Oleophobic Coatings for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Fingerprint Applications
OCT 11, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oleophobic Coating Technology Background and Objectives
Oleophobic coatings have emerged as a critical technology in modern surface engineering, evolving significantly since their initial development in the late 1990s. These specialized coatings create surfaces that repel oils, fingerprints, and other organic contaminants, making them increasingly valuable across multiple industries including consumer electronics, automotive, optical devices, and architectural applications. The fundamental principle behind oleophobic coatings lies in their ability to modify surface energy characteristics, creating interfaces that minimize adhesion of oily substances.
The evolution of oleophobic coating technology has followed a trajectory from simple fluoropolymer-based solutions to sophisticated multi-layered systems incorporating nanomaterials. Early developments focused primarily on fluorinated compounds due to their inherently low surface energy properties. However, environmental concerns regarding perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and related compounds have driven research toward more sustainable alternatives while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
Recent technological advancements have introduced hybrid organic-inorganic compositions, self-healing capabilities, and enhanced durability under various environmental conditions. The integration of nanotechnology has been particularly transformative, enabling unprecedented control over surface morphology at the nanoscale, which directly influences oleophobic performance. These innovations have expanded the practical applications of oleophobic coatings beyond simple stain resistance to include improved cleanability, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced user experience with touch-based interfaces.
Market trends indicate growing demand for oleophobic solutions across multiple sectors, with consumer electronics leading adoption rates. The proliferation of touchscreen devices has created particular urgency for fingerprint-resistant surfaces that maintain optical clarity and tactile responsiveness. Simultaneously, sustainability considerations are reshaping research priorities, with increasing focus on bio-based alternatives and environmentally benign processing methods.
The primary technical objectives for next-generation oleophobic coatings center around several key parameters: durability under repeated contact and cleaning cycles, transparency for optical applications, cost-effective manufacturing processes suitable for large-scale implementation, and reduced environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Additionally, there is growing interest in multifunctional coatings that combine oleophobicity with other desirable properties such as antimicrobial activity, scratch resistance, and self-cleaning capabilities.
This research aims to comprehensively evaluate current oleophobic coating technologies, identify performance limitations and technical challenges, and explore innovative approaches to overcome these barriers. The ultimate goal is to develop next-generation coating systems that deliver superior oil and fingerprint resistance while meeting increasingly stringent requirements for durability, optical performance, and environmental sustainability across diverse application environments.
The evolution of oleophobic coating technology has followed a trajectory from simple fluoropolymer-based solutions to sophisticated multi-layered systems incorporating nanomaterials. Early developments focused primarily on fluorinated compounds due to their inherently low surface energy properties. However, environmental concerns regarding perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and related compounds have driven research toward more sustainable alternatives while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
Recent technological advancements have introduced hybrid organic-inorganic compositions, self-healing capabilities, and enhanced durability under various environmental conditions. The integration of nanotechnology has been particularly transformative, enabling unprecedented control over surface morphology at the nanoscale, which directly influences oleophobic performance. These innovations have expanded the practical applications of oleophobic coatings beyond simple stain resistance to include improved cleanability, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced user experience with touch-based interfaces.
Market trends indicate growing demand for oleophobic solutions across multiple sectors, with consumer electronics leading adoption rates. The proliferation of touchscreen devices has created particular urgency for fingerprint-resistant surfaces that maintain optical clarity and tactile responsiveness. Simultaneously, sustainability considerations are reshaping research priorities, with increasing focus on bio-based alternatives and environmentally benign processing methods.
The primary technical objectives for next-generation oleophobic coatings center around several key parameters: durability under repeated contact and cleaning cycles, transparency for optical applications, cost-effective manufacturing processes suitable for large-scale implementation, and reduced environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Additionally, there is growing interest in multifunctional coatings that combine oleophobicity with other desirable properties such as antimicrobial activity, scratch resistance, and self-cleaning capabilities.
This research aims to comprehensively evaluate current oleophobic coating technologies, identify performance limitations and technical challenges, and explore innovative approaches to overcome these barriers. The ultimate goal is to develop next-generation coating systems that deliver superior oil and fingerprint resistance while meeting increasingly stringent requirements for durability, optical performance, and environmental sustainability across diverse application environments.
