Patent Landscape of Oleophobic and Superhydrophobic Coating Technologies
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oleophobic Coating Evolution and Objectives
Oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies have evolved significantly over the past several decades, transforming from rudimentary water-repellent treatments to sophisticated multi-functional surface engineering solutions. The journey began in the 1940s with the development of fluoropolymers like PTFE (Teflon), which demonstrated remarkable water and oil repellency. However, these early coatings lacked durability and versatility across different substrate materials.
The 1990s marked a pivotal turning point with the discovery and biomimetic replication of the "lotus effect," which revealed how micro and nano-scale surface structures could dramatically enhance hydrophobicity. This natural phenomenon inspired researchers to develop the first generation of superhydrophobic coatings that combined chemical composition with physical surface topography to achieve contact angles exceeding 150 degrees.
By the early 2000s, researchers began focusing on oleophobic properties alongside hydrophobicity, recognizing the commercial value of surfaces that could repel both water and oils. This period saw the emergence of fluorosilane-based treatments and the development of hierarchical surface structures that could maintain repellency even under challenging conditions.
The 2010s witnessed significant advancements in durability and environmental sustainability. As regulatory concerns about perfluorinated compounds grew, alternative chemistries based on silicones, hydrocarbons, and ceramic materials gained prominence. Concurrently, manufacturing techniques evolved from laboratory-scale processes to industrially viable methods including spray coating, dip coating, and various deposition technologies.
Current research objectives center on addressing several persistent challenges in oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies. These include enhancing mechanical durability without compromising repellency performance, developing environmentally friendly formulations free from fluorinated compounds, creating transparent coatings for optical applications, and achieving cost-effective scalable manufacturing processes.
The ultimate technological goals include developing multi-functional coatings that combine oleophobicity and superhydrophobicity with additional properties such as anti-icing, self-healing, antimicrobial activity, and corrosion resistance. There is also significant interest in creating adaptive or stimuli-responsive surfaces that can switch between different wetting states in response to external triggers, potentially enabling new applications in microfluidics, sensing, and smart materials.
As we look toward future developments, the integration of these advanced coatings with emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, wearable electronics, and sustainable infrastructure represents a promising frontier with substantial commercial and societal impact potential.
The 1990s marked a pivotal turning point with the discovery and biomimetic replication of the "lotus effect," which revealed how micro and nano-scale surface structures could dramatically enhance hydrophobicity. This natural phenomenon inspired researchers to develop the first generation of superhydrophobic coatings that combined chemical composition with physical surface topography to achieve contact angles exceeding 150 degrees.
By the early 2000s, researchers began focusing on oleophobic properties alongside hydrophobicity, recognizing the commercial value of surfaces that could repel both water and oils. This period saw the emergence of fluorosilane-based treatments and the development of hierarchical surface structures that could maintain repellency even under challenging conditions.
The 2010s witnessed significant advancements in durability and environmental sustainability. As regulatory concerns about perfluorinated compounds grew, alternative chemistries based on silicones, hydrocarbons, and ceramic materials gained prominence. Concurrently, manufacturing techniques evolved from laboratory-scale processes to industrially viable methods including spray coating, dip coating, and various deposition technologies.
Current research objectives center on addressing several persistent challenges in oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies. These include enhancing mechanical durability without compromising repellency performance, developing environmentally friendly formulations free from fluorinated compounds, creating transparent coatings for optical applications, and achieving cost-effective scalable manufacturing processes.
The ultimate technological goals include developing multi-functional coatings that combine oleophobicity and superhydrophobicity with additional properties such as anti-icing, self-healing, antimicrobial activity, and corrosion resistance. There is also significant interest in creating adaptive or stimuli-responsive surfaces that can switch between different wetting states in response to external triggers, potentially enabling new applications in microfluidics, sensing, and smart materials.
As we look toward future developments, the integration of these advanced coatings with emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, wearable electronics, and sustainable infrastructure represents a promising frontier with substantial commercial and societal impact potential.
