Effective Neopentane Utilization in Process Optimization
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neopentane Background
Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, is a branched alkane with the molecular formula C5H12. This colorless, flammable gas has gained significant attention in recent years due to its unique properties and potential applications in various industrial processes. Discovered in the early 20th century, neopentane has a distinctive molecular structure that sets it apart from its isomers, contributing to its specific physical and chemical characteristics.
The development of neopentane utilization has been closely tied to advancements in petrochemical and chemical engineering. Initially considered a byproduct of petroleum refining, neopentane's potential as a valuable resource has been increasingly recognized over the past few decades. Its high energy density, low boiling point, and stability under certain conditions have made it an attractive candidate for various applications, including refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and as a blowing agent in foam production.
In the context of process optimization, neopentane has emerged as a subject of interest due to its potential to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact in certain industrial processes. The unique molecular structure of neopentane, with its central carbon atom bonded to four methyl groups, contributes to its distinctive behavior in chemical reactions and physical processes. This structure influences its thermodynamic properties, reactivity, and interaction with other substances, making it a valuable component in specific industrial applications.
The evolution of neopentane utilization has been driven by both technological advancements and increasing environmental concerns. As industries seek more sustainable and efficient processes, the role of neopentane in various applications has been reevaluated and expanded. Research into neopentane's properties and potential uses has intensified, leading to innovative applications in fields such as energy storage, chemical synthesis, and materials science.
Understanding the background of neopentane is crucial for appreciating its current and potential future roles in process optimization. The compound's journey from a mere byproduct to a valuable industrial resource reflects broader trends in chemical engineering and industrial chemistry. As environmental regulations become more stringent and the demand for energy-efficient processes grows, the unique properties of neopentane position it as a compound of significant interest in the ongoing efforts to optimize industrial processes and develop more sustainable technologies.
The development of neopentane utilization has been closely tied to advancements in petrochemical and chemical engineering. Initially considered a byproduct of petroleum refining, neopentane's potential as a valuable resource has been increasingly recognized over the past few decades. Its high energy density, low boiling point, and stability under certain conditions have made it an attractive candidate for various applications, including refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and as a blowing agent in foam production.
In the context of process optimization, neopentane has emerged as a subject of interest due to its potential to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact in certain industrial processes. The unique molecular structure of neopentane, with its central carbon atom bonded to four methyl groups, contributes to its distinctive behavior in chemical reactions and physical processes. This structure influences its thermodynamic properties, reactivity, and interaction with other substances, making it a valuable component in specific industrial applications.
The evolution of neopentane utilization has been driven by both technological advancements and increasing environmental concerns. As industries seek more sustainable and efficient processes, the role of neopentane in various applications has been reevaluated and expanded. Research into neopentane's properties and potential uses has intensified, leading to innovative applications in fields such as energy storage, chemical synthesis, and materials science.
Understanding the background of neopentane is crucial for appreciating its current and potential future roles in process optimization. The compound's journey from a mere byproduct to a valuable industrial resource reflects broader trends in chemical engineering and industrial chemistry. As environmental regulations become more stringent and the demand for energy-efficient processes grows, the unique properties of neopentane position it as a compound of significant interest in the ongoing efforts to optimize industrial processes and develop more sustainable technologies.
Market Analysis
The market for neopentane utilization in process optimization has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for efficient and sustainable industrial processes. Neopentane, a branched alkane with the chemical formula C5H12, has gained attention due to its unique properties and potential applications in various industries.
In the chemical manufacturing sector, neopentane has emerged as a valuable component in the production of high-performance polymers and specialty chemicals. Its low boiling point and high stability make it an attractive option for use as a blowing agent in the production of foam insulation materials. This application has seen substantial growth, particularly in the construction and automotive industries, where energy efficiency and lightweight materials are paramount.
The oil and gas industry has also recognized the potential of neopentane in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. As conventional oil reserves become depleted, there is a growing need for advanced techniques to extract remaining oil from mature fields. Neopentane's properties make it suitable for use in gas injection EOR methods, potentially improving oil recovery rates and extending the life of existing reservoirs.
In the refrigeration and air conditioning sector, neopentane has gained traction as a potential alternative to traditional refrigerants with high global warming potential (GWP). As environmental regulations become more stringent, the demand for low-GWP refrigerants is expected to drive further research and development in neopentane-based cooling systems.