Market Analysis for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Fingerprint Solutions
The global market for anti-fouling and anti-fingerprint solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for devices with cleaner, smear-free surfaces. The market size for oleophobic coatings was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $1.9 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 9.8%.
Consumer electronics represents the largest application segment, accounting for nearly 45% of the market share. Smartphones, tablets, and touchscreen displays have become ubiquitous in daily life, creating substantial demand for surfaces resistant to fingerprints and smudges. Major manufacturers like Apple, Samsung, and Huawei have made oleophobic coatings a standard feature in their premium devices, significantly influencing consumer expectations.
The automotive sector emerges as the fastest-growing segment with an estimated growth rate of 12.3% annually. As vehicles incorporate more touch interfaces and display panels, the need for anti-fingerprint solutions has intensified. Luxury automotive brands are particularly driving this trend, implementing these coatings on interior touchscreens, navigation systems, and even exterior surfaces.
Marine applications constitute another substantial market segment, where anti-fouling coatings prevent the accumulation of marine organisms on ship hulls and offshore structures. This segment was valued at approximately $780 million in 2022, with environmental regulations increasingly favoring non-toxic, sustainable coating solutions over traditional biocide-based products.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, accounting for 38% of global demand, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (24%). China and South Korea lead manufacturing capacity, while Japan excels in research and development of advanced formulations. The fastest market growth is observed in India and Southeast Asian countries, where rapid industrialization and increasing consumer electronics production create expanding opportunities.
Market challenges include price sensitivity in mid-range and budget product segments, where manufacturers must balance performance with cost considerations. Additionally, environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, particularly regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and perfluorinated compounds in coating formulations.
Customer preferences are evolving toward multi-functional coatings that combine oleophobic properties with additional benefits such as antimicrobial protection, enhanced durability, and self-healing capabilities. This trend is creating new premium segments within the market, particularly in healthcare, food service, and public infrastructure applications where hygiene concerns are paramount.
Consumer electronics represents the largest application segment, accounting for nearly 45% of the market share. Smartphones, tablets, and touchscreen displays have become ubiquitous in daily life, creating substantial demand for surfaces resistant to fingerprints and smudges. Major manufacturers like Apple, Samsung, and Huawei have made oleophobic coatings a standard feature in their premium devices, significantly influencing consumer expectations.
The automotive sector emerges as the fastest-growing segment with an estimated growth rate of 12.3% annually. As vehicles incorporate more touch interfaces and display panels, the need for anti-fingerprint solutions has intensified. Luxury automotive brands are particularly driving this trend, implementing these coatings on interior touchscreens, navigation systems, and even exterior surfaces.
Marine applications constitute another substantial market segment, where anti-fouling coatings prevent the accumulation of marine organisms on ship hulls and offshore structures. This segment was valued at approximately $780 million in 2022, with environmental regulations increasingly favoring non-toxic, sustainable coating solutions over traditional biocide-based products.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, accounting for 38% of global demand, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (24%). China and South Korea lead manufacturing capacity, while Japan excels in research and development of advanced formulations. The fastest market growth is observed in India and Southeast Asian countries, where rapid industrialization and increasing consumer electronics production create expanding opportunities.
Market challenges include price sensitivity in mid-range and budget product segments, where manufacturers must balance performance with cost considerations. Additionally, environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, particularly regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and perfluorinated compounds in coating formulations.
Customer preferences are evolving toward multi-functional coatings that combine oleophobic properties with additional benefits such as antimicrobial protection, enhanced durability, and self-healing capabilities. This trend is creating new premium segments within the market, particularly in healthcare, food service, and public infrastructure applications where hygiene concerns are paramount.
Current Challenges in Oleophobic Coating Development
Despite significant advancements in oleophobic coating technology, several critical challenges continue to impede the development of optimal solutions for anti-fouling and anti-fingerprint applications. The durability of these coatings remains a primary concern, as most current formulations demonstrate limited resistance to mechanical abrasion and chemical exposure. Even high-performance coatings typically maintain their oleophobic properties for only 3-6 months under regular usage conditions, falling short of industry expectations for long-term functionality.