Market Analysis for Superhydrophobic Surface Applications
The global market for superhydrophobic surface applications has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries. The market size was valued at approximately $1.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.7% during the forecast period.
The electronics sector currently dominates the application landscape, accounting for nearly 35% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the critical need for water and oil-repellent coatings in smartphones, tablets, and other consumer electronics to enhance durability and user experience. The automotive industry follows closely, representing about 28% of the market, where superhydrophobic coatings are increasingly utilized for windshields, side mirrors, and exterior body parts to improve visibility during adverse weather conditions and reduce cleaning requirements.
Construction and building materials constitute approximately 20% of the market, with applications in self-cleaning windows, facades, and solar panels. The remaining market share is distributed among textile, healthcare, and maritime industries, each finding unique value propositions in superhydrophobic technologies.
Regionally, North America leads the market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 14.2% during the forecast period, primarily due to rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness about advanced coating technologies in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demand trends indicate a strong preference for environmentally friendly and durable superhydrophobic solutions. The market is increasingly shifting toward fluorine-free formulations in response to environmental regulations and sustainability concerns. Additionally, there is growing interest in multifunctional coatings that combine superhydrophobicity with other properties such as anti-icing, anti-corrosion, or antimicrobial capabilities.
Key market drivers include technological advancements in nanomaterials, increasing awareness about water conservation, and the growing need for maintenance-free surfaces across industries. However, challenges such as high production costs, durability issues in harsh environments, and limited scalability of current manufacturing processes continue to constrain market growth potential.
The electronics sector currently dominates the application landscape, accounting for nearly 35% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the critical need for water and oil-repellent coatings in smartphones, tablets, and other consumer electronics to enhance durability and user experience. The automotive industry follows closely, representing about 28% of the market, where superhydrophobic coatings are increasingly utilized for windshields, side mirrors, and exterior body parts to improve visibility during adverse weather conditions and reduce cleaning requirements.
Construction and building materials constitute approximately 20% of the market, with applications in self-cleaning windows, facades, and solar panels. The remaining market share is distributed among textile, healthcare, and maritime industries, each finding unique value propositions in superhydrophobic technologies.
Regionally, North America leads the market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 14.2% during the forecast period, primarily due to rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing awareness about advanced coating technologies in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demand trends indicate a strong preference for environmentally friendly and durable superhydrophobic solutions. The market is increasingly shifting toward fluorine-free formulations in response to environmental regulations and sustainability concerns. Additionally, there is growing interest in multifunctional coatings that combine superhydrophobicity with other properties such as anti-icing, anti-corrosion, or antimicrobial capabilities.
Key market drivers include technological advancements in nanomaterials, increasing awareness about water conservation, and the growing need for maintenance-free surfaces across industries. However, challenges such as high production costs, durability issues in harsh environments, and limited scalability of current manufacturing processes continue to constrain market growth potential.
Global R&D Status and Technical Barriers
The global landscape of oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies reveals significant disparities in research and development across different regions. North America, particularly the United States, leads in patent filings and commercial applications, with major contributions from corporations like 3M, DuPont, and academic institutions such as MIT and Stanford University. The European region follows closely, with countries like Germany, France, and the UK demonstrating strong research capabilities in specialized applications for automotive and aerospace industries.
East Asia has emerged as a rapidly growing hub, with Japan historically strong in precision coating technologies and China showing exponential growth in patent filings over the past decade. South Korea has carved a niche in consumer electronics applications of these coatings, particularly for mobile devices and displays.
Despite these advancements, several significant technical barriers persist across the global R&D landscape. Durability remains the foremost challenge, as most superhydrophobic coatings deteriorate under mechanical abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical contact. Current solutions typically offer effective performance for months rather than years, limiting widespread industrial adoption.
