Enhancing Cosmetic Products with Propionic Acid
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid in Cosmetics: Background and Objectives
Propionic acid has emerged as a significant ingredient in the cosmetics industry, with its roots tracing back to the early 20th century. Initially recognized for its antimicrobial properties, this organic compound has gradually gained prominence in various skincare and personal care formulations. The evolution of propionic acid in cosmetics mirrors the industry's shift towards multifunctional ingredients that offer both preservative and active benefits.
Over the years, the cosmetics sector has witnessed a growing demand for natural and sustainable products, driving the exploration of organic acids like propionic acid. This trend aligns with consumer preferences for "clean" beauty solutions and has propelled research into the diverse applications of propionic acid beyond its traditional preservative role. The compound's potential in addressing skin concerns such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and aging has sparked renewed interest among formulators and researchers alike.
The technical objectives for enhancing cosmetic products with propionic acid are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a focus on optimizing its preservative efficacy while minimizing potential irritation, a balance crucial for sensitive skin formulations. Researchers aim to develop innovative delivery systems that can improve the stability and bioavailability of propionic acid in various cosmetic matrices, from creams and lotions to serums and masks.
Another key objective is to explore synergistic combinations of propionic acid with other active ingredients to create more potent and versatile cosmetic formulations. This includes investigating its potential as a pH adjuster, exfoliant, and skin-conditioning agent. The goal is to harness the full spectrum of propionic acid's benefits while addressing formulation challenges such as odor control and product stability.
Furthermore, the cosmetics industry is keen on understanding the long-term effects of propionic acid on skin health and microbiome balance. This involves comprehensive studies on its interaction with the skin's natural flora and its impact on barrier function. The objective is to develop products that not only enhance immediate skin appearance but also contribute to overall skin health and resilience over time.
As sustainability becomes increasingly crucial, there is also a growing interest in developing eco-friendly production methods for propionic acid. This includes exploring biotechnological approaches and green chemistry techniques to minimize environmental impact while ensuring scalable production to meet industry demands.
In conclusion, the background and objectives surrounding propionic acid in cosmetics reflect a dynamic interplay between consumer trends, scientific advancements, and industry needs. The ongoing research and development efforts aim to position propionic acid as a versatile, effective, and sustainable ingredient in the next generation of cosmetic products.
Over the years, the cosmetics sector has witnessed a growing demand for natural and sustainable products, driving the exploration of organic acids like propionic acid. This trend aligns with consumer preferences for "clean" beauty solutions and has propelled research into the diverse applications of propionic acid beyond its traditional preservative role. The compound's potential in addressing skin concerns such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and aging has sparked renewed interest among formulators and researchers alike.
The technical objectives for enhancing cosmetic products with propionic acid are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a focus on optimizing its preservative efficacy while minimizing potential irritation, a balance crucial for sensitive skin formulations. Researchers aim to develop innovative delivery systems that can improve the stability and bioavailability of propionic acid in various cosmetic matrices, from creams and lotions to serums and masks.
Another key objective is to explore synergistic combinations of propionic acid with other active ingredients to create more potent and versatile cosmetic formulations. This includes investigating its potential as a pH adjuster, exfoliant, and skin-conditioning agent. The goal is to harness the full spectrum of propionic acid's benefits while addressing formulation challenges such as odor control and product stability.
Furthermore, the cosmetics industry is keen on understanding the long-term effects of propionic acid on skin health and microbiome balance. This involves comprehensive studies on its interaction with the skin's natural flora and its impact on barrier function. The objective is to develop products that not only enhance immediate skin appearance but also contribute to overall skin health and resilience over time.
As sustainability becomes increasingly crucial, there is also a growing interest in developing eco-friendly production methods for propionic acid. This includes exploring biotechnological approaches and green chemistry techniques to minimize environmental impact while ensuring scalable production to meet industry demands.