Surface adhesion presents another significant technical hurdle. Creating strong bonds between oleophobic coatings and diverse substrate materials—particularly glass, metals, and polymers—without compromising the coating's functional properties requires sophisticated surface modification techniques. The inherent contradiction between the need for strong substrate adhesion and the requirement for low surface energy creates fundamental engineering challenges.
Environmental and health considerations have increasingly restricted the use of traditional fluorinated compounds, which historically provided excellent oleophobic properties. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) face regulatory restrictions worldwide due to their persistence in the environment and potential health impacts. This regulatory landscape has forced researchers to explore alternative chemistries that often deliver inferior performance compared to fluorinated predecessors.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness represent substantial barriers to widespread commercial adoption. Laboratory-scale processes that produce excellent oleophobic properties often prove difficult to scale to industrial production volumes without significant performance degradation. Manufacturing techniques like plasma deposition and vapor deposition deliver high-quality coatings but remain prohibitively expensive for mass-market applications.
Transparency and optical properties create additional complications, particularly for consumer electronics and automotive applications. Many effective oleophobic formulations impart a slight haze or color shift that proves unacceptable for high-end displays and optical components. Achieving the perfect balance between oleophobicity and optical clarity continues to challenge materials scientists.
Multi-functionality requirements further complicate development efforts. Modern applications increasingly demand coatings that simultaneously provide oleophobicity, hydrophobicity, anti-bacterial properties, and scratch resistance. Creating formulations that excel across all these parameters without compromising core performance represents a significant materials science challenge.
Standardization issues also hinder progress, as the industry lacks universally accepted testing protocols for oleophobic performance. Different manufacturers employ varied methodologies for measuring contact angles, durability, and fingerprint resistance, making direct comparisons between competing technologies difficult and slowing overall innovation in the field.
Surface adhesion presents another significant technical hurdle. Creating strong bonds between oleophobic coatings and diverse substrate materials—particularly glass, metals, and polymers—without compromising the coating's functional properties requires sophisticated surface modification techniques. The inherent contradiction between the need for strong substrate adhesion and the requirement for low surface energy creates fundamental engineering challenges.
Environmental and health considerations have increasingly restricted the use of traditional fluorinated compounds, which historically provided excellent oleophobic properties. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) face regulatory restrictions worldwide due to their persistence in the environment and potential health impacts. This regulatory landscape has forced researchers to explore alternative chemistries that often deliver inferior performance compared to fluorinated predecessors.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness represent substantial barriers to widespread commercial adoption. Laboratory-scale processes that produce excellent oleophobic properties often prove difficult to scale to industrial production volumes without significant performance degradation. Manufacturing techniques like plasma deposition and vapor deposition deliver high-quality coatings but remain prohibitively expensive for mass-market applications.
Transparency and optical properties create additional complications, particularly for consumer electronics and automotive applications. Many effective oleophobic formulations impart a slight haze or color shift that proves unacceptable for high-end displays and optical components. Achieving the perfect balance between oleophobicity and optical clarity continues to challenge materials scientists.
Multi-functionality requirements further complicate development efforts. Modern applications increasingly demand coatings that simultaneously provide oleophobicity, hydrophobicity, anti-bacterial properties, and scratch resistance. Creating formulations that excel across all these parameters without compromising core performance represents a significant materials science challenge.
Standardization issues also hinder progress, as the industry lacks universally accepted testing protocols for oleophobic performance. Different manufacturers employ varied methodologies for measuring contact angles, durability, and fingerprint resistance, making direct comparisons between competing technologies difficult and slowing overall innovation in the field.
Current Oleophobic Coating Formulations and Methods
01 Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings
Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic properties due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluoropolyethers (PFPE) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that repel oils, water, and fingerprints. The fluorinated chains create a barrier that prevents oils from adhering to the surface, making them ideal for anti-fingerprint applications on electronic devices, glass surfaces, and other high-touch areas.- Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic coatings: Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic properties due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluoropolyethers (PFPE) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that repel oils, water, and fingerprints. The fluorinated chains create a barrier that prevents oils from adhering to the surface, making them ideal for anti-fingerprint applications on electronic devices, glass surfaces, and other high-touch areas.
