for high-resolution display applications where even minor visual impairments are unacceptable.
Adhesion to diverse substrate materials represents a persistent challenge, especially for devices incorporating multiple surface types. Current coating technologies often require different formulations or surface treatments for glass, polymers, and metals, complicating manufacturing processes for complex devices that integrate multiple materials. This limitation has restricted the comprehensive protection of entire device surfaces with consistent performance characteristics.
Current Technical Solutions for Oleophobic Surface Treatment
01 Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings
Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic properties due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluoropolyethers (PFPEs) or fluorosilanes that create a surface that repels oils and other organic substances. The fluoropolymer chains orient themselves to create a barrier that minimizes contact with oils. These coatings are particularly useful for electronic devices, optical surfaces, and industrial applications where oil repellency is critical.- Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings: Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic properties due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluoropolyethers, fluorosilanes, or fluoroacrylates that create a surface that repels oils and other hydrophobic substances. The fluorine-containing functional groups orient themselves away from the substrate, creating a surface with minimal interaction with oils. These coatings are commonly applied to electronic devices, optical components, and glass surfaces to prevent fingerprints and oil contamination.
- Silicone-based oleophobic coatings: Silicone-based oleophobic coatings utilize modified silicone compounds to create oil-repellent surfaces. These coatings often incorporate silanes, siloxanes, or silicone polymers with specific functional groups that reduce surface energy. The silicone backbone provides durability while the functional groups provide the oleophobic properties. These coatings can be applied through various methods including vapor deposition, dip-coating, or spray application. They are particularly useful for applications requiring both oleophobic and hydrophobic properties, such as automotive glass, electronic displays, and architectural surfaces.
- Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings: Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings incorporate nanomaterials such as silica, titanium dioxide, or carbon nanostructures to improve the performance of the coating. These nanoparticles create a hierarchical surface structure that enhances the oleophobic effect through increased surface roughness at the nanoscale. The combination of chemical composition and physical surface structure creates a more effective barrier against oils. These coatings often demonstrate improved durability, transparency, and resistance to abrasion compared to conventional oleophobic coatings, making them suitable for high-wear applications like touchscreens and optical lenses.
- Application methods for oleophobic coatings: Various application methods can be used to apply oleophobic coatings to different substrates. These include vapor deposition techniques, solution-based methods like dip-coating or spray coating, and plasma-enhanced deposition. Each method offers different advantages in terms of coating uniformity, thickness control, and adhesion to the substrate. The choice of application method depends on factors such as the substrate material, desired coating properties, and production requirements. Post-application treatments such as heat curing or UV exposure are often used to enhance the durability and performance of the oleophobic coating.
- Oleophobic coatings for electronic devices: Oleophobic coatings specifically designed for electronic devices focus on maintaining touch sensitivity while providing protection against fingerprints and oils. These coatings are typically ultra-thin (nanometer scale) to maintain optical clarity and touch responsiveness. They often combine oleophobic and hydrophobic properties to repel both water and oils from touchscreen surfaces. The formulations are designed to withstand frequent touching and cleaning without degradation of the oleophobic properties. Advanced versions may also incorporate anti-microbial properties or self-healing capabilities to extend the functional lifetime of the coating on consumer electronics.