Scalability presents another major obstacle, with laboratory-developed coatings often failing to maintain their properties when scaled to industrial production. The precise nano/micro-structure required for superhydrophobicity is difficult to maintain consistently across large surface areas, creating manufacturing yield issues.
Cost-effectiveness continues to impede market penetration, as high-performance coatings frequently require expensive materials like fluorinated compounds or complex multi-step application processes. This economic barrier particularly affects mass-market applications where cost sensitivity is high.
Environmental and regulatory challenges have intensified with increasing restrictions on perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) traditionally used in oleophobic coatings. The search for eco-friendly alternatives that maintain performance standards has become a critical research focus, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations like the European Union.
Substrate compatibility represents another significant barrier, as coating technologies that work excellently on glass or metals often perform poorly on polymers, textiles, or composite materials. This limitation restricts the versatility of coating solutions across different industries and applications.
East Asia has emerged as a rapidly growing hub, with Japan historically strong in precision coating technologies and China showing exponential growth in patent filings over the past decade. South Korea has carved a niche in consumer electronics applications of these coatings, particularly for mobile devices and displays.
Despite these advancements, several significant technical barriers persist across the global R&D landscape. Durability remains the foremost challenge, as most superhydrophobic coatings deteriorate under mechanical abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical contact. Current solutions typically offer effective performance for months rather than years, limiting widespread industrial adoption.
Scalability presents another major obstacle, with laboratory-developed coatings often failing to maintain their properties when scaled to industrial production. The precise nano/micro-structure required for superhydrophobicity is difficult to maintain consistently across large surface areas, creating manufacturing yield issues.
Cost-effectiveness continues to impede market penetration, as high-performance coatings frequently require expensive materials like fluorinated compounds or complex multi-step application processes. This economic barrier particularly affects mass-market applications where cost sensitivity is high.
Environmental and regulatory challenges have intensified with increasing restrictions on perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) traditionally used in oleophobic coatings. The search for eco-friendly alternatives that maintain performance standards has become a critical research focus, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations like the European Union.
Substrate compatibility represents another significant barrier, as coating technologies that work excellently on glass or metals often perform poorly on polymers, textiles, or composite materials. This limitation restricts the versatility of coating solutions across different industries and applications.
Current Technical Solutions for Repellent Coatings
01 Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings
Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic and superhydrophobic properties due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically incorporate fluorinated compounds such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), fluorosilanes, or perfluoropolyethers. The fluorine-containing molecules create a surface that repels both water and oils effectively. These coatings can be applied through various methods including spray coating, dip coating, or vapor deposition to create durable water and oil-repellent surfaces for industrial and consumer applications.- Fluoropolymer-based oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings: Fluoropolymer-based coatings provide excellent oleophobic and superhydrophobic properties due to their low surface energy. These coatings typically incorporate fluorinated compounds such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), fluorosilanes, or perfluoropolyethers. The fluorine-containing molecules create a surface that repels both water and oils effectively. These coatings can be applied through various methods including spray coating, dip coating, or chemical vapor deposition, resulting in durable surfaces with high contact angles for both water and oil droplets.
- Nanoparticle-enhanced superhydrophobic coatings: Incorporating nanoparticles into coating formulations creates micro and nano-scale roughness that enhances superhydrophobic properties. Common nanoparticles used include silica, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, and carbon nanotubes. These particles create a hierarchical surface structure that traps air pockets, allowing water droplets to sit on top with minimal contact area. The combination of surface roughness and low surface energy materials results in extremely high water contact angles (>150°) and low roll-off angles, creating self-cleaning surfaces where water droplets easily roll off, carrying contaminants away.
- Sol-gel based hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings: Sol-gel technology offers a versatile approach for creating oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings through controlled hydrolysis and condensation reactions. These coatings typically use silica-based precursors modified with hydrophobic functional groups. The process allows for precise control of surface morphology and chemistry, creating coatings with tunable properties. Sol-gel coatings can be applied to various substrates including glass, metals, and polymers, offering good adhesion and durability. The resulting coatings provide excellent water and oil repellency while maintaining optical transparency in many applications.