In conclusion, the background and objectives surrounding propionic acid in cosmetics reflect a dynamic interplay between consumer trends, scientific advancements, and industry needs. The ongoing research and development efforts aim to position propionic acid as a versatile, effective, and sustainable ingredient in the next generation of cosmetic products.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid-Enhanced Cosmetics
The global market for propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for multifunctional and innovative beauty products. This segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate projected to exceed the overall cosmetics industry average.
The rising popularity of propionic acid in cosmetics can be attributed to its versatile properties. As a natural preservative, it extends the shelf life of products while also offering antimicrobial benefits. This dual functionality aligns with the growing consumer preference for clean and safe beauty formulations. Additionally, propionic acid's potential to balance skin pH and improve product texture has further boosted its appeal in the cosmetics industry.
Market research indicates that skincare products, particularly facial creams and serums, represent the largest application area for propionic acid in cosmetics. This trend is driven by the increasing focus on anti-aging and skin health among consumers across various age groups. The haircare segment is also showing promising growth, with propionic acid being incorporated into shampoos and conditioners for its clarifying and preservative properties.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics, owing to their well-established beauty industries and consumer awareness of advanced ingredients. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth market, fueled by rising disposable incomes, changing lifestyles, and a growing middle-class population in countries like China and India.
Consumer demographics play a crucial role in shaping the market. Millennials and Gen Z consumers, in particular, are driving demand for sustainable and multifunctional beauty products. This demographic is more likely to seek out cosmetics with natural preservatives like propionic acid, perceiving them as safer and more environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic options.
The competitive landscape of the propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics market is characterized by a mix of established beauty conglomerates and niche, clean beauty brands. Major players are investing in research and development to create innovative formulations that maximize the benefits of propionic acid while meeting consumer demands for efficacy and safety.
Looking ahead, the market for propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics is poised for continued growth. Factors such as increasing awareness of ingredient safety, the rise of clean beauty trends, and ongoing product innovations are expected to drive market expansion. However, challenges such as regulatory scrutiny and competition from other natural preservatives may impact market dynamics in the coming years.
The rising popularity of propionic acid in cosmetics can be attributed to its versatile properties. As a natural preservative, it extends the shelf life of products while also offering antimicrobial benefits. This dual functionality aligns with the growing consumer preference for clean and safe beauty formulations. Additionally, propionic acid's potential to balance skin pH and improve product texture has further boosted its appeal in the cosmetics industry.
Market research indicates that skincare products, particularly facial creams and serums, represent the largest application area for propionic acid in cosmetics. This trend is driven by the increasing focus on anti-aging and skin health among consumers across various age groups. The haircare segment is also showing promising growth, with propionic acid being incorporated into shampoos and conditioners for its clarifying and preservative properties.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics, owing to their well-established beauty industries and consumer awareness of advanced ingredients. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth market, fueled by rising disposable incomes, changing lifestyles, and a growing middle-class population in countries like China and India.
Consumer demographics play a crucial role in shaping the market. Millennials and Gen Z consumers, in particular, are driving demand for sustainable and multifunctional beauty products. This demographic is more likely to seek out cosmetics with natural preservatives like propionic acid, perceiving them as safer and more environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic options.
The competitive landscape of the propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics market is characterized by a mix of established beauty conglomerates and niche, clean beauty brands. Major players are investing in research and development to create innovative formulations that maximize the benefits of propionic acid while meeting consumer demands for efficacy and safety.
Looking ahead, the market for propionic acid-enhanced cosmetics is poised for continued growth. Factors such as increasing awareness of ingredient safety, the rise of clean beauty trends, and ongoing product innovations are expected to drive market expansion. However, challenges such as regulatory scrutiny and competition from other natural preservatives may impact market dynamics in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Cosmetic Formulations
The incorporation of propionic acid into cosmetic formulations presents several significant challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address. One of the primary obstacles is the strong, pungent odor associated with propionic acid, which can be off-putting to consumers and potentially mask the desired fragrance of the product. This olfactory issue necessitates the development of effective masking agents or encapsulation techniques to mitigate the unpleasant smell without compromising the acid's beneficial properties.