02 Silicone-based oleophobic coatings
Silicone-based oleophobic coatings utilize modified silicone compounds to create surfaces that repel oils and greases. These coatings often incorporate silanes or siloxanes with functional groups that enhance their oil-repellent properties. The silicone backbone provides durability while the functional groups create the oleophobic effect. These coatings can be applied to various substrates including glass, metals, and polymers, offering good adhesion and longevity while maintaining their oil-repellent characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings
Incorporating nanoparticles into oleophobic coating formulations can significantly enhance their performance. Nanoparticles such as silica, titanium dioxide, or zinc oxide create a textured surface at the nanoscale, which increases the contact angle with oils and reduces adhesion. These nanostructured surfaces mimic natural oleophobic surfaces like lotus leaves. The combination of nanoparticles with oleophobic polymers creates a synergistic effect, resulting in superior oil repellency and improved durability compared to conventional coatings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Oleophobic coatings for electronic devices
Specialized oleophobic coatings have been developed specifically for electronic device surfaces, particularly touchscreens and display panels. These coatings are designed to repel fingerprints, oils from skin contact, and other contaminants while maintaining optical clarity and touch sensitivity. The formulations typically include thin, transparent layers of fluorinated or silicone-based compounds that provide oleophobic properties without affecting the device's functionality. These coatings must also be durable enough to withstand frequent touching and cleaning.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application methods for oleophobic coatings
Various application methods are used to apply oleophobic coatings to different substrates. These include vapor deposition, dip coating, spray coating, and plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). Each method offers specific advantages depending on the substrate material and desired coating properties. The application process often involves surface preparation steps to ensure proper adhesion and uniform coverage. Post-application treatments such as heat curing or UV exposure may be used to enhance the durability and performance of the oleophobic coating.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Oleophobic Coating Market
The oleophobic coatings market for optical and electronic device protection is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for water and oil-resistant surfaces in consumer electronics. The global market is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth as device manufacturers prioritize durability and user experience. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications, with companies like Apple, Corning, and 3M leading innovation through established proprietary coating technologies. Emerging players such as Favored Nanotechnology are advancing nano-coating solutions, while research institutions like Cornell University and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft contribute fundamental breakthroughs. The competitive landscape features both diversified industrial giants and specialized coating technology firms, with ongoing R&D focused on improving durability, transparency, and environmental sustainability.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has developed advanced oleophobic coatings for their touchscreen devices, particularly iPhones and iPads. Their proprietary formulation uses fluoropolymer-based compounds that chemically bond to the glass surface at a molecular level. The coating process involves vapor deposition technology that creates an ultra-thin (nanometers thick) transparent layer resistant to fingerprints and oil residues. Apple's approach incorporates silane coupling agents to enhance durability and adhesion to the glass substrate. Their latest iterations include self-healing properties that allow minor scratches to gradually disappear over time through molecular rearrangement. The coating maintains high transparency (>99.5% light transmission) while providing a smooth tactile experience with reduced friction coefficient compared to untreated glass.
Strengths: Exceptional durability (maintains oleophobicity for 2+ years of normal use), excellent optical clarity, and smooth touch experience. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs compared to standard treatments, potential for degradation under extreme environmental conditions, and limited effectiveness against mechanical abrasion over extended periods.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a comprehensive oleophobic coating platform based on their expertise in fluorochemistry. Their technology utilizes perfluoropolyether (PFPE) derivatives with specialized end-group modifications to enhance bonding to various substrates including glass, polymers, and metals. 3M's approach involves a two-step application process: first, a primer layer containing silane coupling agents creates strong adhesion to the substrate; second, a functional layer containing fluorinated compounds provides the oleophobic properties. The company has pioneered spray application methods that enable cost-effective large-area coating for consumer electronics and optical devices. Their formulations achieve contact angles exceeding 110° for oils and 140° for water, demonstrating excellent repellency. 3M has also incorporated UV-stabilizers to prevent degradation under prolonged sun exposure, extending coating lifetime by up to 40% compared to conventional formulations.
Strengths: Versatile application across multiple substrate types, scalable manufacturing processes suitable for mass production, and excellent environmental stability. Weaknesses: Moderate durability against mechanical abrasion compared to some competitors, and potential for reduced effectiveness after repeated cleaning with harsh solvents.
Core Patents and Innovations in Oleophobic Coating Technology
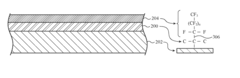
Oleophobic coatings for glass structures in electronic devices
PatentActiveUS11921259B2
Innovation
- A durable oleophobic coating is applied to the transparent protective layers using a catalyst, such as sodium fluoride, which promotes bonding with an adhesion promotion layer like silicon oxide, enhancing the coating's resistance to wear and tear.