- Environmentally friendly superhydrophobic coatings: Recent developments focus on creating environmentally friendly superhydrophobic coatings that avoid harmful fluorinated compounds. These green alternatives use biodegradable polymers, plant-derived waxes, or modified natural materials like cellulose. Sustainable approaches include using renewable resources, water-based formulations, and reducing volatile organic compounds. These eco-friendly coatings achieve superhydrophobicity through biomimetic surface structures inspired by natural water-repellent surfaces like lotus leaves. While maintaining high water contact angles, these coatings aim to provide comparable performance to traditional formulations while reducing environmental impact.
- Durable and abrasion-resistant superhydrophobic coatings: Enhancing the durability and abrasion resistance of superhydrophobic coatings addresses their main limitation in practical applications. These advanced formulations incorporate crosslinking agents, adhesion promoters, and hard ceramic materials to improve mechanical properties. Some approaches use multi-layer systems with a durable base layer and a functional top layer. Self-healing capabilities can be achieved by incorporating microcapsules containing hydrophobic agents that release upon damage. These durable coatings maintain their water and oil repellency even after physical abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical contact, making them suitable for long-term outdoor applications.
02 Nanoparticle-enhanced superhydrophobic coatings
Incorporating nanoparticles into coating formulations creates micro and nano-scale roughness that enhances superhydrophobic properties. Common nanoparticles used include silica, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, and carbon nanotubes. These particles create a hierarchical surface structure that traps air pockets, resulting in extremely high contact angles for water droplets (typically >150°). The combination of nanoparticle-induced surface roughness with low surface energy binders produces coatings with exceptional water-repellent properties while maintaining transparency and durability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sol-gel based oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings
Sol-gel technology offers a versatile approach for creating oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings through controlled hydrolysis and condensation reactions. These coatings typically use silica-based precursors modified with functional groups that provide oil and water repellency. The sol-gel process allows for precise control of surface morphology and chemistry, resulting in coatings with tunable wetting properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates including glass, metals, and polymers, providing excellent adhesion and durability while maintaining superhydrophobic and oleophobic characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmentally friendly superhydrophobic coating technologies
Recent developments focus on environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional fluorinated compounds for superhydrophobic coatings. These green technologies utilize bio-based materials such as plant waxes, cellulose derivatives, and chitosan combined with non-toxic nanoparticles to create sustainable water-repellent surfaces. The formulations avoid harmful perfluorinated compounds while still achieving high water contact angles and good durability. These eco-friendly coatings can be applied using conventional methods and are suitable for applications in food packaging, textiles, and building materials where environmental concerns are paramount.Expand Specific Solutions05 Durable and self-healing superhydrophobic coatings
Advanced superhydrophobic coatings with enhanced durability and self-healing properties address the challenge of mechanical damage and longevity. These coatings incorporate elastomeric polymers, dynamic chemical bonds, or encapsulated healing agents that can restore superhydrophobic properties after abrasion or damage. Some formulations feature multi-layer designs with a protective top layer and a reservoir layer containing hydrophobic agents that can migrate to the surface when needed. These technologies significantly extend the functional lifetime of superhydrophobic surfaces in harsh environments and high-touch applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Patent Holders and Competitive Landscape
The oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technology landscape is currently in a growth phase, with market size projected to reach significant expansion due to increasing applications in electronics, automotive, and construction industries. The competitive field features diverse players including academic institutions (Cornell University, MIT, University of Florida), established corporations (3M, Corning, IBM, Daikin), and specialized coating companies (Favored Nanotechnology). Technical maturity varies across applications, with companies like 3M and Corning demonstrating advanced commercial implementations, while research institutions continue pushing boundaries in nano-structured surfaces. Regional innovation clusters are evident with strong representation from American, European, and Asian entities, particularly Chinese universities and corporations developing proprietary formulations and application methods for next-generation water and oil-repellent surfaces.