The pharmaceutical industry has shown interest in neopentane as a solvent and reaction medium for certain drug synthesis processes. Its inert nature and low reactivity make it suitable for sensitive chemical reactions, potentially leading to more efficient and cost-effective drug manufacturing methods.
Market analysts project that the global neopentane market will continue to expand at a steady rate over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of neopentane in various industrial applications and the ongoing research into new uses for this versatile compound.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of neopentane. The relatively high cost of production compared to some alternative materials may limit its use in certain price-sensitive applications. Additionally, safety concerns related to its flammability and potential environmental impact require careful handling and storage procedures, which may pose barriers to entry for some industries.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for neopentane utilization in process optimization remains positive. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the unique properties of neopentane are likely to drive innovation and create new opportunities for its application in diverse sectors.
In the chemical manufacturing sector, neopentane has emerged as a valuable component in the production of high-performance polymers and specialty chemicals. Its low boiling point and high stability make it an attractive option for use as a blowing agent in the production of foam insulation materials. This application has seen substantial growth, particularly in the construction and automotive industries, where energy efficiency and lightweight materials are paramount.
The oil and gas industry has also recognized the potential of neopentane in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. As conventional oil reserves become depleted, there is a growing need for advanced techniques to extract remaining oil from mature fields. Neopentane's properties make it suitable for use in gas injection EOR methods, potentially improving oil recovery rates and extending the life of existing reservoirs.
In the refrigeration and air conditioning sector, neopentane has gained traction as a potential alternative to traditional refrigerants with high global warming potential (GWP). As environmental regulations become more stringent, the demand for low-GWP refrigerants is expected to drive further research and development in neopentane-based cooling systems.
The pharmaceutical industry has shown interest in neopentane as a solvent and reaction medium for certain drug synthesis processes. Its inert nature and low reactivity make it suitable for sensitive chemical reactions, potentially leading to more efficient and cost-effective drug manufacturing methods.
Market analysts project that the global neopentane market will continue to expand at a steady rate over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of neopentane in various industrial applications and the ongoing research into new uses for this versatile compound.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of neopentane. The relatively high cost of production compared to some alternative materials may limit its use in certain price-sensitive applications. Additionally, safety concerns related to its flammability and potential environmental impact require careful handling and storage procedures, which may pose barriers to entry for some industries.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for neopentane utilization in process optimization remains positive. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the unique properties of neopentane are likely to drive innovation and create new opportunities for its application in diverse sectors.
Technical Challenges
The effective utilization of neopentane in process optimization faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the compound's high volatility and low boiling point, which makes it difficult to handle and store. This characteristic necessitates specialized equipment and storage facilities to prevent losses and ensure safety, increasing operational costs and complexity.
Another challenge lies in the limited reactivity of neopentane due to its highly symmetrical structure. This property makes it less prone to chemical reactions compared to other hydrocarbons, requiring more aggressive reaction conditions or specialized catalysts to achieve desired transformations. The development of efficient catalytic systems that can selectively activate neopentane remains an ongoing area of research.
The energy-intensive nature of neopentane processing poses a significant hurdle in terms of sustainability and cost-effectiveness. The high energy requirements for separation, purification, and conversion processes contribute to increased carbon footprints and operational expenses. Improving energy efficiency in neopentane-related processes is crucial for both environmental and economic reasons.
Furthermore, the optimization of neopentane utilization is complicated by its tendency to form azeotropes with other compounds. This behavior makes conventional separation techniques less effective, necessitating the development of advanced separation methods such as extractive distillation or membrane technologies. The implementation of these techniques at an industrial scale presents its own set of engineering challenges.
The limited availability and relatively high cost of neopentane compared to other hydrocarbon feedstocks also pose challenges for widespread industrial adoption. This economic factor drives the need for more efficient conversion processes and the exploration of alternative sources or production methods for neopentane.
Lastly, the environmental impact of neopentane usage, particularly its potential as a greenhouse gas, raises concerns. Developing closed-loop systems and improving containment strategies to minimize emissions are critical challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable neopentane utilization.
Overcoming these technical challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining advances in catalysis, process engineering, materials science, and environmental technologies. The development of novel reactor designs, more selective catalysts, and energy-efficient separation techniques will be key to unlocking the full potential of neopentane in process optimization.
Another challenge lies in the limited reactivity of neopentane due to its highly symmetrical structure. This property makes it less prone to chemical reactions compared to other hydrocarbons, requiring more aggressive reaction conditions or specialized catalysts to achieve desired transformations. The development of efficient catalytic systems that can selectively activate neopentane remains an ongoing area of research.