- Silicone-based anti-fingerprint coatings: Silicone-based formulations provide durable oleophobic properties with excellent transparency. These coatings typically incorporate modified siloxanes or silicone oils that create a smooth, low-friction surface that resists fingerprint adhesion. The silicone compounds form a thin, invisible layer that maintains the optical clarity of the underlying substrate while providing oil and water repellency. These coatings are particularly effective for touchscreens, optical lenses, and decorative glass surfaces.
- Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings: Incorporating nanoparticles such as silica, titanium dioxide, or zinc oxide into coating formulations can significantly enhance oleophobic and anti-fingerprint properties. These nanoparticles create a micro-textured surface that reduces the contact area for oils and fingerprints. The combination of nanoparticles with hydrophobic binders creates a dual-action effect that repels both water and oil-based contaminants. These coatings often exhibit self-cleaning properties and improved durability compared to conventional oleophobic treatments.
- Sol-gel derived anti-fouling coatings: Sol-gel technology enables the creation of highly durable oleophobic coatings through a solution-based process. These coatings typically involve the hydrolysis and condensation of metal alkoxides (such as silicon alkoxides) to form a three-dimensional network with oleophobic functional groups. The resulting coatings feature excellent adhesion to various substrates, high transparency, and resistance to environmental degradation. Sol-gel derived coatings can be customized with different functional groups to optimize their anti-fingerprint and anti-fouling properties for specific applications.
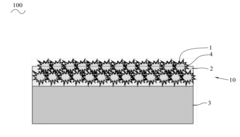
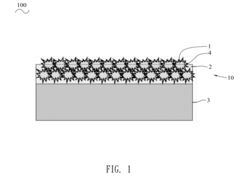
- Multi-layer oleophobic coating systems: Multi-layer coating systems combine different materials to achieve superior oleophobic performance and durability. These systems typically include a primer layer for adhesion, a functional middle layer with oleophobic properties, and a top layer for enhanced durability and scratch resistance. The layered approach allows for optimization of different properties, such as adhesion to the substrate, oleophobicity, transparency, and mechanical durability. These sophisticated coating systems are particularly valuable for high-end consumer electronics, automotive applications, and architectural glass where long-lasting anti-fingerprint properties are essential.
02 Silicone-based anti-fingerprint coatings
Silicone-based formulations provide durable oleophobic properties with excellent transparency. These coatings typically incorporate modified siloxanes or silicone oils that create a smooth, non-stick surface that repels oils and prevents fingerprint adhesion. The silicone compounds form a thin, invisible layer that maintains the optical clarity of the underlying substrate while providing resistance to smudges and stains. These coatings are particularly useful for touchscreens, optical lenses, and decorative glass surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanoparticle-enhanced oleophobic coatings
Incorporating nanoparticles such as silica, titanium dioxide, or zinc oxide into coating formulations can significantly enhance oleophobic and anti-fingerprint properties. These nanoparticles create a micro-textured surface that reduces the contact area for oils and fingerprints. The combination of nanoparticles with hydrophobic and oleophobic binders creates a dual-function coating that repels both water and oils. These coatings often exhibit self-cleaning properties and improved durability compared to conventional oleophobic treatments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sol-gel based anti-fouling coatings
Sol-gel technology provides a versatile platform for creating durable oleophobic and anti-fouling coatings. These coatings typically involve the hydrolysis and condensation of metal alkoxides (such as silicon alkoxides) to form a three-dimensional network with oleophobic functional groups. The resulting coating combines hardness and scratch resistance with excellent oil and water repellency. Sol-gel coatings can be applied to various substrates including glass, metals, and polymers, making them suitable for a wide range of applications from consumer electronics to architectural surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application methods for oleophobic coatings
Various application methods can be employed to apply oleophobic coatings, including spray coating, dip coating, spin coating, and vapor deposition. Each method offers specific advantages depending on the substrate geometry, production volume, and desired coating thickness. Post-application treatments such as heat curing or UV curing are often necessary to achieve optimal performance. The application process significantly impacts coating uniformity, durability, and oleophobic efficiency. Advanced techniques like plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition can create ultra-thin, highly durable oleophobic layers with excellent anti-fingerprint properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The oleophobic coatings market for anti-fouling and anti-fingerprint applications is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for smudge-resistant consumer electronics and optical products. The global market size is expanding rapidly, estimated to reach several billion dollars by 2025, with significant adoption in smartphones, tablets, automotive displays, and eyewear. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with companies like Apple, Corning, and 3M leading innovation with established commercial solutions. Samsung Electronics, Huawei, and PPG Industries are advancing mid-tier solutions, while academic institutions like Cornell University and West Virginia University contribute fundamental research. Emerging players like Shenzhen Goodix Technology and Gansu Hualongxin are developing novel formulations, creating a competitive landscape spanning mature multinational corporations to specialized materials technology startups.