Jiangsu Favored Nanotechnology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Jiangsu Favored Nanotechnology has developed innovative nano-structured oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies based on sol-gel chemistry combined with functionalized nanoparticles. Their approach utilizes modified silica nanoparticles with grafted hydrophobic groups that self-assemble into hierarchical structures during the coating process. The company's patented "NanoShield" technology incorporates both physical surface structuring and chemical modification to achieve water contact angles exceeding 165° and oil contact angles above 140°[9]. Their coatings feature a dual-layer architecture with a robust base layer providing adhesion to substrates and a functional top layer delivering repellent properties. Jiangsu Favored has pioneered room-temperature curable formulations that can be applied to heat-sensitive substrates, expanding application possibilities beyond traditional materials. Their spray-applicable products contain specially engineered nanoparticle dispersions that maintain stability during storage while forming durable networks upon application. Recent innovations include self-healing superhydrophobic coatings containing encapsulated repellent agents that are released upon surface damage, restoring functionality through an autonomous repair mechanism[10].
Strengths: Cost-effective manufacturing processes suitable for large-scale production; room-temperature curing capabilities; good balance of water and oil repellency; relatively environmentally friendly compared to heavily fluorinated alternatives. Weaknesses: Lower durability against mechanical abrasion compared to industry leaders; more complex application requirements for optimal performance; limited track record in high-performance applications; potential nanoparticle agglomeration issues during storage.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies based on fluorochemical compounds combined with structured surfaces. Their approach utilizes fluorinated silanes and acrylate polymers to create durable repellent coatings with hierarchical micro/nano-textures. The company employs vapor deposition techniques to apply these coatings to various substrates, achieving contact angles exceeding 150° for water and 140° for oils[1]. 3M's patented technologies include spray-applicable formulations containing fluoropolymer particles suspended in solvent systems that create self-organizing surface structures upon drying. Their multi-layer coating systems incorporate both a durable base layer and a functional top layer with repellent properties, allowing for application on consumer electronics, automotive surfaces, and medical devices[2]. Recent innovations include self-healing superhydrophobic coatings that can restore functionality after surface damage through migration of functional components from within the coating matrix.
Strengths: Exceptional durability compared to competitors, with coatings maintaining functionality after abrasion testing; versatile application methods including spray, dip, and vapor deposition; extensive commercial manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher cost due to fluorinated compounds; environmental concerns regarding PFAS chemicals in some formulations; potential regulatory challenges in certain markets.
Key Patent Analysis in Superhydrophobic Technologies
Articles having superhydrophobic and oleophobic surfaces
PatentInactiveUS20130230695A1
Innovation
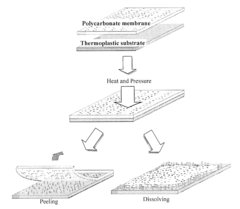
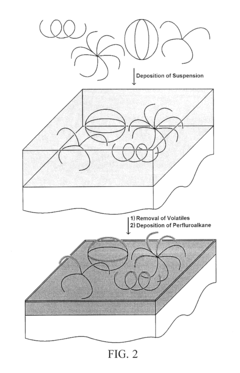
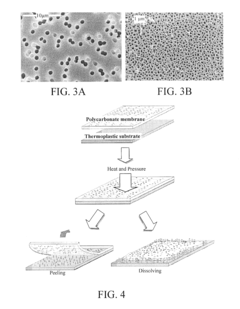
- A thermoplastic article with re-entrant structures is created using a mold with voids, followed by a conformal coating of perfluoroalkane, allowing for the formation of superhydrophobic and oleophobic surfaces that are robust and maintain self-cleaning properties even in the presence of oily materials.
