Exploring Eco-Friendly Applications of Propionic Acid
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Background and Objectives
Propionic acid, a three-carbon carboxylic acid, has been known to science since the mid-19th century. Initially discovered as a byproduct of bacterial fermentation, it has since become a versatile compound with applications spanning various industries. The evolution of propionic acid technology has been driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly solutions in chemical production and industrial processes.
The primary objective of exploring eco-friendly applications of propionic acid is to harness its potential as a green alternative to traditional petrochemical-based products. This aligns with the global shift towards sustainable development and circular economy principles. By focusing on propionic acid's environmentally friendly characteristics, researchers and industries aim to reduce the carbon footprint associated with various chemical processes and end-products.
Historically, propionic acid production has relied on petrochemical routes, primarily through the oxidation of propanol or the carbonylation of ethylene. However, the growing emphasis on sustainability has led to increased interest in bio-based production methods. Fermentation processes using renewable feedstocks have emerged as promising alternatives, offering a more environmentally friendly approach to propionic acid synthesis.
The technological trajectory of propionic acid applications has expanded significantly over the years. From its initial use as a food preservative, it has found its way into diverse sectors such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and polymer production. This evolution reflects the compound's versatility and the continuous efforts to unlock its full potential in eco-friendly applications.
Current research and development efforts are focused on optimizing bio-based production methods, enhancing the efficiency of propionic acid synthesis, and exploring novel applications that leverage its unique properties. The goal is to position propionic acid as a key player in the transition towards a more sustainable chemical industry.
As we delve deeper into the eco-friendly applications of propionic acid, it is crucial to consider the broader context of green chemistry and sustainable development. The exploration of this compound's potential aligns with several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly those related to responsible consumption and production, climate action, and industry innovation.
The technological objectives in this field extend beyond mere substitution of existing products. They encompass the creation of entirely new applications that can contribute to solving environmental challenges. From biodegradable plastics to advanced agricultural solutions, the potential of propionic acid in eco-friendly applications is vast and largely untapped.
The primary objective of exploring eco-friendly applications of propionic acid is to harness its potential as a green alternative to traditional petrochemical-based products. This aligns with the global shift towards sustainable development and circular economy principles. By focusing on propionic acid's environmentally friendly characteristics, researchers and industries aim to reduce the carbon footprint associated with various chemical processes and end-products.
Historically, propionic acid production has relied on petrochemical routes, primarily through the oxidation of propanol or the carbonylation of ethylene. However, the growing emphasis on sustainability has led to increased interest in bio-based production methods. Fermentation processes using renewable feedstocks have emerged as promising alternatives, offering a more environmentally friendly approach to propionic acid synthesis.
The technological trajectory of propionic acid applications has expanded significantly over the years. From its initial use as a food preservative, it has found its way into diverse sectors such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and polymer production. This evolution reflects the compound's versatility and the continuous efforts to unlock its full potential in eco-friendly applications.
Current research and development efforts are focused on optimizing bio-based production methods, enhancing the efficiency of propionic acid synthesis, and exploring novel applications that leverage its unique properties. The goal is to position propionic acid as a key player in the transition towards a more sustainable chemical industry.
As we delve deeper into the eco-friendly applications of propionic acid, it is crucial to consider the broader context of green chemistry and sustainable development. The exploration of this compound's potential aligns with several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly those related to responsible consumption and production, climate action, and industry innovation.
The technological objectives in this field extend beyond mere substitution of existing products. They encompass the creation of entirely new applications that can contribute to solving environmental challenges. From biodegradable plastics to advanced agricultural solutions, the potential of propionic acid in eco-friendly applications is vast and largely untapped.
Market Demand for Green Propionic Acid Applications
The market demand for eco-friendly applications of propionic acid has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations across various industries. This trend is particularly evident in the food and beverage sector, where propionic acid is widely used as a natural preservative. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with clean labels and natural ingredients, creating a significant opportunity for green propionic acid applications.
In the agriculture industry, there is a rising demand for sustainable feed additives and crop protection solutions. Propionic acid's ability to inhibit mold growth in animal feed and its potential as a bio-based herbicide align well with this market need. The shift towards organic farming practices further amplifies the demand for environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic chemicals.
