Evaluating Magnesium Nitrate in Anticorrosive Paint Formulations
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Nitrate Paint Background
Magnesium nitrate has emerged as a promising component in anticorrosive paint formulations, drawing significant attention from researchers and industry professionals in recent years. The exploration of this compound in protective coatings stems from the growing need for more effective and environmentally friendly corrosion prevention solutions. Corrosion remains a persistent challenge across various sectors, including construction, automotive, and marine industries, leading to substantial economic losses and safety concerns worldwide.
The interest in magnesium nitrate for anticorrosive applications can be traced back to the broader research on inorganic compounds as potential alternatives to traditional chromate-based inhibitors. Chromates, while highly effective, have faced increasing regulatory scrutiny due to their toxicity and environmental impact. This shift in focus has led to the investigation of various metal salts and oxides, with magnesium compounds gaining particular attention due to their relative abundance, low toxicity, and potential synergistic effects with other corrosion inhibitors.
Magnesium nitrate's role in anticorrosive paint formulations is primarily attributed to its ability to form protective layers on metal surfaces. When incorporated into paint systems, it can react with the substrate to create insoluble compounds that act as barriers against corrosive agents. Additionally, the nitrate component may contribute to the overall inhibition mechanism through anodic passivation processes.
The development of magnesium nitrate-based anticorrosive paints aligns with the broader trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly coating technologies. As industries seek to reduce their environmental footprint and comply with stricter regulations, the demand for non-toxic, biodegradable corrosion inhibitors has intensified. Magnesium nitrate, being a naturally occurring compound with minimal environmental impact, fits well within this paradigm shift.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology and materials science have further expanded the potential applications of magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive formulations. Researchers are exploring novel methods to enhance its effectiveness, such as encapsulation techniques and the development of hybrid organic-inorganic systems. These innovations aim to improve the long-term stability and performance of magnesium nitrate-based coatings across a wide range of environmental conditions.
As the field progresses, the evaluation of magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations continues to evolve. Researchers are focusing on optimizing its concentration, understanding its interactions with different binder systems, and assessing its performance in combination with other inhibitors. The goal is to develop robust, multi-functional coating systems that can provide superior protection against corrosion while meeting the increasing demands for sustainability and cost-effectiveness in industrial applications.
The interest in magnesium nitrate for anticorrosive applications can be traced back to the broader research on inorganic compounds as potential alternatives to traditional chromate-based inhibitors. Chromates, while highly effective, have faced increasing regulatory scrutiny due to their toxicity and environmental impact. This shift in focus has led to the investigation of various metal salts and oxides, with magnesium compounds gaining particular attention due to their relative abundance, low toxicity, and potential synergistic effects with other corrosion inhibitors.
Magnesium nitrate's role in anticorrosive paint formulations is primarily attributed to its ability to form protective layers on metal surfaces. When incorporated into paint systems, it can react with the substrate to create insoluble compounds that act as barriers against corrosive agents. Additionally, the nitrate component may contribute to the overall inhibition mechanism through anodic passivation processes.
The development of magnesium nitrate-based anticorrosive paints aligns with the broader trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly coating technologies. As industries seek to reduce their environmental footprint and comply with stricter regulations, the demand for non-toxic, biodegradable corrosion inhibitors has intensified. Magnesium nitrate, being a naturally occurring compound with minimal environmental impact, fits well within this paradigm shift.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology and materials science have further expanded the potential applications of magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive formulations. Researchers are exploring novel methods to enhance its effectiveness, such as encapsulation techniques and the development of hybrid organic-inorganic systems. These innovations aim to improve the long-term stability and performance of magnesium nitrate-based coatings across a wide range of environmental conditions.
As the field progresses, the evaluation of magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations continues to evolve. Researchers are focusing on optimizing its concentration, understanding its interactions with different binder systems, and assessing its performance in combination with other inhibitors. The goal is to develop robust, multi-functional coating systems that can provide superior protection against corrosion while meeting the increasing demands for sustainability and cost-effectiveness in industrial applications.