Liquid coating compositions for use in methods for forming a superhydrophobic, superoleophobic or superamphiphobic layer
PatentWO2016001377A1
Innovation
- A method involving a liquid coating composition with dispersed silicone nanoparticles, formed by polymerization in an aprotic solvent, is applied to the substrate, where the solvent is evaporated to create a superhydrophobic, superoleophobic, or superamphiphobic layer, allowing for efficient property imparting without the need for controlled atmospheres or prolonged exposure.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies extends across their entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. These coatings, while offering significant functional benefits, contain compounds that may pose environmental risks if not properly managed.
Production processes for these specialized coatings often involve fluorinated compounds, particularly per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which have raised significant environmental concerns due to their persistence in the environment. Recent patent analysis reveals a growing trend toward developing alternative, more environmentally friendly formulations that maintain performance while reducing ecological footprint.
Water conservation represents a positive environmental aspect of these technologies. Superhydrophobic surfaces require significantly less water for cleaning, potentially reducing water consumption in applications ranging from architectural facades to consumer electronics. Patents filed between 2015-2022 show increasing emphasis on this water-saving potential, particularly in water-scarce regions.
Energy efficiency improvements constitute another environmental benefit. Buildings with superhydrophobic exterior coatings demonstrate enhanced thermal regulation properties, potentially reducing heating and cooling requirements. Several patents highlight this dual functionality, where water repellency is coupled with thermal insulation properties to create multifunctional environmentally beneficial coatings.
Waste reduction capabilities are evident in patents focusing on self-cleaning surfaces. These technologies can extend product lifespans and reduce the need for chemical cleaners, thereby decreasing chemical waste streams. However, end-of-life considerations remain problematic, as many current formulations are not biodegradable and may contribute to microplastic pollution when they deteriorate.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing these environmental concerns. The European Union's REACH regulations and similar initiatives in North America have spurred innovation in more sustainable coating technologies, as evidenced by the patent landscape shift toward bio-based alternatives and non-fluorinated compounds in recent years.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies cited in recent patent applications demonstrate that newer generation oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings can reduce overall environmental impact by 30-45% compared to conventional technologies when considering factors such as global warming potential, resource depletion, and ecotoxicity. This improvement trajectory suggests continued environmental optimization will remain a key driver of innovation in this field.
Production processes for these specialized coatings often involve fluorinated compounds, particularly per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which have raised significant environmental concerns due to their persistence in the environment. Recent patent analysis reveals a growing trend toward developing alternative, more environmentally friendly formulations that maintain performance while reducing ecological footprint.
Water conservation represents a positive environmental aspect of these technologies. Superhydrophobic surfaces require significantly less water for cleaning, potentially reducing water consumption in applications ranging from architectural facades to consumer electronics. Patents filed between 2015-2022 show increasing emphasis on this water-saving potential, particularly in water-scarce regions.
Energy efficiency improvements constitute another environmental benefit. Buildings with superhydrophobic exterior coatings demonstrate enhanced thermal regulation properties, potentially reducing heating and cooling requirements. Several patents highlight this dual functionality, where water repellency is coupled with thermal insulation properties to create multifunctional environmentally beneficial coatings.
Waste reduction capabilities are evident in patents focusing on self-cleaning surfaces. These technologies can extend product lifespans and reduce the need for chemical cleaners, thereby decreasing chemical waste streams. However, end-of-life considerations remain problematic, as many current formulations are not biodegradable and may contribute to microplastic pollution when they deteriorate.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing these environmental concerns. The European Union's REACH regulations and similar initiatives in North America have spurred innovation in more sustainable coating technologies, as evidenced by the patent landscape shift toward bio-based alternatives and non-fluorinated compounds in recent years.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies cited in recent patent applications demonstrate that newer generation oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings can reduce overall environmental impact by 30-45% compared to conventional technologies when considering factors such as global warming potential, resource depletion, and ecotoxicity. This improvement trajectory suggests continued environmental optimization will remain a key driver of innovation in this field.