The personal care and cosmetics industry is another key market segment showing increased interest in green propionic acid applications. With consumers becoming more conscious of the ingredients in their personal care products, there is a growing demand for natural preservatives and pH adjusters. Propionic acid's antimicrobial properties make it an attractive option for formulators looking to replace synthetic preservatives.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the push for sustainable manufacturing processes has created new opportunities for eco-friendly propionic acid applications. Its use as a precursor in drug synthesis and as a solvent in various pharmaceutical processes is gaining traction as companies strive to reduce their environmental footprint.
The packaging industry is also exploring green propionic acid applications, particularly in the development of biodegradable plastics and coatings. As governments worldwide implement stricter regulations on single-use plastics, there is a growing market for bio-based alternatives, where propionic acid derivatives could play a significant role.
The textile industry presents another promising market for eco-friendly propionic acid applications. With increasing awareness of the environmental impact of textile production, there is a demand for sustainable dyeing and finishing processes. Propionic acid's potential as a natural mordant and its ability to improve dye fixation offer environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional methods.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the market potential for green propionic acid applications is expected to expand further. This growth is likely to be supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at discovering new eco-friendly applications and improving existing ones. The versatility of propionic acid, combined with its natural origin and biodegradability, positions it well to meet the evolving demands of environmentally conscious markets across various sectors.
In the agriculture industry, there is a rising demand for sustainable feed additives and crop protection solutions. Propionic acid's ability to inhibit mold growth in animal feed and its potential as a bio-based herbicide align well with this market need. The shift towards organic farming practices further amplifies the demand for environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic chemicals.
The personal care and cosmetics industry is another key market segment showing increased interest in green propionic acid applications. With consumers becoming more conscious of the ingredients in their personal care products, there is a growing demand for natural preservatives and pH adjusters. Propionic acid's antimicrobial properties make it an attractive option for formulators looking to replace synthetic preservatives.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the push for sustainable manufacturing processes has created new opportunities for eco-friendly propionic acid applications. Its use as a precursor in drug synthesis and as a solvent in various pharmaceutical processes is gaining traction as companies strive to reduce their environmental footprint.
The packaging industry is also exploring green propionic acid applications, particularly in the development of biodegradable plastics and coatings. As governments worldwide implement stricter regulations on single-use plastics, there is a growing market for bio-based alternatives, where propionic acid derivatives could play a significant role.
The textile industry presents another promising market for eco-friendly propionic acid applications. With increasing awareness of the environmental impact of textile production, there is a demand for sustainable dyeing and finishing processes. Propionic acid's potential as a natural mordant and its ability to improve dye fixation offer environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional methods.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the market potential for green propionic acid applications is expected to expand further. This growth is likely to be supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at discovering new eco-friendly applications and improving existing ones. The versatility of propionic acid, combined with its natural origin and biodegradability, positions it well to meet the evolving demands of environmentally conscious markets across various sectors.
Current State and Challenges in Eco-Friendly Propionic Acid Use
The current state of eco-friendly propionic acid applications is characterized by a growing interest in sustainable production methods and diverse green applications. Traditionally produced through petrochemical processes, propionic acid is now being explored for bio-based production routes, aligning with global sustainability goals. Fermentation processes using renewable feedstocks have shown promise, with companies like BASF and Corbion leading research efforts.
In the food industry, propionic acid's natural preservative properties are being leveraged to extend shelf life without synthetic additives. This aligns with consumer demand for clean label products. The agriculture sector is exploring propionic acid as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and herbicides, potentially reducing environmental impact.
However, several challenges hinder widespread adoption of eco-friendly propionic acid applications. The cost of bio-based production remains higher than traditional petrochemical routes, making it less economically viable for large-scale implementation. Inconsistent quality and yield in fermentation processes pose technical hurdles that require further research and development.
Regulatory frameworks lag behind technological advancements, creating uncertainty for companies investing in green propionic acid solutions. The lack of standardized sustainability metrics makes it difficult to quantify and communicate the environmental benefits of eco-friendly applications, potentially slowing market adoption.
Scale-up challenges persist in transitioning from laboratory success to industrial-scale production. Optimizing fermentation processes, improving microbial strains, and developing efficient downstream processing techniques are areas requiring significant investment and innovation.