Anticorrosive Paint Market Analysis
The global anticorrosive paint market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from various end-use industries such as construction, automotive, marine, and industrial manufacturing. The market is characterized by a growing emphasis on environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance, which has led to the development of eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a shift towards water-based anticorrosive paints, as they offer improved performance and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solvent-based alternatives. This trend is particularly prominent in developed regions such as North America and Europe, where stringent environmental regulations are in place.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth driver for the anticorrosive paint market, fueled by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing automotive production in countries like China and India. The region is expected to maintain its dominant position in the global market due to ongoing urbanization and industrial expansion.
The marine sector represents a significant segment of the anticorrosive paint market, with growing demand for protective coatings in shipbuilding and offshore structures. The harsh marine environment necessitates high-performance anticorrosive solutions, driving innovation in paint formulations and application techniques.
The construction industry is another major consumer of anticorrosive paints, particularly for steel structures, bridges, and industrial facilities. The increasing focus on infrastructure development and renovation projects in both developed and developing economies is expected to sustain market growth in this sector.
In terms of product types, epoxy-based anticorrosive paints continue to dominate the market due to their excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability. However, there is growing interest in alternative technologies such as polyurethane, acrylic, and zinc-rich coatings, each offering specific advantages for different applications.
The competitive landscape of the anticorrosive paint market is characterized by the presence of both global players and regional manufacturers. Key market participants are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are common strategies employed by companies to expand their market presence and technological capabilities.
Looking ahead, the anticorrosive paint market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by increasing awareness of corrosion-related costs and the need for long-lasting protective solutions across various industries. The ongoing research into novel anticorrosive agents, such as magnesium nitrate, presents opportunities for further market expansion and product differentiation.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a shift towards water-based anticorrosive paints, as they offer improved performance and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solvent-based alternatives. This trend is particularly prominent in developed regions such as North America and Europe, where stringent environmental regulations are in place.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth driver for the anticorrosive paint market, fueled by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing automotive production in countries like China and India. The region is expected to maintain its dominant position in the global market due to ongoing urbanization and industrial expansion.
The marine sector represents a significant segment of the anticorrosive paint market, with growing demand for protective coatings in shipbuilding and offshore structures. The harsh marine environment necessitates high-performance anticorrosive solutions, driving innovation in paint formulations and application techniques.
The construction industry is another major consumer of anticorrosive paints, particularly for steel structures, bridges, and industrial facilities. The increasing focus on infrastructure development and renovation projects in both developed and developing economies is expected to sustain market growth in this sector.
In terms of product types, epoxy-based anticorrosive paints continue to dominate the market due to their excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability. However, there is growing interest in alternative technologies such as polyurethane, acrylic, and zinc-rich coatings, each offering specific advantages for different applications.
The competitive landscape of the anticorrosive paint market is characterized by the presence of both global players and regional manufacturers. Key market participants are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are common strategies employed by companies to expand their market presence and technological capabilities.
Looking ahead, the anticorrosive paint market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by increasing awareness of corrosion-related costs and the need for long-lasting protective solutions across various industries. The ongoing research into novel anticorrosive agents, such as magnesium nitrate, presents opportunities for further market expansion and product differentiation.
Corrosion Protection Challenges
Corrosion protection remains a significant challenge in various industries, particularly in sectors such as marine, oil and gas, and infrastructure. The primary issue lies in the aggressive nature of corrosive environments, which can rapidly degrade metallic structures and equipment, leading to substantial economic losses and potential safety hazards. Traditional anticorrosive paint formulations often struggle to provide long-lasting protection in these harsh conditions, necessitating frequent maintenance and reapplication.
One of the key challenges in corrosion protection is the development of coatings that can withstand multiple types of corrosive attacks simultaneously. For instance, in marine environments, materials are exposed to salt spray, UV radiation, and mechanical stress concurrently. This multi-faceted assault on protective coatings requires innovative solutions that can address each aspect of the corrosive process effectively.
Another significant hurdle is the environmental impact of conventional anticorrosive paints. Many traditional formulations contain heavy metals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which pose risks to both human health and the environment. As regulations become increasingly stringent, there is a pressing need for eco-friendly alternatives that do not compromise on performance.