Another critical challenge lies in maintaining the stability of propionic acid within various cosmetic matrices. The acid's reactivity can lead to unwanted interactions with other ingredients, potentially altering the product's efficacy, texture, or shelf life. Formulators must carefully balance the pH of the final product to ensure optimal stability and performance, which often requires extensive testing and reformulation efforts.
The concentration of propionic acid in cosmetic products is also a delicate matter. While higher concentrations may offer enhanced antimicrobial benefits, they can also increase the risk of skin irritation or sensitization in some individuals. Determining the ideal concentration that maximizes efficacy while minimizing adverse effects is a complex task that demands thorough clinical testing and safety assessments.
Compatibility with packaging materials poses another significant challenge. Propionic acid's corrosive nature can potentially degrade certain types of containers or applicators, leading to product instability or contamination. This necessitates the selection of appropriate, resistant packaging materials that can withstand long-term exposure to the acid without compromising product integrity or safety.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of propionic acid in cosmetics varies globally, adding complexity to product development and marketing strategies. Manufacturers must navigate different regulatory requirements and concentration limits across various markets, which can impact formulation decisions and product claims.
The potential for propionic acid to cause skin irritation, especially in individuals with sensitive skin or pre-existing skin conditions, remains a significant concern. Developing formulations that minimize this risk while maintaining the acid's beneficial properties requires extensive research into skin-friendly delivery systems and protective ingredients.
Lastly, the challenge of educating consumers about the benefits of propionic acid in cosmetic products without raising undue concerns about its chemical nature is substantial. Marketing teams must work closely with scientific experts to craft messaging that accurately conveys the product's advantages while addressing potential consumer apprehensions about using acid-containing skincare products.
Another critical challenge lies in maintaining the stability of propionic acid within various cosmetic matrices. The acid's reactivity can lead to unwanted interactions with other ingredients, potentially altering the product's efficacy, texture, or shelf life. Formulators must carefully balance the pH of the final product to ensure optimal stability and performance, which often requires extensive testing and reformulation efforts.
The concentration of propionic acid in cosmetic products is also a delicate matter. While higher concentrations may offer enhanced antimicrobial benefits, they can also increase the risk of skin irritation or sensitization in some individuals. Determining the ideal concentration that maximizes efficacy while minimizing adverse effects is a complex task that demands thorough clinical testing and safety assessments.
Compatibility with packaging materials poses another significant challenge. Propionic acid's corrosive nature can potentially degrade certain types of containers or applicators, leading to product instability or contamination. This necessitates the selection of appropriate, resistant packaging materials that can withstand long-term exposure to the acid without compromising product integrity or safety.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of propionic acid in cosmetics varies globally, adding complexity to product development and marketing strategies. Manufacturers must navigate different regulatory requirements and concentration limits across various markets, which can impact formulation decisions and product claims.
The potential for propionic acid to cause skin irritation, especially in individuals with sensitive skin or pre-existing skin conditions, remains a significant concern. Developing formulations that minimize this risk while maintaining the acid's beneficial properties requires extensive research into skin-friendly delivery systems and protective ingredients.
Lastly, the challenge of educating consumers about the benefits of propionic acid in cosmetic products without raising undue concerns about its chemical nature is substantial. Marketing teams must work closely with scientific experts to craft messaging that accurately conveys the product's advantages while addressing potential consumer apprehensions about using acid-containing skincare products.
Existing Propionic Acid Integration Methods
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and some bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations as excipients, pH adjusters, or active ingredients. They are used in various drug delivery systems and topical preparations.
- Propionic acid in industrial applications: Propionic acid is utilized in various industrial processes, including the production of plastics, herbicides, and solvents. It also serves as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.