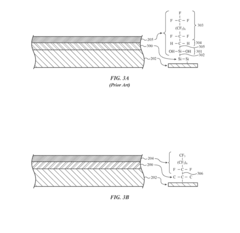
Oleophobic coatings on amorphous carbon coated surfaces of an electronic device
PatentInactiveUS20170066930A1
Innovation
- An amorphous carbon layer is deposited on the substrate, serving as an intermediate bonding site for an oleophobic fluoropolymer coating, forming a durable carbon-carbon bond that enhances scratch resistance and prevents debris accumulation, while maintaining optical transparency and reducing visibility of the coatings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of oleophobic coating technologies has become increasingly significant as electronic device production continues to scale globally. Traditional oleophobic coatings often contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), which have been identified as persistent organic pollutants with bioaccumulative properties. These substances can remain in the environment for decades and have been detected in wildlife, drinking water sources, and human blood samples worldwide.
Manufacturing processes for oleophobic coatings typically involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants that contribute to air quality degradation and potential health risks for workers. The application methods, particularly spray coating and vapor deposition, can result in material waste and energy consumption that further increase the environmental footprint of these protective technologies.
Recent sustainability initiatives have focused on developing fluorine-free alternatives that maintain comparable performance characteristics. Silicone-based and hydrocarbon-based formulations have shown promising results, with reduced environmental persistence while still providing adequate oleophobic properties. These alternatives typically degrade more readily in the environment and present lower bioaccumulation risks.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing traditional fluorinated coatings with newer sustainable alternatives indicate significant reductions in global warming potential, aquatic toxicity, and resource depletion when using the latter. However, these studies also highlight trade-offs in durability, with some eco-friendly coatings requiring more frequent reapplication, potentially increasing overall material consumption over a device's lifetime.
End-of-life considerations present another environmental challenge. The strong chemical bonds in fluorinated coatings make them difficult to separate during recycling processes, potentially contaminating recovered materials or requiring energy-intensive separation techniques. This complicates electronic waste management and can reduce the recovery rate of valuable materials from discarded devices.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly restricting the use of certain fluorinated compounds in consumer products. The European Union's REACH regulation, the United States EPA's PFAS Action Plan, and similar initiatives in Asia are driving industry transition toward more sustainable coating technologies. Companies developing next-generation oleophobic solutions must navigate this evolving regulatory landscape while meeting performance requirements.
Biomimetic approaches inspired by natural water-repellent surfaces such as lotus leaves and butterfly wings represent a promising frontier for sustainable oleophobic coating development. These bio-inspired technologies often utilize hierarchical micro and nanostructures rather than chemical treatments alone, potentially reducing reliance on environmentally persistent substances while maintaining or even enhancing functional performance.
Manufacturing processes for oleophobic coatings typically involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants that contribute to air quality degradation and potential health risks for workers. The application methods, particularly spray coating and vapor deposition, can result in material waste and energy consumption that further increase the environmental footprint of these protective technologies.
Recent sustainability initiatives have focused on developing fluorine-free alternatives that maintain comparable performance characteristics. Silicone-based and hydrocarbon-based formulations have shown promising results, with reduced environmental persistence while still providing adequate oleophobic properties. These alternatives typically degrade more readily in the environment and present lower bioaccumulation risks.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing traditional fluorinated coatings with newer sustainable alternatives indicate significant reductions in global warming potential, aquatic toxicity, and resource depletion when using the latter. However, these studies also highlight trade-offs in durability, with some eco-friendly coatings requiring more frequent reapplication, potentially increasing overall material consumption over a device's lifetime.
End-of-life considerations present another environmental challenge. The strong chemical bonds in fluorinated coatings make them difficult to separate during recycling processes, potentially contaminating recovered materials or requiring energy-intensive separation techniques. This complicates electronic waste management and can reduce the recovery rate of valuable materials from discarded devices.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly restricting the use of certain fluorinated compounds in consumer products. The European Union's REACH regulation, the United States EPA's PFAS Action Plan, and similar initiatives in Asia are driving industry transition toward more sustainable coating technologies. Companies developing next-generation oleophobic solutions must navigate this evolving regulatory landscape while meeting performance requirements.