The durability of anticorrosive coatings in extreme temperatures and pH conditions presents another major challenge. Many industrial processes involve exposure to high temperatures or acidic/alkaline environments, which can rapidly break down standard protective layers. Developing coatings that maintain their integrity under these extreme conditions is crucial for extending the lifespan of critical infrastructure and equipment.
Adhesion is another critical factor in corrosion protection. Poor adhesion between the coating and the substrate can lead to delamination, allowing corrosive agents to penetrate and attack the underlying material. Improving the bonding mechanisms of anticorrosive paints, especially on diverse substrates, remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
The incorporation of smart or self-healing properties into anticorrosive coatings represents a frontier in corrosion protection research. These advanced materials aim to detect and respond to corrosion in its early stages, potentially extending the life of the coating and the protected structure. However, developing cost-effective and scalable solutions in this area remains a significant challenge.
In the context of evaluating magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations, researchers are exploring its potential to address some of these challenges. Magnesium nitrate's unique properties may offer improvements in areas such as adhesion, environmental friendliness, and resistance to extreme conditions. However, integrating this compound effectively into paint formulations while maintaining or enhancing overall performance presents its own set of technical hurdles that must be overcome.
One of the key challenges in corrosion protection is the development of coatings that can withstand multiple types of corrosive attacks simultaneously. For instance, in marine environments, materials are exposed to salt spray, UV radiation, and mechanical stress concurrently. This multi-faceted assault on protective coatings requires innovative solutions that can address each aspect of the corrosive process effectively.
Another significant hurdle is the environmental impact of conventional anticorrosive paints. Many traditional formulations contain heavy metals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which pose risks to both human health and the environment. As regulations become increasingly stringent, there is a pressing need for eco-friendly alternatives that do not compromise on performance.
The durability of anticorrosive coatings in extreme temperatures and pH conditions presents another major challenge. Many industrial processes involve exposure to high temperatures or acidic/alkaline environments, which can rapidly break down standard protective layers. Developing coatings that maintain their integrity under these extreme conditions is crucial for extending the lifespan of critical infrastructure and equipment.
Adhesion is another critical factor in corrosion protection. Poor adhesion between the coating and the substrate can lead to delamination, allowing corrosive agents to penetrate and attack the underlying material. Improving the bonding mechanisms of anticorrosive paints, especially on diverse substrates, remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
The incorporation of smart or self-healing properties into anticorrosive coatings represents a frontier in corrosion protection research. These advanced materials aim to detect and respond to corrosion in its early stages, potentially extending the life of the coating and the protected structure. However, developing cost-effective and scalable solutions in this area remains a significant challenge.
In the context of evaluating magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations, researchers are exploring its potential to address some of these challenges. Magnesium nitrate's unique properties may offer improvements in areas such as adhesion, environmental friendliness, and resistance to extreme conditions. However, integrating this compound effectively into paint formulations while maintaining or enhancing overall performance presents its own set of technical hurdles that must be overcome.
Current Magnesium Nitrate Formulations
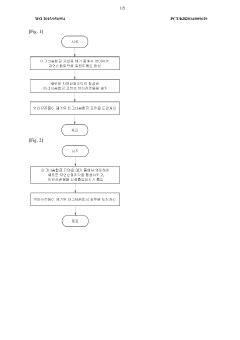
01 Magnesium nitrate as a corrosion inhibitor
Magnesium nitrate can be used as an effective corrosion inhibitor in various applications. It forms a protective layer on metal surfaces, preventing direct contact with corrosive agents. This compound is particularly useful in protecting steel and other ferrous metals from oxidation and corrosion in aqueous environments.- Magnesium nitrate as a corrosion inhibitor: Magnesium nitrate exhibits anticorrosive properties and can be used as a corrosion inhibitor in various applications. It forms a protective layer on metal surfaces, preventing direct contact with corrosive agents and reducing the rate of corrosion.
- Combination with other compounds for enhanced protection: Magnesium nitrate can be combined with other compounds to create more effective anticorrosive formulations. These combinations may include organic inhibitors, inorganic salts, or polymers, which work synergistically to provide improved corrosion resistance.