The integration of eco-friendly propionic acid into existing supply chains and manufacturing processes presents logistical and technical challenges. Industries accustomed to petrochemical-derived propionic acid may need to adapt their processes and equipment to accommodate bio-based alternatives.
Despite these challenges, the potential for eco-friendly propionic acid applications remains promising. Collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies are crucial to overcoming current obstacles. Advances in synthetic biology and process engineering offer pathways to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important across industries, the demand for green alternatives like eco-friendly propionic acid is expected to grow. Overcoming the current challenges will require sustained research, investment, and policy support to unlock the full potential of this versatile compound in environmentally conscious applications.
In the food industry, propionic acid's natural preservative properties are being leveraged to extend shelf life without synthetic additives. This aligns with consumer demand for clean label products. The agriculture sector is exploring propionic acid as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and herbicides, potentially reducing environmental impact.
However, several challenges hinder widespread adoption of eco-friendly propionic acid applications. The cost of bio-based production remains higher than traditional petrochemical routes, making it less economically viable for large-scale implementation. Inconsistent quality and yield in fermentation processes pose technical hurdles that require further research and development.
Regulatory frameworks lag behind technological advancements, creating uncertainty for companies investing in green propionic acid solutions. The lack of standardized sustainability metrics makes it difficult to quantify and communicate the environmental benefits of eco-friendly applications, potentially slowing market adoption.
Scale-up challenges persist in transitioning from laboratory success to industrial-scale production. Optimizing fermentation processes, improving microbial strains, and developing efficient downstream processing techniques are areas requiring significant investment and innovation.
The integration of eco-friendly propionic acid into existing supply chains and manufacturing processes presents logistical and technical challenges. Industries accustomed to petrochemical-derived propionic acid may need to adapt their processes and equipment to accommodate bio-based alternatives.
Despite these challenges, the potential for eco-friendly propionic acid applications remains promising. Collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies are crucial to overcoming current obstacles. Advances in synthetic biology and process engineering offer pathways to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important across industries, the demand for green alternatives like eco-friendly propionic acid is expected to grow. Overcoming the current challenges will require sustained research, investment, and policy support to unlock the full potential of this versatile compound in environmentally conscious applications.
Existing Eco-Friendly Propionic Acid Solutions
01 Production methods of propionic acid
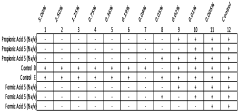
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and some bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery goods and dairy products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations. They are used as excipients, pH adjusters, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients for various therapeutic purposes.
- Industrial applications of propionic acid: Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as an intermediate in various chemical processes. The acid and its derivatives also find use in the manufacturing of solvents and perfumes.
- Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling: The handling, storage, and disposal of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Innovations in this area focus on developing safer handling methods, reducing environmental footprint, and improving workplace safety in industries using propionic acid.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry
Propionic acid finds applications in the pharmaceutical industry as a precursor for drug synthesis and as an excipient in various formulations. It is used in the production of certain medications and can also serve as a pH adjuster in pharmaceutical preparations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The handling and storage of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper containment, neutralization techniques, and waste management strategies are essential for minimizing risks associated with propionic acid use in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and quality control of propionic acid
Various purification techniques and quality control measures are employed to ensure the purity and consistency of propionic acid for different applications. These may include distillation, crystallization, and analytical methods to remove impurities and maintain desired specifications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Propionic Acid Industry
The eco-friendly applications of propionic acid are in an emerging stage, with the market showing promising growth potential. The global propionic acid market size was valued at $1.55 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.97 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 3.1%. The technology is advancing towards maturity, with key players like Dow Global Technologies, Nippon Shokubai, and BASF leading research and development efforts. Universities such as The Ohio State University and University of Campinas are contributing to academic research, while companies like Braskem and Evonik are exploring industrial applications. The focus on sustainability and bio-based production methods is driving innovation in this field, with potential applications in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and green solvents.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed eco-friendly applications of propionic acid in biodegradable polymers. Their technology involves incorporating propionic acid into the polymer chain to enhance biodegradability and reduce environmental impact[1]. The company has also explored using propionic acid as a green solvent in various industrial processes, replacing more harmful alternatives[2]. Additionally, Dow has researched the use of propionic acid in sustainable packaging materials, where it acts as a preservative and antimicrobial agent, extending shelf life while maintaining eco-friendliness[3]. Their approach includes optimizing the production process of propionic acid from renewable resources, potentially using fermentation of biomass feedstocks[4].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and diverse application portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs associated with eco-friendly processes and materials compared to traditional methods.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has focused on developing eco-friendly applications of propionic acid in animal nutrition and feed preservation. Their research has led to the creation of glyceryl monopropionate, a novel feed additive derived from propionic acid that offers improved antimicrobial properties while being more environmentally friendly[1]. The company has also explored the use of propionic acid in sustainable coatings and adhesives, where it serves as a bio-based alternative to petrochemical-derived compounds[2]. Evonik's approach includes optimizing the production of propionic acid through biotechnological processes, utilizing renewable raw materials and reducing energy consumption[3]. They have also investigated the potential of propionic acid in biodegradable plastics, aiming to create more sustainable packaging solutions[4].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainability, innovative biotechnology approaches, and diverse application areas. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up bio-based production methods and competing with established petrochemical alternatives.