Corning, Inc.
Technical Solution: Corning has developed advanced oleophobic coatings utilizing fluoropolymer technology combined with nano-structured surfaces. Their proprietary Gorilla Glass with oleophobic coating employs a multi-layer approach where a base layer provides adhesion to the glass substrate, while the top fluorinated layer creates a low surface energy barrier. The coating is applied through vapor deposition processes that ensure molecular-level uniformity. Corning's research has demonstrated that their oleophobic coatings maintain effectiveness after 18,000+ abrasion cycles, significantly outperforming conventional coatings[1]. Their technology incorporates perfluoropolyether (PFPE) derivatives that create a surface with contact angles exceeding 110° for oils and 160° for water, effectively repelling both fingerprints and other contaminants while maintaining optical clarity with >99.9% light transmission[3].
Strengths: Superior durability against abrasion compared to competitors; exceptional optical clarity; established manufacturing infrastructure for mass production. Weaknesses: Higher production costs than standard coatings; environmental concerns regarding fluorinated compounds; requires specialized application equipment.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has developed sophisticated oleophobic coating technology specifically optimized for touchscreen devices. Their approach combines fluorosilane chemistry with precision vapor deposition techniques to create ultra-thin (approximately 3-5nm) coatings that maintain the tactile sensitivity of touchscreens while providing excellent fingerprint resistance. Apple's research has focused on balancing oleophobicity with durability, resulting in coatings that maintain effectiveness throughout the expected device lifetime. Their technology incorporates proprietary additives that enhance scratch resistance without compromising the oleophobic properties. Apple's coatings demonstrate oil contact angles of approximately 60-70° and water contact angles of 90-100°, sufficient for effective fingerprint resistance while maintaining optimal touch sensitivity[4]. The company has also developed specialized reapplication methods for service centers to restore oleophobic properties on damaged screens, extending the functional lifetime of their devices.
Strengths: Optimized specifically for touchscreen applications; excellent balance between oleophobicity and touch sensitivity; integrated into high-volume manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Less effective against heavy oils compared to some industrial coatings; gradual degradation with normal use; proprietary nature limits broader applications outside Apple's ecosystem.
Key Patents and Innovations in Oleophobic Materials
Hydrophobic and/or oleophobic coating on microstructured glass surfaces providing an anti-fingerprint effect
PatentInactiveEP1555249A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising 0.1% to 10% alkylsilane, 0.01% to 10% reactive silicone, and a solvent, which forms a long-term stable hydrophobic and oleophobic coating by reacting with the glass surface, utilizing polymer chains with low surface energy and reactive silane residues for adhesion and repellency, respectively.
Method of manufacturing an Anti-fingerprint paint and use of the Anti-fingerprint paint
PatentInactiveUS20120251706A1
Innovation
- A method involving blending fluorinated polymers with fluorocarbon solvents, adding nano-particles coated with fluorinated molecules, and mixing under room temperature to create an anti-fingerprint paint, which is then applied and cured to form a low-surface-energy coating on substrates, achieving hydrophobic and oleophobic properties without requiring expensive equipment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of oleophobic coatings has become increasingly significant as these technologies proliferate across consumer electronics, automotive surfaces, and architectural applications. Traditional oleophobic coatings often contain fluorinated compounds such as perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), which have been identified as persistent organic pollutants with bioaccumulative properties. These substances can remain in the environment for decades and have been detected in wildlife, drinking water sources, and human blood samples globally.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including the European Union's REACH regulation and the Stockholm Convention, have imposed restrictions on many fluorinated compounds, driving the industry toward more sustainable alternatives. This regulatory pressure has accelerated research into bio-based oleophobic materials derived from renewable resources such as plant waxes, cellulose derivatives, and silicone-based formulations that maintain performance while reducing environmental persistence.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of oleophobic coatings reveal significant environmental considerations across their production, application, use, and disposal phases. The manufacturing processes often involve energy-intensive vapor deposition techniques or solvent-based application methods that release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions contribute to air quality degradation and potential health impacts for workers and surrounding communities.