- Purification and analysis methods for propionic acid: Various techniques for purifying and analyzing propionic acid are described, including distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods. These processes aim to improve the quality and purity of propionic acid for different applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries
Propionic acid finds applications in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. It is used as a pH adjuster, preservative, and in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. In cosmetics, it can be found in certain skincare and haircare products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and industrial applications of propionic acid
Propionic acid is utilized in various environmental and industrial applications, including wastewater treatment, as a chemical intermediate in the production of plastics and other chemicals, and as a solvent in certain industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Derivatives and related compounds of propionic acid
Research and development efforts focus on creating and studying derivatives and related compounds of propionic acid. These include esters, salts, and other modified forms that may offer improved properties or specific functionalities for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid and Cosmetic Sector
The market for enhancing cosmetic products with propionic acid is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer demand for innovative and effective skincare solutions. The global cosmetics industry, valued at over $500 billion, provides a substantial market opportunity for this technology. Major players like L'Oréal, Shiseido, and Beiersdorf are investing in research and development to incorporate propionic acid into their product lines. The technology's maturity is advancing, with companies such as BASF and Henkel leading in ingredient development. Emerging players like Bloomage Biotechnology and Intercos are also contributing to the field, indicating a competitive and dynamic landscape. As the technology evolves, we can expect to see more specialized applications and formulations across various cosmetic categories.
Shiseido Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shiseido has developed an innovative approach to incorporating propionic acid in their cosmetic products, focusing on its potential skin benefits beyond its preservative properties. Their research has led to the discovery that propionic acid, when combined with specific amino acids, can enhance the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF)[7]. This synergistic effect has been incorporated into their advanced moisturizing formulations. Additionally, Shiseido has explored the use of propionic acid in conjunction with probiotics to support the skin's microbiome, creating a new category of "microbiome-friendly" preservatives[9]. They have also developed a proprietary delivery system that allows for the slow release of propionic acid, ensuring prolonged antimicrobial activity while minimizing potential skin irritation[11].
Strengths: Innovative use of propionic acid for enhancing skin's natural moisturizing factor. Development of microbiome-friendly preservative systems. Advanced delivery system for controlled release. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs associated with complex formulations. May face challenges in consumer acceptance of probiotic-based cosmetics.
Beiersdorf AG
Technical Solution: Beiersdorf has taken a unique approach to incorporating propionic acid in their cosmetic products, focusing on its potential as a multifunctional ingredient. Their research has led to the development of a proprietary complex combining propionic acid with specific plant extracts, which not only acts as a preservative but also provides skin-soothing benefits[8]. This complex has been shown to reduce skin sensitivity and redness, making it particularly suitable for products designed for sensitive skin. Beiersdorf has also explored the use of propionic acid in combination with niacinamide to enhance the skin's barrier function, leading to improved hydration and reduced transepidermal water loss[10]. Furthermore, they have investigated the potential of propionic acid esters as emollients, providing both preservative and skin-softening properties in a single ingredient[12].
Strengths: Multifunctional approach combining preservative action with skin-soothing benefits. Innovative complex suitable for sensitive skin products. Research into propionic acid esters as dual-function ingredients. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in formulating with plant extracts for long-term stability. May face regulatory hurdles in some markets due to novel ingredient combinations.
Innovative Approaches in Propionic Acid Formulations
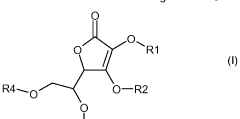
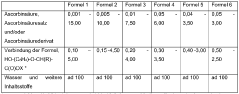
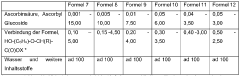
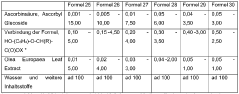
Cosmetic compositions for lightening the skin
PatentWO2017037002A1
Innovation
- Cosmetic compositions combining ascorbic acid or its derivatives with specific propionic acid derivatives, such as Hydroxyphenoxy Propionic Acid, and plant extracts like Olive Leaf Extract, to inhibit melanin and lipofuscin production, promoting even skin tone and hydration.