Core Innovations in Green Propionic Acid Technology
Propionic acid as an herbicide
PatentWO2009055632A2
Innovation
- Propionic acid is used as a pre- and post-emergence herbicide, either applied to soil or directly to weeds, in compositions with carriers and essential oils, offering a safer alternative that prevents weed germination and growth without causing harm to mature plants or the environment.
Chromatographic separation of propionic acid using strong base anion exchange resin
PatentWO2017095685A1
Innovation
- Chromatographic separation using a strong base anion exchange resin, specifically a gel-type, Type I resin, to separate propionic acid from liquid feed mixtures containing various organic acids, alcohols, and carbohydrates, effectively addressing the limitations of existing methods.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Propionic acid, a naturally occurring carboxylic acid, has gained attention for its potential eco-friendly applications. To assess its environmental impact, it is crucial to examine various aspects of its production, use, and disposal.
The production of propionic acid traditionally relies on petrochemical processes, which can have significant environmental drawbacks. However, recent advancements in biotechnology have led to the development of more sustainable production methods. Fermentation processes using renewable resources such as glucose or glycerol as feedstocks have shown promise in reducing the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid production.
When considering the use phase, propionic acid demonstrates several environmentally beneficial properties. As a food preservative, it extends the shelf life of various products, potentially reducing food waste and the associated environmental burdens. In agriculture, its application as a mold inhibitor in animal feed contributes to improved livestock health and reduced use of antibiotics, indirectly mitigating the environmental impact of intensive farming practices.
The biodegradability of propionic acid is a key factor in its environmental profile. Unlike many synthetic chemicals, propionic acid readily breaks down in natural environments, reducing the risk of long-term accumulation in ecosystems. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for applications where release into the environment is possible or expected.
In terms of aquatic toxicity, propionic acid exhibits relatively low impact compared to many conventional chemicals used for similar purposes. However, care must be taken to prevent large-scale releases, as concentrated amounts can still cause localized pH changes in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic life.
The use of propionic acid in eco-friendly plastics and polymers represents another area of environmental interest. As a building block for biodegradable plastics, it offers potential alternatives to persistent petroleum-based polymers, contributing to efforts in reducing plastic pollution.
Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with propionic acid's lifecycle should also be considered. While bio-based production methods show improvements over traditional petrochemical routes, there is still room for optimization to further reduce the overall environmental footprint.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of propionic acid reveals a complex picture with both positive and negative aspects. Its potential for sustainable production, biodegradability, and diverse eco-friendly applications position it as a promising candidate for green chemistry initiatives. However, continued research and development are necessary to fully optimize its production processes and expand its environmentally beneficial applications while minimizing any potential negative impacts.
The production of propionic acid traditionally relies on petrochemical processes, which can have significant environmental drawbacks. However, recent advancements in biotechnology have led to the development of more sustainable production methods. Fermentation processes using renewable resources such as glucose or glycerol as feedstocks have shown promise in reducing the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid production.
When considering the use phase, propionic acid demonstrates several environmentally beneficial properties. As a food preservative, it extends the shelf life of various products, potentially reducing food waste and the associated environmental burdens. In agriculture, its application as a mold inhibitor in animal feed contributes to improved livestock health and reduced use of antibiotics, indirectly mitigating the environmental impact of intensive farming practices.