Durability represents another critical sustainability factor, as more resilient coatings reduce replacement frequency and associated resource consumption. Current research indicates that nano-structured hierarchical surfaces can enhance durability while potentially reducing the concentration of problematic chemicals. These approaches mimic natural oleophobic surfaces like lotus leaves, creating physical rather than purely chemical repellency.
End-of-life considerations present particular challenges, as oleophobic coatings may complicate recycling processes for the underlying materials. When electronic devices with oleophobic-coated screens are recycled, these coatings can introduce contaminants into the recycling stream. Developing coatings that can be easily removed during recycling or that do not interfere with established recycling protocols represents an emerging research priority.
Water consumption during manufacturing and application processes presents another environmental concern, particularly in regions experiencing water scarcity. Advanced application technologies such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition can reduce water requirements compared to traditional wet chemical processes, though they may increase energy consumption.
The sustainability trajectory for oleophobic coatings points toward green chemistry principles, emphasizing atom economy, reduced toxicity, and renewable feedstocks. Biomimetic approaches that achieve oleophobicity through structural features rather than persistent chemicals offer promising pathways for next-generation coatings that balance performance requirements with environmental responsibility.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including the European Union's REACH regulation and the Stockholm Convention, have imposed restrictions on many fluorinated compounds, driving the industry toward more sustainable alternatives. This regulatory pressure has accelerated research into bio-based oleophobic materials derived from renewable resources such as plant waxes, cellulose derivatives, and silicone-based formulations that maintain performance while reducing environmental persistence.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of oleophobic coatings reveal significant environmental considerations across their production, application, use, and disposal phases. The manufacturing processes often involve energy-intensive vapor deposition techniques or solvent-based application methods that release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions contribute to air quality degradation and potential health impacts for workers and surrounding communities.
Durability represents another critical sustainability factor, as more resilient coatings reduce replacement frequency and associated resource consumption. Current research indicates that nano-structured hierarchical surfaces can enhance durability while potentially reducing the concentration of problematic chemicals. These approaches mimic natural oleophobic surfaces like lotus leaves, creating physical rather than purely chemical repellency.
End-of-life considerations present particular challenges, as oleophobic coatings may complicate recycling processes for the underlying materials. When electronic devices with oleophobic-coated screens are recycled, these coatings can introduce contaminants into the recycling stream. Developing coatings that can be easily removed during recycling or that do not interfere with established recycling protocols represents an emerging research priority.
Water consumption during manufacturing and application processes presents another environmental concern, particularly in regions experiencing water scarcity. Advanced application technologies such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition can reduce water requirements compared to traditional wet chemical processes, though they may increase energy consumption.
The sustainability trajectory for oleophobic coatings points toward green chemistry principles, emphasizing atom economy, reduced toxicity, and renewable feedstocks. Biomimetic approaches that achieve oleophobicity through structural features rather than persistent chemicals offer promising pathways for next-generation coatings that balance performance requirements with environmental responsibility.
Durability Testing and Performance Standards
Durability testing and performance standards are critical aspects in the development and commercialization of oleophobic coatings for anti-fouling and anti-fingerprint applications. These evaluations ensure that coatings maintain their functional properties throughout their intended service life under various environmental conditions and usage scenarios.
Standard testing protocols for oleophobic coatings typically include contact angle measurements over time, which quantify the degradation of hydrophobic and oleophobic properties. The industry standard requires maintaining contact angles above 90° for oils and above 110° for water after accelerated aging tests. These measurements provide valuable data on coating longevity and performance retention under normal usage conditions.