- Application in protective coatings: Magnesium nitrate can be incorporated into protective coatings for metals and alloys. These coatings form a barrier against corrosive environments and can be applied through various methods such as spraying, dipping, or electrodeposition.
- Use in concrete and construction materials: Magnesium nitrate can be used as an additive in concrete and other construction materials to improve their corrosion resistance. It helps in reducing the permeability of concrete and enhances its durability in aggressive environments.
- Environmental and cost-effective corrosion protection: Magnesium nitrate offers an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution for corrosion protection. It is less toxic compared to some traditional corrosion inhibitors and can be produced from readily available raw materials, making it a sustainable choice for various industries.
02 Synergistic anticorrosive formulations
Combining magnesium nitrate with other compounds can create synergistic anticorrosive formulations. These mixtures often include organic inhibitors, other inorganic salts, or polymers to enhance the overall protective effect. Such formulations can provide improved corrosion resistance compared to using magnesium nitrate alone.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in concrete and construction materials
Magnesium nitrate is utilized in concrete and construction materials to improve their corrosion resistance properties. It can be added to cement mixtures or applied as a surface treatment to enhance the durability of reinforced concrete structures, particularly in aggressive environments such as marine or industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in anticorrosive coatings
Magnesium nitrate is incorporated into anticorrosive coatings and paints to provide protection for metal surfaces. These coatings can be applied to various substrates, offering long-lasting protection against corrosion in different environmental conditions. The compound helps to form a barrier between the metal surface and corrosive elements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Corrosion inhibition in cooling systems
Magnesium nitrate is employed as a corrosion inhibitor in cooling systems, including industrial cooling towers and heat exchangers. It helps to prevent scale formation and corrosion of metal components in these systems, extending their operational life and maintaining efficiency. The compound is often used in combination with other water treatment chemicals for optimal results.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Anticorrosive Paint Manufacturers
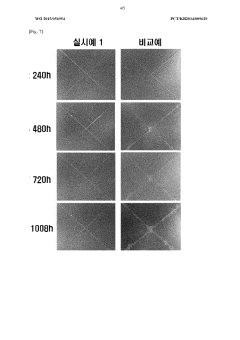
The market for magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for corrosion-resistant coatings across various industries. The global anticorrosive coatings market is expected to reach significant size in the coming years, with magnesium nitrate playing a crucial role. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like BASF Coatings GmbH, Chemetall GmbH, and Chugoku Marine Paints leading innovation. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to develop more effective and environmentally friendly formulations. However, the technology is still evolving, with ongoing research at institutions like West Pomeranian University of Technology Szczecin and Instituto Superior Técnico de Lisboa contributing to advancements in the field.
Chemetall GmbH
Technical Solution: Chemetall GmbH has pioneered a unique approach to incorporating magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations through their patented "smart release" technology. This system involves embedding magnesium nitrate within specially designed nanocontainers that are responsive to changes in pH. When corrosion begins and the local pH drops, these nanocontainers release magnesium nitrate, providing targeted corrosion inhibition exactly where it's needed[7]. The company has also developed a multi-layer coating system that combines this smart release technology with traditional barrier coatings, offering comprehensive protection against various types of corrosion. Laboratory tests have shown that this system can provide effective corrosion protection for aluminum alloys in aerospace applications for up to 3000 hours of salt spray exposure[10].
Strengths: Targeted, on-demand corrosion inhibition; effective for various metal substrates including aluminum. Weaknesses: Complex formulation may lead to higher production costs; potential regulatory challenges with nanomaterials.
NIPPON STEEL CORP.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL CORP. has developed an innovative anticorrosive paint formulation that utilizes magnesium nitrate in conjunction with their proprietary iron oxide-based pigments. This unique combination creates a synergistic effect that enhances both the barrier properties and the active corrosion inhibition of the coating. The company's research has shown that the interaction between magnesium nitrate and the iron oxide pigments leads to the formation of a stable, protective layer on the metal surface, significantly reducing the corrosion rate[11]. NIPPON STEEL's formulation also incorporates advanced polymer technology that improves the coating's adhesion and flexibility, making it particularly suitable for use on large steel structures subject to thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Field trials on bridge structures in coastal environments have demonstrated the coating's ability to maintain its protective properties for over 15 years with minimal maintenance[13].