Biomimetic approaches inspired by natural water-repellent surfaces such as lotus leaves and butterfly wings represent a promising frontier for sustainable oleophobic coating development. These bio-inspired technologies often utilize hierarchical micro and nanostructures rather than chemical treatments alone, potentially reducing reliance on environmentally persistent substances while maintaining or even enhancing functional performance.
Durability Testing and Performance Metrics
Durability testing and performance metrics for oleophobic coatings represent critical evaluation frameworks that determine the practical viability of these protective solutions in real-world applications. The assessment of coating longevity typically involves accelerated aging tests that simulate extended exposure to environmental stressors such as UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and humidity cycles. These controlled laboratory conditions compress years of natural weathering into weeks or months, providing valuable predictive data on coating degradation rates.
Standard abrasion resistance tests employ calibrated instruments like the Taber Abraser or linear abrading machines to quantify a coating's ability to withstand mechanical wear. The industry commonly measures performance using cycles-to-failure metrics, where higher values indicate superior durability. For electronic device applications, the coating must withstand between 5,000-10,000 abrasion cycles while maintaining functional oleophobicity to be considered commercially viable.
Chemical resistance evaluation involves exposing coatings to common substances encountered during device usage, including skin oils, cosmetics, cleaning agents, and acidic or alkaline solutions. Performance is measured by contact angle retention after chemical exposure, with premium coatings maintaining at least 80% of their initial contact angle values.
Adhesion testing follows standardized protocols such as ASTM D3359 (tape test) and ASTM D4541 (pull-off test) to ensure the coating remains bonded to the substrate under stress conditions. For optical applications, additional metrics include light transmission maintenance, haze development over time, and resistance to fingerprint accumulation after repeated touch events.
Quantitative performance benchmarks have evolved significantly, with current industry standards requiring oleophobic coatings to maintain water contact angles above 90° and oil contact angles above 60° after 500,000 touch interactions. Advanced coatings now incorporate self-healing capabilities that can recover from minor abrasions, extending functional lifespans by 30-50% compared to conventional formulations.
Field testing complements laboratory evaluations by placing coated devices with actual users who document real-world performance through structured feedback protocols. This approach captures usage patterns and failure modes that laboratory testing might miss, providing valuable insights for iterative improvement. The correlation between accelerated testing and actual field performance remains an active research area, with manufacturers continuously refining predictive models to better estimate product lifespans under diverse usage conditions.
Standard abrasion resistance tests employ calibrated instruments like the Taber Abraser or linear abrading machines to quantify a coating's ability to withstand mechanical wear. The industry commonly measures performance using cycles-to-failure metrics, where higher values indicate superior durability. For electronic device applications, the coating must withstand between 5,000-10,000 abrasion cycles while maintaining functional oleophobicity to be considered commercially viable.
Chemical resistance evaluation involves exposing coatings to common substances encountered during device usage, including skin oils, cosmetics, cleaning agents, and acidic or alkaline solutions. Performance is measured by contact angle retention after chemical exposure, with premium coatings maintaining at least 80% of their initial contact angle values.
Adhesion testing follows standardized protocols such as ASTM D3359 (tape test) and ASTM D4541 (pull-off test) to ensure the coating remains bonded to the substrate under stress conditions. For optical applications, additional metrics include light transmission maintenance, haze development over time, and resistance to fingerprint accumulation after repeated touch events.
Quantitative performance benchmarks have evolved significantly, with current industry standards requiring oleophobic coatings to maintain water contact angles above 90° and oil contact angles above 60° after 500,000 touch interactions. Advanced coatings now incorporate self-healing capabilities that can recover from minor abrasions, extending functional lifespans by 30-50% compared to conventional formulations.
Field testing complements laboratory evaluations by placing coated devices with actual users who document real-world performance through structured feedback protocols. This approach captures usage patterns and failure modes that laboratory testing might miss, providing valuable insights for iterative improvement. The correlation between accelerated testing and actual field performance remains an active research area, with manufacturers continuously refining predictive models to better estimate product lifespans under diverse usage conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!