Abrasion resistance testing represents another crucial evaluation parameter, commonly conducted using linear or rotary abrasion testers with standardized abrasive materials. The Taber Abraser test (ASTM D4060) is widely employed, with high-quality oleophobic coatings expected to maintain functionality after 500-1000 cycles, depending on the application requirements. For consumer electronics, more stringent standards may require performance retention after 5000+ cycles.
Chemical resistance testing evaluates coating durability against common substances including oils, solvents, cleaning agents, and cosmetics. The ASTM D1308 standard outlines procedures for spot testing with various chemicals, while ISO 2812 provides guidelines for immersion testing. Premium oleophobic coatings should demonstrate resistance to pH ranges from 3 to 11 without significant degradation of their functional properties.
Environmental stability testing subjects coatings to accelerated weathering conditions including UV exposure (ASTM G154), temperature cycling (-40°C to +85°C), and humidity exposure (85% RH at 85°C). These tests simulate years of real-world exposure in controlled laboratory settings. High-performance coatings should maintain at least 80% of their initial oleophobic properties after 1000 hours of accelerated weathering.
Adhesion testing, following standards like ASTM D3359 (tape test) and ISO 2409 (cross-cut test), ensures that coatings remain firmly bonded to substrates under mechanical stress. For commercial applications, a minimum rating of 4B on the ASTM scale is typically required, with premium products achieving 5B ratings even after environmental aging.
Industry-specific standards also exist, such as MIL-STD-810 for military applications and IEC 60529 for electronic device protection. Consumer electronics manufacturers often develop proprietary testing protocols that exceed these standards, evaluating resistance to common scenarios like repeated finger swiping (50,000+ cycles) and exposure to skin oils and cosmetics.
Emerging performance standards are beginning to incorporate sustainability metrics, evaluating not only durability but also environmental impact throughout the coating's lifecycle. These include assessments of VOC content, biodegradability of wear particles, and end-of-life recyclability considerations.
Standard testing protocols for oleophobic coatings typically include contact angle measurements over time, which quantify the degradation of hydrophobic and oleophobic properties. The industry standard requires maintaining contact angles above 90° for oils and above 110° for water after accelerated aging tests. These measurements provide valuable data on coating longevity and performance retention under normal usage conditions.
Abrasion resistance testing represents another crucial evaluation parameter, commonly conducted using linear or rotary abrasion testers with standardized abrasive materials. The Taber Abraser test (ASTM D4060) is widely employed, with high-quality oleophobic coatings expected to maintain functionality after 500-1000 cycles, depending on the application requirements. For consumer electronics, more stringent standards may require performance retention after 5000+ cycles.
Chemical resistance testing evaluates coating durability against common substances including oils, solvents, cleaning agents, and cosmetics. The ASTM D1308 standard outlines procedures for spot testing with various chemicals, while ISO 2812 provides guidelines for immersion testing. Premium oleophobic coatings should demonstrate resistance to pH ranges from 3 to 11 without significant degradation of their functional properties.
Environmental stability testing subjects coatings to accelerated weathering conditions including UV exposure (ASTM G154), temperature cycling (-40°C to +85°C), and humidity exposure (85% RH at 85°C). These tests simulate years of real-world exposure in controlled laboratory settings. High-performance coatings should maintain at least 80% of their initial oleophobic properties after 1000 hours of accelerated weathering.
Adhesion testing, following standards like ASTM D3359 (tape test) and ISO 2409 (cross-cut test), ensures that coatings remain firmly bonded to substrates under mechanical stress. For commercial applications, a minimum rating of 4B on the ASTM scale is typically required, with premium products achieving 5B ratings even after environmental aging.
Industry-specific standards also exist, such as MIL-STD-810 for military applications and IEC 60529 for electronic device protection. Consumer electronics manufacturers often develop proprietary testing protocols that exceed these standards, evaluating resistance to common scenarios like repeated finger swiping (50,000+ cycles) and exposure to skin oils and cosmetics.
Emerging performance standards are beginning to incorporate sustainability metrics, evaluating not only durability but also environmental impact throughout the coating's lifecycle. These include assessments of VOC content, biodegradability of wear particles, and end-of-life recyclability considerations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!