Strengths: Long-term protection for large steel structures; excellent performance in coastal environments. Weaknesses: May be less suitable for non-ferrous metals; potentially higher initial cost compared to traditional coatings.
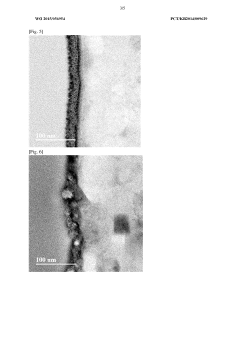
Magnesium Nitrate Corrosion Inhibition Mechanisms
Anti-corrosion surface treatment method of magnesium alloy, and magnesium alloy material surface-treated thereby
PatentWO2015056954A1
Innovation
- A method involving polishing the magnesium alloy surface in the atmosphere or with a liquid phase or inert gas to remove the existing native oxide film and form a new one, followed by painting, which does not use toxic substances and simplifies the treatment process, forming a natural oxide film for corrosion resistance.
Anti-corrosion coating with improved adhesion
PatentWO2009049836A1
Innovation
- A zinc-based coating with a defined admixture of magnesium, which interferes with the formation of a hard aluminum oxide layer, promoting instead an evenly structured oxide layer that enhances paint adhesion and forms a darker, more emissive surface upon annealing.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The incorporation of magnesium nitrate in anticorrosive paint formulations necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment. This evaluation is crucial to understand the potential effects of this chemical compound on ecosystems and human health throughout its lifecycle, from production to application and eventual disposal.
Magnesium nitrate, while effective in corrosion prevention, may pose certain environmental risks. When released into aquatic environments, it can contribute to eutrophication, a process that leads to excessive algal growth and oxygen depletion in water bodies. This can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting the balance of ecosystems and potentially causing fish kills.
In terrestrial environments, the accumulation of magnesium nitrate in soil may alter soil chemistry and affect plant growth. High concentrations can lead to soil salinization, impacting agricultural productivity and native vegetation. Furthermore, nitrate leaching into groundwater sources is a concern, as it can contaminate drinking water supplies and pose health risks to humans and animals.
The production process of magnesium nitrate also warrants scrutiny. Manufacturing may involve energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals, contributing to air and water pollution if not properly managed. Emissions from production facilities could include greenhouse gases and particulate matter, impacting local air quality and contributing to climate change.
During the application of anticorrosive paints containing magnesium nitrate, there is potential for environmental contamination through overspray, spills, or improper disposal of paint residues. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during paint application and drying can contribute to smog formation and have adverse effects on air quality.
The long-term persistence of magnesium nitrate in the environment is another factor to consider. While it is generally considered biodegradable, its rate of decomposition and potential for bioaccumulation in various organisms should be thoroughly investigated to assess any long-term ecological impacts.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, several strategies can be implemented. These include optimizing production processes to reduce emissions and waste, developing more environmentally friendly application methods, and implementing proper disposal and recycling programs for paint containers and residues. Additionally, research into alternative, less environmentally impactful corrosion inhibitors should be encouraged to reduce reliance on potentially harmful compounds.
In conclusion, while magnesium nitrate offers significant benefits in anticorrosive paint formulations, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. A balanced approach that considers both the protective properties of the compound and its potential environmental risks is essential for sustainable use in industrial applications.
Magnesium nitrate, while effective in corrosion prevention, may pose certain environmental risks. When released into aquatic environments, it can contribute to eutrophication, a process that leads to excessive algal growth and oxygen depletion in water bodies. This can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting the balance of ecosystems and potentially causing fish kills.
In terrestrial environments, the accumulation of magnesium nitrate in soil may alter soil chemistry and affect plant growth. High concentrations can lead to soil salinization, impacting agricultural productivity and native vegetation. Furthermore, nitrate leaching into groundwater sources is a concern, as it can contaminate drinking water supplies and pose health risks to humans and animals.