Industrial Application Scenarios
Oleophobic and superhydrophobic coating technologies have found extensive applications across multiple industrial sectors, transforming conventional products into high-performance alternatives with enhanced durability and functionality. These coatings have revolutionized the consumer electronics industry, where manufacturers apply them to smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices to create fingerprint-resistant and water-repellent surfaces that significantly improve user experience while extending product lifespan.
In the automotive sector, these advanced coatings are increasingly utilized for windshields and exterior body parts, providing self-cleaning properties that maintain visibility during adverse weather conditions and reduce the frequency of washing. The coatings also protect against environmental contaminants such as bird droppings, tree sap, and industrial fallout that can damage automotive finishes.
The aerospace industry has embraced these technologies for aircraft exteriors, where superhydrophobic coatings reduce drag and prevent ice formation, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and enhanced safety during flight operations. Interior applications include cabin surfaces that resist staining and are easier to maintain, contributing to operational cost reduction and passenger comfort.
Building and construction applications represent another significant market segment, with oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings being applied to architectural glass, concrete, and metal surfaces to create self-cleaning facades that maintain aesthetic appeal while reducing maintenance costs. These coatings also provide protection against graffiti and environmental degradation in urban environments.
In the textile industry, the technologies enable the production of water-resistant fabrics for outdoor apparel, upholstery, and technical textiles without compromising breathability or comfort. The medical sector utilizes these coatings on surgical instruments and medical devices to prevent bacterial adhesion and facilitate cleaning, contributing to improved infection control protocols.
Marine applications include ship hulls and offshore structures, where superhydrophobic coatings reduce biofouling and corrosion, leading to decreased maintenance requirements and improved fuel efficiency. The energy sector has adopted these technologies for solar panels, where self-cleaning properties maintain optimal energy generation by preventing dust and dirt accumulation on panel surfaces.
Industrial equipment manufacturers increasingly incorporate these coatings on machinery components exposed to harsh environments, extending service life and reducing downtime associated with maintenance activities. The food processing industry utilizes oleophobic coatings on production equipment to prevent food adhesion and facilitate cleaning, enhancing production efficiency and food safety.
In the automotive sector, these advanced coatings are increasingly utilized for windshields and exterior body parts, providing self-cleaning properties that maintain visibility during adverse weather conditions and reduce the frequency of washing. The coatings also protect against environmental contaminants such as bird droppings, tree sap, and industrial fallout that can damage automotive finishes.
The aerospace industry has embraced these technologies for aircraft exteriors, where superhydrophobic coatings reduce drag and prevent ice formation, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and enhanced safety during flight operations. Interior applications include cabin surfaces that resist staining and are easier to maintain, contributing to operational cost reduction and passenger comfort.
Building and construction applications represent another significant market segment, with oleophobic and superhydrophobic coatings being applied to architectural glass, concrete, and metal surfaces to create self-cleaning facades that maintain aesthetic appeal while reducing maintenance costs. These coatings also provide protection against graffiti and environmental degradation in urban environments.
In the textile industry, the technologies enable the production of water-resistant fabrics for outdoor apparel, upholstery, and technical textiles without compromising breathability or comfort. The medical sector utilizes these coatings on surgical instruments and medical devices to prevent bacterial adhesion and facilitate cleaning, contributing to improved infection control protocols.
Marine applications include ship hulls and offshore structures, where superhydrophobic coatings reduce biofouling and corrosion, leading to decreased maintenance requirements and improved fuel efficiency. The energy sector has adopted these technologies for solar panels, where self-cleaning properties maintain optimal energy generation by preventing dust and dirt accumulation on panel surfaces.
Industrial equipment manufacturers increasingly incorporate these coatings on machinery components exposed to harsh environments, extending service life and reducing downtime associated with maintenance activities. The food processing industry utilizes oleophobic coatings on production equipment to prevent food adhesion and facilitate cleaning, enhancing production efficiency and food safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!