The biodegradability of propionic acid is a key factor in its environmental profile. Unlike many synthetic chemicals, propionic acid readily breaks down in natural environments, reducing the risk of long-term accumulation in ecosystems. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for applications where release into the environment is possible or expected.
In terms of aquatic toxicity, propionic acid exhibits relatively low impact compared to many conventional chemicals used for similar purposes. However, care must be taken to prevent large-scale releases, as concentrated amounts can still cause localized pH changes in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic life.
The use of propionic acid in eco-friendly plastics and polymers represents another area of environmental interest. As a building block for biodegradable plastics, it offers potential alternatives to persistent petroleum-based polymers, contributing to efforts in reducing plastic pollution.
Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with propionic acid's lifecycle should also be considered. While bio-based production methods show improvements over traditional petrochemical routes, there is still room for optimization to further reduce the overall environmental footprint.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of propionic acid reveals a complex picture with both positive and negative aspects. Its potential for sustainable production, biodegradability, and diverse eco-friendly applications position it as a promising candidate for green chemistry initiatives. However, continued research and development are necessary to fully optimize its production processes and expand its environmentally beneficial applications while minimizing any potential negative impacts.
Regulatory Framework for Green Chemical Applications
The regulatory framework for green chemical applications plays a crucial role in promoting and governing the eco-friendly use of propionic acid. As environmental concerns continue to grow, governments and international organizations have implemented various policies and regulations to encourage sustainable practices in the chemical industry.
At the global level, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has established the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM), which provides a policy framework to foster the sound management of chemicals throughout their lifecycle. This initiative directly impacts the development and application of green chemicals, including propionic acid, by setting guidelines for their production, use, and disposal.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation serves as a comprehensive framework for chemical safety. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information, which has significant implications for the use of propionic acid in eco-friendly applications. The regulation promotes the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, encouraging the development of greener chemical processes.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which regulates the introduction of new or already existing chemicals. Under the TSCA, the EPA has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemicals, including propionic acid, to assess potential risks to human health and the environment.
Many countries have also adopted Green Chemistry initiatives to promote the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. These initiatives often provide incentives for companies to develop and implement eco-friendly applications of chemicals like propionic acid.
Specific to propionic acid, regulations often focus on its use as a food preservative and animal feed additive. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines for the safe use of propionic acid in food products. These regulations ensure that the application of propionic acid in food preservation aligns with environmental and health safety standards.
As the demand for sustainable practices grows, regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing life cycle assessments (LCA) for chemicals. This approach considers the environmental impact of a substance from production to disposal, encouraging manufacturers to develop more sustainable production methods for propionic acid and its derivatives.
The regulatory landscape also includes voluntary certification programs, such as the Green Seal and EcoLogo, which set standards for environmentally preferable products. These programs can provide a competitive advantage for products using propionic acid in eco-friendly applications, as they offer third-party verification of environmental claims.
At the global level, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has established the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM), which provides a policy framework to foster the sound management of chemicals throughout their lifecycle. This initiative directly impacts the development and application of green chemicals, including propionic acid, by setting guidelines for their production, use, and disposal.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation serves as a comprehensive framework for chemical safety. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information, which has significant implications for the use of propionic acid in eco-friendly applications. The regulation promotes the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, encouraging the development of greener chemical processes.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which regulates the introduction of new or already existing chemicals. Under the TSCA, the EPA has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemicals, including propionic acid, to assess potential risks to human health and the environment.
Many countries have also adopted Green Chemistry initiatives to promote the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. These initiatives often provide incentives for companies to develop and implement eco-friendly applications of chemicals like propionic acid.
Specific to propionic acid, regulations often focus on its use as a food preservative and animal feed additive. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines for the safe use of propionic acid in food products. These regulations ensure that the application of propionic acid in food preservation aligns with environmental and health safety standards.
As the demand for sustainable practices grows, regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing life cycle assessments (LCA) for chemicals. This approach considers the environmental impact of a substance from production to disposal, encouraging manufacturers to develop more sustainable production methods for propionic acid and its derivatives.
The regulatory landscape also includes voluntary certification programs, such as the Green Seal and EcoLogo, which set standards for environmentally preferable products. These programs can provide a competitive advantage for products using propionic acid in eco-friendly applications, as they offer third-party verification of environmental claims.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!