Cosmetic compositions for lightening the skin
PatentInactiveEP3344226A1
Innovation
- A cosmetic composition combining ascorbic acid or its derivatives with specific propionic acid derivatives, such as Hydroxyphenoxy Propionic Acid, and olive leaf extract, which inhibits melanin and lipofuscin production, providing improved skin hydration and a more even skin tone.
Regulatory Framework for Cosmetic Preservatives
The regulatory framework for cosmetic preservatives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of cosmetic products enhanced with propionic acid. Globally, regulatory bodies have established guidelines and restrictions for the use of preservatives in cosmetics, including propionic acid and its salts.
In the European Union, the use of preservatives in cosmetics is governed by Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on cosmetic products. This regulation includes a positive list of approved preservatives, with specific concentration limits and conditions of use. Propionic acid and its salts are listed as permitted preservatives, with a maximum concentration of 2% (as acid) in leave-on products and rinse-off products.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act. While the FDA does not maintain a positive list of approved preservatives, it requires that all cosmetic products be safe for consumers under normal conditions of use. Propionic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for use in food products, which often translates to acceptance in cosmetic applications.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics through the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The Japanese regulatory framework includes a positive list of approved preservatives, with propionic acid and its salts permitted for use in cosmetic products.
China's regulatory framework for cosmetics is overseen by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). The NMPA maintains a list of permitted preservatives, including propionic acid and its salts, with specific concentration limits and usage conditions.
Manufacturers seeking to enhance cosmetic products with propionic acid must navigate these regulatory frameworks, ensuring compliance with the specific requirements of each market. This includes adhering to concentration limits, labeling requirements, and any additional safety assessments mandated by regulatory authorities.
It is important to note that regulatory frameworks are subject to periodic updates and revisions. Manufacturers must stay informed about changes in regulations and adapt their formulations accordingly. Additionally, some regions may require pre-market approval or notification for cosmetic products containing certain preservatives, including propionic acid.
The global nature of the cosmetics industry necessitates a comprehensive understanding of various regulatory frameworks. Manufacturers must consider the most stringent regulations when developing products for multiple markets, ensuring compliance across all intended distribution regions.
In the European Union, the use of preservatives in cosmetics is governed by Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on cosmetic products. This regulation includes a positive list of approved preservatives, with specific concentration limits and conditions of use. Propionic acid and its salts are listed as permitted preservatives, with a maximum concentration of 2% (as acid) in leave-on products and rinse-off products.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act. While the FDA does not maintain a positive list of approved preservatives, it requires that all cosmetic products be safe for consumers under normal conditions of use. Propionic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for use in food products, which often translates to acceptance in cosmetic applications.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics through the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The Japanese regulatory framework includes a positive list of approved preservatives, with propionic acid and its salts permitted for use in cosmetic products.
China's regulatory framework for cosmetics is overseen by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). The NMPA maintains a list of permitted preservatives, including propionic acid and its salts, with specific concentration limits and usage conditions.
Manufacturers seeking to enhance cosmetic products with propionic acid must navigate these regulatory frameworks, ensuring compliance with the specific requirements of each market. This includes adhering to concentration limits, labeling requirements, and any additional safety assessments mandated by regulatory authorities.
It is important to note that regulatory frameworks are subject to periodic updates and revisions. Manufacturers must stay informed about changes in regulations and adapt their formulations accordingly. Additionally, some regions may require pre-market approval or notification for cosmetic products containing certain preservatives, including propionic acid.
The global nature of the cosmetics industry necessitates a comprehensive understanding of various regulatory frameworks. Manufacturers must consider the most stringent regulations when developing products for multiple markets, ensuring compliance across all intended distribution regions.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid in Cosmetics
The environmental impact of propionic acid in cosmetics is a crucial consideration for both manufacturers and consumers. Propionic acid, while effective as a preservative and pH adjuster in cosmetic products, can have various effects on the environment throughout its lifecycle.