The production process of magnesium nitrate also warrants scrutiny. Manufacturing may involve energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals, contributing to air and water pollution if not properly managed. Emissions from production facilities could include greenhouse gases and particulate matter, impacting local air quality and contributing to climate change.
During the application of anticorrosive paints containing magnesium nitrate, there is potential for environmental contamination through overspray, spills, or improper disposal of paint residues. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during paint application and drying can contribute to smog formation and have adverse effects on air quality.
The long-term persistence of magnesium nitrate in the environment is another factor to consider. While it is generally considered biodegradable, its rate of decomposition and potential for bioaccumulation in various organisms should be thoroughly investigated to assess any long-term ecological impacts.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, several strategies can be implemented. These include optimizing production processes to reduce emissions and waste, developing more environmentally friendly application methods, and implementing proper disposal and recycling programs for paint containers and residues. Additionally, research into alternative, less environmentally impactful corrosion inhibitors should be encouraged to reduce reliance on potentially harmful compounds.
In conclusion, while magnesium nitrate offers significant benefits in anticorrosive paint formulations, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. A balanced approach that considers both the protective properties of the compound and its potential environmental risks is essential for sustainable use in industrial applications.
Regulatory Compliance for Anticorrosive Coatings
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of anticorrosive coating formulations, including those incorporating magnesium nitrate. The use of anticorrosive paints is subject to various regulations and standards aimed at ensuring product safety, environmental protection, and performance efficacy.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the use of chemicals in paint formulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Manufacturers must ensure that magnesium nitrate and other components used in anticorrosive paints are listed on the TSCA inventory or exempt from listing. Additionally, the EPA's Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) regulations limit the amount of VOCs that can be present in coatings, which may impact the formulation of anticorrosive paints.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals used in their products, including those in anticorrosive coatings. Magnesium nitrate and other components must be registered if they are produced or imported in quantities of one tonne or more per year.
International maritime regulations, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), govern the use of anticorrosive coatings on ships. The IMO's Performance Standard for Protective Coatings (PSPC) specifies requirements for protective coatings in ballast tanks and cargo oil tanks, which may influence the formulation and application of magnesium nitrate-based anticorrosive paints.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, require proper labeling and safety data sheets for anticorrosive coatings. These regulations ensure that workers are informed about potential hazards associated with the use and application of these coatings.
Compliance with industry standards, such as those set by ASTM International and ISO, is crucial for ensuring the quality and performance of anticorrosive coatings. These standards often specify testing methods and performance criteria that coatings must meet, which can influence the formulation process and the use of specific components like magnesium nitrate.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations are evolving to promote more sustainable and eco-friendly coating solutions. This trend may impact the use of certain chemicals in anticorrosive paint formulations and drive innovation towards more environmentally benign alternatives.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the use of chemicals in paint formulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Manufacturers must ensure that magnesium nitrate and other components used in anticorrosive paints are listed on the TSCA inventory or exempt from listing. Additionally, the EPA's Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) regulations limit the amount of VOCs that can be present in coatings, which may impact the formulation of anticorrosive paints.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals used in their products, including those in anticorrosive coatings. Magnesium nitrate and other components must be registered if they are produced or imported in quantities of one tonne or more per year.
International maritime regulations, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), govern the use of anticorrosive coatings on ships. The IMO's Performance Standard for Protective Coatings (PSPC) specifies requirements for protective coatings in ballast tanks and cargo oil tanks, which may influence the formulation and application of magnesium nitrate-based anticorrosive paints.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, require proper labeling and safety data sheets for anticorrosive coatings. These regulations ensure that workers are informed about potential hazards associated with the use and application of these coatings.
Compliance with industry standards, such as those set by ASTM International and ISO, is crucial for ensuring the quality and performance of anticorrosive coatings. These standards often specify testing methods and performance criteria that coatings must meet, which can influence the formulation process and the use of specific components like magnesium nitrate.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations are evolving to promote more sustainable and eco-friendly coating solutions. This trend may impact the use of certain chemicals in anticorrosive paint formulations and drive innovation towards more environmentally benign alternatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!