The energy-intensive nature of neopentane processing poses a significant hurdle in terms of sustainability and cost-effectiveness. The high energy requirements for separation, purification, and conversion processes contribute to increased carbon footprints and operational expenses. Improving energy efficiency in neopentane-related processes is crucial for both environmental and economic reasons.
Furthermore, the optimization of neopentane utilization is complicated by its tendency to form azeotropes with other compounds. This behavior makes conventional separation techniques less effective, necessitating the development of advanced separation methods such as extractive distillation or membrane technologies. The implementation of these techniques at an industrial scale presents its own set of engineering challenges.
The limited availability and relatively high cost of neopentane compared to other hydrocarbon feedstocks also pose challenges for widespread industrial adoption. This economic factor drives the need for more efficient conversion processes and the exploration of alternative sources or production methods for neopentane.
Lastly, the environmental impact of neopentane usage, particularly its potential as a greenhouse gas, raises concerns. Developing closed-loop systems and improving containment strategies to minimize emissions are critical challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable neopentane utilization.
Overcoming these technical challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining advances in catalysis, process engineering, materials science, and environmental technologies. The development of novel reactor designs, more selective catalysts, and energy-efficient separation techniques will be key to unlocking the full potential of neopentane in process optimization.
Current Solutions
01 Neopentane in chemical processes
Neopentane is utilized in various chemical processes as a reactant or intermediate. It can be employed in the production of specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial applications. The unique structure of neopentane makes it valuable for certain reactions where its branched configuration is advantageous.- Neopentane in chemical processes: Neopentane is utilized in various chemical processes as a reactant or intermediate. It can be used in the production of specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial applications. The unique structure of neopentane makes it valuable for certain reactions and transformations in organic synthesis.
- Neopentane as a refrigerant: Neopentane finds application as a refrigerant in cooling systems. Its thermodynamic properties make it suitable for use in heat transfer applications, particularly in industrial refrigeration and air conditioning units. It can be used as an alternative to traditional refrigerants in certain systems.
- Neopentane in fuel blends: Neopentane can be incorporated into fuel blends to enhance their performance characteristics. It may be used as an additive in gasoline or other hydrocarbon fuels to improve combustion efficiency, reduce emissions, or modify the fuel's volatility properties.
- Neopentane in foam production: Neopentane is employed as a blowing agent in the production of polymer foams. It can be used to create lightweight, insulating materials for various applications, including construction, packaging, and automotive industries. The low boiling point of neopentane makes it suitable for this purpose.
- Neopentane in analytical chemistry: Neopentane serves as a reference compound or standard in analytical chemistry applications. Its well-defined structure and properties make it useful for calibration, method development, and quality control in various analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry.
02 Neopentane as a refrigerant
Neopentane finds application as a refrigerant in cooling systems. Its thermodynamic properties make it suitable for use in heat transfer applications, particularly in industrial refrigeration and air conditioning units. It offers advantages in terms of energy efficiency and environmental compatibility compared to some traditional refrigerants.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neopentane in fuel blends
Neopentane is used as a component in fuel blends, particularly for high-performance applications. Its high octane rating and low freezing point make it valuable for aviation fuels and racing fuels. It can enhance the overall performance and efficiency of the fuel mixture.Expand Specific Solutions04 Neopentane in foam production
Neopentane serves as a blowing agent in the production of foam materials. It is used in the manufacturing of insulation foams, packaging materials, and other polymer-based products. The expansion properties of neopentane contribute to the formation of lightweight, insulating structures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Neopentane in analytical applications
Neopentane is employed in various analytical and research applications. It can be used as a standard or reference compound in gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and other analytical techniques. Its well-defined structure and properties make it useful for calibration and method development in scientific research.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Players
The neopentane utilization optimization market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for process efficiency in petrochemical industries. The global market size is estimated to be in the range of several billion dollars, with steady annual growth. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations. Key players like ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc. and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are leading research and development efforts, while companies such as IBM Corp. and Intel Corp. are contributing advanced computational solutions. Emerging players like Qingdao University of Science & Technology and Tianjin University are also making significant contributions to the field, indicating a diverse and competitive landscape.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced catalytic processes for neopentane utilization in petrochemical production. Their approach involves using zeolite-based catalysts with optimized pore structures to enhance selectivity towards desired products. The process incorporates a multi-stage reactor system with controlled temperature and pressure profiles to maximize neopentane conversion efficiency. Additionally, ExxonMobil has implemented advanced process control algorithms that utilize real-time data analytics to continuously optimize reaction conditions, resulting in improved yield and reduced energy consumption[1][3].