In the production phase, the synthesis of propionic acid typically involves petrochemical processes, which contribute to carbon emissions and energy consumption. However, recent advancements in biotechnology have led to more sustainable production methods using renewable resources, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint.
When cosmetic products containing propionic acid are used, a portion of the compound may be washed off and enter wastewater systems. Fortunately, propionic acid is readily biodegradable in aquatic environments, with studies showing that it can be broken down by microorganisms within a few days to weeks. This rapid biodegradation helps minimize its persistence in water bodies and reduces the risk of long-term aquatic toxicity.
However, the concentration of propionic acid in wastewater can be a concern if it exceeds certain thresholds. High levels may temporarily alter the pH of aquatic ecosystems, potentially affecting sensitive aquatic organisms. Wastewater treatment facilities are generally equipped to handle and neutralize such compounds, but the effectiveness can vary depending on the treatment methods employed.
In terms of air quality, propionic acid has a low vapor pressure, which means it does not readily evaporate at room temperature. This characteristic limits its contribution to air pollution and reduces the potential for atmospheric reactions that could lead to the formation of secondary pollutants.
The packaging of cosmetic products containing propionic acid also plays a role in its environmental impact. Single-use plastic containers, which are common in the cosmetics industry, contribute to plastic pollution if not properly recycled or disposed of. Efforts to develop more sustainable packaging solutions, such as biodegradable materials or refillable containers, can help mitigate this aspect of environmental impact.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental footprint of propionic acid in cosmetics extends beyond its direct effects. The sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, transportation, and disposal of product packaging all contribute to the overall environmental impact. As such, a holistic approach to sustainability in cosmetic formulations is necessary to minimize negative environmental consequences.
In conclusion, while propionic acid itself has relatively low environmental persistence due to its biodegradability, its use in cosmetics still warrants careful consideration of the entire product lifecycle. Ongoing research and innovation in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are essential for further reducing the environmental impact of propionic acid and other cosmetic ingredients.
In the production phase, the synthesis of propionic acid typically involves petrochemical processes, which contribute to carbon emissions and energy consumption. However, recent advancements in biotechnology have led to more sustainable production methods using renewable resources, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint.
When cosmetic products containing propionic acid are used, a portion of the compound may be washed off and enter wastewater systems. Fortunately, propionic acid is readily biodegradable in aquatic environments, with studies showing that it can be broken down by microorganisms within a few days to weeks. This rapid biodegradation helps minimize its persistence in water bodies and reduces the risk of long-term aquatic toxicity.
However, the concentration of propionic acid in wastewater can be a concern if it exceeds certain thresholds. High levels may temporarily alter the pH of aquatic ecosystems, potentially affecting sensitive aquatic organisms. Wastewater treatment facilities are generally equipped to handle and neutralize such compounds, but the effectiveness can vary depending on the treatment methods employed.
In terms of air quality, propionic acid has a low vapor pressure, which means it does not readily evaporate at room temperature. This characteristic limits its contribution to air pollution and reduces the potential for atmospheric reactions that could lead to the formation of secondary pollutants.
The packaging of cosmetic products containing propionic acid also plays a role in its environmental impact. Single-use plastic containers, which are common in the cosmetics industry, contribute to plastic pollution if not properly recycled or disposed of. Efforts to develop more sustainable packaging solutions, such as biodegradable materials or refillable containers, can help mitigate this aspect of environmental impact.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental footprint of propionic acid in cosmetics extends beyond its direct effects. The sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, transportation, and disposal of product packaging all contribute to the overall environmental impact. As such, a holistic approach to sustainability in cosmetic formulations is necessary to minimize negative environmental consequences.
In conclusion, while propionic acid itself has relatively low environmental persistence due to its biodegradability, its use in cosmetics still warrants careful consideration of the entire product lifecycle. Ongoing research and innovation in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are essential for further reducing the environmental impact of propionic acid and other cosmetic ingredients.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!