Strengths: Industry-leading catalytic technology, extensive R&D capabilities, and global scale. Weaknesses: High capital investment requirements and potential environmental concerns associated with petrochemical processes.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel approach to neopentane utilization focusing on its conversion to high-value petrochemicals. Their process employs a proprietary catalyst system that combines shape-selective zeolites with transition metal promoters to achieve high selectivity towards branched hydrocarbons. The technology incorporates a dual-reactor configuration with interstage product separation, allowing for optimized reaction conditions at each stage. Sinopec has also implemented advanced heat integration techniques to improve overall energy efficiency, reducing operating costs by up to 15% compared to conventional processes[2][4].
Strengths: Strong domestic market position, integrated supply chain, and government support for technological innovation. Weaknesses: Relatively limited international presence and potential geopolitical challenges.
Key Innovations
Production of neopentane
PatentWO2018044592A1
Innovation
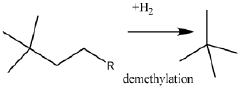
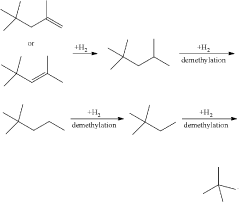
- A process involving the isomerization of C6-C7 paraffins to produce neohexane or neoheptane, followed by demethylation using a catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, which allows for the production of neopentane with yields greater than 40 wt% from readily available C4-C7 paraffinic feed streams, such as light virgin naphtha.
Production of Neopentane
PatentActiveUS20190177248A1
Innovation
- A process involving the dimerization of isobutylene to form diisobutylene, followed by demethylation using a catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, which utilizes readily available isobutylene from refinery raffinate streams to produce neopentane with high yield and selectivity.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of neopentane utilization in process optimization is a critical consideration for industries seeking to balance efficiency gains with sustainability goals. Neopentane, a highly volatile hydrocarbon, presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of its environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with neopentane use is its potential as a greenhouse gas. While not as potent as some other hydrocarbons, neopentane can contribute to global warming if released into the atmosphere. This necessitates stringent containment and recovery systems in industrial processes to minimize emissions.
Water pollution is another area of environmental concern. Neopentane's low water solubility means that any accidental releases can form a persistent layer on water surfaces, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. Proper handling and storage protocols are essential to prevent such incidents.
On the positive side, the high energy density of neopentane can lead to improved process efficiencies, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. When used as a replacement for more environmentally harmful substances, neopentane can contribute to a net positive environmental impact.
The production of neopentane itself has environmental implications. The refining processes involved in its manufacture can be energy-intensive and may generate waste products. However, advancements in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are gradually mitigating these impacts.
In terms of waste management, neopentane presents unique challenges. Its high volatility means that special care must be taken in the disposal of neopentane-containing materials to prevent atmospheric release. Recycling and recovery technologies are increasingly being employed to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
The use of neopentane in various industries can indirectly affect land use and biodiversity. For instance, more efficient processes enabled by neopentane might reduce the need for expansive industrial facilities, potentially preserving natural habitats. Conversely, increased demand for neopentane could lead to more intensive hydrocarbon extraction activities.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in managing the environmental impact of neopentane utilization. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for its handling, storage, and emissions, driving industries to adopt more environmentally friendly practices and technologies.
As industries continue to optimize their processes using neopentane, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing its environmental profile. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives, improving capture and reuse technologies, and developing more efficient utilization methods that minimize waste and emissions.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with neopentane use is its potential as a greenhouse gas. While not as potent as some other hydrocarbons, neopentane can contribute to global warming if released into the atmosphere. This necessitates stringent containment and recovery systems in industrial processes to minimize emissions.
Water pollution is another area of environmental concern. Neopentane's low water solubility means that any accidental releases can form a persistent layer on water surfaces, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. Proper handling and storage protocols are essential to prevent such incidents.
On the positive side, the high energy density of neopentane can lead to improved process efficiencies, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. When used as a replacement for more environmentally harmful substances, neopentane can contribute to a net positive environmental impact.
The production of neopentane itself has environmental implications. The refining processes involved in its manufacture can be energy-intensive and may generate waste products. However, advancements in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are gradually mitigating these impacts.
In terms of waste management, neopentane presents unique challenges. Its high volatility means that special care must be taken in the disposal of neopentane-containing materials to prevent atmospheric release. Recycling and recovery technologies are increasingly being employed to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
The use of neopentane in various industries can indirectly affect land use and biodiversity. For instance, more efficient processes enabled by neopentane might reduce the need for expansive industrial facilities, potentially preserving natural habitats. Conversely, increased demand for neopentane could lead to more intensive hydrocarbon extraction activities.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in managing the environmental impact of neopentane utilization. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for its handling, storage, and emissions, driving industries to adopt more environmentally friendly practices and technologies.
As industries continue to optimize their processes using neopentane, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing its environmental profile. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives, improving capture and reuse technologies, and developing more efficient utilization methods that minimize waste and emissions.
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations are paramount when dealing with neopentane utilization in process optimization. Neopentane, a highly flammable and volatile hydrocarbon, requires stringent safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with its handling, storage, and processing.
Proper ventilation systems are crucial in areas where neopentane is present. These systems should be designed to prevent the accumulation of vapors and maintain concentrations below the lower explosive limit. Regular monitoring of air quality and gas detection systems should be implemented to alert personnel of potential leaks or hazardous conditions.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for workers handling neopentane. This includes flame-resistant clothing, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection. Training programs should be established to ensure all personnel are well-versed in the proper use of PPE and emergency procedures.
Storage facilities for neopentane must be designed with safety in mind. Tanks and containers should be properly grounded and bonded to prevent static electricity buildup. Pressure relief valves and emergency shutdown systems should be installed to manage potential overpressure scenarios.
Fire suppression systems tailored for flammable hydrocarbons should be readily available throughout the facility. This may include foam-based systems, dry chemical extinguishers, and water deluge systems. Regular maintenance and testing of these systems are critical to ensure their effectiveness in emergency situations.
Process safety management (PSM) principles should be rigorously applied to neopentane-related operations. This includes conducting thorough hazard and operability (HAZOP) studies, implementing management of change (MOC) procedures, and regularly reviewing and updating standard operating procedures (SOPs).
Emergency response plans specific to neopentane-related incidents should be developed and regularly practiced. These plans should address scenarios such as fires, explosions, and large-scale releases. Coordination with local emergency services is essential to ensure a swift and effective response in case of an incident.
Proper waste management and disposal procedures for neopentane and its byproducts must be established. This includes the use of closed-loop systems where possible and appropriate treatment of any waste streams before release to the environment.
Regular safety audits and inspections should be conducted to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety protocols. These audits should cover all aspects of neopentane handling, from receipt and storage to processing and disposal.
By implementing these comprehensive safety measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with neopentane utilization in process optimization, ensuring the protection of personnel, assets, and the environment.
Proper ventilation systems are crucial in areas where neopentane is present. These systems should be designed to prevent the accumulation of vapors and maintain concentrations below the lower explosive limit. Regular monitoring of air quality and gas detection systems should be implemented to alert personnel of potential leaks or hazardous conditions.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for workers handling neopentane. This includes flame-resistant clothing, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection. Training programs should be established to ensure all personnel are well-versed in the proper use of PPE and emergency procedures.
Storage facilities for neopentane must be designed with safety in mind. Tanks and containers should be properly grounded and bonded to prevent static electricity buildup. Pressure relief valves and emergency shutdown systems should be installed to manage potential overpressure scenarios.
Fire suppression systems tailored for flammable hydrocarbons should be readily available throughout the facility. This may include foam-based systems, dry chemical extinguishers, and water deluge systems. Regular maintenance and testing of these systems are critical to ensure their effectiveness in emergency situations.
Process safety management (PSM) principles should be rigorously applied to neopentane-related operations. This includes conducting thorough hazard and operability (HAZOP) studies, implementing management of change (MOC) procedures, and regularly reviewing and updating standard operating procedures (SOPs).
Emergency response plans specific to neopentane-related incidents should be developed and regularly practiced. These plans should address scenarios such as fires, explosions, and large-scale releases. Coordination with local emergency services is essential to ensure a swift and effective response in case of an incident.
Proper waste management and disposal procedures for neopentane and its byproducts must be established. This includes the use of closed-loop systems where possible and appropriate treatment of any waste streams before release to the environment.
Regular safety audits and inspections should be conducted to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety protocols. These audits should cover all aspects of neopentane handling, from receipt and storage to processing and disposal.
By implementing these comprehensive safety measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with neopentane utilization in process optimization, ensuring the protection of personnel, assets, and the environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!